

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 622.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160773
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2016-11-07
Online:2017-04-10
Published:2017-03-23
Contact:
BI Erping
E-mail:bi@cugb.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
QUAN Yao, BI Erping. Adsorption Characteristics of Different Forms of Ofloxacin to Attapulgite†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 622.
| pH | Sm/(mmol·kg-1) | KL/(L·mol-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.88—2.16 | 214.60 | 26.85 | 0.96 |
| 7.10—7.70 | 281.16 | 9.72 | 0.99 |
| 9.00—10.00 | 200.87 | 3.85 | 0.98 |
Table 1 Langmuir isotherm parameters of the adsorption of OFL by ATP with different pH values
| pH | Sm/(mmol·kg-1) | KL/(L·mol-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.88—2.16 | 214.60 | 26.85 | 0.96 |
| 7.10—7.70 | 281.16 | 9.72 | 0.99 |
| 9.00—10.00 | 200.87 | 3.85 | 0.98 |
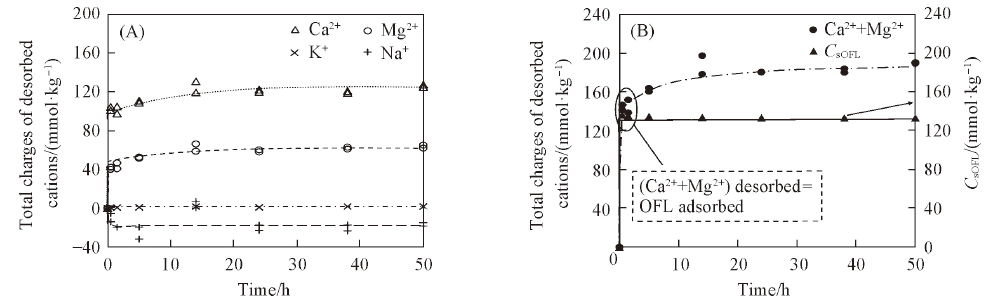
Fig.5 Desorption of Ca2+, Mg2+, K+ and Na+ accompanying OFL adsorption to ATP(A) and comparison of the total desorbed Ca2+ and Mg2+ with the adsorbed OFL(B)
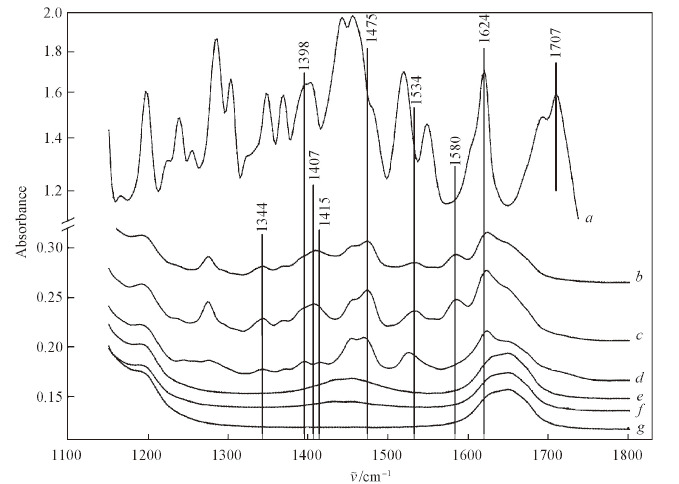
Fig.7 ATR-FTIR spectra of OFL, ATPs and different forms of OFL adsorbed to ATPa. OFL powder(purity 98%); b. OFL-+ATP(pH=9.00—10.00), Cs=143.56 mmol/kg; c. OFL±+ATP(pH=7.10—7.70), Cs=212.16 mmol/kg; d. OFL++ATP(pH=1.65—1.88), Cs=180.87 mmol/kg; e. ATP used for OFL+ experiments; f. ATP used for OFL± experiments; g. ATP used for OFL- experiments.
| [1] | Paul T., Machesky M. L., Strathmann T. J., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 11896—11904 |
| [2] | Wu F. H., Xu F., Chen L., Jiang B. B., Sun W. B., Wei X. W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(3), 468—473 |
| [3] | Goyne K. W., Chorover J., Kubicki J. D., Zimmerman A. R., Brantley S. L., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2005, 283, 160—170 |
| [4] | Peng H., Pan B., Wu M., Liu Y., Zhang D., Xing B., J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 233/234, 89—96 |
| [5] | Kolpin D. W., Furlong E. T., Meyer M. T., Thurman E. M., Zaugg S. D., Barber L. B., Buxton H. T., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2002, 36, 1202—1211 |
| [6] | Fick J., Söderström H., Lindberg R. H., Phan C., Tysklind M., Larsson D. G. J., Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2009, 28, 2522—2527 |
| [7] | Jia A., Wan Y., Xiao Y., Hu J., Water Res., 2012, 46, 387—394 |
| [8] | Yan Q., Gao X., Huang L., Gan X. M., Zhang Y. X., Chen Y. P., Peng X. Y., Guo J. S., Chemosphere,2014, 99, 160—170 |
| [9] | Yan H., Wang H., Qin X., Liu B., Du J., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2011, 54, 53—57 |
| [10] | van Doorslaer X., Dewulf J., van Langenhove H., Demeestere K., Sci. Total Environ., 2014, 500/501, 250—269 |
| [11] | Vasquez M. I., Garcia-Käufer M., Hapeshi E., Menz J., Kostarelos K., Fatta-Kassinos D., Kümmerer K., Sci. Total Environ., 2013, 450, 356—365 |
| [12] | Xu W., Zhang G., Li X., Zou S., Li P., Hu Z., Li J., Water Res., 2007, 41, 4526—4534 |
| [13] | Ternes T. A., Joss A., Siegrist J., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, 38, 393A—399A |
| [14] | Chen H., Wang A., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 307, 309—316 |
| [15] | Alvarez-Ayuso E., Garcia-Sanchez A., J. Hazard Mater., 2007, 147, 594—600 |
| [16] | Wang C. J., Li Z., Jiang W. T., Jean J. S., Liu C. C., J. Hazard Mater., 2010, 183, 309—314 |
| [17] | Chang P. H., Jiang W. T., Li Z., Kuo C. Y., Wu Q., Jean J. S., Lv G., J. Hazard. Mater., 2016, 303, 55—63 |
| [18] | Li Z., Hong H., Liao L., Ackley C. J., Schulz L. A., MacDonald R. A., Mihelich A. L., Emard S. M., Colloids Surf., B: Biointerfaces, 2011, 88, 339—344 |
| [19] | Wang C. J., Li Z., Jiang W. T., Applied Clay Science, 2011, 53, 723—728 |
| [20] | Gu C., Karthikeyan K. G., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 39, 9166—9173 |
| [21] | Nowara A., Burhenne J., Spiteller M., J. Agric. Food. Chem., 1997, 45, 1459—1463 |
| [22] | Otker H. M., Akmehmet-Balcioglu I., J. Hazard. Mater., 2005, 122, 251—258 |
| [23] | Sirtori C., Zapata A., Oller I., Gernjak W., Aguera A., Malato S., Water Res., 2009, 43, 661—668 |
| [24] | Chen Z., Ren N., Wang A., Zhang Z. P., Shi Y., Water Res., 2008, 42, 3385—3392 |
| [25] | Oktem Y. A., Ince O., Sallis P., Donnelly T., Ince B. K., Bioresour. Technol., 2008, 99, 1089—1096 |
| [26] | Zhang Z., Wang W., Wang A., J. Environ.Sci. (China), 2015, 33, 106—115 |
| [27] | Wang W., Wang F., Kang Y., Wang A., Water, Air Soil Pollut., 2015, 226, 83 |
| [28] | Wan M., Li Z., Hong H., Wu Q., J. Asian Earth Sci., 2013, 77, 287—294 |
| [29] | Park H. R., Chung K. Y., Lee H. C., Bull. Korean Chem Soc., 2000, 21, 849—854 |
| [30] | Chapman D., Nature, 1954, 174, 887—888 |
| [31] | Irving H., Williams R. J. P., Nature,1948, 162, 746—747 |
| [32] | Vasudevan D., Bruland G. L., Torrance B. S., Upchurch V. G., MacKay A. A., Geoderma., 2009, 151, 68—76 |
| [33] | Liu W., Zhang J., Zhang C., Ren L., Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 171, 431—438 |
| [34] | Martin S., Shchukarev A., Hanna K., Boily J. F., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49, 12197—12205 |
| [35] | Sagdinc S., Bayarı S., J. Mol. Struct., 2004, 691, 107—113 |
| [36] | Rakshit S., Sarkar D., Elzinga E. J., Punamiya P., Datta R., J. Hazard Mater., 2013, 246/247, 221—226 |
| [1] | WU Shanshan,WEI Chanling,ZHAO Lijuan,TIAN Yang,WANG Xia,GONG Bolin. Preparation and Enrichment Properties of Novel Magnetic Restricted Access Media-molecularly Imprinted Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1150. |
| [2] | ZHAO Jie,SONG Qiang,GUO Xiao,WU Fei,TIAN Haochuan,LU Zhaowei. Synthesis of SnNb2O6 Nanoplates and Its Application for Danofloxacin Adsorption† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1121. |
| [3] | SUN Lin, ZHANG Han, DU Yiping. Preparation of Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates Based on SBA-15 Material and the Detection of Enrofloxacin in Chicken and Chicken Feed† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 455. |
| [4] | SONG Kaili, YANG Binsheng. Spectroscopic Study on Ternary Complexes of Pyoverdine-terbium(Ⅲ)-ciprofloxacin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 408. |
| [5] | CAO Xiaoqiang, YAN Bingqi, WANG Qian, WANG Yaping, QIU Jun, HUANG Yongqing, LI Lin, ZHANG Yan, HU Shugang, KANG Ling, LÜ Xianjun. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) from Aqueous Solutions on Organic Modified Laponite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 173. |
| [6] | LIU Kaihong, LIN Qi, CUI Zhenggang, PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong. pH-Responsive Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles in Combination with N-Dodecyl-β-aminopropionate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 85. |
| [7] | FENG Jilu, QI Junru, LIU Qianru. Fabrication of Soy Protein Isolate-soluble Soy Polysaccharide Core-shell Nanogels via Maillard Reaction and Self-assembly† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 1999. |
| [8] | YANG Mingxuan, MA Jie, SUN Yiran, XIONG Xinzhu, LI Chenlu, LI Qiang, CHEN Junhong. Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes/FeS Fenton-like Catalyst and Its Catalytic Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 570. |
| [9] | LIN Yifeng, HUANG Xuehong, ZHENG Rongxue, LIN Juan, DING Fuchuan, LING Qidan. Synthesis and Properties of Comb-shaped Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) as Cation Exchange Membrane by RAFT† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 633. |
| [10] | WANG Yan-Ling, LIU Jun-Bo, TANG Shan-Shan, CHANG Hai-Bo, LIANG Da-Dong. Preparation and Properties of Molecularly Imprinted Nanofiber Memberanes Towards Enrofloxacin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(12): 2880. |
| [11] | LIU Jun-Bo, TANG Shan-Shan, SUN Jia-Ni, JIN Rui-Fa. Theoretical Research on Self-assembly System of Molecular Imprinted Polymers Formed by Ciprofloxacin and Trifluoromethacrylic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(11): 2566. |
| [12] | WEI Hong, LI Juan, LI Ke-Bin, SUN Jian-Yu, ZHAO Feng. Effect of CCl4 on Antibiotics Levofloxacin’s Ultrasonic Degradation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(07): 1438. |
| [13] | XIE Guo-Fang, LU Tian-Hong, YANG Gai-Xiu, CHEN Yu, ZHOU Yi-Ming, TANG Ya-Wen*. Preparation and Mechanism of Carbon Supported Pt Catalyst Using Pt(NO3)2 and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(6): 1373. |
| [14] | LI Hui-Zhen, LIU Shao-Xuan, HUA Xiao-Hui, PAN Qing-Hua, YANG Zhan-Lan, .... Studies on the Protonation Structure of Ofloxacin in Concentrated Sulfuric Acid Solutions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(9): 1747. |
| [15] | HUANG Chun-Yu, BU Feng-Quan, MA Ren-Ping, QI Dian-Peng, Lü Nan* . Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles with Controllable Density on the Conducting Polymer Film [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(7): 1288. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
