

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1769.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160298
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XUE Peng1,2, WEI Yana1,3, YUE Fan1, ZHANG Yi2, WANG Jide1,*( )
)
Received:2016-04-29
Online:2016-10-10
Published:2016-09-20
Contact:
WANG Jide
E-mail:awangjd@sina.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XUE Peng, WEI Yana, YUE Fan, ZHANG Yi, WANG Jide. Effects of Functional Groups in α-Amino Acids on Reversible Oxygenation Performance of Co(Ⅱ) Complexes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1769.
| Ligand(L) | cCo(Ⅱ)/(mmol·L-1) | cL/(mmol·L-1) | V(DMF)∶V(H2O) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| His | 5.00 | 10.0 | 5∶5 | 7.3 |
| Fmoc-His(Fmoc) | 5.00 | 10.0 | 9∶1 | 9.0 |
| Phe | 5.00 | 10.0 | 7∶3 | 8.6 |
| Fmoc-Phe | 5.00 | 10.0 | 7∶3 | 8.8 |
| His-OMe | 1.25 | 2.5 | 1∶0 | 8.6 |
| Hist | 10.00 | 30.0 | 1∶0 | 9.0 |
Table 1 Concentration of Co(Ⅱ) and ligands, volume ratio of the solvent and pH value of the reaction
| Ligand(L) | cCo(Ⅱ)/(mmol·L-1) | cL/(mmol·L-1) | V(DMF)∶V(H2O) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| His | 5.00 | 10.0 | 5∶5 | 7.3 |
| Fmoc-His(Fmoc) | 5.00 | 10.0 | 9∶1 | 9.0 |
| Phe | 5.00 | 10.0 | 7∶3 | 8.6 |
| Fmoc-Phe | 5.00 | 10.0 | 7∶3 | 8.8 |
| His-OMe | 1.25 | 2.5 | 1∶0 | 8.6 |
| Hist | 10.00 | 30.0 | 1∶0 | 9.0 |
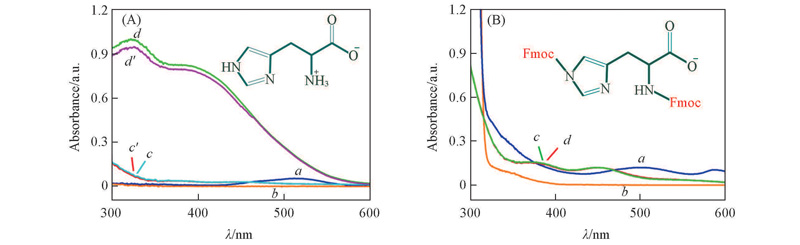
Fig.2 UV-Vis spectra of His-Co(Ⅱ)(A) and Fmoc-His(Fmoc)-Co(Ⅱ)(B) complexes (A) a. Co(Ⅱ); b. His; c/c'. His-Co(Ⅱ)-N2 1st/2nd; d/d'. His-Co(Ⅱ)-O2 1st/2nd;(B) a. Co(Ⅱ); b. Fmoc-His(Fmoc); c/d. Fmoc-His(Fmoc)-Co(Ⅱ)-N2/O2.
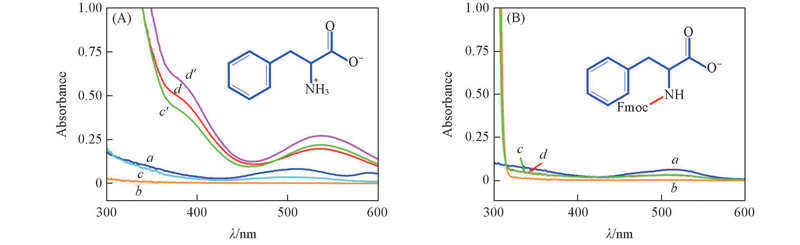
Fig.4 UV-Vis spectra of Phe-Co(Ⅱ)(A) and Fmoc-Phe-Co(Ⅱ)(B) complexes(A) a. Co(Ⅱ); b. Phe; c/c'. Phe-Co(Ⅱ)-N21st/2nd; d/d'. Phe-Co(Ⅱ)-O21st/2nd;(B) a. Co(Ⅱ); b. Fmoc-Phe; c/d. Fmoc-Phe-Co(Ⅱ)-N2/O2.
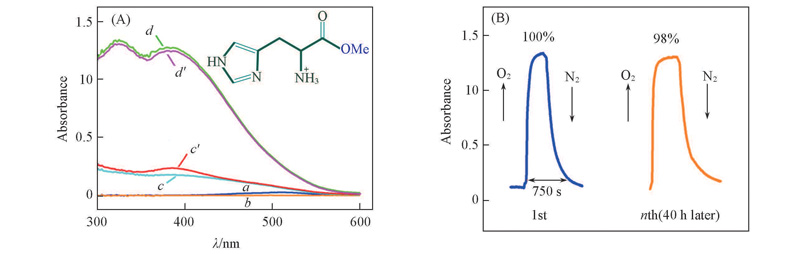
Fig.5 UV-Vis spectra(A) and dynamics test(B) of (His-OMe)-Co(Ⅱ) complexesa. Co(Ⅱ); b. His-OMe; c/c':(His-OMe)-Co(Ⅱ)-N2 1st/2nd; d/d':(His-OMe)-Co(Ⅱ)-O21st/2nd.
| [1] | Niederhoffer E. C., Timmons J. H., Martell A. E., Chem. Rev., 1984, 84(2), 137—203 |
| [2] | Murray L. J., Dinca M., Yano J., Chavan S., Bordiga S., Brown C. M., Long J. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(23), 7856—7857 |
| [3] | Johnson C., Ottiger S., Pini R., Gorman E. M., Nguyen J. G., Munson E. J., Mazzotti M., Borovik A., Subramaniam B., AICHE J., 2009, 55(4), 1040—1045 |
| [4] | Wang J. D., Collange E., Aymes D. J., Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., 1994, 131,37—44 |
| [5] | Wang J. D., Martell A. E., Reibenspies J. H., Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2002, 328,53—60 |
| [6] | Vogt L. H., Faigenbaum H. M., Wiberly S. E., Chem. Rev., 1963, 63(3), 269—277 |
| [7] | Johnson C., Long B., Nguyen J. G., Day V. W., Borovik A., Subramaniam B., Guzman J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(32), 12272—12281 |
| [8] | Yang H. Q., Zhang L., Zhong L., Yang Q. H., Li C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46(36), 6861—6865 |
| [9] | Hong S., So H., Yoon H., Cho K., Lee Y., Fukuzumi S., Dalton Trans., 2013, 42(22), 7842—7845 |
| [10] | Liu L. L., Li H. X., Wan L. M., Ren Z. G., Wang H. F., Lang J. P., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47,11146—11148 |
| [11] | Henderson I. M., Hayward R. C., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(40), 21366—21369 |
| [12] | Wei Y. N., Zhang X. C., Li H., Xu Q., Yue F., Wang J. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2), 354—360 |
| (魏雅娜, 张新村, 李辉, 徐骞, 岳凡, 王吉德.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(2), 354—360) | |
| [13] | Martell A. E., J. Mol. Catal., 1988, 44(1), 1—14 |
| [14] | Martell A. E., Motekaitis R. J., Chen D., Murase I., Pure Appl. Chem., 1993, 65(5), 959—964 |
| [15] | Simplicio J., Wilkins R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1967, 89(24), 6092—6095 |
| [16] | Guo M., Dong H., Li J., Cheng B., Huang Y. Q., Feng Y. Q., Lei A. W., Nat. Commun., 2012, 3,1190 |
| [17] | Burk D., Hearon J., Caroline L., Schade A. L., J. Biol. Chem., 1946, 165(2), 723—724 |
| [18] | Harris W. R., McLendon G., Martell A. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1976, 98(26), 8378—8381 |
| [19] | Wen H. M., Zhang X., Li H., Yue F., Wang J. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10), 2262—2269 |
| (文红梅, 张旭, 李辉, 岳凡, 王吉德.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(10), 2262—2269) | |
| [20] | Zhang X.C., Yue F., Li H., Huang Y., Zhang Y., Wen H. M., Wang J. D., Bioinorg. Chem. Appl., 2016, 2016, |
| [21] | Zhang X. C., Yue F., Huang Y., Fu P., Cheng X., Wang J. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(7), 1370—1375 |
| (张新村, 岳凡, 黄艳, 付佩, 程翔, 王吉德.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(7), 1370—1375) | |
| [22] | Yue F., Song N., Huang Y., Wang J. D., Xie Z. F., Lei H. Q., Zhang X. C., Fu P., Tao R. P., Chen X., Shi M. S., Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2013, 398,141—146 |
| [23] | Zhang X. C., Yue F., Huang Y., Cheng X., Wen H.M., Hu D., Wang J. D., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(11), 2387—2393 |
| (张新村, 岳凡, 黄艳, 程翔, 文红梅, 胡地, 王吉德.无机化学学报, 2013,29(11), 2387—2393) | |
| [24] | Fu J. H., Li J.F., Fu P., Yue F., Zhang X. L., Wang J. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(7), 1483—1487 |
| (符继红, 李俊芳, 付佩, 岳凡, 张旭龙, 王吉德.高等学校化学学报, 2011,32(7), 1483—1487) | |
| [25] | Fu P., Fu J. H., Li J.F., Yue F., Zhang X. L., Wang J. D., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28(7), 1360—1364 |
| (付佩, 符继红, 李俊芳, 岳凡, 张旭龙, 王吉德.无机化学学报, 2012,28(7), 1360—1364) | |
| [26] | Harris W. R., Martell A. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1977, 90(20), 6746—6750 |
| [27] | Yang Y., Deng Y. L., Yue F., Chen H. M., Sun D. C., Wang J. D., Comput. Appl. Chem., 2013, 30(6), 633—637 |
| (杨杨, 邓雅丽, 岳凡, 陈华梅, 孙都成, 王吉德.计算机与应用化学, 2013,30(6), 633—637) |
| [1] | TIAN Xueqin, MO Zheng, DING Xin, WU Pengyan, WANG Yu, WANG Jian. A Squaramide-containing Luminescent Metal-organic Framework as a High Selective Sensor for Histidine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210589. |
| [2] | LI Rongqing,LIU Jialu,FAN Ruochen,BAI Pengyang,ZHANG Liying,QUAN Chunshan. Preparation and Application of Specificity Phosphohistidine Antibody† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1552. |
| [3] | LIU Zhaoyang, SONG Yongxin, WANG Tianshu, SHAN Guiye. Preparation of Histidine Modified Prussian Blue and Its Interaction with Silver Ions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1492. |
| [4] | WU Yan,LIAN Huiting,SUN Xiangying,LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin Polymeric Membrane Sensor Based on Graphene and Potential Recognition for Histidine Enantiomer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 230. |
| [5] | CHENG Weiliang, ZHU Mengqian, QIN Wu, HOU Cuicui. Chemical Looping Combustion Characteristics of Fe2O3(104) and CO Under Synergistic Action of ZrO2/TiO2 Carrier† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 506. |
| [6] | DENG Guixian, LI Kongzhai, CHENG Xianming, GU Zhenhua, LU Chunqiang, ZHU Xing. Red Mud as Oxygen Carrier for Chemical Looping Combustion of Methane: Reactivity and Cyclic Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 327. |
| [7] | HUANG Yandong, WU Ruofei, CHU Yanqiu, DING Chuanfan. Effect of Side Chain of α-Amino Acids and Esters on the Stability Constants for β-Cyclodextrin Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 743. |
| [8] | ZENG Liangpeng, HUANG Fan, ZHU Xing, ZHENG Min, LI Kongzhai. Chemical Looping Conversion of Methane over CeO2-based and Co3O4-based Co3O4-CeO2 Oxygen Carriers:Controlling of Product Selectivity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 115. |
| [9] | LI Lei, LI Shushi, WANG Changsheng. Theoretical Studies on Noncovalent Interactions Between Charged Histidine Side Chain and DNA Base† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 56. |
| [10] | LI Xu, JIANG Jianhong, HAN Buxing, GU Huiwen, XIE Zhaofeng, CHEN Lan, XIAO Shengxiong, LI Chuanhua, LI Aitao, LI Xia, YAO Feihong, WANG Qun, LI Qiangguo. Synthesis and Biological Activities of o-Vanillin-histidine Schiff-base and Its Lanthanum Complex† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 856. |
| [11] | QIN Wu, LIN Changfeng, CHENG Weiliang, XIAO Xianbin. Enhancing the Activity of Iron Based Oxygen Carrier via Surface Controlled Preparation for Lignite Chemical Looping Combustion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 116. |
| [12] | WEN Hong-Mei, ZHANG Xu, LI Hui, YUE Fan, WANG Ji-De. Contrast Study of the Oxygenation of Co(Ⅱ) Complexes with Different Bi-/Poly-dentate Ligands [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2262. |
| [13] | DUAN Shu-E, ZHAI Yun-Hui, QU Ying-Juan, MA Ming-Yang. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver-histidine Complex Doped Montmorillonite Antibacterial Agent [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12): 2617. |
| [14] | SHAN Ning, WANG Bin-Bin, LIAN Wen-Hui, YU Miao, SHI Tong-Shun. Synthesis and Surface Photovoltage Property of Tailed Histidine-linked Lanthanon Metalloporphyrins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(08): 1651. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xin-Cun, YUE Fan, HUANG Yan, FU Pei, CHENG Xiang, WANG Ji-De. Reversible Oxygenation Properties of 2,3-Diaminopropanoic Acid Cobalt Complex [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(07): 1370. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||