

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (9): 1678.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160277
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUO Yilin1, SHI Ying1, WANG Qinyue1, LI Luoyuan1, YU Longjiang2,3, WANG Peng1,*( ), ZHANG Jianping1, WANG Zhengyu2
), ZHANG Jianping1, WANG Zhengyu2
Received:2016-04-25
Online:2016-09-10
Published:2016-08-26
Contact:
WANG Peng
E-mail:wpeng@iccas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUO Yilin, SHI Ying, WANG Qinyue, LI Luoyuan, YU Longjiang, WANG Peng, ZHANG Jianping, WANG Zhengyu. Spectroscopic Properties of LH2 from Thermochromatium tepidum in Liposome and Detergent Micelles†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1678.
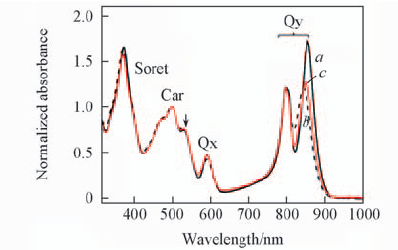
Fig.1 Absorption of LH2 from Tch. tepidum in various environments at pH=8 a. in DMM; b. in LDAO; c. in liposome. The arrow shows the absorption of spirilloxanthin.
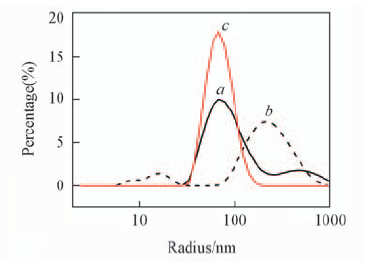
Fig.3 DLS data of the LH2 from Tch. tepidum in various detergents micelles or liposome systems a. in DMM(106 nm/565 nm); b. in LDAO(14 nm/257 nm); c. in liposome(73 nm). The data in the corresponding parentheses are the Rh of the vesicles for each system.
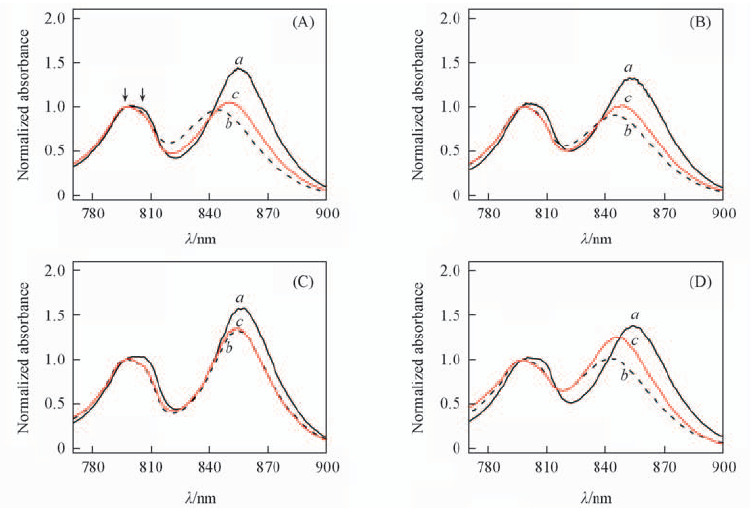
Fig.5 Qy absorption comparison of LH2 from Tch. tepidum in 0.05% DDM(a), 0.1% LDAO(b) and PC(c) liposome, under pH=8(A, C) and 3(B, D), and without Ca2+(A, B) or with 200 mmol/L Ca2+(C, D)(all the spectra are normalized at 797 nm), respectively Arrows in (A) show the splitting peaks position of B800.
| System | Without Ca2+ | With 200 mmol/L Ca2+ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH=8 | pH=3 | pH=8 | pH=3 | |||||
| λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | |
| In DDM | 855 | 1.41 | 854 | 1.28 | 857 | 1.53 | 855 | 1.35 |
| In LDAO | 845 | 0.96 | 845 | 0.90 | 854 | 1.32 | 843 | 1.02 |
| In liposome | 850 | 1.05 | 848 | 1.01 | 854 | 1.33 | 846 | 1.26 |
| In chromatophoreb | 854 | 1.41 | 852 | 1.18 | 858 | 1.38 | 857 | 1.32 |
Table 1 Qy absorption characteristics of LH2 from Tch. tepidum under various conditionsa
| System | Without Ca2+ | With 200 mmol/L Ca2+ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH=8 | pH=3 | pH=8 | pH=3 | |||||
| λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | λmax, B850/nm | ODB850/ODB800 | |
| In DDM | 855 | 1.41 | 854 | 1.28 | 857 | 1.53 | 855 | 1.35 |
| In LDAO | 845 | 0.96 | 845 | 0.90 | 854 | 1.32 | 843 | 1.02 |
| In liposome | 850 | 1.05 | 848 | 1.01 | 854 | 1.33 | 846 | 1.26 |
| In chromatophoreb | 854 | 1.41 | 852 | 1.18 | 858 | 1.38 | 857 | 1.32 |
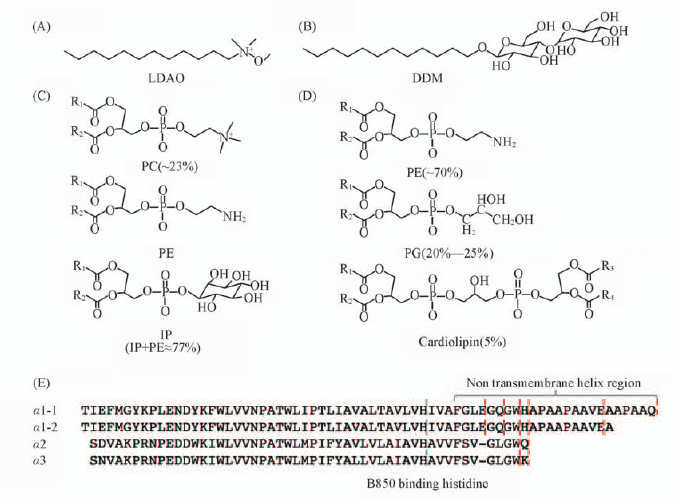
Fig.6 Molecular structure and components of detergents(A, B) or lipid(C), molecular structure and components of lipids of chromatophore from Tch. Tepidum(D) and the amino acid sequence of α-apoproteins of LH2 from Tch. Tepidum[4](E) R1—R4 are the aliphatic chain with various length and degree of unsaturation. The gray broken line indicates the B850 bacteriochlorophyll binding histidine, and the red broken line indicates the possible binding points for calcium ion or proton.
| [1] | Cogdell R. J., Gall A., Köhler J. Q., Rev. Biophys., 2006, 39(3), 227—324 |
| [2] | Koepke J., Hu X., Muenke C., Schulten K., Michel H., Structure,1996, 4(5), 581—597 |
| [3] | Papiz M. Z., Prince S. M., Howard T., Cogdell R. J., Isaacs N. W., J. Mol. Biol., 2003, 326(5), 1523—1538 |
| [4] | Sekine F., Horiguchi K., Kashino Y., Shimizu Y., Yu L. J., Kobayashi M., Wang Z. Y., Photosynth. Res., 2012, 111(1/2), 9—18 |
| [5] | Van Dijk B., Nozawa T., Hoff A. J., Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 1998, 54(9), 1269—1278 |
| [6] | Yang F., Yu L. J., Wang P., Ai X. C., Wang Z. Y., Zhang J. P., J. Phys. Chem. B,2011, 115(24), 7906—7913 |
| [7] | Shi Y., Zhao N. J., Wang P., Fu L. M., Yu L. J., Zhang J. P., Wang Z. Y., J. Phys. Chem. B,2015, 119(47), 14871—14879 |
| [8] | Ma F., Kimura Y., Yu L. J., Wang P., Ai X. C., Wang Z. Y., Zhang J. P., FEBS J., 2009, 276(6), 1739—1749 |
| [9] | Kimura Y., Yu L. J., Hirano Y., Suzuki H., Wang Z. Y., J. Biol. Chem., 2009, 284(1), 93—99 |
| [10] | Kimura Y., Inada Y., Numata T., Arikawa T., Li Y., Zhang J. P., Wang Z. Y., Ohno T., Biochim. Biophys. Acta,2012, 1817(7), 1022—1029 |
| [11] | Ma F., Kimura Y., Zhao X. H., Wu Y. S., Wang P., Fu L. M., Wang Z. Y., Zhang J. P., Biophys. J., 2008, 95(7), 3349—3357 |
| [12] | Niwa S., Yu L. J., Takeda K., Hirano Y., Kawakami T., Wang Z. Y., Miki K., Nature,2014, 508(7495), 228—232 |
| [13] | Dewa T., Sumino A., Watanabe N., Noji T., Nango M., Chem. Phys., 2013, 419, 200—204 |
| [14] | Schubert A., Stenstam A., Beenken W. J. D., Herek J. L., Cogdell R. J., Pullertis T., Sundström V., Biophys. J., 2004, 86(4), 2363—2373 |
| [15] | Zhou F., Liu S., Hu Z., Kuang T., Paulsen H., Yang C., Photosynth. Res., 2009, 99(3), 185—193 |
| [16] | Sumino A., Dewa T., Noji T., Nakano Y., Watanabe N., Hildner R., Bösch N., Köhler J., Nango M., J. Phys. Chem. B,2013, 117(36), 10395—10404 |
| [17] | Frese R. N., Sieber C. A., Niederman R. A., Hunter C. N., Ottot C., Grandelle R. V., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,2004, 101(2004), 17994—17999 |
| [18] | Tschirner N., Schenderlein M., Brose K., Schlodder E., Mroginski M. A., Thomsena C., Hildebrandt P., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11(48), 11471—11478 |
| [19] | Niedzwiedzki D. M., Kobayashi M., Blankenship R. E., Photosynth. Res., 2011, 107(2), 177—186 |
| [20] | Mukai-Kuroda Y., Fujii R., Ko-chi N., Sashima T., Koyama Y., Abe M., Gebhard R., Hoef I. V. D., Lugtenburg J., J. Phys. Chem. A., 2002, 106(14), 3566—3579 |
| [21] | Ruban A. V., Johnson M. P., Duffy C. D. P., Biochim. Biophys. Acta,2012, 1817(1), 167—181 |
| [22] | Löhner A., Carey A. M., Hacking K., Picken N., Kelly S., Cogdell R., Köhler J., Photosynth. Res., 2015, 123(1), 23—31 |
| [23] | Fowler G. J. S., Visschers R. W., Grief G. G., Grondelle R. V., Hunter C. N., Nature,1992, 355, 848—850 |
| [24] | Fowler G. J. S., Sockalingum G. D., Robert B., Hunter C. N., Biochem. J., 1994, 299(3), 695—700 |
| [25] | Sturgis J.N., Robert B., J. Phys. Chem. B,1997, 101(37), 7227—7231 |
| [1] | WANG Tingting, LEI Yuhan, LIN Yujuan, HUANG Jialing, LIU Cuie, ZHENG Fengying, LI Shunxing. Preparation of Liposome-terminated CsPbX3(X=Cl,Br,I) Nanocrystals and Applications in Light-emitting Diode Devices [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1896. |
| [2] | ZHANG Zhang,WANG Dong,WANG Xiaolei,XU Yan. Regulation of Ester Synthesis Activity of Rhizopus chinensis Lipase† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 747. |
| [3] | ZHAO Wencai, HAN Lili, PENG Yingjun, WANG Xiaojing, LIU Shengyu, LI Pengfei, HUANG Yibing, CHEN Yuxin. Effect of Basic Amino Acids on the Biological Activity of Helical Antimicrobial Peptide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 681. |
| [4] | WEI Yanshan, WEI Bangzhi, HUANG Aimin, MA Lin. Membrane Structure Alteration of DOPC Liposome Induced by Interaction with Gene Carrier Polyethyleneimine† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2271. |
| [5] | XIONG Wen, QUAN Chunshan, WANG Lina, ZHANG Xuning, ZHAO Jing, ZHENG Wei, FAN Shengdi. Effect of Different Charged Liposomes on Transmembrane Incorporation Efficiency of the Staphylococcus Aureus Receptor Histidine Kinase AgrC† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 1901. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xiao-Fei, SUN Run-Guang, HAO Chang-Chun, YANG Qian, ZHAO Yan. Morphology and Mechanics Character of PVP-Modified Liposome [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(08): 1751. |
| [7] | LI Guang-Hui, SHEN Hai-Xing, QIAN Jun, SI Zhan, ZHU Jian-Hua*. 125I-AIBZM Nanoliposomes Targeting Brain as Imaging Agents [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(6): 1295. |
| [8] | LIU Yi, SUN Kao-Xiang*, YAO Wen-Jun, LIANG Na, MU Hong-Jie, LIANG Rong-Cai, YAO . Preparation, Characterization of PAMAM Dendrimers-coated Liposomes and Evaluation for Ophthalmic Drug Delivery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(4): 800. |
| [9] | CHEN Yong-Zhu, QIU Feng, ZHAO Xiao-Jun*. Self-assembling Structure and Mechanism of a Wedge-shaped Peptide Detergent A3V3D [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(7): 1337. |
| [10] | LIANG Xiao-Fei, WANG Han-Jie, TIAN Hui, LUO Hao, CHENG Jing, HAO Li-Juan, CHANG Jin*. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Magnetic Cationic Polymeric Liposomes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(4): 858. |
| [11] | DONG Zhi-Qiang1, XIA Zhi-Ning1,2*, JIANG Xue-Mei2. Method Measuring of Hydrophobic Parameter of Organic Compounds via a Novel Liposome Capillary Electrophoresis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(7): 1273. |
| [12] | CHEN Ying-Ying, SUN Run-Guang*, WANG Bo, ZHANG Ming. Separation of Caveolae and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of Them [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(12): 2299. |
| [13] | SUN Yue, LU Min, YIN Xua-Feng. Intracellular Delivery of Fluorescent Dyes Mediated by Nanometer-Liposomes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(4): 632. |
| [14] | SUN Chun-Yan, LI Di, WANG Mei-Jia, TANG Jiang, LIU Yang, LI Jing-Hong. Studies on Solubilization of Phospholipid Liposomes by Water-miscible Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(3): 515. |
| [15] | SUN Jin, FAN Xiao-Wen, ZHANG Tian-Hong, HE Zhong-Gui. Unusual Molecular Charge Property of Amphoteric Quinolones in Physiological Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(11): 2185. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||