

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 607.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160013
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Caiping, LI Youfen*( ), ZHANG Yidong
), ZHANG Yidong
Received:2016-01-08
Online:2016-04-10
Published:2016-03-22
Contact:
LI Youfen
E-mail:yfli@ mail. buct. edu. cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Caiping, LI Youfen, ZHANG Yidong. Preparation of Glass Ceramics Containing CaF2 by One-step Method and Analysis of the Fluorescent Probe of Eu3+ Ion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(4): 607.
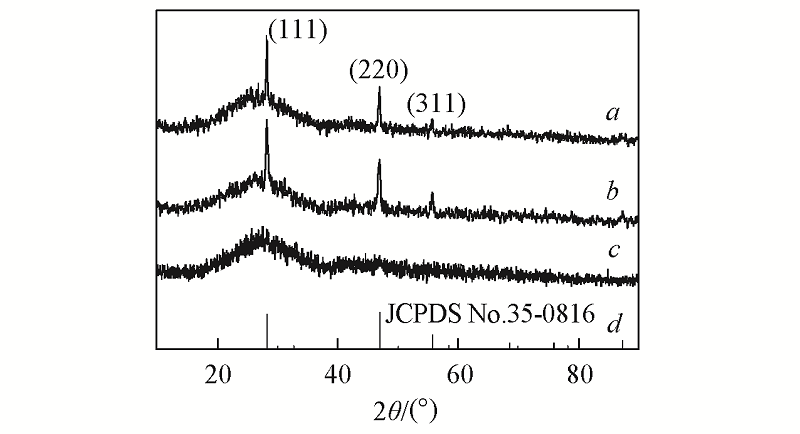
Fig.1 XRD patterns of glass and glass ceramicsa. Glass ceramic prepared at 850 ℃; b. glass ceramic prepared at 650 ℃; c. glass; d. standard patterns of CaF2.
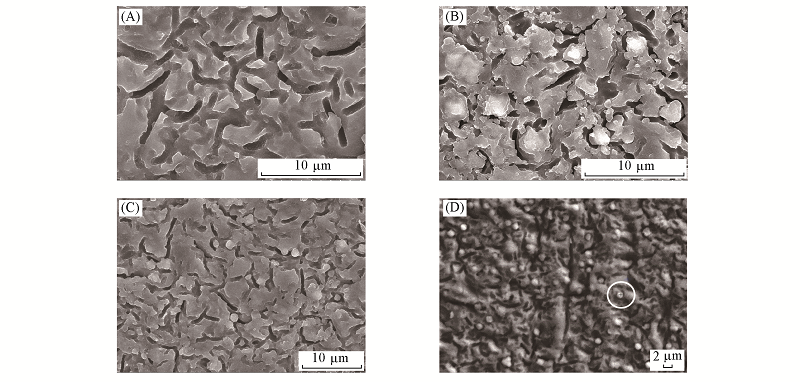
Fig.2 SEM images of the glass and glass ceramics prepared at different temperatures (A) Glass; (B) glass ceramics prepared at 650 ℃; (C) glass ceramics prepared at 750 ℃; (D) glass ceramic prepared at 850 ℃. Circled area for EDS sprectrum.
| Element | Actual content(mass ratio, %) | Theoretical content(mass ratio, %) | Atomic content(atomic ratio, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 29.29 | 25.59 | 39.64 |
| O | 16.38 | 14.31 | 16.65 |
| F | 25.97 | 22.69 | 22.23 |
| Na | 3.94 | 3.44 | 2.78 |
| Al | 8.87 | 7.75 | 5.34 |
| Si | 6.76 | 5.90 | 3.91 |
| K | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.32 |
| Ca | 22.48 | 19.64 | 9.12 |
Table 1 Elementary composition and content of glass ceramics
| Element | Actual content(mass ratio, %) | Theoretical content(mass ratio, %) | Atomic content(atomic ratio, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 29.29 | 25.59 | 39.64 |
| O | 16.38 | 14.31 | 16.65 |
| F | 25.97 | 22.69 | 22.23 |
| Na | 3.94 | 3.44 | 2.78 |
| Al | 8.87 | 7.75 | 5.34 |
| Si | 6.76 | 5.90 | 3.91 |
| K | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.32 |
| Ca | 22.48 | 19.64 | 9.12 |
| Temperature/℃(Sample) | I2/ | I4/ | 1020Ω2/cm2 | 1020Ω4/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 650 | 2.650 | 0.476 | 3.236 | 1.792 |
| 750 | 2.694 | 0.476 | 3.317 | 1.793 |
| 800 | 2.715 | 0.500 | 3.342 | 1.883 |
| 850 | 2.769 | 0.517 | 3.409 | 1.947 |
| 900 | 2.687 | 0.475 | 3.308 | 1.789 |
Table 2 Intensity ratio and J-O intensity parameters of glass ceramics prepared at different temperatures
| Temperature/℃(Sample) | I2/ | I4/ | 1020Ω2/cm2 | 1020Ω4/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 650 | 2.650 | 0.476 | 3.236 | 1.792 |
| 750 | 2.694 | 0.476 | 3.317 | 1.793 |
| 800 | 2.715 | 0.500 | 3.342 | 1.883 |
| 850 | 2.769 | 0.517 | 3.409 | 1.947 |
| 900 | 2.687 | 0.475 | 3.308 | 1.789 |
| [1] | Wang Y., Ohwaki J., Appl. Phy. Lett., 1993, 63(24), 3268—3270 |
| [2] | Fan M.W., Study on the Laser Performance of Nd3+(Yb3+) Doped CaF2 Crystal, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, 2014 |
| (范明纹. 掺Nd3+(Yb3+)的CaF2晶体激光特性研究, 济南: 山东师范大学, 2014) | |
| [3] | Fu J., Parker J.M., Flower P. S.,Mater. Res. Bull., 2002, (37), 1843—1849 |
| [4] | Meng Q. G., Zhang H. J., J. Inorg. Mater., 1999, 4(4), 630—634 |
| (孟庆国, 张洪杰. 无机材料学报, 1999, 4(4), 630—634) | |
| [5] | Li Y. H., Zhao L., Zhang Y. M., Li Y. C., Dong W. S., Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(12), 41—44 |
| (李艳红, 赵丽, 张永明, 李英春, 董文嗣. 材料热处理学报, 2013, 34(12), 41—44) | |
| [6] | Chen B. J., Wang H. Y., Huang S. H., Acta Optica Sinica, 2001, 21(6), 762—765 |
| (陈宝玖, 王海宇, 黄世华. 光学学报, 2001, 21(6), 762—765) | |
| [7] | Yu H., Sun J., Liu B. R., Song J., Zhao L. J., Xu J. J., Acta Physica Sinica, 2006, 55(11), 6152—6156 |
| (余华, 孙健, 刘宝荣, 宋杰, 赵丽娟, 许京军. 物理学报, 2006, 55(11), 6152—6156) | |
| [8] | Chen H., Zhao X., Gao H., Zhu H. D., Jiang L. H., Ling Q. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1), 41—47 |
| (陈鸿, 赵璇, 高慧, 朱海娣, 姜丽红, 凌启淡. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(1), 41—47) | |
| [9] | Kawamoto Y., Kanno R., Qiu J., J. Mater. Sci., 1998, 33(1), 63—67 |
| [10] | Gu Y. P., Shen H. Z., Li L., Liu W. Q., Wang W. Q., Xu D. P., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(6), 879—884 |
| [11] | Lang J. H., Wang J. Y., Zhang Q., Xu S. S., Han Q., Zhang Y., Zhai H. J., Cao J., Yan Y. S., Yang J. H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(4), 538—542 |
| [12] | Meng Z., Liu S. J., Shen J. X., Gao B., Journal of Ceramics, 2010, 31(1), 82—86 |
| (孟政, 刘树江, 沈建兴, 高彬. 陶瓷学报, 2010, 31(1), 82—86) | |
| [13] | Tian Y.L., Sun S. B., New Edition of Glass Industry, China Light Industry Press, Beijing, 2009, 5—12 |
| (田英良, 孙诗兵编. 新编玻璃工艺学, 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2009, 5—12) | |
| [14] | Meng J., Zhao L. J., Yu H., Tang L Q., Liang Q., Acta Physica Sinica, 2005, 54(3),1442—1446 |
| (孟婕, 赵丽娟, 余华, 唐莉勤, 梁沁. 物理学报, 2005, 54(3), 1442—1446) | |
| [15] | Wang J., Study of the Structure and Properties of MgO-A12O3-SiO2 Transparent Glass-ceramics, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, 2013 |
| (王静. MgO-Al2O3-SiO2透明微晶玻璃结构与性能的研究, 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2013) | |
| [16] | Judd B. R., Phys. Rev., 1961, 127(3), 750—761 |
| [17] | Ofelt G. S., J. Chem. Phys., 1962, 37(3), 511—520 |
| [18] | Chen B. J., Wang H. Y., E S. L., Huang S. H., Chin. J. Lumin., 2001, 22(2), 139—142 |
| (陈宝玖, 王海宇, 鄂书林, 黄世华. 发光学报, 2001, 22(2), 139—142) | |
| [19] | Xu W., Investigation on the Probe Property of Eu3+and Fluorescence Property of Oxy-fluoride Glasses Doped with Rare Earth Ions, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian, 2010 |
| (徐伟. Eu3+离子探针特性与稀土掺杂氟氧化物玻璃荧光特性的研究, 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2010) |
| [1] | Yingying ZHANG,Yiwen HUANG,Bing ZHAO,Liyan WANG,Bo SONG. Synthesis of a Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe of Cr 3+ and Its Application in Cell Imaging † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2486. |
| [2] |
YU Zhaochuan, MA Wenhui, WU Tao, WEN Jing, ZHANG Yong, WANG Liyan, CHU Hongtao.
Preparation of B, N, S co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Fluorescence Detection of Fe 3+ and H2P |
| [3] | HUANG Chibao,PAN Qi,CHEN Huashi,LIANG Xing,LÜ Guoling. Dicyanostilbene-derived Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Lead Ions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 897. |
| [4] | ZHANG Hanbing, LI Chengren, LI Shufeng, GAO Xinyu, HONG Yuanzhi, LI Zhichao, SUN Jingchang. White Light Emission Performance of Y2O3∶Eu3+,Dy3+ Nanophosphors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 193. |
| [5] | HAN Ruixia,LÜ Jitao,ZHANG Shuzhen. Molecular Probe for the Determination of Hydroxyl Radicals in Heterogeneous Systems: Coumarin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2658. |
| [6] | XU Wanzhen, QIU Chunxiao, HUANG Weihong, LIU Hong, YANG Wenming. Computer Simulation Design, Preparation and Application of Fluorescence Sensors Based on Quantum Dots for Selective Detection of 4-Nitrophenol in River Water† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1155. |
| [7] | HUANG Chibao, PAN Qi, CHEN Xiaoyuan, ZHAO Guanglian, CHEN Huashi, LIANG Xing, LÜ Guoling. Dicyanostilbene-derived Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Mercury Ions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1751. |
| [8] | SONG Chunxia, YANG Xiaohai, WANG Kemin, WANG Qing, LIU Jianbo, HUANG Jin, LI Wenshan, HUANG Haihua, LIU Wei. Application of Polymers in Fluorescence Analysis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 201. |
| [9] | MI Xiaolong, JIAO Xiaojie, LIU Chang, HE Song, ZENG Xianshun. Rhodamine-based Cell Permeable Fluoresecent Turn-on Probes for Cupric Ion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1784. |
| [10] | HUANG Chibao, LIANG Xing, ZENG Qihua, CHEN Huashi, ZENG Boping, YI Daosheng, CHEN Xiaoyuan. Dicyanostilbene-derived Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Free Zinc Ions in Live Cells and Living Tissues† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 646. |
| [11] | XU Hui, DAI Yanna, SHAN Hongyan, FEI Qiang, HUAN Yanfu, LI Guanghua, FENG Guodong. Rhodamine Derivative ABDO/Er3+ Composite Fluorescent Probe in Response to Temperature† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 736. |
| [12] | MIN Chungang, LENG Yan, YANG Xikun, HUANG Shaojun, REN Aimin. Electronic Structures and Photophysical Properties of Firefly Oxyluciferin and Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 564. |
| [13] | CHEN Yi, ZHANG Yan, ZENG Xi, MU Lan, LI Jun, SUN Qiang, ZHANG Jian-Xin, WEI Gang. Synthesis and Probe Properties of Rhodamine-triazine Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7): 1598. |
| [14] | KOU Ying-Ying, MENG Qing-Bin, LIU Ke-Liang. Coassembly of Palmitic Acid Modified α-Helical Peptide Amphiphiles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(11): 2476. |
| [15] | CAO Xia, ZENG Xi, MU Lan, CHEN Yi, WANG Rui-Xiao, ZHANG Yun-Qian, ZHANG Jian-Xin, WEI Gang. Synthesis, Characterization and Aggregation Induced Enhanced Emission of New Phenothiazine Hydrazone [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10): 2184. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||