

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 2087.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150747
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
PANG Ran1, JIN Xi1, ZHAO Liubin2, DING Songyuan1, WU Deyin1,*( ), TIAN Zhongqun1
), TIAN Zhongqun1
Received:2015-09-25
Online:2015-11-10
Published:2015-10-28
Contact:
WU Deyin
E-mail:dywu@xmu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
PANG Ran, JIN Xi, ZHAO Liubin, DING Songyuan, WU Deyin, TIAN Zhongqun. Quantum Chemistry Study of Electrochemical Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2087.
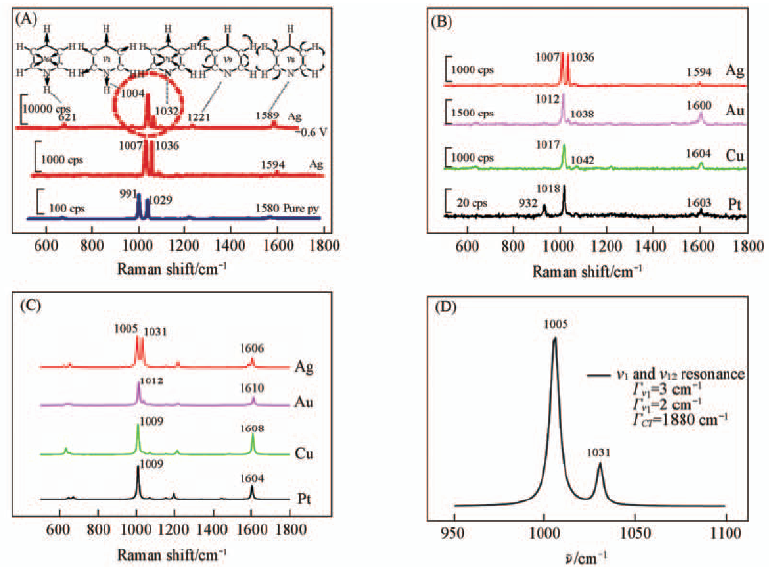
Fig.3 Raman spectra of liquid pyridine, SERS spectra of pyridine adsorbed on silver electrode at open circuit potential and the peak potential at -0.6 V(vs. SCE)(A)[3], SERS spectra of pyridine on different electrodes at open circuit potentials(B), simulated SERS spectra of pyridine(C) and effect of the charge transfer excited state on resonance Raman spectra of the pyridine-silver complex(D)[32] Ref.[3] copyright from the Royal Society of Chemistry; ref.[32] copyright from Elsevier.
| Mode | ν2 | ν13 | ν20a | ν8a | ν19a | ν9a | ν18a | ν12 | ν1 | ν6a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.288 | 0.021 | 0.339 | 0.052 | 0.035 | 0.309 | 0.152 |
| ωGround state/cm-1 | 3097.2 | 3076.5 | 3067.7 | 1605.4 | 1485.4 | 1217.2 | 1071.7 | 1030.8 | 1005.6 | 623.9 |
| ωExcited state/cm-1 | 3054.8 | 3100.5 | 3077.9 | 1579.0 | 1435.3 | 1189.0 | 985.2 | 1019.4 | 937.6 | 613.8 |
Table 1 Huang-Rhys factors(s) and vibrational frequencies(ω) of totally symmetry modes for the ground and excited states of Py-Ag2, calculated at the B3LYP/6-311+G**/LANL2DZ level*
| Mode | ν2 | ν13 | ν20a | ν8a | ν19a | ν9a | ν18a | ν12 | ν1 | ν6a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.288 | 0.021 | 0.339 | 0.052 | 0.035 | 0.309 | 0.152 |
| ωGround state/cm-1 | 3097.2 | 3076.5 | 3067.7 | 1605.4 | 1485.4 | 1217.2 | 1071.7 | 1030.8 | 1005.6 | 623.9 |
| ωExcited state/cm-1 | 3054.8 | 3100.5 | 3077.9 | 1579.0 | 1435.3 | 1189.0 | 985.2 | 1019.4 | 937.6 | 613.8 |
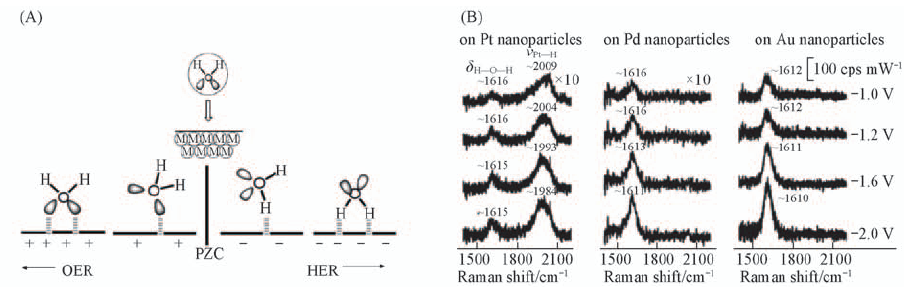
Fig.4 Adsorded directions of water changed with the surface charges upon more negative potential(A) and SERS spectra of water molecules adsorded on Pt, Pd and Au nanoparticles(B)[60] Copyright from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
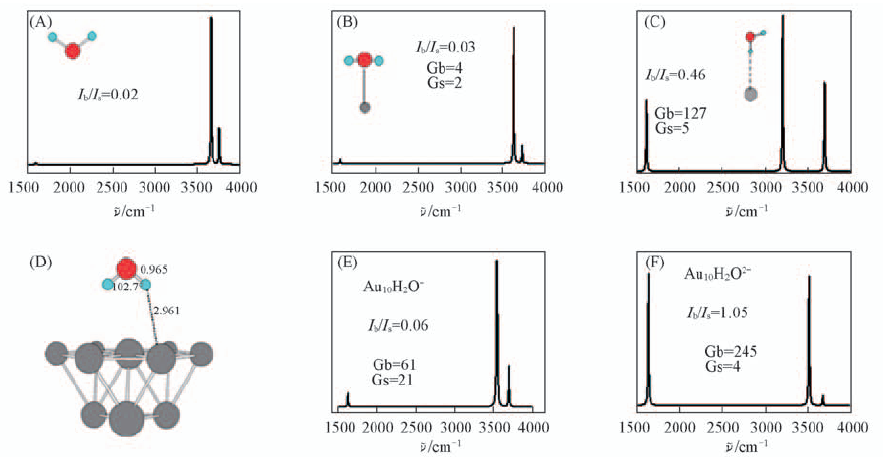
Fig.5 Calculated structures and SERS spectra from cluster models for a water molecule adsorbed on negatively charged Auδ10(δ=-1, -2)[44] Copyright from the Royal Society of Chemistry. (A) Simulated Raman spectrum of free water molecule; (B) simulated raman spectrum of H2O…Au through the interaction between O and Au atoms; (C) simulated Raman spectrum of HOH…Au- through the interaction between H atom and Au anion; (D) [Au10-H2O]δ(δ=-1, -2) clusters; (E) simulated Raman spectrum of Au10-H2O- complex; (F) simulated Raman spectrum of Au10-H2O2- complex.
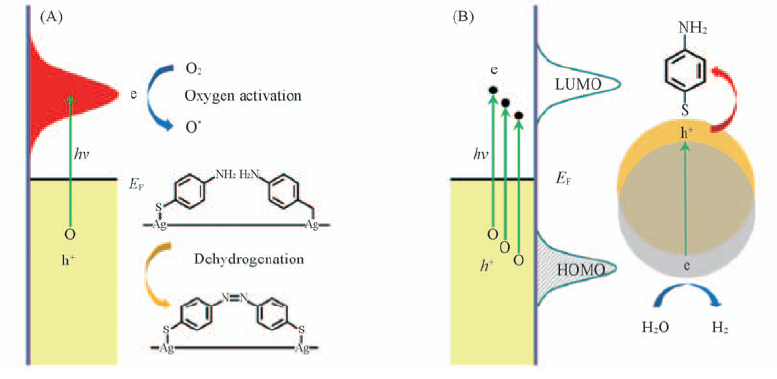
Fig.7 Schematic diagrams of the mechanisms of surface plasmon enhanced photoelectrochemical reaction (A) Oxygen activation at solid-gas interfaces; (B) hole oxidization at electrode-electrolyte interfaces.
| [1] | Fleischmann M., Hendra P. J., Mcquillan A., J. Chem. Phys. Lett., 1974, 26, 163—166 |
| [2] | Jouanne M., Beserman R., Balkanski M., Jain K. P., Solid State Communications, 1974, 15(2), 251—253 |
| [3] | Wu D. Y., Li J. F., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37(5), 1025—1041 |
| [4] | Tian Z.Q., Ren B., Li J. F., Yang Z. L.,Chem. Commun., 2007, (34), 3514—3534 |
| [5] | Nie S. M., Emery S. R., Science, 1997, 275(5303), 1102—1106 |
| [6] | Tian Z. Q., Ren B., Wu D. Y., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(37), 9463—9483 |
| [7] | Tian Z. Q., Ren B., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2004, 55, 197—229 |
| [8] | Abdelsalam M., Bartlett P. N., Russell A. E., Baumberg J. J., Calvo E. J., Tognalli N. G., Fainstein A., Langmuir, 2008, 24(13), 7018—7023 |
| [9] | Ding S. Y., Yi J., Li J. F., Tian Z. Q., Surf. Sci., 2015, 631, 73—80 |
| [10] | Lombardi J. R., Birke R. L., Lu T., Xu J., J. Chem. Phys., 1986, 84, 4174—4180 |
| [11] | Otto A. J., Raman Spectrosc., 2005, 36(6/7), 497—509 |
| [12] | Ding S. Y., Wu D. Y., Yang Z. L., Ren B., Xu X., Tian Z. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(12), 2569—2581 |
| (丁松园, 吴德印, 杨志林, 任赋, 徐昕, 田中群. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(12), 2569—2581) | |
| [13] | Tian Z.Q., Wu D. Y., Unified Theory of Surface Enhanced Spectroscopy, 10000 Selected Problems in Sciences: Chemistry, Science Press, Beijing, 2009, 210 |
| (田中群, 吴德印. 表面增强光谱学的统一理论, 10000个科学难题, 化学卷, 北京: 科学出版社, 2009, 210) | |
| [14] | Lombardi J. R., Birke R. L., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(14), 5605—5617 |
| [15] | Wu D. Y., Liu X. M., Huang Y. F., Ren B., Xu X., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(42), 18212—18222 |
| [16] | Su S., Huang R., Zhao L. B., Wu D. Y., Tian Z. Q., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2011, 27(4), 781—792 |
| [17] | Wang A., Huang Y. F., Sur U. K., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Rondinini S., Amatore C., Tian Z. Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(28), 9534—9536 |
| [18] | Ding S. Y., Liu B. J., Jiang Q. N., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Xu X., Tian Z. Q., Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 4962—4964 |
| [19] | Wu D. Y., Hayashi M., Chang C. H., Liang K. K., Lin S. H., J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 118(9), 4073—4085 |
| [20] | Huang R., Yang H. T., Cui L., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(45), 23730—23737 |
| [21] | Tao S., Yu L. J., Pang R., Huang Y. F., Wu D. Y., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(37), 18891—18903 |
| [22] | Krishnan R., Binkley J. S., Seeger R., Pople J. A., J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72(1), 650—654 |
| [23] | Kendall R. A., Dunning T. H., Harrison R. J., J. Chem. Phys., 1992, 96(9), 6796—6806 |
| [24] | Hay P. J., Wadt W. R., J. Chem. Phys., 1985, 82(1), 299—310 |
| [25] | Wu D. Y., Hayashi M., Shiu Y. J., Liang K. K., Chang C. H., Yeh Y. L., Lin S. H., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2003, 107(45), 9658—9667 |
| [26] | Wu D. Y., Ren B., Xu X., Liu G. K., Yang Z. L., Tian Z. Q., J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 119(3), 1701—1709 |
| [27] | Liu J. L., Guo Y., Xue Y., Yan G. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(1), 100—105 |
| (刘靖丽, 郭勇, 薛英, 鄢国森, 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(1), 100—105) | |
| [28] | Xue Y., Xie D. Q., Yan G. S., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2000, 76(6), 686—699 |
| [29] | Wu D. Y., Ren B., Jiang Y. X., Xu X., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2002, 106(39), 9042—9052 |
| [30] | Wu D. Y., Liu X. M., Duan S., Xu X., Ren B., Lin S. H., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(11), 4195—4204 |
| [31] | Wu D. Y., Duan S., Liu X. M., Xu Y. C., Jiang Y. X., Ren B., Xu X., Lin S. H., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2008, 112(6), 1313—1321 |
| [32] | Wu D. Y., Hayashi M., Lin S. H., Tian Z. Q., Spectroc. Acta Pt. A: Molec. Biomolec. Spectr., 2004, 60(1/2), 137—146 |
| [33] | Lee M. T., Wu D. Y., Tian Z. Q., Lin S. H., J. Chem. Phys., 2005, 122(9), 094719 |
| [34] | Bruckbauer A., Otto A., J. Raman Spectrosc., 1998, 29(8), 665—672 |
| [35] | Billmann J., Otto A., Solid State Commun., 1982, 44(2), 105—107 |
| [36] | Osamura Y., Yamaguchi Y., Schaefer H. F., J. Chem. Phys., 1982, 77(1), 383—390 |
| [37] | Nakai H., Nakatsuji H., J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 103(6), 2286—2294 |
| [38] | Rubim J. C., Corio P., Ribeiro M. C. C., Matz M., J. Phys. Chem., 1995, 99(43), 15765—15774 |
| [39] | Zhao L. L., Jensen L., Schatz G. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(9), 2911—2919 |
| [40] | Kambhampati P., Child C. M., Foster M. C., Campion A., J. Chem. Phys., 1998, 108(12), 5013—5026 |
| [41] | Avouris P., Demuth J. E., J. Chem. Phys., 1981, 75, 4783—4794 |
| [42] | Fang Y., Liu Z., Science China Chemistry, 2010, 53(3), 543—552 |
| [43] | Jinnouchi R., Anderson A. B., Physical Review B, 2008, 77(24) |
| [44] | Li J. F., Huang Y. F., Duan S., Pang R., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Xu X., Tian Z. Q., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12(10), 2493—2502 |
| [45] | Pang R., Yu L. J., Wu D. Y., Mao B. W., Tian Z. Q., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 101, 272—278 |
| [46] | Creighton J.A., Eds.: Tian Z. Q., Ren B., Progress in Surface Raman Spectros Copy Theory, Techniques & Applications, University Press: Xiamen, 2000, 11—16 |
| [47] | Klots T. D., Spectroc. Acta Pt. A: Molec. Biomolec. Spectr., 1998, 54(10), 1481—1498 |
| [48] | Schlucker S., Singh R. K., Asthana B. P., Popp J., Kiefer W., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2001, 105(43), 9983—9989 |
| [49] | Creighton J. A., Surface Science, 1986, 173(2/3), 665—672 |
| [50] | Jensen L., Zhao L. L., Schatz G. C., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(12), 4756—4764 |
| [51] | Wu D. Y., Zheng J. Z., Ren B., Xu X., Tian Z. Q., Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal., 2005, 25(3), 365—368 |
| [52] | Ingram J. C., Pemberton J. E., Langmuir, 1992, 8(8), 2034—2039 |
| [53] | Arenas J. F., Tocon I. L., Otero J. C., Marcos J. I., J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(22), 9254—9261 |
| [54] | Islampour R., Hayashi M., Lin S. H., J. Raman Spectrosc., 1997, 28(5), 331—338 |
| [55] | Xie Y., Wu D. Y., Liu G. K., Huang Z. F., Ren B., Yan J. W., Yang Z. L., Tian Z. Q., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2003, 554/555, 417—425 |
| [56] | Clark J. H., Dines T., J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 1986, 25, 131—158 |
| [57] | Matz D. L., Pemberton J. E., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(21), 11548—11555 |
| [58] | Toney M. F., Howard J. N., Richer J., Borges G. L., Gordon J. G., Melroy O. R., Wiesler D. G., Yee D., Sorensen L. B., Nature, 1994, 368(6470), 444—446 |
| [59] | Velasco-Velez J. J., Wu C. H., Pascal T. A., Wan L. F., Guo J., Prendergast D., Salmeron M., Science, 2014, 346(6211), 831—834 |
| [60] | Jiang Y. X., Li J. F., Wu D. Y., Yang Z. L., Ren B., Hu J. W., Chow Y. L., Tian Z. Q., Chem. Commun., 2007, 43(44), 4608—4610 |
| [61] | Gao P., Gosztola D., Weaver M. J., J. Phys. Chem., 1988, 92(25), 7122—7130 |
| [62] | Sun S., Birke R. L., Lombardi J. R., Leung K. P., Genack A. Z., J. Phys. Chem., 1988, 92(21), 5965—5972 |
| [63] | Matsuda N., Yoshii K., Ataka K., Osawa M.,Chem. Lett., 1992, 1385—1388 |
| [64] | Osawa M., Matsuda N., Yoshii K., Uchida I., J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98(48), 12702—12707 |
| [65] | Hill W., Wehling B., J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97(37), 9451—9455 |
| [66] | Yang X. M., Tryk D. A., Hashimoto K., Fujishima A., J. Raman Spectroscopy, 1998, 29(8), 725—732 |
| [67] | Wu D. Y., Zhao L. B., Liu X. M., Huang R., Huang Y. F., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(9), 2520—2522 |
| [68] | Huang Y. F., Zhu H. P., Liu G. K., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(27), 9244—9246 |
| [69] | Zhao L. B., Zhang M., Huang Y. F., Williams C. T., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. Letters, 2014, 5(7), 1259—1266 |
| [70] | Huang Y. F., Zhang M., Zhao L. B., Feng J. M., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(9), 2353—2357 |
| [71] | Zhao L. B., Huang Y. F., Liu X. M., Anema J. R., Wu D. Y., Ren B., Tian Z. Q., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(37), 12919—12929 |
| [72] | Sun M., Xu H., Small, 2012, 8(18), 2777—2786 |
| [1] | CHEN Jiamin, QU Xiaozhang, QI Guohua, XU Weiqing, JIN Yongdong, XU Shuping. SERS Nanoprobe for the Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cells Produced by Electrostimulus [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220033. |
| [2] | LI Yidi, TIAN Xiaochun, LI Junpeng, CHEN Lixiang, ZHAO Feng. Electron Transfer on the Semiconductor-microbe Interface and Its Environmental Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220089. |
| [3] | XUE Jin, CAO Xiaowei, LIU Yifan, WANG Min. Preparation of Paper Hollow Gold Nanocage SERS Sensor and Its Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection for miRNAs in Sputum of Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2393. |
| [4] | CHEN Feng, CHENG Na, ZHAO Jianwei, SONG Yitian, SUN Yanyan, LOU Xinli, TONG Xiayan. Electrodeposition Mechanism and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopic Effect of Nano-sized Silver Layer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1891. |
| [5] | WANG Yawen, LI Dong, LIANG Wenkai, SUN Yinghui, JIANG Lin. Multiplex Structures of Plasmonic Metal Nanoparticles and Their Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1213. |
| [6] | GE Haoying, DU Jianjun, LONG Saran, SUN Wen, FAN Jiangli, PENG Xiaojun. Surface Functionalized Gold Nanomaterials in Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1202. |
| [7] | MA Yanrong, JIANG Shengnan, JIN Yan. Sensitive and Electrochemical Detection of Telomerase Activity Based on the Signal Amplification of Strand Displacement Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 745. |
| [8] | YANG Pengfei, SHI Yuping, ZHANG Yanfeng. Large-scale Syntheses and Versatile Applications of Two-dimensional Metal Dichalcogenides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 504. |
| [9] | PAN Jing, XU Minmin, YUAN Yaxian, YAO Jianlin. Rapid Detection of Banned Dyes in Textiles Based on Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3716. |
| [10] | ZHANG Aiqin, WANG Man, SHEN Gangyi, JIN Jun. Interactions Between Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Using SPR and Molecular Docking [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2054. |
| [11] | HAN Juntian,CUI Yaoxing,SU Zhijun,WU Yi,CHEN Liuping,XU Junhui. Two-Electron Storage Viologen for Aqueous Organic Redox Flow Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1035. |
| [12] | LIU Lu,WU Hanyue,LI Jing,SHE Lan. Tuning Microstructures of Iron-Nickel Alloy Catalysts for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1083. |
| [13] | LI Wenshuai, WU Guorui, ZHANG Xijing, YUE Aiqin, DU Weijun, ZHAO Jinzhong, LIU Dingbin. Advances in Bacterial Detection Based on Raman Spectroscopy † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 872. |
| [14] | HAN Fangjie, DAI Mengjiao, LIANG Zhishan, SONG Zhongqian, HAN Dongxue, NIU Li. Research Progress of Photoelectrochemical Technology Applied in Antioxidant Analysis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 591. |
| [15] | LI Dong,SUN Yinghui,WANG Zhongshun,HUANG Jing,Lü Nan,JIANG Lin. Large-scale Multiplexed Surface Plasmonic Gold Nanostructures Based on Nanoimprint and Self-assembly † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 221. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||