

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 290.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150743
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Shumin, ZHENG Yudong*( ), LI Wei, SUN Yi, YUE Lina, ZHAO Zhenjiang
), LI Wei, SUN Yi, YUE Lina, ZHAO Zhenjiang
Received:2015-09-22
Online:2016-02-10
Published:2016-01-14
Contact:
ZHENG Yudong
E-mail:zhengyudong@mater.ustb.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Shumin, ZHENG Yudong, LI Wei, SUN Yi, YUE Lina, ZHAO Zhenjiang. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of 3D-nanohole PVA/a-MWCNTs Hydrogel Electrode Membrane†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 290.
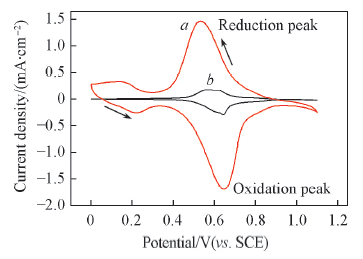
Fig.4 Cyclic voltammogram curves of different electrodes in 1.0 mmol/L K3Fe(CN)6 PBS solution a. The copper sheet modified by PVA/a-MWCNTs hydrogel membrane; b. copper sheet. Scan rate: 100 mV/s.
| Electrode material | Ipa/(mA·cm-2) | Ipc/(mA·cm-2) | S/cm2 | Epa/mV | Epc/mV | ΔE/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/a-MWCNTs-modified copper sheet | 1.692 | 1.486 | 1.824 | 640 | 541 | 99 |
| Copper sheet | 0.289 | 0.192 | 0.310 | 639 | 550 | 89 |
Table 1 Parameters of cyclic voltammograms on different electrodes*
| Electrode material | Ipa/(mA·cm-2) | Ipc/(mA·cm-2) | S/cm2 | Epa/mV | Epc/mV | ΔE/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/a-MWCNTs-modified copper sheet | 1.692 | 1.486 | 1.824 | 640 | 541 | 99 |
| Copper sheet | 0.289 | 0.192 | 0.310 | 639 | 550 | 89 |
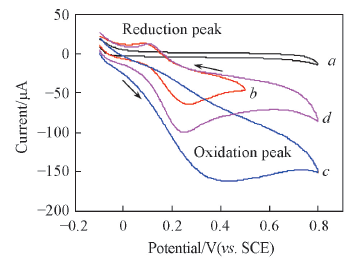
Fig.6 Cyclic voltammogram curves of PVA/a-MWCNTs hydrogel membrane-modified electrode in different systems a. PBS; b. PBS+DA(1 mmol/L); c. PBS+AA(2 mmol/L);d. PBS+DA(1 mmol/L)+AA(2 mmol/L).
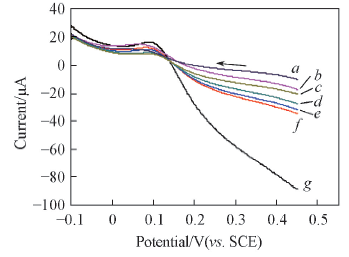
Fig.7 Partial cyclic voltammogram curves of PVA/a-MWCNTs hydrogel membrane-modified electrode with 0.04 mol/L AA and different concentrations of DA c(DA)/(mmol·L-1) from a to g: 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 2.0.
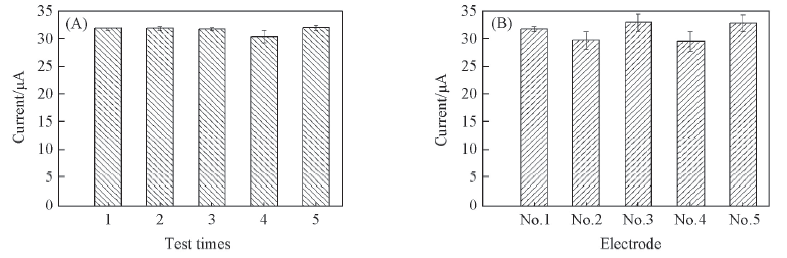
Fig.8 Repeatability of the PVA/a-MWCNTs hydrogel membrane-modified electrode (A) Peak currents of the same electrode with different test times;(B) Peak currents of different electrodes with the same preparation process.
| [1] | Redgrave P., Gurney K., Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2006, 7, 967—975 |
| [2] | Lim S. Y., O'Sullivan S. S., Kotschet K., Gallagher D. A., Lacey C., Lawrence A. D., Lees A. J., O'Sullivan D. J., Peppard R. F., Rodrigues J. P., J. Clin. Neuroscien., 2009, 16, 1148—1152 |
| [3] | Rubí B., Maechler P., Endocrinology, 2010, 151, 5570—5578 |
| [4] | Liu S. Q., Sun W. H., Hu F. T., Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2012, 173, 497—504 |
| [5] | Wang Z. H., Liu J., Yan L. S., Wang Y. M., Luo G. A., Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 30, 1053—1057 |
| (王宗花, 刘军, 颜流水, 王义明, 罗国安. 分析化学, 2002, 30, 1053—1057) | |
| [6] | Alarcón-Angelesa G., Corona-Avendañob S., Palomar-Pardavéb M., Rojas-Hernándeza A., Romero-Romob M., Ramírez-Silvaa M. T., Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53, 3013—3020 |
| [7] | Suzuki A., Ivandini T. A., Yoshimi K., Fujishima A., Oyama G., Nakazato T., Hattori N., Kitazawa S., Einaga Y., Anal. Chem., 2007, 79, 8608—8615 |
| [8] | Zhang J. L., Lan C. L., Shi B. F., Liu F., Zhao D. D., Tan X. C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(6), 905—909 |
| [9] | Bi H. Q., Li Y. H., Liu S. F., Guo P. Z., Wei Z. B., Lv C. X., Zhang J. Z., Zhao X. S., Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2012, 171, 1132—1140 |
| [10] | Wang M. W., Hsu T. C., Weng C. H., European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 2008, 42(3), 241—246 |
| [11] | Łuczak T., Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53, 5725—5731 |
| [12] | Lin D.M., Che J. F.,Progress in Chemistry, 2010, 1195—1202 |
| (林德盟, 车剑飞. 化学进展, 2010, 1195—1202) | |
| [13] | Wu K. B., Hu S. S., Microchimica Acta, 2004, 144, 131—137 |
| [14] | Ardakani M. M., Beitollahi H., Ganjipour B., Nejati H. N., Bioelectrochemistry, 2009, 75, 1—8 |
| [15] | Li Y. X., Lin X. Q., Li Y. X., Lin X. Q., Sensors and Actuators B Chemical, 2006, 115, 134—139 |
| [16] | Huang Y. Y., Zheng Y. D., Song W. H., Ma Y. X., Wu J., Fan L. Z., Composites Part A Applied Science & Manufacturing, 2011, 42, 1398—1405 |
| [17] | Fukada Y., Nagarajan N., Mekky W., Bao Y., Kim H. S., Nicholson P. S., J. Mater Sci., 2004, 39, 787—801 |
| [18] | Gao S. Z., Chen J. D., Qi Q. Q., Shu R. D., Qiu Z. P., Ren J. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(10), 2437—2440 |
| (高素照, 陈际达, 亓倩倩, 舒荣德, 邱智萍, 任竞争. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(10), 2437—2440) | |
| [19] | Wu X. Y., Huang S. W., Zhang J. T., Zhuo R. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(2), 382—384 |
| (武旭业, 黄世文, 张建涛, 卓仁禧. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(2), 382—384) | |
| [20] | Robert N. W., Ind. Eng. Chem., 1936, 28, 988—994 |
| [21] | Yang G. F., Jia N. Q., Wang Z. Y., Journal of Electrochemistry, 2007, 13, 63—65 |
| (杨国锋, 贾能勤, 王志勇. 电化学, 2007, 13, 63—65) | |
| [22] | Yuan L., Yang M. H., Qu F. L., Shen G. L., Yu R. Q., Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53, 3559—3565 |
| [1] | WANG Xuebin, XUE Yuan, MAO Hua’nyu, XIANG Yanxin, BAO Chunyan. Preparation of Photo/reduction Dual-responsive Hydrogel Microspheres and Their Application in Three-dimensional Cell Culture [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220116. |
| [2] | ZHAO Runyao, JI Guipeng, LIU Zhimin. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction over Pyrrole Nitrogen-coordinated Single-atom Copper Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| [3] | YU Pengdong, GUAN Xinghua, WANG Dongdong, XIN Zhirong, SHI Qiang, YIN Jinghua. Preparation and Properties of Novel Optical and Thermal Dual Response Shape Memory Polymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220085. |
| [4] | HUANG Yi, LYU Lingling, PAN Xiaopeng, SUN Guangdong, LI Yongqiang, YAO Juming, SHAO Jianzhong. Three-dimensional Printing of Photocrosslinked Self-supporting Silk Fibroin Hydrogels [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210841. |
| [5] | GAO Jing, HE Wentao, WANG Xinxin, XIANG Yushu, LONG Lijuan, QIN Shuhao. Preparation of DOPO Derivative Modified Carbon Nanotubes and Their Effect on Flame Retardancy of Polylactic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210670. |
| [6] | YAN Wenqing, ZHANG Zeyao, LI Yan. Controlled Preparation of Carbon Nanotube Transparent Conductive Films [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210626. |
| [7] | ZHOU Yonghui, LI Yao, WU Yuxuan, TIAN Jing, XU Longquan, FEI Xu. Synthesis of A Novel Photoluminescence Self-healing Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210606. |
| [8] | ZHAO Mengyang, HUANG Ziyang. Preparation and in vitro Bioactivity of HA/CuO/SrCO3 Gradiently Composite Coating [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210644. |
| [9] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [10] | YAN Shuting, YAO Yuan, TAO Xinfeng, LIN Shaoliang. Synthesis and Properties of Polypeptoid Hydrogels Containing Sulfonium Groups [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220381. |
| [11] | GAO Huiling, CAO Zhenzhen, GU Fang, WANG Haijun. Monte Carlo Simulation on Self-healing Behaviour of Hydrogen-bonded Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220482. |
| [12] | DING Qin, ZHANG Zixuan, XU Peicheng, LI Xiaoyu, DUAN Limei, WANG Yin, LIU Jinghai. Effects of Cu, Ni and Co Hetroatoms on Constructions and Electrocatalytic Properties of Fe-based Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220421. |
| [13] | HOU Congcong, WANG Huiying, LI Tingting, ZHANG Zhiming, CHANG Chunrui, AN Libao. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH Composite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [14] | XU Xiaojian, LI Bo, LIN Mengxiao, ZHAN Shuo. Vacuum Freeze Drying to Prepare Porous Carbon Based Composite Membranes for Efficient Solar Steam Generation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220361. |
| [15] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||