

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 232.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150563
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Jiayi, SU Wei, WANG Enju*( )
)
Received:2015-07-20
Online:2016-02-10
Published:2015-12-26
Contact:
WANG Enju
E-mail:enjuwang@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Jiayi, SU Wei, WANG Enju. Highly Selective Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Hg2+Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Between 1,8-Naphthalimide and Rhodamine B†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 232.
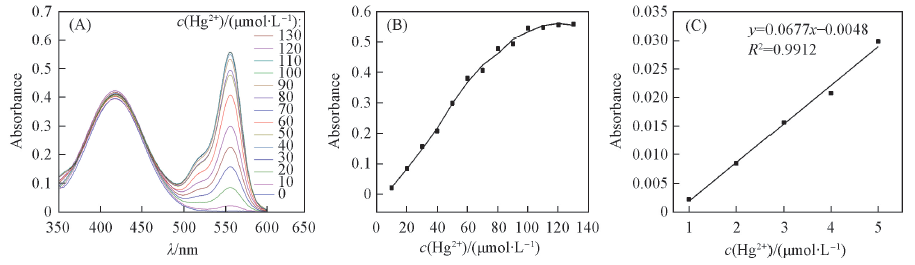
Fig.1 UV-Vis spectra of RN(10 μmol/L) under different conditions (B) Effect of Hg2+ concentration at 556 nm; (C) with different concentrations of Hg2+ (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 μmol/L) at 556 nm.
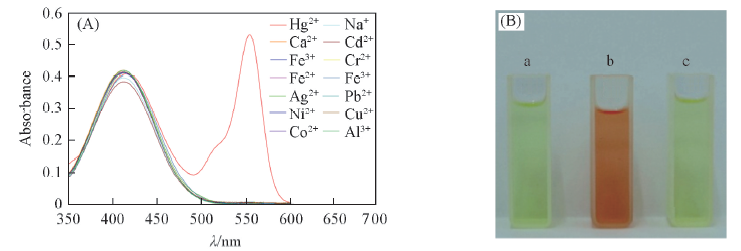
Fig.2 UV-Vis spectra(A) and color changes of RN(10 μmol/L)(B) (A) With different metal ions, c(metal ions)=100 μmol/L; (B) addition of Hg2+ under natural light, a. only RN, b. addition of Hg2+(100 μmol/L), c. addition of a mixture of Al3+, Na+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Cr3+, Ag+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+, each concentration was 100 μmol/L.
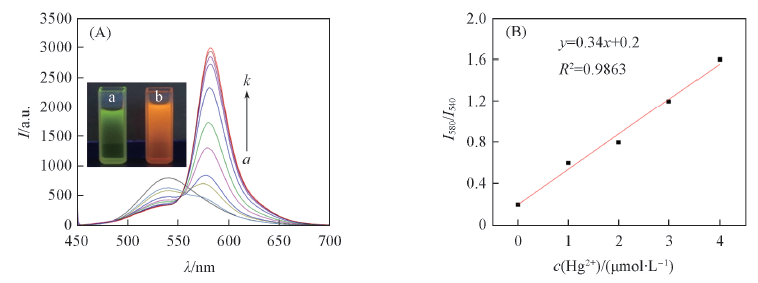
Fig.3 Fluorescence spectra of RN(10 μmol/L) (A) c(Hg2+)/(μmol·L-1), a—k: 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100. λex=440 nm. Inset: a and b represent colors of RN solution(10 μmol/L) before and after the addition of Hg2+(100 μmol/L) in dark-box ultraviolet analyzer when excited at 365 nm, respectively; (B) fluorescent intensities ratio(I580 nm/I540 nm) as a function of Hg2+ (0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 μmol/L).
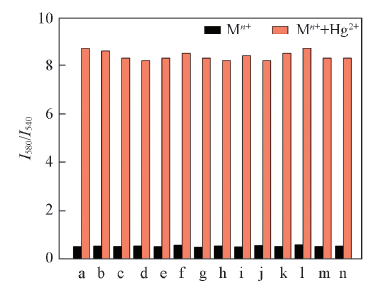
Fig.7 Selective responses of RN(10 μmol/L) to Hg2+(100 μmol/L) in the presence of different cations(200 μmol/L) a. None; b. Al3+; c. Na+; d. Mn2+; e. Co2+; f. Ni2+; g. Cu2+; h. Cr3+; i. Ag+; j. Pb2+; k. Zn2+; l. Cd2+; m. Fe3+; n. Fe2+.
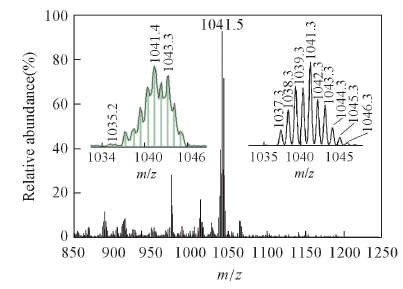
Fig.8 ESI-MS of RN in the presence of Hg2+ and trace amounts of Cl- Inset: observed(left) and calculated(right) isotopic patterns for the [RN+Hg+Cl]+.
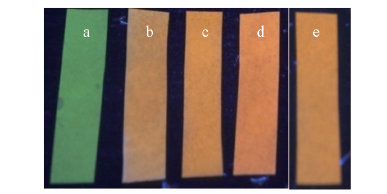
Fig.9 Test papers after being sprayed with Hg2+ in water a. None; b. 5.0×10-5 mol/L; c. 1.0×10-4 mol/L; d. 5.0×10-4 mol/L; e. 1.0×10-4 mol/L in filtered lake water.
| [1] | Selid P. D., Xu H., Collins E. M., Striped Face-Collins M., Zhao J. X., Sensors, 2009, 9, 5446—5459 |
| [2] | Ou S., Lin Z., Duan C., Zhang H., Bai Z., Chem. Commun., 2006, 42, 4392—4394 |
| [3] | Yoon S., Miller E. W., He Q., Do P. H., Chang C. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 6658—6661 |
| [4] | Yang H., Hu Q., Ma G., Chen G., Tao M., Zhang W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(6), 910—914 |
| [5] | Yuan L., Lin W., Zhang K., Zhu S., Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46, 1462—1473 |
| [6] | Qiao B., Sun S., Jiang N., Zhang S., Peng X., Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 4626—4630 |
| [7] | Kaewtong C., Niamsa N., Wanno B., Morakot N., Pulpokab B., Tuntulani T., New J. Chem., 2014, 38, 3831—3839 |
| [8] | He G., Zhang X., He C., Zhao X., Duan C., Tetrahedron, 2010, 66, 9762—9768 |
| [9] | Chen X., Pradhan T., Wang F., Kim J.S., Yoon J., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112 , 1910—1956 |
| [10] | Kim H. N., Lee M. H., Kim H. J., Kim J. S., Yoon J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 1465—1472 |
| [11] | Xu H., Dai Y. N., Shan H. Y., Fei Q., Huan Y. F., Li G. H., Feng G. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4), 736—740 |
| (徐惠, 代艳娜, 单洪岩, 费强, 郇延富, 李光华, 冯国栋. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(4), 736—740) | |
| [12] | Beija M., Afonso C. A. M., Martinho J. M. G., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 2410—2433 |
| [13] | Wu D., Huang W., Duan C., Lin Z., Meng Q., Inorg. Chem., 2007, 46, 1538—1540 |
| [14] | Wang H., Li Y., Xu S., Li Y., Zhou C., Fei X., Sun L., Zhang C., Li Y., Yang Q., Xu X., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 2850—2855 |
| [15] | Yang Z., Hao L., Yin B., She M., Obst M., Kappler A., Li J., Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 4334—4337 |
| [16] | Lin W., Cao X., Ding Y., Yuan L., Yu Q., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010, 8, 3618—3620 |
| [17] | Zhang X., Huang X. J., Zhu Z. J., RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 24891—24895 |
| [18] | Zhan X. Q., Qian Z. H., Zheng H., Su B. Y., Lan Z., Xu J. G., Chem. Commun., 2008, 16, 1859—1861 |
| [19] | Lin W., Cao X., Ding Y., Yuan L., Yu Q., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010, 8, 3618—3620 |
| [20] | He S., Liu Q., Li Y., Wei F., Cai S., Lu Y., Zeng X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(1), 32—36 |
| [21] | Biswala B., Bag B., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 4975—4992 |
| [22] | Zhou Z., Yu M., Yang H., Huang K., Li F., Yi T., Huang C., Chem. Commun., 2008, 29, 3387—3389 |
| [23] | Wang Q., Li C., Zou Y., Wang H., Yi T., Huang C., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 6740—6746 |
| [24] | Mahato P., Saha S., Suresh E., Liddo R. D., Parnigotto P. P., Conconi M. T., Kesharwani M. K., Ganguly B., Das A., Inorg. Chem., 2012, 51, 1769—1777 |
| [25] | Wang C., Zhang D., Huang X., Ding P., Wang Z., Zhao Y., Ye Y., Sens. Actuat. B Chem., 2014, 198, 33—40 |
| [26] | Bao X., Shi J., Nie X., Zhou B., Wang X., Zhang L., Liao H., Pang T., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2014, 22, 4826—4835 |
| [27] | Dai H., Xu H., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2011, 21, 5141—5144 |
| [28] | Li C. Y., Xu F., Li Y. F., Zhou K., Zhou Y., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2012, 717, 122—126 |
| [29] | Liu Y., Lv X., Zhao Y., Chen M., Liu J., Wang P., Guo W., Dyes Pigments, 2012, 92, 909—915 |
| [30] | Kim H. N., Lee M. H., Kim H. J., Kim J. S., Yoon J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 1465—1472 |
| [31] | Chen Y., Zhang Y., Zeng X., Mu L., Li J., Sun Q., Zhang J. X., Wei G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7), 1598—1605 |
| (陈义, 张艳, 曾晞, 牟兰, 李俊, 孙强, 张建新, 卫钢. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(7), 1598—1605) | |
| [32] | Dujols V., Ford F., Czarnik A. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 7386—7387 |
| [1] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [2] | TANG Qian, DAN Feijun, GUO Tao, LAN Haichuang. Synthesis and Application of Quinolinone-coumarin-based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Recognition of Hg2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210660. |
| [3] | LI Xiaoqian, ZHANG Hua, LU Haijian, LIU Chang, LIU Qinglong, MA Xiayu, FANG Yuanping, LIANG Dapeng. Mechanism of Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B by TiO2 Nanowire Array with Internal Extraction Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2003. |
| [4] | ZHANG Chenglu, SUN Yuedong, WANG Jing, HE Yu, ZHANG Yanpeng, ZHANG Lu, SONG Fulu. Synthesis and Application of Quinolinone Derivative Fluorescent Probe for High Selective Detection of Hg2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1785. |
| [5] | WANG Mengyu, CAO Simin, LI Haoyang, ZHANG Mengjie, LI Dong, ZHAO Zenan, XU Jianhua. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Between Coenzyme NADH and Tryptophan [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2473. |
| [6] | FENG Wei,WANG Bowei,JIANG Yang,LI Longyun. Design, Preparation and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering(SERS) Spectrum of Single Ag Nanodot† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1345. |
| [7] | LIANG Donglei, SONG Qiusheng, YAO Yutian, LIU Ben. Preparation of Complex Nanogel with Up-conversion Fluorescence-responsive Performance and Its Fluorescence Energy Transfer Behavior† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 583. |
| [8] | LIU Meihong, TAO Ran, LI Bing, LI Xinghua, HAN Chaohan, LI Xiaowei, SHAO Changlu. Controllable Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Three-dimensional Porous Zinc-tungsten Oxide Heterojunctions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2367. |
| [9] | XUE Jiao, WANG Runwei, ZHANG Zongtao, QIU Shilun. Preparation and Photocatalytic Performance of Novel Zn-doped C/Nb2O5 Nanoparticles Catalyst† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 319. |
| [10] |
LI Jian,XIE Linxia,LIANG Zupei,GUO Rong,LIU Chenyu,MA Shulan.
Luminescence Property and Detection Capability Towards Hg2+ of LEuH Composites with Mo |
| [11] | LIU Huiqiang, PENG Chao, CHEN Ning, LIU Yangping. Novel Fluorescent/EPR Difunctional Probe for Detecting Hypochlorite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1542. |
| [12] | WEI Lanlan, YAN Yan, KANG Xuejue. Application of Packed-nanofibers Solid-phase Extraction for Determination of Rhodamine B in Dry Chilli, Fruit Drink and Red Wine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 935. |
| [13] | LI Ting, CAO Zhong, LI Panpan, HE Jinglin, XIAO Hui, YANG Chan. High-sensitive Fluorescent Enhancement Detection of Hg(Ⅱ) Ions Based on Poly(thymine)-templated Copper Nanoclusters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1616. |
| [14] | GE Hao,HUANG Hailong,XU Min. Preparation and Properties of Surface Imprinted Magnetic Cellulose Microsphere with Highly Selective Adsorption† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1551. |
| [15] | YANG Chuanxiao, YU Mengwen, SONG Duoduo, SUN Xiangying. Determination of Cr(Ⅵ) by Ratiometric and Visual Fluorescence Method Based on Formaldehyde Functionalized Polyethyleneimine-rhodamine B Hydrazide System† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 852. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||