

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 2372.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150413
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Xiang1, ZHANG Lei1,*( ), ZOU Yue1, HUANG Xinhua1, PAN Chengling1,*(
), ZOU Yue1, HUANG Xinhua1, PAN Chengling1,*( ), HOU Changmin2, XU Jiqing2
), HOU Changmin2, XU Jiqing2
Received:2015-05-20
Online:2015-12-10
Published:2015-11-19
Contact:
ZHANG Lei,PAN Chengling
E-mail:yutian1224@126.com;chengling_pan@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Xiang, ZHANG Lei, ZOU Yue, HUANG Xinhua, PAN Chengling, HOU Changmin, XU Jiqing. Hydrothermal Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Activities of Nanosheets-assembled Bi12SiO20 Microcubes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2372.
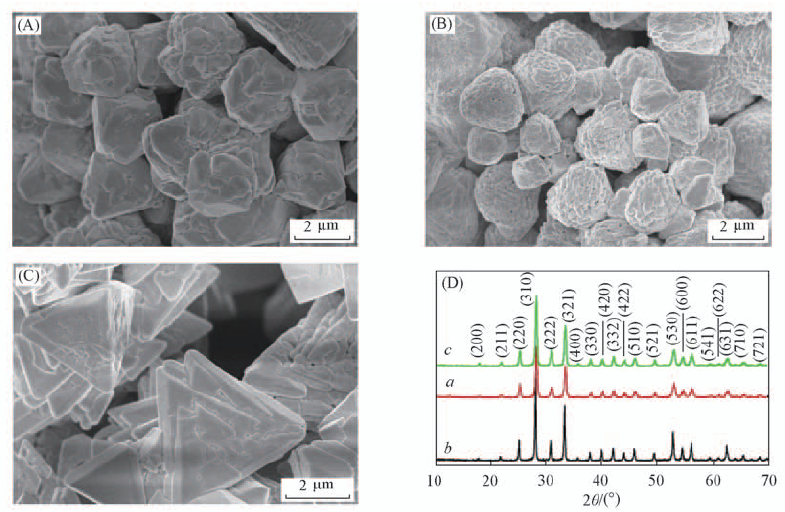
Fig.5 SEM images(A—C) and XRD patterns(D) of the samples prepared in the absence of PAM and/or Na3Cit (A) and a. Without Na3Cit; (B) and b. without PAM; (C) and c. without PAM and Na3Cit.
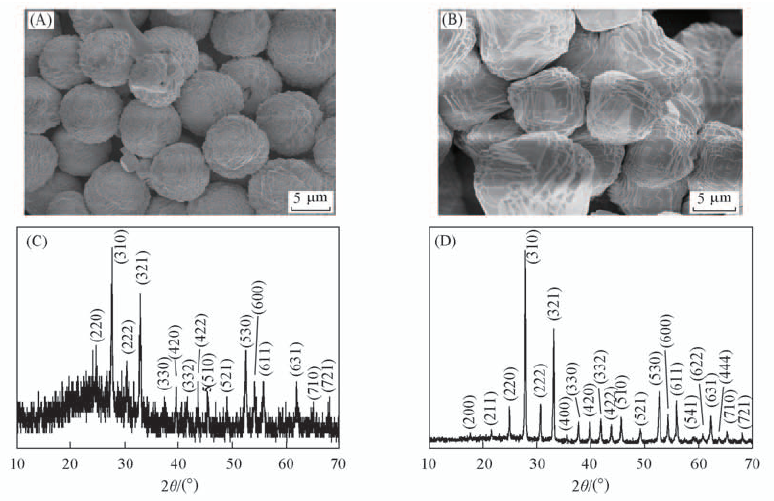
Fig.6 SEM images(A, B) and XRD(C, D) patterns of the samples prepared at different reaction temperatures Reaction temperature/℃: (A), (C) 120; (B), (D) 180.
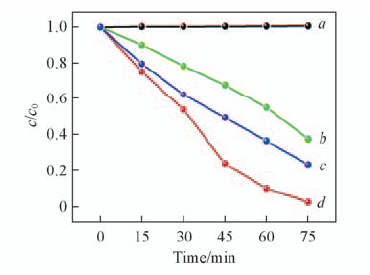
Fig.9 Photodegradation efficiencies of RhB as a function of irradiation time with UV-Vis light a. Photolysis; b. BSO prepared without sodium citrate; c. BSO prepared without PAM; d. BSO hierarchical microcubes.
| [1] | Zhou C., Zhao Y. F., Bian T., Shang L., Yu H. J., Wu L. Z., Tung C. H., Zhang T. R., Chem. Commun., 2013, 49(84), 9872—9874 |
| [2] | Yan Y., Guo X., Zhang Y. H, Tang Y., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2015, 5(2), 772—785 |
| [3] | Wang W. S., Zhen L., Xu C.Y., Yang L., Shao W. Z., J. Phys. Chem. C,2008, 112(49), 19390—19398 |
| [4] | Ong W. J., Tan L. L., Chai S. P., Yong S. T., Mohamed A. R., Nanoscale, 2014, 6(4), 1946—2008 |
| [5] | Sun L. N., Guo Q. R., Wu X. L., Luo S. J., Pan W. L., Huang K. L., Lu J. F., Ren L., Cao M. H., Hu C. W., J. Phys. Chem. C,2007, 111(2), 532—537 |
| [6] | Lei F., Yan B., Chen H. H., Zhang Q., Zhao J. T., Cryst. Growth Des., 2009, 9(8), 3730—3736 |
| [7] | Yao W. F., Wang H., Xu X. H., Zhou J. T., Yang X. N., Zhang Y., Shang S. X., Wang M., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 377(5/6), 501—506 |
| [8] | Zhang Y. M., Ni Y. H., Wang X. M., Xia J., Hong J. M., Cryst. Growth Des., 2011, 11(10), 4368—4377 |
| [9] | Wang G. Q., Zhuo S. P., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(33), 13801—13804 |
| [10] | Bai H. W., Liu Z. Y., Sun D. D., Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(35), 6542—6544 |
| [11] | Yao H. B., Fang H. Y., Wang X. H., Yu S. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(7), 3764—3785 |
| [12] | Lin G. H., Lu W. S., Dong W. J., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2013, 15(34), 6690—6694 |
| [13] | Liu Z., Wen X. D., Wu X. L., Gao Y. J., Chen H. T., Zhu J., Chu P. K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(26), 9405—9412 |
| [14] | Deng Z. X., Tian Y., Lee S. H., Ribbe A. E., Mao C. D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(23), 3582—3585 |
| [15] | Shen X. S., Wang G. Z., Hong X., Zhu W., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2009, 11(5), 753—755 |
| [16] | Wang L., Zhang X. H., Chen K. Z., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2013, 15(24), 4860—4864 |
| [17] | Wang Y. G., He R., Yang M., Wen T., Zhang H., Liang J., Lin Z. S., Wang Y. X., Li G. B., Lin J. H., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2012, 14(3), 1063—1068 |
| [18] | Aggarwal M. D., Wang W. S., Choi J., Cochrane J. C., Wang Z. Y., J. Cryst. Growth,1994, 137(1/2), 132—135 |
| [19] | Arenas D. J., Middleton C., Kemper A. F., Phys. Rev. B,2015, 91(14), 144103 |
| [20] | Hou D. F., Hu X. L., Wen Y. W., Shan B., Hu P., Xiong X. Q., Qiao Y., Huang Y. H., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(47), 20698—20705 |
| [21] | He C. H., Gu M. Y., Scripta Mater., 2006, 55(5), 481—484 |
| [22] | Lal B., Patro S. K., Singh S., J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2010, 56(3), 340—344 |
| [23] | Han Q. F., Zhang J., Wang X., Zhu J. W., J. Mater. Chem. A,2015, 3(14), 7413—7421 |
| [24] | Sekhar H., Kiran P. P., Rao D. N., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 130(1/2), 113—120 |
| [25] | Alonso J. C., Diamant R., Haro-Poniatowski E., Fernández-Guasti M., Muñoz G., Camarillo I., Jouanne M., Morhange J. F., Appl. Sur. Sci., 1997, 109/110, 359—361 |
| [26] | Zhang L., Lian L., Dai J. S., Liu Y., Micro. Nano. Lett., 2012, 7(11), 1143—1146 |
| [27] | Zhang Y. J., He H. M., Zhu W., Zheng A., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2011, 13(21), 6471—6480 |
| [28] | Cheng W., Tang K. B., Qi Y. X., Sheng J., Liu Z. P., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(9), 1799—1805 |
| [29] | Lee W. R., Piao L., Park C. H., Lim Y. S., Do Y. R., Yoon S., Kim S. H., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2010, 342(1), 198—201 |
| [30] | Ma D. K., Huang S. M., Chen W. X., Hu S. W., Shi F. F., Fan K. L., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113(11), 4369—4374 |
| [31] | Cao X. F., Zhang L., Chen X. T., Xue Z. L., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2011, 13(6), 1939—1945 |
| [32] | Zhang L., Cao X. F., Chen X. T., Xue Z. L., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2011, 13(7), 2464—2471 |
| [33] | Kanie K., Seino Y., Matsubara M., Nakaya M., Muramatsu A., New J. Chem., 2014, 38(8), 3548—3555 |
| [34] | Wan Z., Zhang G. K., Sci. Rep., 2014, 4, 6298 |
| [35] | Zhang L., Cao X. F., Chen X. T., Xue Z. L., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2011, 354(2), 630—636 |
| [36] | Zhang L., Zhang X., Huang Y. Q., Pan C. L., Hu J. S., Hou C. M., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(38), 30239—30247 |
| [37] | Li F., Wang G. Y., Zhang Y., Li H. R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(7), 1351—1357 |
| (李锋, 王桂燕, 张岩, 李洪仁. 高等学校化学学报,2015, 36(7), 1351—1357) | |
| [38] | Ji L., Yu R. M., Wang H. R., Chen L. D., Wang H. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(3), 551—558 |
| (姬磊, 于瑞敏, 王浩人, 陈丽铎, 汪怀远. 高等学校化学学报,2015, 36(3), 551—558) | |
| [39] | Liu Y., Ji H. W., Zhou D. F., Zhu X. F., Li C. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(1), 19—25 |
| (刘阳, 季宏伟, 周德凤, 朱晓飞, 李朝辉. 高等学校化学学报,2014, 35(1), 19—25) | |
| [40] | Feng J., Wang Y. T., Zou L. Y., Li B. W., He X. F., Liu S. N., Chen T. T., Fan Z. J., Ren Y. M., Lu Y. Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2015, 31(3), 439—442 |
| [1] | LI Yidi, TIAN Xiaochun, LI Junpeng, CHEN Lixiang, ZHAO Feng. Electron Transfer on the Semiconductor-microbe Interface and Its Environmental Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220089. |
| [2] | WANG Jianqiao, MA Yuguang. Extent and Changeable Rule of HOMO and LUMO Energy of Organic Semiconductors in Nonequilibrium States and a Phenomenological Understanding for the Formation of “Hot Excitons” in OLED [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210856. |
| [3] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [4] | LIANG Xuejing, ZHAO Fulai, WANG Yu, ZHANG Yichao, WANG Yaling, FENG Yiyu, FENG Wei. Preparation and Photoelectric Properties of Germanium Sulphoselenide Photodetector [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2661. |
| [5] | LIN Chengce, PENG Boyu, LI Hanying. Recent Progress in Organic Single Crystal Integrated Circuits [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1672. |
| [6] | ZHANG Huishuang, GAO Yanxiao, WANG Qiuxian, LI Xiangnan, LIU Wenfeng, YANG Shuting. High-low Temperature Properties of Ni-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material by Hydrothermal Synthesis with CTAB Assisted [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 819. |
| [7] | WANG Ye, ZHANG Xiaosi, SUN Lijing, LI Bing, LIU Lin, YANG Miao, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Morphology Control of SAPO Molecular Sieves under the Assistance of Organosilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 683. |
| [8] | WANG Jianyu, ZHANG Qiang, YAN Wenfu, YU Jihong. Roles of Hydroxyl Radicals in Zeolite Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 11. |
| [9] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [10] | LIU Yabing,LI Mingyang,TIAN Ge,ALATENG Shaga,PEI Tonghe,NIE Jingsi. Syntheses, Structures and Catalytic Properties of Two Supramolecular Complexes Based on 2-Pyridylamine and Cluster † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 995. |
| [11] | SUN Hui, LAI Xiaoyong. Progress in Preparation and Gas-sensing Application of Hollow Multi-shell Structured Materials † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 855. |
| [12] | ZHUO Mengning,LI Fei,JIANG Hao,CHEN Qianwen,LI Peng,WANG Lizhang. Preparation of SnO2/GDE Cathodes and Their Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to Produce Formic Acid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 530. |
| [13] | DONG Le, HUANG Xingliang, REN Junjie, DAI Xiaoping, LIU Zongyan, TIAN Hongfeng, WANG Zhidong, WU Xiaotong. Influence Mechanism of Particle Size and Distribution of Silica Sol in the Synthesis of Ferrierite Zeolite with High SiO2/Al2O3 Ratio [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2449. |
| [14] | ZHOU Hai, CHEN Hao, GUO Ya, KANG Min. Synthesis of Meso-porous Co3O4 Polyhedra and Their Electrochemical Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1374. |
| [15] | GAO Yang, LI Daixi, LIU Baolin, GUO Baisong, WEI Dongqing. Inhibitory Mechanism of Glycerol on the Growth of Ice Crystals by Molecular Dynamics† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 763. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||