

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (7): 1422.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150174
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Min, GE Hao, SONG Jianhui, XU Min*( )
)
Received:2015-03-03
Online:2015-07-10
Published:2015-06-05
Contact:
XU Min
E-mail:xumin@phy.ecnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Min, GE Hao, SONG Jianhui, XU Min. Solid-state NMR Study on the Dynamics of Thermo-sensitive Cellulose/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Composite Hydrogel†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(7): 1422.
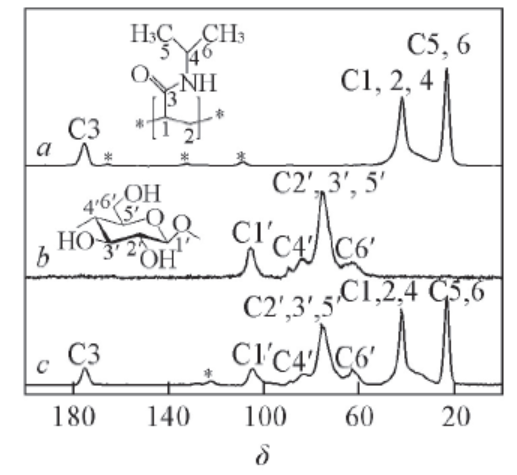
Fig.4 Solid-state 13C CP/MAS NMR spectra of neat PNIPAM(a), neat cellulose(b) and CL/PNIPAM composite polymer(c)The peaks labeled with “*” are sidebands.
| Sample | tCDP/μs | η(C5,6) | η(C1'—C6') | n(AGU)/n(NIPAM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2%C/PNP | 200 | 1.28 | 1.27 | 0.96 |
| 4%C/PNP | 200 | 1.83 | 1.85 | 0.80 |
| 6%C/PNP | 100 | 1.72 | 2.23 | 0.73 |
| 200 | 2.46 | 2.33 | 0.72 | |
| 8%C/PNP | 200 | 1.40 | 1.37 | 0.69 |
| 10%C/PNP | 200 | 1.90 | 1.83 | 0.67 |
Table 1 Quantitative results of cellulose/PNIPAM from QCP NMR*
| Sample | tCDP/μs | η(C5,6) | η(C1'—C6') | n(AGU)/n(NIPAM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2%C/PNP | 200 | 1.28 | 1.27 | 0.96 |
| 4%C/PNP | 200 | 1.83 | 1.85 | 0.80 |
| 6%C/PNP | 100 | 1.72 | 2.23 | 0.73 |
| 200 | 2.46 | 2.33 | 0.72 | |
| 8%C/PNP | 200 | 1.40 | 1.37 | 0.69 |
| 10%C/PNP | 200 | 1.90 | 1.83 | 0.67 |
| Label of peak | δ | Fitting area(%) | Attribution | Label of peak | δ | Fitting area(%) | Attribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.30 | 1.65 | Few impurity | 5 | 3.83 | 7.56 | b |
| 2 | 1.05 | 46.21 | a | 6 | 4.78 | 5.54 | H2O |
| 3 | 1.95 | 25.36 | c,d | 7 | 5.65 | 5.77 | CL |
| 4 | 2.80 | 7.91 | CL |
Table 2 Nonlinear least squares fitting(NLSF)results of static 1H NMR spectra of CL/PNIPAM composite gel*
| Label of peak | δ | Fitting area(%) | Attribution | Label of peak | δ | Fitting area(%) | Attribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.30 | 1.65 | Few impurity | 5 | 3.83 | 7.56 | b |
| 2 | 1.05 | 46.21 | a | 6 | 4.78 | 5.54 | H2O |
| 3 | 1.95 | 25.36 | c,d | 7 | 5.65 | 5.77 | CL |
| 4 | 2.80 | 7.91 | CL |
| Temperature/K | Δδ | Fitting area(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wide peak | Narrow peak | Wide peak | Narrow peak | |
| 298 | 145.94 | 3.62 | 26.82 | 73.18 |
| 304 | 142.68 | 3.63 | 27.20 | 72.80 |
| 306 | 115.08 | 4.60 | 41.65 | 58.35 |
| 307 | 100.98 | 6.50 | 56.52 | 43.48 |
| 308 | 93.85 | 6.91 | 63.35 | 36.65 |
| 310 | 88.46 | 6.60 | 68.28 | 31.72 |
| 312 | 85.39 | 6.26 | 70.70 | 29.30 |
Table 3 Gauss and Lorentz fitting results of static 1H NMR spectra of CL/PNIPAM gel at different temperature*
| Temperature/K | Δδ | Fitting area(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wide peak | Narrow peak | Wide peak | Narrow peak | |
| 298 | 145.94 | 3.62 | 26.82 | 73.18 |
| 304 | 142.68 | 3.63 | 27.20 | 72.80 |
| 306 | 115.08 | 4.60 | 41.65 | 58.35 |
| 307 | 100.98 | 6.50 | 56.52 | 43.48 |
| 308 | 93.85 | 6.91 | 63.35 | 36.65 |
| 310 | 88.46 | 6.60 | 68.28 | 31.72 |
| 312 | 85.39 | 6.26 | 70.70 | 29.30 |
| Temperature/K | 298 | 302 | 304 | 305 | 306 | 307 | 308 | 310 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity ratio | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 5.5 | 4 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
Table 4 Static 1H NMR spectra of CL/PNIPAM gel at different temperatures before and after spin diffusion intensity ratio
| Temperature/K | 298 | 302 | 304 | 305 | 306 | 307 | 308 | 310 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity ratio | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 5.5 | 4 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| [1] | Halake K. S., Lee J., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2014, 105, 184—192 |
| [2] | Yuan Z. W., Fan Q. R., Dai X. N., Zhao C., Lü A. J., Zhang J. J., Xu G. Y., Qin M. H., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2014, 102, 431—437 |
| [3] | Cai J., Zhang L. N., Liu S. L., Liu Y. T., Xu X. J., Chen X. M., Chu B. J. M., Guo X. L., Xu J., Cheng H., Han C. C., Kuga S., Macromolecules, 2008, 41, 9345—9351 |
| [4] | Song Y. B., Gan W. P., Li Q., Guo Y., Zhou J. P., Zhang L. N., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 86(1), 171—176 |
| [5] | Calejo M. T., Cardoso A. M. S., Marques E. F., Araújo M. J., Kjøniksen A. L., Sande S. A., Lima M. C. P., Jurado A. S., Nyström B., Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2013, 102, 682—686 |
| [6] | Bajpai S.K., Banger P.,Polymer Engineering & Science, 2013, 2129—2140 |
| [7] | Song Y. B., Zhou J. P., Zhang L. N., Wu X. J., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2008, 73(1), 18—25 |
| [8] | Pelton R., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 348(2), 673—674 |
| [9] | Wu L., Zhou H., Sun H. J., Zhao Y. B., Yang X. L., Cheng S. Z. D., Yang G., Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14, 1078—1084 |
| [10] | Wang T., Liu D., Lian C. X., Zheng S. D., Liu X. X., Wang C. Y., Tong Z., Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2011, 71(4), 447—454 |
| [11] | Tagit O., Jańczewski D., Tomczak N., Han M. Y., Herek J. L., Vancso G. J., European Polymer Journal, 2010, 46(7), 1397—1403 |
| [12] | Li H., Luo J. X., Zhu D. Y., Zhou D. W., Liang L. Y., Lu M. G., Fine Chemicals, 2010, 27(10), 968—976 |
| (李欢, 罗建新, 朱东雨, 周德文, 梁利岩, 吕满庚. 精细化工, 2010, 27(10), 968—976) | |
| [13] | Chen J. J., Hou L. T., Jiang Y., Zhang X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3), 645—651 |
| (陈娇娇, 侯蔺桐, 蒋奕, 张霞. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(3), 645—651) | |
| [14] | Chang C. Y., Han K., Zhang L. N., Polymers Advanced Technologies, 2011, 22, 122—127 |
| [15] | Zhao H.P., Quantitative Cross Polarization NMR and Its Application to the Structural Characterization of Bulk Materials, East China Normal University, Shanghai, 2012 |
| (赵辉鹏. 定量交叉极化核磁共振方法及其在固体材料结构表征中的应用, 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012) | |
| [16] | Shu J., Chen Q., Zhang S. M., Chemical Physics Letters, 2008, 462(1—3), 125—128 |
| [17] | Xue H.J., Studies of Confined Molecular by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, 2012 |
| (薛红娟. 受限分子的核磁共振研究, 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012) | |
| [18] | Li K., Song J. H., Xu M., Kuga S., Zhang L. N., Cai J., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(10), 7204—7213 |
| [19] | Ma C., Studies of Dynamic Heterogeneities of Polymers at Glass Transition Determined by Variable-temperature Proton Wide-line NMR, East China Normal University, Shanghai, 2012 |
| (马超. 均相高分子体系的运动不均匀性研究, 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012) |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [3] | CHEN Hanxiang, BIAN Shaoju, HU Bin, LI Wu. Molecular Simulation of the Osmotic Pressures for LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O Solution System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [4] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [5] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [7] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [8] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [9] | LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling, LIU Chengbu. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pulsed Electric Field O/W Emulsion Demulsification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| [10] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [11] | FU Jinzhou, WANG Hanwei, LI Yingying, WANG Chao, LI Caicai, SUN Qingfeng, LI Huiqiao. Micro/Nanocellulose Functional Membranes for Energy and Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1407. |
| [12] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [13] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [14] | ZHAO Shufang, HUANG Jun. Study by Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy on the Acidity and Shape-selectivity of Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 165. |
| [15] | ZHAO Ziyi,ZHENG Hongzhi,XU Yan. Multi-color Circularly Polarized Luminescence Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1120. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||