

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (10): 2016.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150121
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zhipan, PENG Yingxiang, YANG Shifeng, ZHANG Rui, LI Kai, ZUO Xia*( )
)
Received:2015-02-02
Online:2015-10-10
Published:2015-09-18
Contact:
ZUO Xia
E-mail:zuoxia@mail.cnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Zhipan, PENG Yingxiang, YANG Shifeng, ZHANG Rui, LI Kai, ZUO Xia. Preparation and Oxygen Reduction Catalytic Performance of Iron-phthalocyanine Polymer/Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes Composites†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2016.
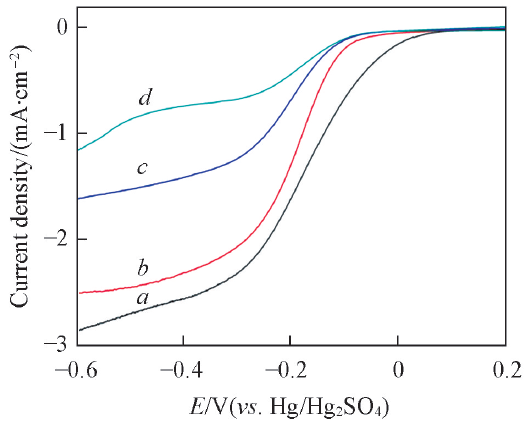
Fig.3 LSV curves of Poly-FePc/MWCNTs in O2 saturated 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 at a scan rate of 5 mV/sa. FePPc/MWCNTs; b. HFePPc/MWCNTs;c. BAFePPc/MWCNTs; d. BBFePPc/MWCNTs.
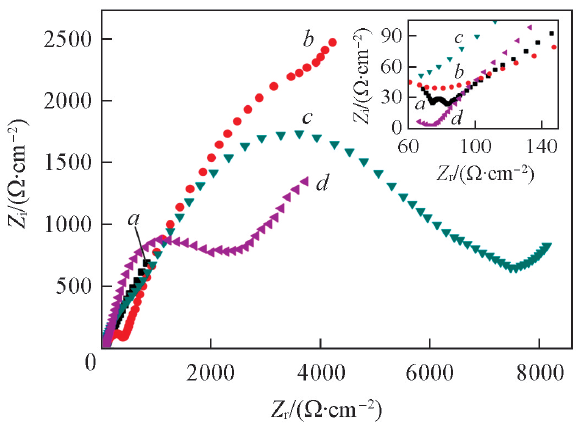
Fig.4 EIS of Poly-FePc/MWCNTs in 0.1 mol/L KCl containing 0.05 mol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/K4[Fe(CN)6]a. FePPc/MWCNTs; b. HFePPc/MWCNTs; c. BAFePPc/MWCNTs; d. BBFePPc/MWCNTs.
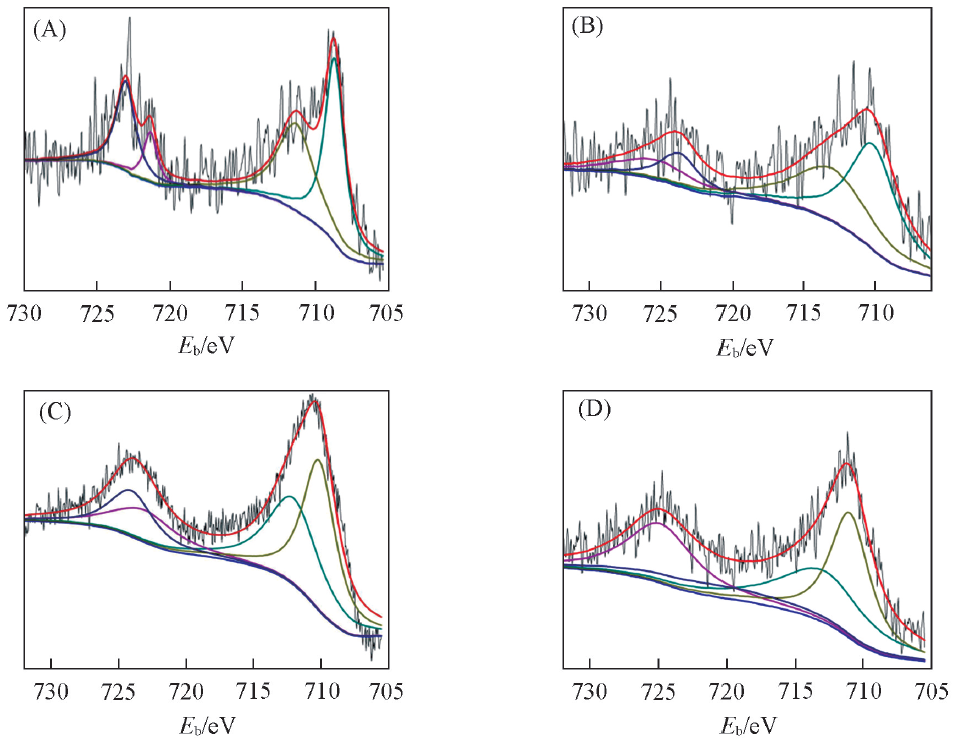
Fig.6 XPS peak-differentation spectra for Fe2p doublet in Poly-FePc/MWCNTs(A) FePPc/MWCNTs; (B) HFePPc/MWCNTs; (C) BAFePPc/MWCNTs; (D) BBFePPc/MWCNTs.
| Sample | Component of F | Component of F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 709.2 eV-Fe(Ⅱ) | 711.2 eV-Fe(Ⅲ) | 722.8 eV-Fe(Ⅱ) | 724.8 eV-Fe(Ⅲ) | |
| FePPc/MWCNTs | 32.489 | 43.931 | 4.975 | 18.604 |
| HFePPc/MWCNTs | 40.588 | 35.861 | 8.941 | 14.610 |
| BAFePPc/MWCNTs | 35.968 | 32.686 | 14.305 | 17.041 |
| BBFePPc/MWCNTs | 36.356 | 26.138 | 15.555 | 21.951 |
Table 1 Results of the Fe2p quadrature component spectra
| Sample | Component of F | Component of F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 709.2 eV-Fe(Ⅱ) | 711.2 eV-Fe(Ⅲ) | 722.8 eV-Fe(Ⅱ) | 724.8 eV-Fe(Ⅲ) | |
| FePPc/MWCNTs | 32.489 | 43.931 | 4.975 | 18.604 |
| HFePPc/MWCNTs | 40.588 | 35.861 | 8.941 | 14.610 |
| BAFePPc/MWCNTs | 35.968 | 32.686 | 14.305 | 17.041 |
| BBFePPc/MWCNTs | 36.356 | 26.138 | 15.555 | 21.951 |
| [1] | Dresselhaus M. S., Thomas I. L., Nature, 2001, 414(6861), 332—337 |
| [2] | Steele B. C. H., Heinzel A., Nature, 2001, 414(6861), 345—352 |
| [3] | Stamenkovic' V., Schmidt T. J., Ross P. N., Markovic' N. M., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(46), 11970—11979 |
| [4] | Chen W. X., Han G., Lee J. Y., Liu Z. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(12), 2285—2287 |
| (陈卫祥, 韩贵, LEE Jim Yang, 刘昭林. 高等学校化学学报,2003, 24(12), 2285—2287) | |
| [5] | Wu G., More K. L., Johnston C. M., Zelenay P., Science, 2011, 332(6028), 443—447 |
| [6] | Zhao X., Yin M., Ma L., Liang L., Liu C. P., Liao J. H., Lu T. H., Xing W., Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(8), 2736—2753 |
| [7] | Zhong H., Zhang H., Liu G., Liang Y., Hu J., Yi B., Electrochem. Commun., 2006, 8(5), 707—712 |
| [8] | Su D. S., Sun G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(49), 11570—11572 |
| [9] | Chen Z., Higgins D., Yu A., Zhang L., Zhang J., Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(9), 3167—3192 |
| [10] | Zhang L., Zhang J., Wilkinson D. P., Wang H., J. Power Sources, 2006, 156(2), 171—182 |
| [11] | Bezerra C. W. B., Zhang L., Lee K., Liu H., Marques A. L. B., Marques E. P., Wang H., Zhang J., Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(15), 4937—4951 |
| [12] | Baker R., Wilkinson D. P., Zhang J., Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54(11), 3098—3102 |
| [13] | Zagal J. H., Griveau S., Silva J. F., Nyokong T., Bedioui F., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2010, 254(23), 2755—2791 |
| [14] | Dong G., Huang M., Guan L., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(8), 2557—2559 |
| [15] | Orellana W., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2012, 541, 81—84 |
| [16] | Rakov E. G., Russ. Chem. Rev., 2001, 70(10), 827—863 |
| [17] | Baughman R. H., Zakhidov A. A., de Heer W. A., Science, 2002, 297(5582), 787—792 |
| [18] | Akinbulu I. A., Nyokong T., New J. Chem., 2010, 34(12), 2875—2886 |
| [19] | Morozan A., Campidelli S., Filoramo A., Jousselme B., Palacin S., Carbon, 2011, 49(14), 4839—4847 |
| [20] | Yuan Y., Zhao B., Jeon Y., Zhong S., Zhou S., Kim S., Bioresour. Technol., 2011, 102(10), 5849—5854 |
| [21] | Zhang Y., Mo G., Li X., Ye J., J. Power Sources, 2012, 197, 93—96 |
| [22] | Mouahid E. O., Coutanceau C., Belgsir E. M., Crouigneau P., Léger J. M., Lamy C., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1997, 426(1), 117—123 |
| [23] | Xu G., Li Z., Wang S., Yu X., J. Power Sources, 2010, 195(15), 4731—4735 |
| [24] | Kip B. J., Duivenvoorden F. B. M., Koningsberger D. C., Prins R., J. Catal., 1987, 105, 26—38 |
| [25] | Stöhr J., Hermsmeier B. D., Samant M. G., Weller D., Rev. Lett., 1992, 69(52), 2307—2310 |
| [26] | Banerjee S., Hemraj-Benny T., Balasubramanian M., Fischer D. A., Misewich J. A., Wong S. S., Chem. Commun., 2004, 7, 772—773 |
| [27] | Yeh Y. C., Chen H. M., Liu R. S., Asakura K., Lo M. Y., Peng Y. M., Chan T. S., Lee J. F., Chem. Mater., 2009, 21(17), 4030—4036 |
| [28] | Cartier C., Momenteau M., Dartyge E., Fontaine A., Tourillon G., Michalowicz A., Verdaguer M., J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1992, 4, 609—618 |
| [29] | Kandaz M., Bilgiçli A. T., Altındal A., Synth. Met., 2010, 160(1), 52—60 |
| [30] | Sosnik A., Gotelli G., Abraham G. A., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2011, 36(8), 1050—1078 |
| [31] | Nas A., Fandaklı S., Kantekin H., Demirbaᶊ A., Durmuᶊ M., Dyes Pigm., 2012, 95(1), 8—17 |
| [32] | Alvaro M., Carbonell E., Espl M., Garcia H., Appl. Catal., 2005, 57(1), 37—42 |
| [33] | Peng Y. X., Cui L. F., Yang S. F., Fu J. J., Zheng L. R., Liao Y., Li K., Zuo X., Xia D. G., Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 154, 102—109 |
| [34] | Bhargava G., Gouzman I., Chun C., Ramanarayanan T., Bernasek S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253(9), 4322—4329 |
| [35] | Niu W. H., Li L. G., Liu X. J., Wang N., Liu J., Zhou W. J., Tang Z. H., Chen S. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 5555—5562 |
| [36] | Peng Y. X., Li Z. P., Xia D. G., Zheng L. R., Liao Y., Li K., Zuo X., J. Power Sources, 2015 , 291, 20—28 |
| [37] | Shui J. L., Karan N. K., Balasubramanian M., Li S. Y., Liu D. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 16654—16661 |
| [38] | Choi H. J., Kwag G., Kim S., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2001, 508(1), 105—114 |
| [1] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [2] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [3] | GU Yu, XI Baojuan, LI Jiangxiao, XIONG Shenglin. Structure Regulation of Single-atom Catalysts in Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220036. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, XUE Dongping, DU Yu, JIANG Su, WEI Yifan, YAN Wenfu, XIA Huicong, ZHANG Jianan. MOF-derived Carbon-based Electrocatalysts Confinement Catalyst on O2 Reduction and CO2 Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [5] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [6] | HE Yujing, LI Jiale, WANG Dongyang, WANG Fuling, XIAO Zuoxu, CHEN Yanli. Zinc-based Activated Fe/Co/N Doped Biomass Carbon Electrocatalysts with High Oxygen Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [7] | MA Jun, ZHONG Yang, ZHANG Shanshan, HUANG Yijun, ZHANG Lipeng, LI Yaping, SUN Xiaoming, XIA Zhenhai. Design and Theoretical Calculation of Heteroatoms Doped Graphdiyne Towards Efficiently Catalyzing Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 624. |
| [8] | WANG Yuemin, MENG Qinglei, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Enhancement of Performance of Fe-N-C Catalysts by Copper and Sulfur Doping for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1843. |
| [9] | GUAN Fanglan,LI Xin,ZHANG Qun,GONG Yan,LIN Ziyu,CHEN Yao,WANG Lejun. Fabrication and Capacitance Performance of Laser-machined RGO/MWCNT/CF In-plane Flexible Micro-supercapacitor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 300. |
| [10] | YIN Wenjing, LIU Xiao, QIAN Huidong, ZOU Zhiqing. Preparation and Oxygen Reduction Performance of Fe, N co-Doped arbon Nanoplate with High Density of Active Sites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1480. |
| [11] | SUN Mengmeng,CHANG Chunrui,ZHANG Zhiming,AN Libao. Preparation and Electrical Contact Properties of Palladium-doped Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 11. |
| [12] | WANG Jie, SUN Xiaogang, CHEN Wei, LI Xu, HUANG Yapan, WEI Chengcheng, HU Hao, LIANG Guodong. Electrochemical Performance of Hydroxylated Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Sandwich Separator in Lithium-sulfur Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1782. |
| [13] | XU Zhaoquan, MA Junhong, SHI Minhui, FENG Chao, XIE Yahong, MI Hongyu. Preparation and Application of a Novel Natural Product-based Fe and N Codoped Carbon Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1532. |
| [14] | WANG Xiuli, HE Xingquan. Electrocatalytic Performance of Fe9S10 Nanoparticles Loaded Nitrogen and Sulphur Codoped Porous Carbon for Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1524. |
| [15] | HUANG Jipei,LI Yi,YANG Shenhui,ZHOU Yazhou,CHENG Xiaonong,ZHU Jia,YANG Juan. Synthesis of Three-dimensional Pt-Ag Aerogels and Their Electrocatalytic Performance Toward Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 1063. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||