

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 34.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140763
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Yabing1,2,*( ), DUAN Weijie2, CUI Xiaobing2, XU Jiqing2
), DUAN Weijie2, CUI Xiaobing2, XU Jiqing2
Received:2014-08-20
Revised:2014-12-23
Online:2015-01-10
Published:2014-12-23
Contact:
LIU Yabing
E-mail:liuyab@163.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Yabing, DUAN Weijie, CUI Xiaobing, XU Jiqing. Synthesis and Characterization of a 2D Tungstovanadated Derivative: [Cu(en)2]2[VⅤO44{Cu(en)2(H2O)}2]·3H2O†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 34.
| Empirical formula | C16W6.5N16Cu4O49V10.5 | D/(Mg·m-3) | 2.949 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula weight | 3258.86 | μ/mm-1 | 12.633 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Limiting indices | -14≤h≤17 |
| Space group | P | -15≤k≤17 | |
| a/nm | 1.2857(2) | -15≤l≤18 | |
| b/nm | 1.3064(2) | F(000) | 1513 |
| c/nm | 1.3951(3) | Crystal size | 0.24 mm×0.22 mm×0.21 mm |
| α/(°) | 81.324(1) | Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.041 |
| β/(°) | 63.094(1) | Final R indices[I>2σ(I)]* | R1=0.0570 |
| γ/(°) | 65.150(1) | wR2 = 0.1615 | |
| Volume/nm3 | 1.8354(6) | R indices(all data) | R1 = 0.0972 |
| Z | 1 | wR2 = 0.1797 |
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for compound 1
| Empirical formula | C16W6.5N16Cu4O49V10.5 | D/(Mg·m-3) | 2.949 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula weight | 3258.86 | μ/mm-1 | 12.633 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Limiting indices | -14≤h≤17 |
| Space group | P | -15≤k≤17 | |
| a/nm | 1.2857(2) | -15≤l≤18 | |
| b/nm | 1.3064(2) | F(000) | 1513 |
| c/nm | 1.3951(3) | Crystal size | 0.24 mm×0.22 mm×0.21 mm |
| α/(°) | 81.324(1) | Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.041 |
| β/(°) | 63.094(1) | Final R indices[I>2σ(I)]* | R1=0.0570 |
| γ/(°) | 65.150(1) | wR2 = 0.1615 | |
| Volume/nm3 | 1.8354(6) | R indices(all data) | R1 = 0.0972 |
| Z | 1 | wR2 = 0.1797 |
| W1/V1—O10 | 0.1688(8) | W1/V1—O8 | 0.1845(9) | W2/V2—O5 | 0.1804(9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2/V2—O12 | 0.2031(9) | W3/V3—O18 | 0.1884(8) | W3/V3—O4 | 0.2443(1) |
| W4/V4—O20 | 0.1683(8) | W5/V5—O9 | 0.1876(9) | W6/V6—O18 | 0.1989(9) |
| V7—O2 | 0.1689(2) | V7—O3 | 0.1666(1) | V8—O12 | 0.1936(9) |
| V9—O22 | 0.1913(9) | V9—O18 | 0.1977(1) | Cu1—N2 | 0.2004(1) |
| Cu2—N5 | 0.1978(1) | Cu3—N7 | 0.1999(2) | N6—C6 | 0.146(2) |
| O4—V7—O1 | 111.0(7) | O2—V7—O1 | 109.4(7) | V7—O1—W2/V2 | 119.8(6) |
| V8—O23—W1/V1 | 101.8(4) | C8—C7—N7 | 104.0(2) | V9—O22—W5/V5 | 101.6(4) |
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm) and bond angles(°) for compound 1
| W1/V1—O10 | 0.1688(8) | W1/V1—O8 | 0.1845(9) | W2/V2—O5 | 0.1804(9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2/V2—O12 | 0.2031(9) | W3/V3—O18 | 0.1884(8) | W3/V3—O4 | 0.2443(1) |
| W4/V4—O20 | 0.1683(8) | W5/V5—O9 | 0.1876(9) | W6/V6—O18 | 0.1989(9) |
| V7—O2 | 0.1689(2) | V7—O3 | 0.1666(1) | V8—O12 | 0.1936(9) |
| V9—O22 | 0.1913(9) | V9—O18 | 0.1977(1) | Cu1—N2 | 0.2004(1) |
| Cu2—N5 | 0.1978(1) | Cu3—N7 | 0.1999(2) | N6—C6 | 0.146(2) |
| O4—V7—O1 | 111.0(7) | O2—V7—O1 | 109.4(7) | V7—O1—W2/V2 | 119.8(6) |
| V8—O23—W1/V1 | 101.8(4) | C8—C7—N7 | 104.0(2) | V9—O22—W5/V5 | 101.6(4) |
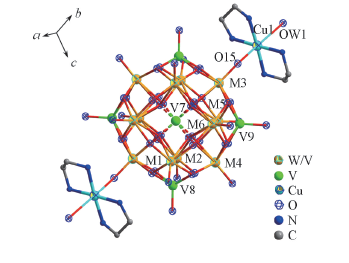
Fig.1 Ball/strick representation of the tetra-capped Keggin polyoxoanion supporting two transition metal complex of compound 1 M1, M2: 0.8W+0.2V; M3, M4: 0.46W+0.54V; M5, M6: 0.36W+0.64V.
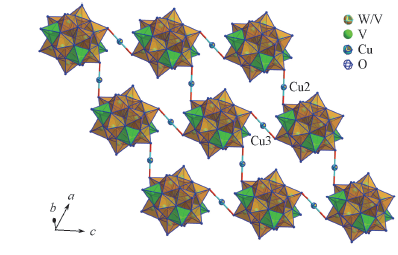
Fig.2 [Cu(en)2]2+ cations join polyoxoanion into 2D layer through Cu—O interactions [Cu1(en)2(H2O)]2+ cations, water and en molecules are omitted for clarity.
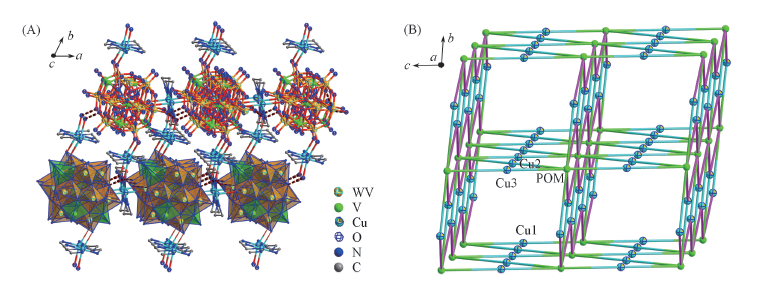
Fig.3 View of 3D supramolecular network structure with hydrogen bonding interactions between water molecules and oxygen atoms from two neighboring 2D layers along b axix(A) and schematic drawing of the 3D supramolecular topology in compound 1(B) (A) Several hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity; (B) covalent bond and weak bond are shown with two-colored lines, and hydrogen bonds are shown with purple lines, respectively.
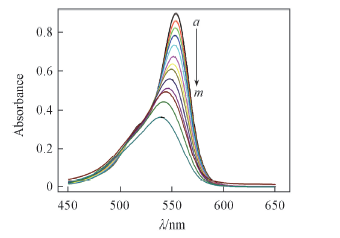
Fig.10 Changes of UV-Vis absorption spectra of RhB solutions with compound 1 Irradiation time(min) from a to m: 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, 240, 270, 300, 330, 360.
| [1] | Davis M. E., Nature , 2002, 417, 813—821 |
| [2] | Fujita M., Kwon Y. J., Sasaki O., Yamaguchi K., Ogura K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117, 7287—7288 |
| [3] | Mizuno N., Misono M., Chem. Rev., 1998, 98, 199—218 |
| [4] | Thiel J., Molina P. I., Symes M. D., Cronin L., Cryst. Growth Des., 2012, 12, 902—908 |
| [5] | Wu Q., Chen W. L., Liu D., Liang C., Li Y. G., Lin S.W., Wang E. B., Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 56—61 |
| [6] | Jiang N., Li F. Y., Xu L., Li Y. G., Li J. M., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2010, 13, 372—375 |
| [7] | Zheng S. T., Zhang J., Li X. X., Fang W. H., Yang G. Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 15102—15103 |
| [8] | Wang L., Wang Y. Y., Li Y., Liang Z. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(8), 1646—1650 |
| (王磊, 王艳艳, 李乙, 梁志强. 高等学校化学学报,2012, 33(8), 1646—1650) | |
| [9] | Wang X. N., Liu S. X., Li S. J., Xie R. H., Zhang X., Liu Y. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5), 1047—1051 |
| (王雪娜, 刘术侠, 李书军, 谢瑞红, 张鑫, 刘艺伟. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(5), 1047—1051) | |
| [10] | Fu H., Wang X. L., Chen W. L., Meng J. X., Li Y. G., Wang E. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9), 2198—2203 |
| (傅海, 王晓兰, 陈维林, 孟靖昕, 李阳光, 王恩波. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(9), 2198—2203) | |
| [11] | Wang X., Peng J., Liu M. G., Wang D. D., Meng C. L., Li Y., Shi Z. Y., CrystEngComm , 2012, 14, 3220—3226 |
| [12] | Cui X. B., Xu J. Q., Meng H., Zheng S. T., Yang G. Y., Inorg. Chem., 2004, 43, 8005—8007 |
| [13] | Vaddypally S., Swapna H., Samar K. D., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2002, 3, 996—999 |
| [14] | Chen Q., Hill C. L., Inorg. Chem., 1996, 35, 2403—2405 |
| [15] | Liu C. M., Zhang D. Q., Zhu D. B., Cryst. Growth Des., 2006, 6, 524—529 |
| [16] | Xiao L.N., Peng Y., Wang Y., Xu J. N., Gao Z. M., Liu Y. B., Zheng D. F., Cui X. B., Xu J. Q., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2011, 12, 1997—2005 |
| [17] | Liu J., Xu J. N., Liu Y. B., Lu Y. K., Song J. F., Zhang X., Cui X. B., Xu J. Q., Wang T. G., J. Solid State Chem., 2007, 180, 3456—3462 |
| [18] | Xu Y., Zhu H.G., Cai H., You X. Z.,Chem. Commun., 1999, 787—788 |
| [19] | Niu J. Y., Chen G., Zhao J. W., Yu C. F., Ma P. T., Wang J. P., Cryst. Growth Des., 2010, 10, 4689—4692 |
| [20] | Feng S. H., Xu R. R., Acc. Chem. Res., 2001, 34, 239—247 |
| [21] | Sheldrick G.M., SHELXL-97, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, 1997 |
| [22] | Brown I. D., Altermatt D., Acta Cryst., 1985, B41, 244—247 |
| [1] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [2] | ZHANG Huishuang, GAO Yanxiao, WANG Qiuxian, LI Xiangnan, LIU Wenfeng, YANG Shuting. High-low Temperature Properties of Ni-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material by Hydrothermal Synthesis with CTAB Assisted [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 819. |
| [3] | WANG Ye, ZHANG Xiaosi, SUN Lijing, LI Bing, LIU Lin, YANG Miao, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Morphology Control of SAPO Molecular Sieves under the Assistance of Organosilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 683. |
| [4] | WANG Jianyu, ZHANG Qiang, YAN Wenfu, YU Jihong. Roles of Hydroxyl Radicals in Zeolite Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 11. |
| [5] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [6] | LIU Yabing,LI Mingyang,TIAN Ge,ALATENG Shaga,PEI Tonghe,NIE Jingsi. Syntheses, Structures and Catalytic Properties of Two Supramolecular Complexes Based on 2-Pyridylamine and Cluster † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 995. |
| [7] | ZHUO Mengning,LI Fei,JIANG Hao,CHEN Qianwen,LI Peng,WANG Lizhang. Preparation of SnO2/GDE Cathodes and Their Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to Produce Formic Acid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 530. |
| [8] | DONG Le, HUANG Xingliang, REN Junjie, DAI Xiaoping, LIU Zongyan, TIAN Hongfeng, WANG Zhidong, WU Xiaotong. Influence Mechanism of Particle Size and Distribution of Silica Sol in the Synthesis of Ferrierite Zeolite with High SiO2/Al2O3 Ratio [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2449. |
| [9] | ZHOU Hai, CHEN Hao, GUO Ya, KANG Min. Synthesis of Meso-porous Co3O4 Polyhedra and Their Electrochemical Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1374. |
| [10] | GAO Ningxiao,XU Yulong,LIU Yong. Preparation of Carbon Dots from Soy Milk Powder and Fluorescent Nanofibers Containing Carbon Dots† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 555. |
| [11] | Baozhen SHI,Shan LI,Dianpeng WANG,Yunzhi ZHOU,Jinyu SUN. Synthesis and Physical Properties of Cobalt-Zinc Hybrid Porous Metal-organic Frameworks † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2443. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jing,DONG Yuming,LIU Xiang,LI Hexing. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Z-Scheme Photocatalyst Sb2WO6/g-C3N4 † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 123. |
| [13] |
JIANG Xianming,WANG Huaiqian,CAO Yu,SUN Zhihui,CAO Yufang,WU Weibin.
Structure Prediction and Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study of Rare Earth-doped Silicon-based Clusters of MS |
| [14] | XIA Kun, ZHOU Dan, YANG Yun, YANG Shuijin, XIA Qinghua. Efficient Synthesis of Highly Uniform AlPO4-11 Microcrystalline and Study on the Crystallization Process† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1624. |
| [15] | SONG Wei, WANG Liqun, ZENG Shuangli, WANG Li, FAN Yong, XU Jianing. In situ Hydrothermal Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Fluorescence Properties of Two Cadmium Coordination Polymers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1406. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||