

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (11): 2455.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140156
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yanen1, CAO Shuang1, WU Weihong1, WU Min2, TANG Yawen2, LU Tianhong2,*( )
)
Received:2014-03-03
Online:2014-11-10
Published:2014-10-20
Contact:
LU Tianhong
E-mail:tianhonglu@263.net
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Yanen, CAO Shuang, WU Weihong, WU Min, TANG Yawen, LU Tianhong. Effect of Particle Size on the Electrocatalytic Activity of Pt/C Catalysts for Oxidation of Formic Acid†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11): 2455.
| Heating temperature/℃ | d/nm(XRD) | S/(m2·g-1) | Relative crystallinity | Surface average dispersion, D(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | 2.2 | 127.4 | 0.61 | 40.7 |
| 60 | 3.2 | 87.6 | 1.56 | 34.5 |
| 50 | 3.8 | 73.8 | 2.32 | 30.9 |
| 40 | 4.3 | 65.2 | 2.86 | 28.3 |
| 30 | 4.8 | 58.4 | 3.30 | 26.0 |
Table 1 Structure parameters of different Pt/C catalysts
| Heating temperature/℃ | d/nm(XRD) | S/(m2·g-1) | Relative crystallinity | Surface average dispersion, D(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | 2.2 | 127.4 | 0.61 | 40.7 |
| 60 | 3.2 | 87.6 | 1.56 | 34.5 |
| 50 | 3.8 | 73.8 | 2.32 | 30.9 |
| 40 | 4.3 | 65.2 | 2.86 | 28.3 |
| 30 | 4.8 | 58.4 | 3.30 | 26.0 |
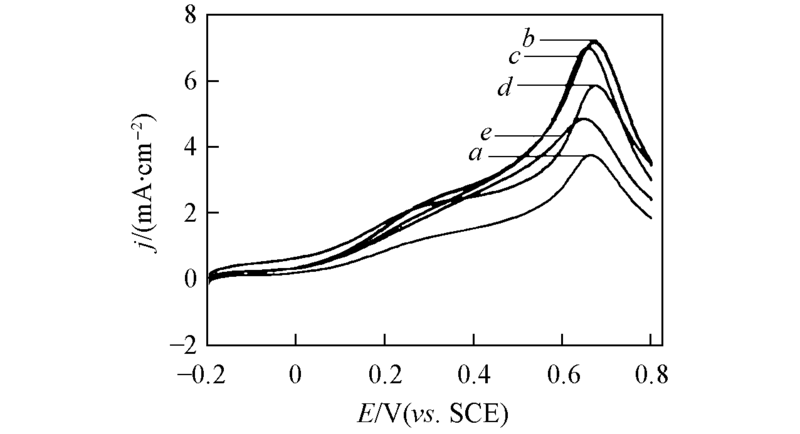
Fig.4 Linear scan voltammograms of Pt/C catalysts with different Pt particles sizes in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 + HCOOH solution Pt particle size/nm: a. 2.2; b. 3.2; c. 3.8; d. 4.3; e. 4.8.
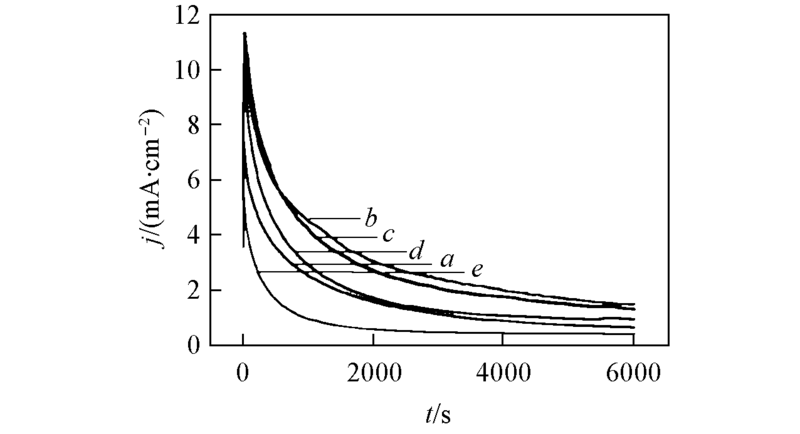
Fig.6 Chronoamperometric curves of Pt/C catalysts with different Pt particles sizes in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 + HCOOH solution at 0.60 V Pt particle size/nm: a. 2.2; b. 3.2; c. 3.8; d. 4.3; e. 4.8.
| [1] | Weber M., Wang J. T., Wasmus S., Savinell R. F., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143(7), 1158—1160 |
| [2] | Ha R. I., Masel R. I., Waszczuk P., Wieckowski A., Barnard T., J. Power Sources,2002, 111(1), 83—89 |
| [3] | Ha S., Rice C. A., Masel R. I., Wieckowski A., J. Power Sources,2002, 112(2), 655—659 |
| [4] | Yuan Q. Y., Tang Y. W., Zhou Y. M., Xing W., Lu T. H., Chin. J. Appl. Chem. ,2005, 22(9), 929—932 |
| (袁青云, 唐亚文, 周益明, 邢巍, 陆天虹. 应用化学 ,2005, 22(9), 929—932) | |
| [5] | Liu C. Y., Xu B., Tang Y. W., Cao G. P., Yang Y. S., Lu T. H., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2011, 27(3), 604—608 |
| (刘春艳, 徐斌, 唐亚文, 曹高萍, 杨裕生, 陆天虹. 物理化学学报, 2011, 27(3), 604—608) | |
| [6] | Zhang Q., Yao Z. Q., Zhou R., Du Y. K., Yang P., Acta Chim. Sinica,2012, 70(20), 2149—2154 |
| (张强, 姚章权, 周蓉, 杜玉扣, 杨平. 化学学报,2012, 70(20), 2149—2154) | |
| [7] | McGovern M. S., Garnett E. C., Rice C., Masel R. I., Wieckowaki A., J. Power Sources,2003, 115(1), 35—39 |
| [8] | Rice C., Ha S., Masel R. I., Wieckowski A., J. Power Sources,2003, 115(2), 229—235 |
| [9] | Liao C., Wei Z. D., Chen S. G., Li L., Ji M. B., Tan Y., Liao M. J., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113(14), 5705—5710 |
| [10] | Lu L., Tang Y. W., Chen Y., Chen T. T., Ge C. W., Lu T. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(7), 1748—1752 |
| (陆亮, 唐亚文, 陈煜, 陈婷婷, 葛存旺, 陆天虹. 高等学校化学学报,2013, 34(7), 1748—1752) | |
| [11] | Lu L., Tang Y. W., Chen Y., Chen T. T., Ge C. W., Lu T. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(1), 115—120 |
| (陆亮, 唐亚文, 陈煜, 陈婷婷, 葛存旺, 陆天虹. 高等学校化学学报,2014, 35(1), 115—120) | |
| [12] | Attwood P., McNicol B., Short R., J. Appl. Electrochem., 1980, 10(2), 213—222 |
| [13] | Takasu Y., Iwazaki T., Sugimoto W., Murakami Y., Electrochem. Commun., 2000, 2(9), 671—674 |
| [14] | Yahikozawa K., Fujii Y., Matsuda Y., Nishimura K., Takasu Y., Electrochimica Acta,1991, 36(5/6), 973—978 |
| [15] | Hamnett A., Catal. Today, 1997, 38(4), 445—457 |
| [16] | Frelink T., Visscher W., Van J. A., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1995, 382(1/2), 65—72 |
| [17] | Watanable M., Stonehart P. J., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1989, 271(1/2), 213—220 |
| [18] | Schmidt T. J., Jusys Z., Gasteiger H. A., Behm R. J., Endruschat U., Boennemann H. J., J. Electroanal. Chem. ,2001, 501(1/2), 132—140 |
| [19] | Antolini E., Cardelini F., J. Alloys Compounds,2001, 315(1/2), 118—122 |
| [20] | Borodziński A., Bonarowska M., Langmuir,1997, 13(21), 5613—5620 |
| [21] | Tang Y. W., Yang H., Xing W., Lu T. H., Chin. Chem. Letts., 2002, 13(5), 478—481 |
| [22] | Takasu Y., Ohashi N., Zhang X. G., Murakami Y., Minagawa H., Sato S., Yahikozawa K., Electrochimica Acta,1996, 41(16), 2595—2600 |
| [23] | Xiang J., Wu B. L., Chen S. L., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. ,2000, 16(10), 906—911 |
| (向娟, 吴秉亮, 陈胜利, 物理化学学报 ,2000, 16(10), 906—911) | |
| [24] | Tang Y. W., Zhang L. L., Wang Y. E., Zhou Y. M., Gao Y., Liu C. P., Xing W., Lu T. H., J. Power Sources,2006, 162(1), 124—131 |
| [1] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [2] | WANG Sicong, PANG Beibei, LIU Xiaokang, DING Tao, YAO Tao. Application of XAFS Technique in Single-atom Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [3] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [4] | YAO Qing, YU Zhiyong, HUANG Xiaoqing. Progress in Synthesis and Energy-related Electrocatalysis of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [5] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [6] | WANG Ruhan, JIA Shunhan, WU Limin, SUN Xiaofu, HAN Buxing. CO2-involved Electrochemical C—N Coupling into Value-added Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220395. |
| [7] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [8] | YANG Lijun, YU Yang, ZHANG Lei. Construction of Dual-functional 2D/3D Hydrid Co2P-CeO x Heterostructure Integrated Electrode for Electrocatalytic Urea Oxidation Assisted Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220082. |
| [9] | XIA Tian, WAN Jiawei, YU Ranbo. Progress of the Structure-property Correlation of Heteroatomic Coordination Structured Carbon-based Single-atom Electrocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220162. |
| [10] | ZHANG Hongwei, CHEN Wen, ZHAO Meiqi, MA Chao, HAN Yunhu. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemistry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220129. |
| [11] | WU Jun, HE Guanchao, FEI Huilong. Self-supported Film Electrodes Decorated with Single Atoms for Energy Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220051. |
| [12] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [13] | CHEN Zhaoyang, XUE Yurui, LI Yuliang. Synthesis and Applications of Graphdiyne Based Zerovalent Atomic Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220063. |
| [14] | DING Qin, ZHANG Zixuan, XU Peicheng, LI Xiaoyu, DUAN Limei, WANG Yin, LIU Jinghai. Effects of Cu, Ni and Co Hetroatoms on Constructions and Electrocatalytic Properties of Fe-based Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220421. |
| [15] | WANG Zumin, MENG Cheng, YU Ranbo. Doping Regulation in Transition Metal Phosphides for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||