

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 1181.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140066
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiaoliu1,*( ), MA Donglai1, YANG Hailong1, TAN Guanhai1, DU Huiru2, WANG Kerang1, ZHANG Pingzhu1, CHEN Hua1
), MA Donglai1, YANG Hailong1, TAN Guanhai1, DU Huiru2, WANG Kerang1, ZHANG Pingzhu1, CHEN Hua1
Received:2014-01-20
Online:2014-06-10
Published:2014-02-25
Contact:
LI Xiaoliu
E-mail:lixl@hbu.cn
Supported by:TrendMD:
LI Xiaoliu, MA Donglai, YANG Hailong, TAN Guanhai, DU Huiru, WANG Kerang, ZHANG Pingzhu, CHEN Hua. Synthesis, Antitumor Activity and DNA Binding of cridine-polyamine Conjugates†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1181.
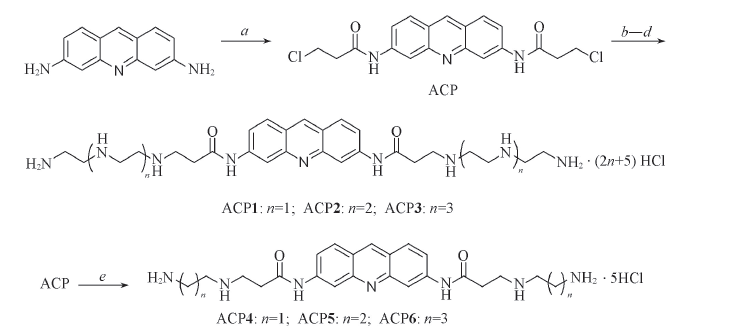
Scheme 1 Synthesis of acridine-polyamine conjugatesReagents and conditions: a. ClCH2CH2COCl, reflux, 4 h; b. H2NCH2(CH2NHCH2)nCH2NH2(n=1-3), EtOH, NaI, reflux, 5 h; c. MeOH, Boc2O, r.t., 2 h; d. 36%(mass fraction) HCl/EtOH(volume ratio: 1∶3); e. H2NCH2(CH2)nNH2(n=1-3), EtOH, NaI, reflux, 5 h, 36%(mass fraction) HCl/EtOH(volume ratio: 1∶3).
| Compd. | IC50/(μmol·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | A549 | K562 | |
| ACP1 | 113.37±11.18 | 32.17±3.14 | 16.55±0.98 |
| ACP2 | 3.56±0.07 | 2.54±0.02 | 1.27±0.06 |
| ACP3 | 54.05±2.66 | 17.47±1.28 | 15.92±0.89 |
| ACP4 | 23.10±1.63 | 9.44±0.50 | 12.53±1.15 |
| ACP5 | 19.29±0.42 | 11.30±0.12 | 7.46±1.14 |
| ACP6 | 30.74±2.65 | 20.17±1.23 | 10.60±1.40 |
| Cis-platin | 9.31±1.31 | 27.57±1.85 | 16.90±1.36 |
Table 1 Cytotoxicity data of ACP1-ACP6
| Compd. | IC50/(μmol·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | A549 | K562 | |
| ACP1 | 113.37±11.18 | 32.17±3.14 | 16.55±0.98 |
| ACP2 | 3.56±0.07 | 2.54±0.02 | 1.27±0.06 |
| ACP3 | 54.05±2.66 | 17.47±1.28 | 15.92±0.89 |
| ACP4 | 23.10±1.63 | 9.44±0.50 | 12.53±1.15 |
| ACP5 | 19.29±0.42 | 11.30±0.12 | 7.46±1.14 |
| ACP6 | 30.74±2.65 | 20.17±1.23 | 10.60±1.40 |
| Cis-platin | 9.31±1.31 | 27.57±1.85 | 16.90±1.36 |
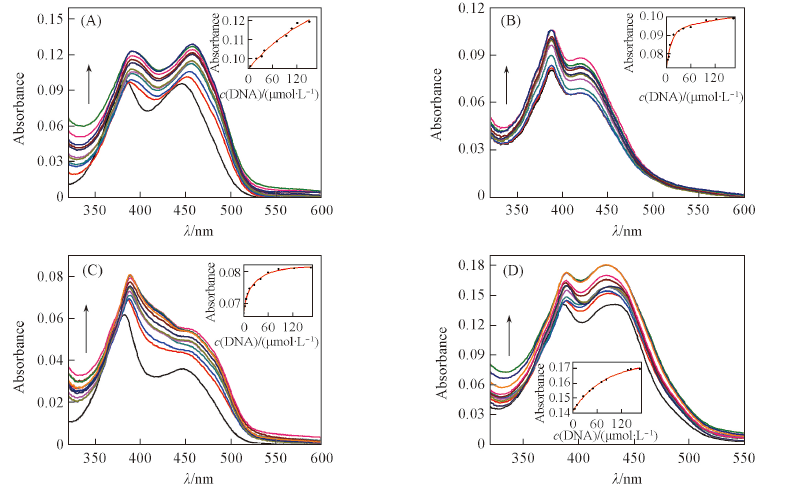
Fig.2 UV-Vis spectral changes of compounds ACP1(A), ACP2(B), ACP3(C) and ACP6(D) at the concentration of 1.0×10-5 mol/L upon addition of Ct-DNA in phosphate buffer(10 mmol/L, pH=7.4) containing 50 mmol/L NaCl at 25 ℃The arrows show the concentration increasing of Ct-DNA(0-166 μmol/L). Insets are the fitting plots of the binding constants for ACP1, ACP2, ACP3 and ACP6 with Ct-DNA obtained at the maximum absorption band.
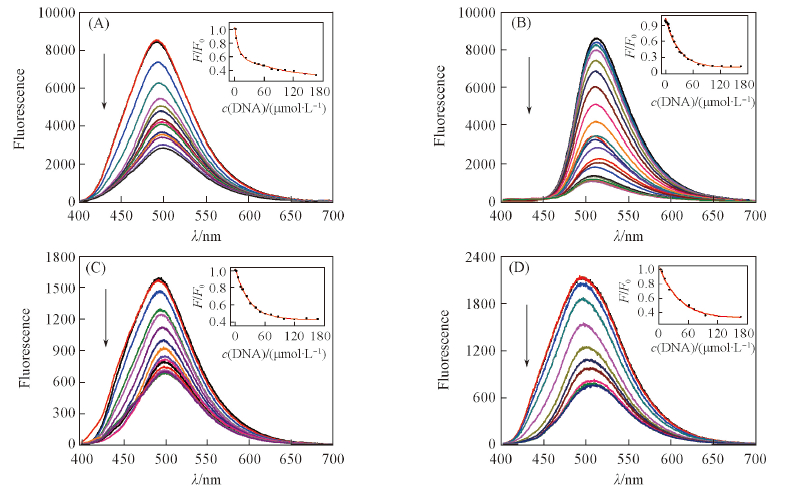
Fig.3 Fluorescence spectral changes of compounds ACP1(A), ACP2(B), ACP3(C) and ACP6(D) at the concentration of 1.0×10-5 mol/L upon addition of Ct-DNA in phosphate buffer(10 mmol/L, pH=7.4) containing 50 mmol/L NaCl at 25 ℃The arrows show the concentration increasing of Ct-DNA(0-166 μmol/L). λex=382.5 nm. Insets show the fluorescence changes for ACP1, ACP2, ACP3 and ACP6 with Ct-DNA obtained at the maximum fluorescence band.
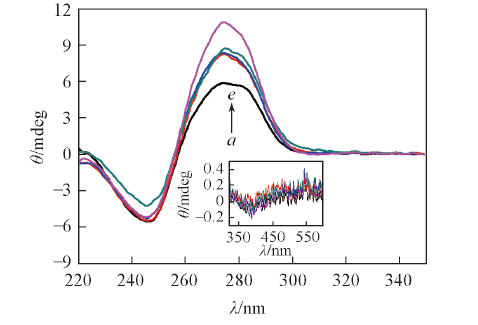
Fig.4 CD spectra of Ct-DNA(5.0×10-5 mol/L) in the absence and presence of ACP1, ACP2, ACP3 and ACP6(2.0×10-5 mol/L) in phosphate buffer(10 mmol/L, pH=7.4) containing 50 mmol/L NaCl at 25 ℃a. Ct-DNA; b. ACP4+Ct-DNA; c. ACP3+Ct-DNA;d. ACP2+Ct-DNA; e. ACP1+Ct-DNA.
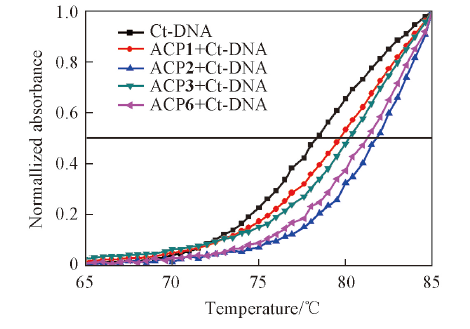
Fig.5 DNA melting curves for Ct-DNA(5.0×10-5 mol/L) in the absence and presence of ACP1, ACP2, ACP3 and ACP6 with concentration of 5.0×10-6 mol/L in phosphate buffer(10 mmol/L, pH=7.4) containing 50 mmol/L NaCl
| Compd. | Ct-DNA | ACP1 | ACP2 | ACP3 | ACP6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm/℃ | 78.35 | 80.25 | 81.76 | 81.23 | 81.42 |
| ΔTm/℃ | 1.90 | 3.41 | 2.88 | 3.07 |
Table 2 Average Tm and ΔTm for Ct-DNA in the absence and presence of ACP1, ACP2, ACP3 and ACP6
| Compd. | Ct-DNA | ACP1 | ACP2 | ACP3 | ACP6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm/℃ | 78.35 | 80.25 | 81.76 | 81.23 | 81.42 |
| ΔTm/℃ | 1.90 | 3.41 | 2.88 | 3.07 |
| [1] | Belmont P., Constant J. F., Demeunynck M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2001, 30, 70-81 |
| [2] | Lagutschenkov A., Dopfer O., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 2011, 268, 66-77 |
| [3] | Moore M. J., Schultes C. M., Cuesta J., Cuenca F., Gunaratnam M., Tanious F. A., Wilson W. D., Neidle S., J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 582-599 |
| [4] | Gamucci T., Paoletti X., Eur. J. Cancer, 2003, 39, 330-334 |
| [5] | Cian A., Cristofari G., Reichenbach P., Lemos E., Monchaud D., Teulade-Fichou M. P., Shinya K., Lacroix L., Lingner J., Mergny J. L., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, 104, 17347-17352 |
| [6] | Harrison R. J., Gowan S. M., Kelland L. R., Neidle S., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 1999, 17, 2463-2468 |
| [7] | Lang X. L., Luan X. D., Gao C. M., Jiang Y. Y., Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24, 1498-1505 |
| (郎许亮, 栾旭东, 高春梅, 蒋宇扬. 化学进展, 2012, 24, 1498-1505) | |
| [8] | Melchiorre C., Bolognesi M. L., Minarini A., Rosini M., Tumiatti V. J., J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53, 5906-5914 |
| [9] | Phanstiel O., Price H. L., Juusola J., Kline M., Shah S. M., J. Org. Chem., 2000, 65, 5590-5599 |
| [10] | Ingrassia L., Lefranc F., Kiss R., Mijatovic T., Curr. Med. Chem., 2009, 16, 1192-1213 |
| [11] | Wang K. R., An H. W., Wang Y. Q., Yan X. H., Li R., Chen H., Zhang P. Z., Li J. M., Li X. L., Zhang J. C., Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2012, 32, 696-702 |
| (王克让, 安红维, 王月清, 闫新豪, 李锐, 陈华, 张平竹, 李金梅, 李小六, 张金超. 有机化学, 2012, 32, 696-702) | |
| [12] | Zhang P. Z., Wei C., Duan X. X., Zhang X. Y., Wang K. R., Chen H., Li X. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(7), 1466-1470 |
| (张平竹, 魏超, 段晓旭, 张晓媛, 王克让, 陈华, 李小六.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(7), 1466-1470) | |
| [13] | Giménez-Arnau E., Missailidis S., Stevenns M. F. S., Anti-cancer Drug Design, 1998, 13, 431-451 |
| [14] | Kumar C. V., Asuncion E. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 8547-8553 |
| [15] | Terenzi A., Barone G., Piccionello A. P., Giorgi G., Guarcello A., Portanova P., Calvaruso G., Buscemi S., Vivona N., Pace A., Dalton Trans., 2010, 39, 9140-9145 |
| [16] | Ma Y., Huang Z. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10), 2217-2222 |
| (马彦, 黄志纾.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(10), 2217-2222) | |
| [17] | Long E. C., Barton J. K., Acc. Chem. Res., 1990, 23, 271-273 |
| [18] | Kozurkov M., Sabolov D., Paulíkov H., Janovec L., Kristian P., Bajdichov M., Buša J. D., Imrich J., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2007, 41, 415-422 |
| [19] | Bazzicalupi C., Chioccioli M., Sissi C., Porcù E., Bonaccini C., Pivetta C., Bencini A., Giorgi C., Valtancoli B., Melani F., Gratteri P., Chem. Med.Chem., 2010,5, 1995-2005 |
| [20] | Janovec L., Kǒzurkov M., Sabolov D., Ungvarsky J., Paulíková H.,Plnukov J., Vantov Z., Imrich J., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2011, 19, 1790-1801 |
| [21] | Chaveerach U., Meenongwa A., Trongpanich Y., Soikum C., Chaveerach P., Polyhedron, 2010, 29, 731-738 |
| [22] | Kelly J. M., Tossi A. B., Mcconnell D. J., Ohuigin C., Nucleic Acids Res., 1985, 13, 6017-6034 |
| [23] | Haq I., Lincoln P., Suh D., Norden B., Chowdhry B. Z., Chaires J. B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117, 4788-4796 |
| [24] | Neyhart G. A., Grover N., Smith S. R., Kalsbeck W. A., Fairley T. A., Cory M., Thorp H. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 4423-4428 |
| [1] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [2] | LI Lei, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei, BO Chunling, FAN Ye. Comparative Effects of Mono/disaccharides on Conjugated Linoleic Acid Vesicles at Near Neutral pH [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210860. |
| [3] | ZHAO Ying, QIAO Ling, ZHAO Guofeng, CHEN Li. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Lycorine Derivatives Containing Malate Ester [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2789. |
| [4] | LIU Huazheng, PAN Xiaoguang, LI Hua, WAN Renzhong, LIU Xigong. Na2CO3-catalyzed 1,6-Conjugate Addition of Trimethylsilyl Azide to δ-CF3-δ-Aryl-disubstituted Para-Quinone Methides: Efficient Construction of Diarylmethanes Bearing CF3- and N3-Substituted Quaternary Stereocenters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2772. |
| [5] | HU Chuanchuan, PANG Jingxiang, HE Chuangchuang, LI Wei, SUN Shutao. Sc(OTf)3 Catalyzed 1,6-Conjugate Allylation of δ-CN p-QMs: Synthesis of Allyl Substituted Diarylacetonitrile Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2805. |
| [6] | MENG Lili, CHEN Linlin, ZHANG Xiaoliang, XIE Linghai, LIU Huan. Controllable Liquid Transfer for Preparing Oriented Polymer Thin Films: Toward the Enhanced Performance of PLED [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1260. |
| [7] | ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Xueqiang. Investigations upon the Bioconjugation-based Construction Technologies and Applications of Aptamer-drug Conjugates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3367. |
| [8] | FAN Ye, LI Qian, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei. Fabrication of Lamellar Liquid Crystals of Conjugated Linoleic Acid as Drug Delivery Systems † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 750. |
| [9] | LUO Wei, LIANG Youcai, HU Zhicheng, TANG Haoran, LIU Xiaocheng, XING Yetong, HUANG Fei. Preparation of Novel Hydrophilic Conjugated Polymers and Their Applicationin Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 456. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xinyu, WANG Hong, FANG Yun, FAN Ye. Stimuli-responsive Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Modified by Conjugated Linoleic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2519. |
| [11] | FAN Ye,LIU Tingting,FANG Yun,XIA Yongmei. Vesiculation and Stability: Oligomer of Conjugated Linoleate Acids Prepared by High Internal Phase Self-emulsion Polymerization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1193. |
| [12] | FAN Ye, ZHENG Yizhou, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei, GAO Di, WANG Jie. Vesiculation of Sodium Conjugated Linoleate in Alkaline Conditions Induced by Oligomerization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1483. |
| [13] | LU Yue, MA Jianbing, HUANG Xingyuan, XIAO Xue, LI Ming, LU Ying, XU Chunhua. Measuring the Reaction Rates of High Affinity Reactions by Single-molecule Magnetic Tweezers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1228. |
| [14] | CHENG Na, HE Yuanyuan, ZHAO Jianwei. Effect of Hetero-atoms on the Electron Transport Behavior in Conjugated Fused Heterocycles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 277. |
| [15] | YANG Mei,LIU Qing,TANG Qing,WANG Chenghui,YANG Meixiang,SUN Tao,HUANG Ying,TAO Zhu. Water-soluble Supramolecular Fluorescent Probe for Sensing Carbendazim and Its Application in Living Cell Imaging† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2665. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||