

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 1771.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131260
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Chengyong1, ZHANG Heng1, ZHENG Liping1, XU Fei1, FENG Wenfang1, NIE Jin1,*( ), HUANG Xuejie2, ZHOU Zhibin1,*(
), HUANG Xuejie2, ZHOU Zhibin1,*( )
)
Received:2013-12-23
Online:2014-08-10
Published:2014-04-29
Contact:
NIE Jin,ZHOU Zhibin
E-mail:niejin@mail.hust.edu.cn;zb-zhou@mail.hust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Chengyong, ZHANG Heng, ZHENG Liping, XU Fei, FENG Wenfang, NIE Jin, HUANG Xuejie, ZHOU Zhibin. Preparation and Properties of Lithium(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)-(trifluoroethoxysulfonyl)imide as Conducting Salt for Nonaqueous Electrolyte Solutions†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1771.
| Electrolyte | ρ/(g·mL-1) | η/(mPa·s-1) | κ/(mS·cm-1) | Va/nm3 | Tg/K | k(T)=AT-1/2exp[-B/(T-T0)] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0/K | A/(S·m-1·K-1/2) | B/K | R2 | |||||||
| Li[TFO-TFSI] | 1.26 | 3.78 | 4.60 | 0.37 | 0.176 | 171 | 130 | 2.32 | 565 | 0.9999 |
| LiBF4 | 1.16 | 2.23 | 3.72 | 0.31 | 0.049 | 154 | 127 | 1.55 | 543 | 0.9999 |
| LiClO4 | 1.18 | 2.77 | 6.26 | 0.40 | 0.055 | 152 | 137 | 2.54 | 509 | 0.9999 |
| LiPF6 | 1.21 | 3.00 | 9.33 | 0.48 | 0.069 | 193 | 153 | 2.86 | 418 | 0.9999 |
| LiTFSI | 1.23 | 3.40 | 7.57 | 0.55 | 0.147 | 156 | 151 | 2.10 | 408 | 0.9999 |
Table 1 Density(ρ), viscosity(η), ionic conductivity(κ) and lithium-ion transference number(tLi+) at 25 ℃, van der Waals volume(Va) of anion[10], glass transition temperature(Tg) and the parameters of VTF equation for various electrolytes
| Electrolyte | ρ/(g·mL-1) | η/(mPa·s-1) | κ/(mS·cm-1) | Va/nm3 | Tg/K | k(T)=AT-1/2exp[-B/(T-T0)] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0/K | A/(S·m-1·K-1/2) | B/K | R2 | |||||||
| Li[TFO-TFSI] | 1.26 | 3.78 | 4.60 | 0.37 | 0.176 | 171 | 130 | 2.32 | 565 | 0.9999 |
| LiBF4 | 1.16 | 2.23 | 3.72 | 0.31 | 0.049 | 154 | 127 | 1.55 | 543 | 0.9999 |
| LiClO4 | 1.18 | 2.77 | 6.26 | 0.40 | 0.055 | 152 | 137 | 2.54 | 509 | 0.9999 |
| LiPF6 | 1.21 | 3.00 | 9.33 | 0.48 | 0.069 | 193 | 153 | 2.86 | 418 | 0.9999 |
| LiTFSI | 1.23 | 3.40 | 7.57 | 0.55 | 0.147 | 156 | 151 | 2.10 | 408 | 0.9999 |
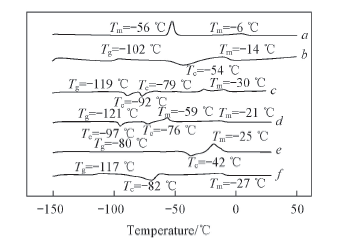
Fig.3 DSC curves for electrolyte solutions and various lithium salts[1.0 mol/L lithium salts in EC/EMC(3∶7, volume ratio)] a. EC/EMC(3∶7); b. Li[TFO-TFSI]; c. LiBF4; d. LiClO4; e. LiPF6; f. LiTFSI.
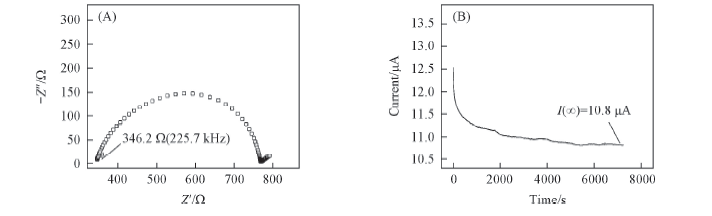
Fig.7 Impedance spectra of electrolyte solutions of 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI]-EC/EMC(3∶7) before polarization(A) and time-dependence response of dc polarization of 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI]-EC/EMC(3∶7) with an applied voltage of 10 mV(B)
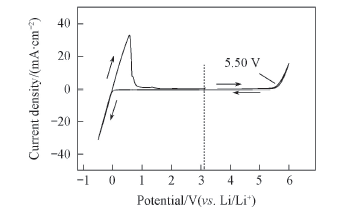
Fig.8 Cyclic voltammogram of electrolyte solutions of 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI]-EC/EMC(3∶7) Working electrode: Pt; reference and counter electrode: Li; scan rate: 0.5 mV/s.
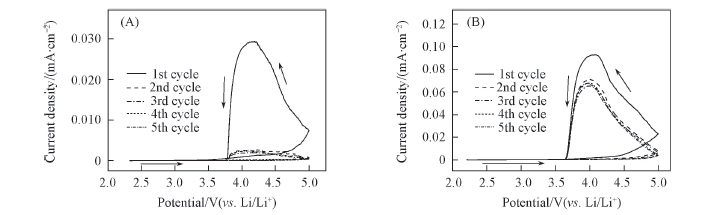
Fig.9 Cyclic voltammograms of electrolyte solutions of 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI]-(A) and LiTFSI(B) in EC/EMC(3∶7) Working electrode: Al; reference and counter electrode: Li; scan rate: 1.0 mV/s.
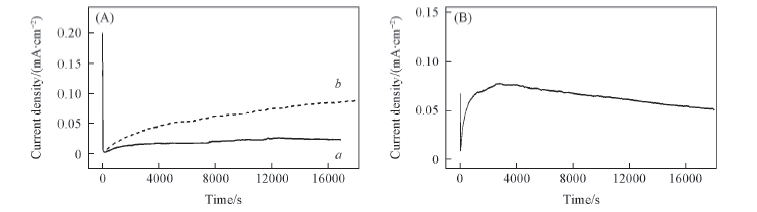
Fig.11 Chronoamperometric profiles of 1.0 mol/L lithium salts in a mixture of EC/EMC(3∶7) (A) Li[TFO-TFSI] recorded at 4.2 V(a) and 4.5 V(b); (B) LiTFSI recorded at 4.2 V.
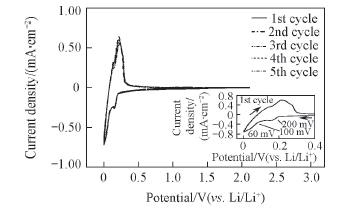
Fig.12 Cyclic voltammograms of electrolyte solutions of 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI]-EC/EMC(3∶7) Working electrode: synthetic graphite; reference and counter electrode: Li; scan rate: 0.01 mV/s.
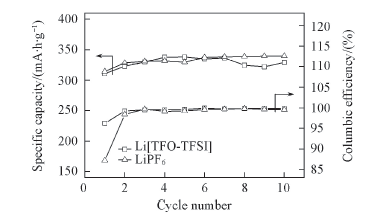
Fig.13 Specific capacity and columbic efficiency as a function of cycle number for Li/graphite half cells using 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI] and LiPF6 in EC/EMC(3∶7) as electrolyte solutions
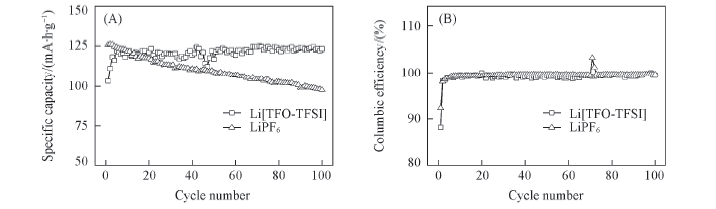
Fig.14 Specific capacity(A) and columbic efficiency(B) as a function of cycle number for graphite/LiCoO2 using 1.0 mol/L Li[TFO-TFSI] and LiPF6 in EC/EMC(3∶7) as electrolyte solutions
| [1] | Campion C. L., Li W., Euler W. B., Lucht B. L., Ravdel B., Dicarlo J. F., Gitzendanner R., Abraham K. M., Electrochem Solid-State Lett., 2004, 7(7), A194—A197 |
| [2] | Campion C. L., Li W., Lucht B. L., J. Electrochemical Soc., 2005, 152(12), A2327—A2334 |
| [3] | Morita M., Shibata T., Yoshimoto N., Ishikawa M., J. Power Sources, 2003, 119—121, 784—788 |
| [4] | Han H. B., Zhou S. S., Zhang D. J., Feng S. W., Li L. F., Liu K., Feng W. F., Nie J., Li H., Huang X. J., Armand M., Zhou Z. B., J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(7), 3623—3632 |
| [5] | Zhang H., Liu C. Y., Gong S. Z., Feng W. F., Xu F., Nie J., Zhou Z. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4), 804—811 |
| (张恒, 刘成勇, 巩守哲, 冯文芳, 徐飞, 聂进, 周志彬. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(4), 804—811) | |
| [6] | Kita F., Kawakami A., Nie J., Sonoda T., Kobayashi H., J. Power Sources, 1997, 68(2), 307—310 |
| [7] | Nie J., Sonoda T., Kobayashi H., J. Fluorine Chem., 1998, 87(1), 45—47 |
| [8] | Zhang H., Han H. B., Gong S. Z., Fu S. T., Nie J., Zhou Z. B., Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(27), 2623—2631 |
| (张恒, 韩鸿波, 巩守哲, 付世涛, 聂进, 周志彬. 科学通报, 2012, 57(27), 2623—2631) | |
| [9] | Armarego W.L. F., Chai C. L. L., Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2012 |
| [10] | Beran M.,Puhoda J., Taraba J., Polyhedron, 2010, 29(3), 991—994 |
| [11] | Han H.B., Alkali Salts and Ionic Liquids Based on Fluorosulfonylimide: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Application in Li-ion Batteries, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 2011 |
| (韩鸿波. 氟磺酰亚胺碱金属盐和离子液体: 合成、 表征以及在锂离子电池中的应用. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2011) | |
| [12] | Li L. F., Zhou S. S., Han H. B., Li H., Nie J., Armand M., Zhou Z. B., Huang X. J., J. Electrochemical Soc., 2011, 158(2), A74—A82 |
| [13] | Hagiwara R., Tamaki K., Kubota K., Goto T., Nohira T., J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2008, 53(2), 355—358 |
| [14] | Yang H., Zhuang G. V., Ross P. N., J. Power Sources, 2006, 161(1), 573—579 |
| [15] | Xu K., Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(10), 4303—4417 |
| [16] | Tsunekawa H., Narumi A., Sano M., Hiwara A., Fujita M., Yokoyama H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(39), 10962—10966 |
| [17] | Petrowsky M., Frech R., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113(17), 5996—6000 |
| [18] | Petrowsky M., Frech R., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112(28), 8285—8290 |
| [19] | Petrowsky M., Frech R., Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55(4), 1285—1288 |
| [20] | Gu G. Y., Bouvier S., Wu C., Laura R., Rzeznik M., Abraham K. M., Electrochim. Acta, 2000, 45(19), 3127—3139 |
| [21] | Gu G. Y., Laura R., Abraham K. M., Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 1999, 2(10), 486—489 |
| [22] | Zugmann S., Fleischmann M., Amereller Gschwind R. M., Wiemhöfer H. D., Gores H., J. Electrochim Acta, 2011, 56(11), 3926—3933 |
| [23] | Doyle M., Fuller T. F., Newman J., Electrochim. Acta, 1994, 39(13), 2073—2081 |
| [24] | Han H. B., Guo J., Feng S. W., Nie J., Zhou Z. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(4), 786—793 |
| (韩鸿波, 郭俊, 冯绍伟, 聂进, 周志彬. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(4), 786—793) | |
| [25] | Levi M. D., Aurbach D., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1997, 101(23), 4630—4640 |
| [26] | Gnanaraj J. S., Levi M. D., Gofer Y., Aurbach D., Schmidt M., J. Electrochemical Soc., 2003, 150(4), A445—A454 |
| (Ed.: S, Z, M) |
| [1] | JIA Yanggang, SHAO Xia, CHENG Jie, WANG Pengpeng, MAO Aiqin. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of Pseudocapacitance-controlled Perovskite High-entropy Oxide La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| [2] | BAO Junquan, ZHENG Shibing, YUAN Xuming, SHI Jinqiang, SUN Tianjiang, LIANG Jing. An Organic Salt PTO(KPD)2 with Enhanced Performance as a Cathode Material in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2911. |
| [3] | WU Zhuoyan, LI Zhi, ZHAO Xudong, WANG Qian, CHEN Shunpeng, CHANG Xinghua, LIU Zhiliang. A Highly Efficient One-step Preparation Method of Nano-silicon and Carbon Composite for High-performance Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2500. |
| [4] | YI Conghua, SU Huajian, QIAN Yong, LI Qiong, YANG Dongjie. Preparation of Lignin Nanocarbon and Its Performance as a Negative Electrode for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1807. |
| [5] | MAO Eryang, WANG Li, SUN Yongming. Advances in Alloy-based High-capacity Li-containing Anodes for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1552. |
| [6] | WANG Yimeng, LIU Kai, WANG Baoguo. Coating Strategies of Ni-rich Layered Cathode in LIBs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1514. |
| [7] | ZHOU Zhan, MA Lufang, TAN Chaoliang. Preparation of Layered (NH4)2V6O16·H2O Nanosheets as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 662. |
| [8] | SUN Quanhu, LU Tiantian, HE Jianjiang, HUANG Changshui. Advances in the Study of Heteratomic Graphdiyne Electrode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 366. |
| [9] | GONG Shanshan, WU Tong, WANG Guange, HUANG Qing, SU Yuefeng, WU Feng. Screening of Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Efficient Recovery of Spent Lithium⁃ion Battery Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3151. |
| [10] | XIANG Houzheng, XIE Hongxiang, LI Wenchao, LIU Xiaolei, MAO Aiqin, YU Haiyun. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Spinel-type High-entropy Oxides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1801. |
| [11] | LU Di,ZHENG Chunman,CHEN Yufang,LI Yujie,ZHANG Hongmei. Synthesis of Li-rich Layers/Spinel/Carbon Composite Cathode Materials with Phenol Formaldehyde Resin and Its Electrochemical Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1684. |
| [12] | CHEN Liangdan,ZOU Wei,WU Liang,XIA Fanjie,HU Zhiyi,LI Yu,SU Baolian. Nano-Al2O3 Coated Li-rich Cathode Material Li1. 2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 for Highly Improved Lithium-ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1329. |
| [13] | LI Xiangnan, WANG Qiuxian, FAN Yong, YU Mingming, ZHANG Huishuang, YANG Shuting. Deposition Method Synthesis of Nano-phosphorus/Biomass Carbon Composites and Their High- and Low-temperature Electrochemical Performances as Anode Material in Lithium-ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1949. |
| [14] | YANG Jinge, LI Yujie, LU Di, CHEN Yufang, SUN Weiwei, ZHENG Chunman. Morphology Control and Lithium Storage Performance of Micro/nano Li-rich Cathode Material† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1495. |
| [15] | YAO Fengnan,LI Yu,FENG Wei. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Carbon-coated FeF2 Nanocomposite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1418. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||