

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (9): 20250133.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250133
收稿日期:2025-05-05
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-05-26
通讯作者:
邓璞,沈杰
E-mail:pdeng01@pku.edu.cn;shenjie@pku.edu.cn
作者简介:邓 璞, 男, 博士, 特聘副研究员, 主要从事DNA自组装、 纳米颗粒自组装器件及其在生物电子方面的应用研究. E-mail: pdeng01@pku.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Zhaoxuan1, DENG Pu1( ), SHEN Jie2(
), SHEN Jie2( )
)
Received:2025-05-05
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-05-26
Contact:
DENG Pu, SHEN Jie
E-mail:pdeng01@pku.edu.cn;shenjie@pku.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
表面等离激元器件的光场束缚能力和光与物质的相互作用可有效突破衍射极限制约, 在纳米光子学与光电器件集成方面展现出巨大潜力. 基于化学合成的贵金属纳米颗粒具备亚波长尺寸特征与优异的等离激元性能, 是构筑高性能表面等离激元器件的理想材料. 为了获得高性能表面等离激元器件, 高通量、 低成本且结构可控的自组装策略是关键.本综述聚焦于以DNA介导组装为代表的组装方法在构造强耦合、 非线性及低损耗的新型等离激元器件中的应用. 以表面等离激元中的关键物理过程为基础, 重点分析了DNA分子的结构精度与可编程特性对光物理过程的赋能作用, 旨在推动从生物高分子到新型纳米光学器件的精确构筑的新范式.最后, 总结了当前自组装光学器件在跨尺度制造、 结构缺陷与损耗调控等方面面临的关键挑战, 并在此基础上提出了未来的重点探索方向和可行的解决方案. DNA介导组装在高性能、 多功能等离激元结构和器件方面展现出广阔前景, 有望在光通信、 量子信息、 人工智能及疾病检测等领域实现重要应用.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
张兆萱, 邓璞, 沈杰. 分子介导组装高性能表面等离激元器件. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(9): 20250133.
ZHANG Zhaoxuan, DENG Pu, SHEN Jie. Molecule-directed Assembly of High-performance Surface Plasmonic Devices. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(9): 20250133.
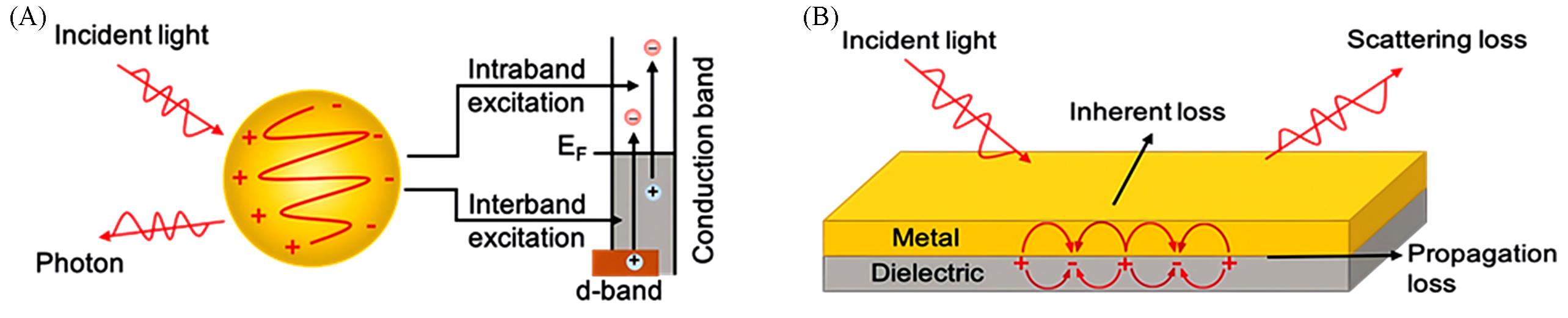
Fig.2 Schematics of the loss pathways of surface plasmons(A) The radiative and non-radiative loss of localized surface plasmons, involving the relaxation of interband and intraband excitations; (B) the loss of surface plasmon polaritons, where the scattering loss represents the radiative loss, the inherent loss and propagation loss represents the Ohmic loss and Landau damping in non-radiative loss, respectively[38].Copyright 2021, Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
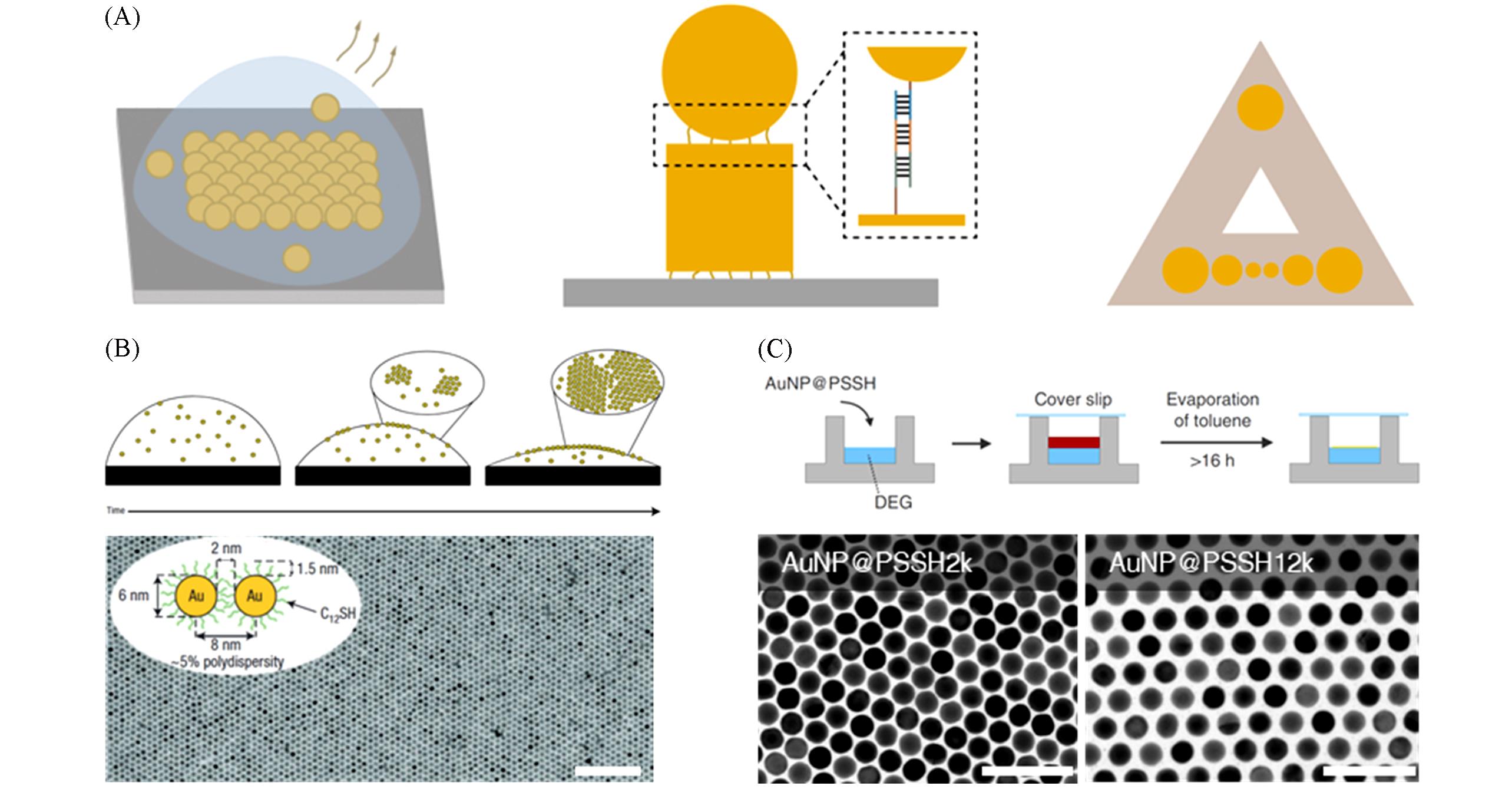
Fig.3 Schematics and morphologies of assembled nanostructures(A) Schematics of different assembly methods: from left to right, evaporation-induced assembly, molecule(DNA)-assisted assembly and DNA template-assisted assembly; (B) schematics and SEM images of the evaporation-induced assembled films(Scale bar, 100 nm)[59]; (C) schematic of the evaporation-induced assemble method at the liquid-liquid interface(top), and the assembled nanoparticle films with ligands with molecular weights of 2000 and 12000, respectively(Scale bars, 100 nm)[60].(B) Copyright 2006, Springer Nature; (C) Copyright 2020, Open access.

Fig.4 DNA⁃assisted nanoparticle assemblies(A) Schematics of nanoparticle surperlattice engineering with DNA, and TEM images of assembled surperlattices with fcc and hcp lattices(Scale bars, 50 nm)[63]. (B) Schematic of DNA-mediated nanoparticle assembly(top) and TEM images of assembled nanoparticle cages with different symmetries(bottom)[64]. White overlays indicate the positions of the cages, and orange outlines highlight their corresponding symmetry and geometric features. (C) Left: scheme of AuNP assembly driven by a DNA strand-displacement catassembly circuit; right: SAXS patterns for aggregates, disordered structures vs. 0.5-nM catassembler- assembled structures[67]. (D) Left: schematic for catassembler-triggered conformation rearrangement; right: pH depended switch between FCC and BCC crystal form[68]. (E) Schematic and SEM images of the gold nanoparticle arrays on DNA origami[69]. (F) Schematic and AFM images of the DNA-framed nanoparticle assemblies, with the insets of zoomed-in assembled structures(scale bars, 200 nm)[70]. (G) Schematic and TEM image of the gold nanoparticle helices(scale bar, 100 nm)[74]. (H) Schematic and TEM image of the gold bowtie nanostructures based on DNA origami templates[78].(A) Copyright 2011, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (B) Copyright 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (C) Copyright 2020, the PNAS; (D) Copyright 2023, Open access; (E) Copyright 2010, American Chemical Society; (F) Copyright 2016, Springer Nature; (G) Copyright 2012, Springer Nature; (H) Copyright 2018, Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
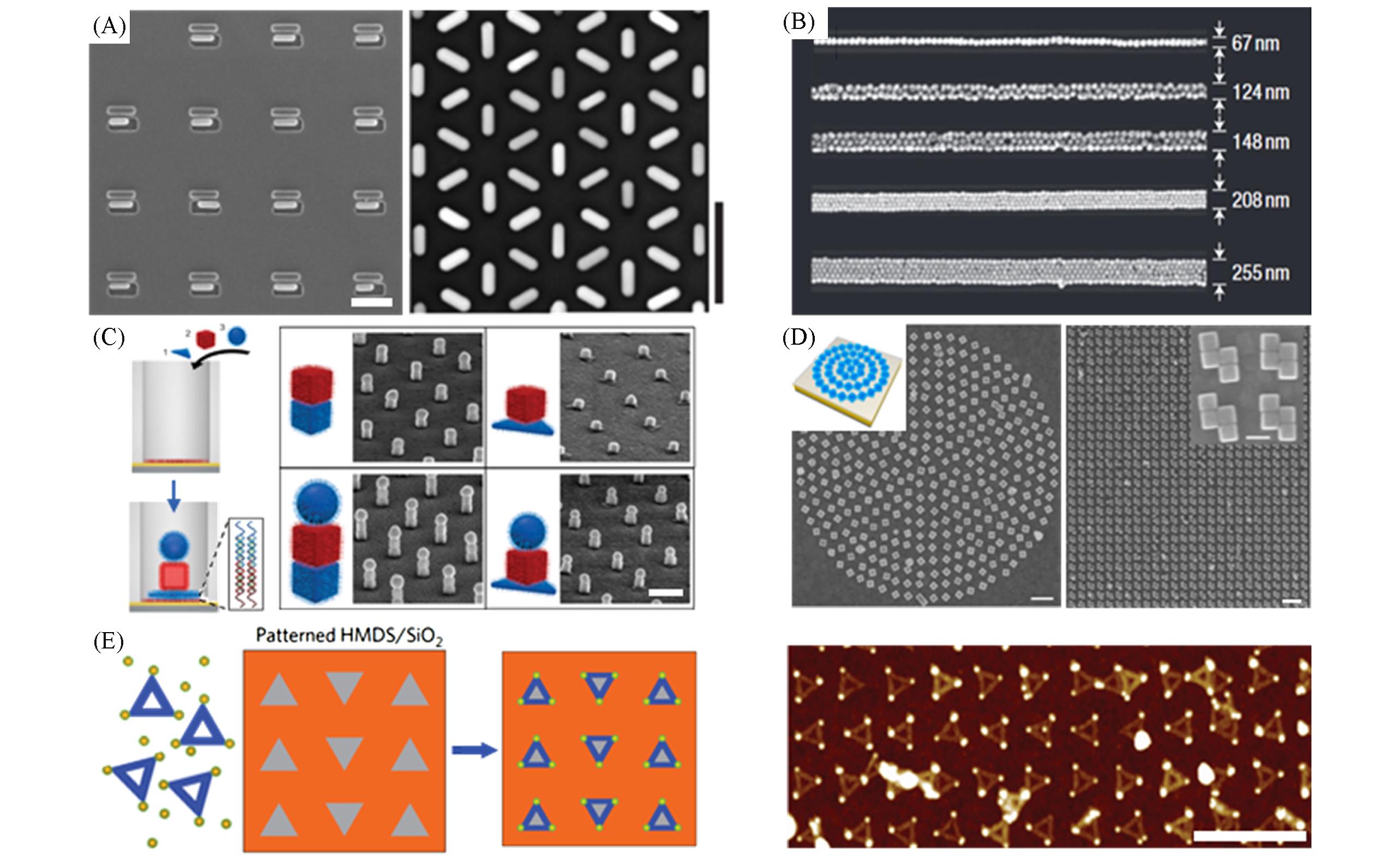
Fig.5 Template⁃assisted nanoparticle assembly(A) SEM images of nanorod arrays assembled by template-assisted capillary assemble method(scale bars, 250 nm)[85]. (B) SEM images of assembled gold nanoparticle lines in the templates[86]. (C) Schematics and SEM images of template-assisted DNA-mediated multi-layer architectures of heterogeneous gold nanoparticles(scale bar, 300 nm)[87]. (D) Schematic and SEM images of precise 2D arrangement of DNA-functionalized nanocubes assembled in shallow templates, with zoomed-in inset(scale bars, 500 nm, inset, 100 nm)[88]. (E) Schematic and AFM images of gold nanoparticle array directed by template-assisted DNA origami(scale bar, 500 nm)[89].(A) Copyright 2016, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2007, Springer Nature; (C) Copyright 2018, Open access; (D) Copyright 2020, the PNAS; (E) Copyright 2009, Springer Nature.
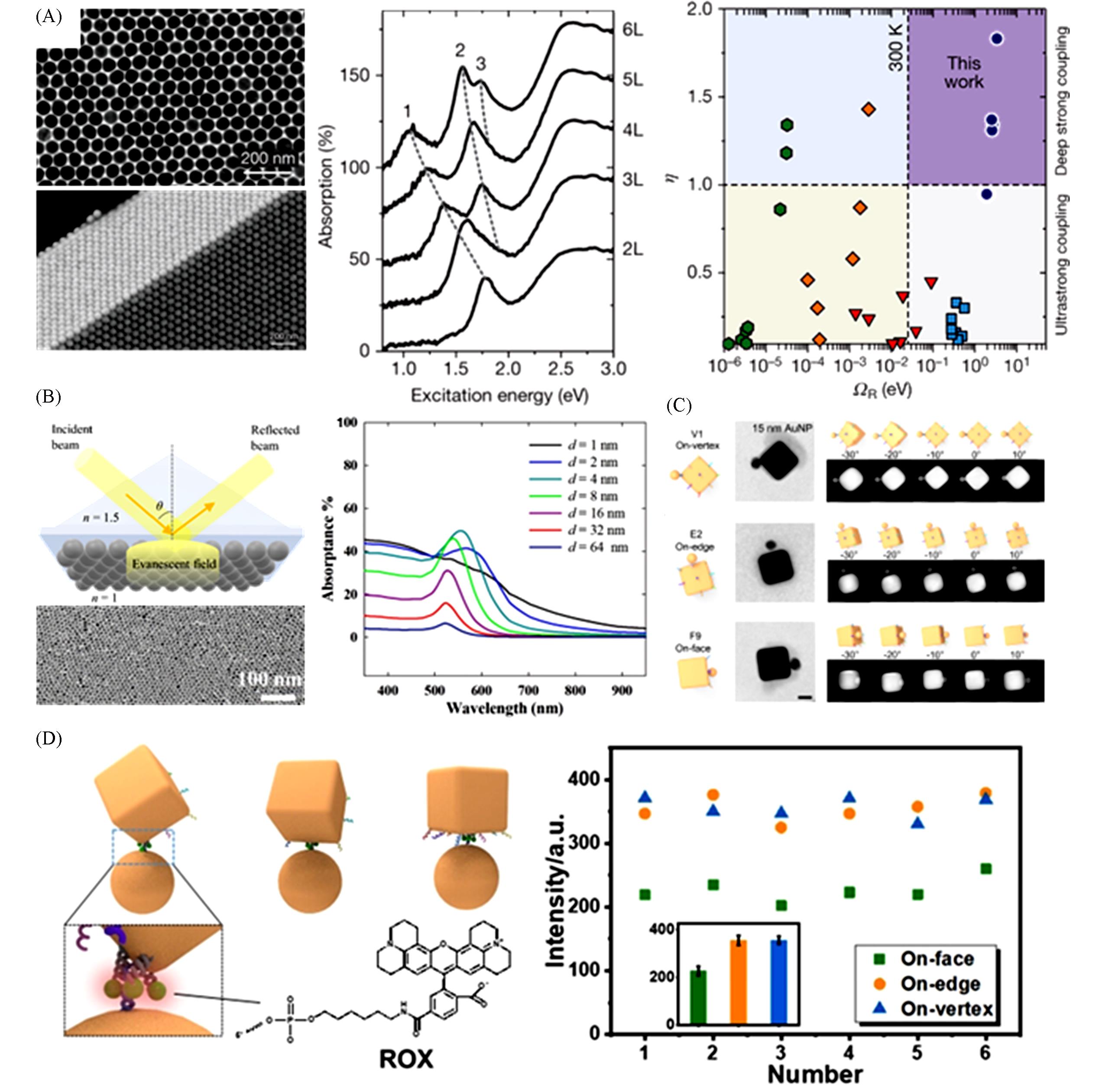
Fig.6 Optical responses originated from the light⁃matter interactions in nanoparticle assemblies(A) Left: TEM images of assembled monolayer and multilayer films. Middle: absorption spectra of 30 nm gold nanoparticle films with 2—6 layers. The dash lines indicate the Rabi splitting. Right: benchmarking of the coupling strengths of ref.[92] and ref.[91].(B) Schematic and SEM images of assembled gold nanoparticle film in the attenuated-total-reflection configuration, with the absorption spectra of gold nanoparticle film with gap distances from 1 nm to 64 nm, respectively[94].(C) STEM images of the AuNC-AuNP nanostructures with continuous position variation along Y-axis by every 10°[80].(D) Left: the schematic of AuNC-AuNP nanostructures with three ROX Raman probes at different morphology. Right: comparison of six sets of Raman spectroscopy taken from these three types of AuNC-AuNP nanostructures[80].(A) Copyright 2020 and 2019, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2022, Open access; (C, D) Copyright 2021, Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
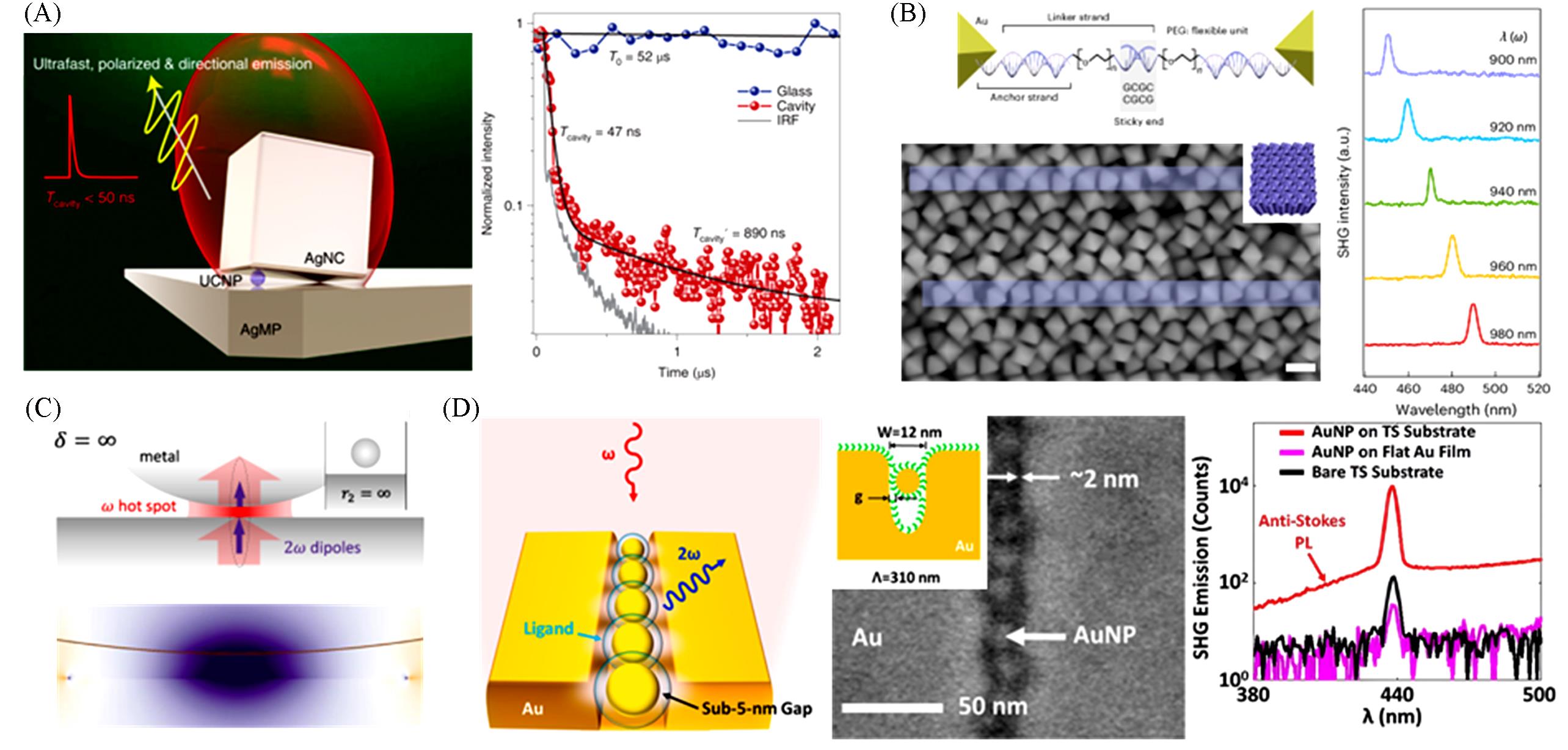
Fig.7 Nonlinear response of assembled nanoparticle structures(A) Schematic and time-resolved luminescence spectrum of the tilted-nanocavity-coupled UCNP[96]; (B) schematic, TEM image and SHG spectra of assembled nanoparticle structures, with dependence on the excitation wavelength[97]; (C) schematics of the origin and polarization distribution of the second-harmonic signals[30]; (D) schematic, SEM image and SHG response of double-gap nanoparticle structures with sub-5 nm gaps of double-gap structures[99].(A) Copyright 2022, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2024, Springer Nature; (C) Copyright 2021, Open access; (D) Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
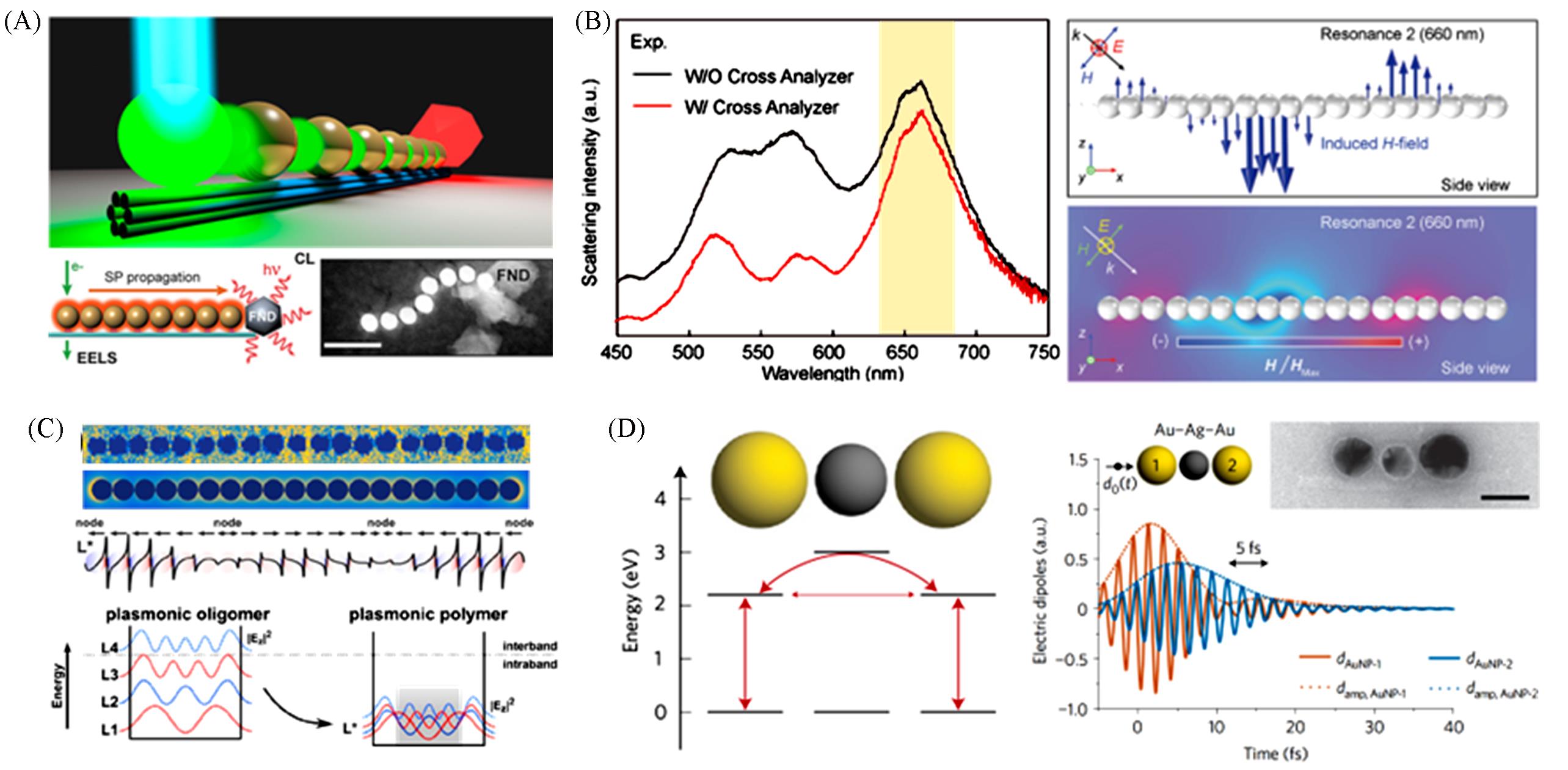
Fig.8 Applications of plasmonic nanoparticle assemblies in energy transport(A) Schematics and TEM images of the 1D gold nanoparticle waveguides(scale bar, 100 nm)[103]; (B) dark-field scattering spectra of electromagnetic and magnetic responses of the nanoparticle chain, with simulated side-view magnetic field distribution of assembled nanoparticle chain[104]; (C) measured, simulated energy loss and electric field distribution along the quasi-infinite nanoparticle chain, with the schematic of the energy structure[106]; (D) energy schematic and the plasmon transfer dynamics of the trimer nanostructure, with the insets of TEM image the structure(scale bar, 40 nm)[107].(A) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2019, Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim; (C) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society; (D) Copyright 2017, Springer Nature.
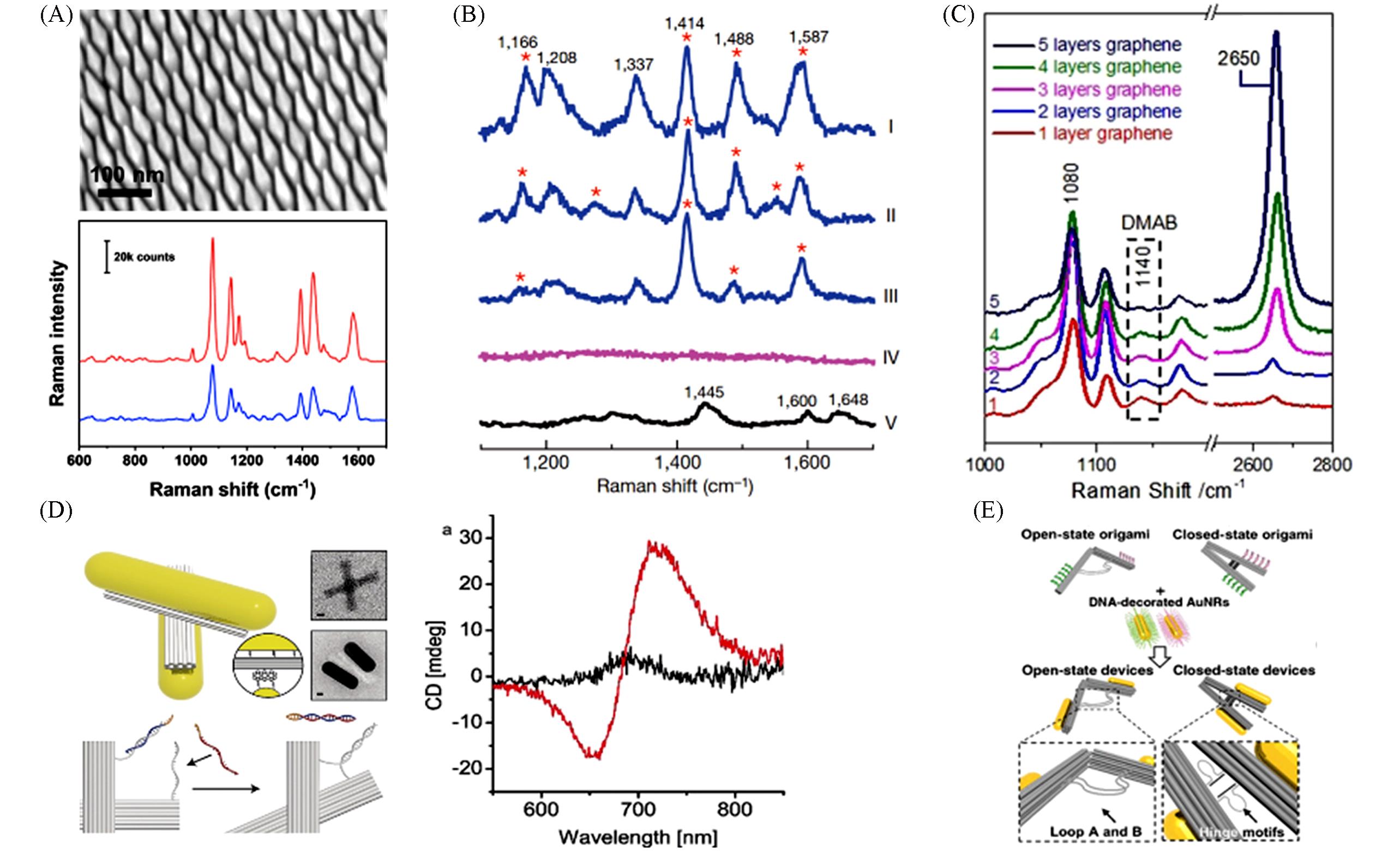
Fig.9 Applications of plasmonic nanoparticle assemblies in sensing(A) TEM image of the tip-on-tip gold nanoparticle film, and SERS spectra of the 4-ATP probes on films with different polarization angles[35]; (B) in situ Raman spectra obtained from different spots of an yeast cell on gold nanoparticle assemblies(I-III), background without cell(IV), and only yeast cell(V)[112]; (C) in situ Raman spectra of the conversion of 4-NTP on the nanoparticle assemblies-graphene interface with different number of layers of graphene[113]; (D) DNA origami chiral nanoprobe[114]; (E) logic-gated plasmonic nanodevices[118].(A) Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH GmbH; (B) Copyright 2010, Springer Nature; (C) Copyright 2021, Wiley‐VCH GmbH; (D) Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim; (E) Copyright 2020, Chinese Chemical Society.
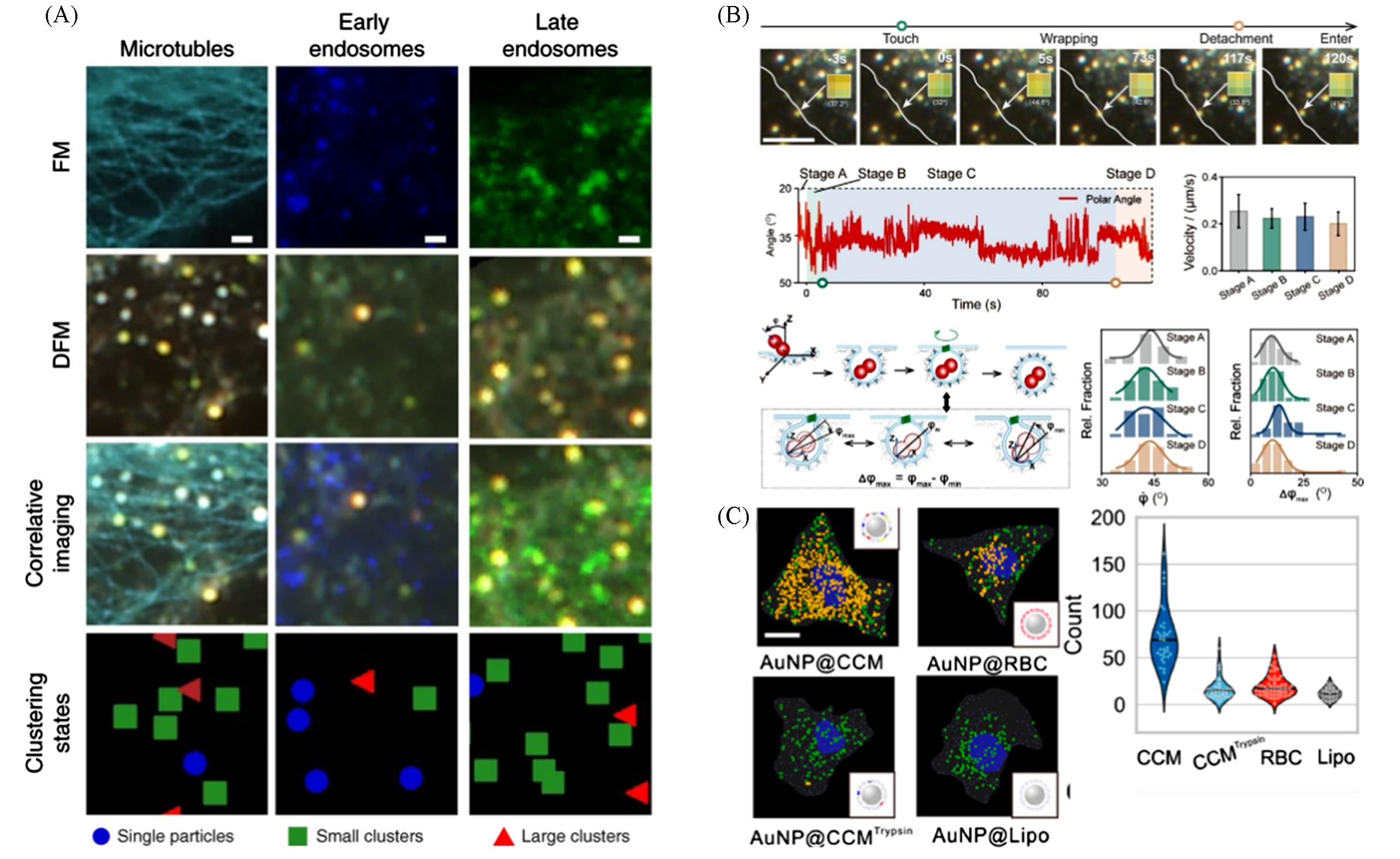
Fig.10 Applications of plasmonic nanoparticle assemblies in bioimaging(A) Representative dark field microscope(DFM) and fluorescence microscope(FM) images of spherical nucleic acids(SNAs) in HeLa cells(scale bar, 1 μm)[119]; (B) rotational and translational dynamics of AuHDs during different stages of endocytosis[120]; (C) single cell plasmonic imaging of membrane camouflaged nanoparticles[121].(A) Copyright 2020, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH GmbH; (C) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| [1] | Gramotnev D. K., Bozhevolnyi S. I., Nat. Photonics, 2010, 4(2), 83—91 |
| [2] | Baumberg J. J., Aizpurua J., Mikkelsen M. H., Smith D. R., Nat. Mater., 2019, 18(7), 668—678 |
| [3] | Gramotnev D. K., Vogel M. W., Stockman M. I., J. Appl. Phys., 2008, 104(3), 034311 |
| [4] | Chikkaraddy R., de Nijs B., Benz F., Barrow S. J., Scherman O. A., Rosta E., Demetriadou A., Fox P., Hess O., Baumberg J. J., Nature, 2016, 535(7610), 127—130 |
| [5] | Ellenbogen T., Seo K., Crozier K. B., Nano Lett., 2012, 12(2), 1026—1031 |
| [6] | Cai W., White J. S., Brongersma M. L., Nano Lett., 2009, 9(12), 4403—4411 |
| [7] | Neutens P., van Dorpe P., de Vlaminck I., Lagae L., Borghs G., Nat. Photonics, 2009, 3(5), 283—286 |
| [8] | Zia R., Schuller J. A., Chandran A., Brongersma M. L., Materials Today, 2006, 9(7/8), 20—27 |
| [9] | Sau T. K., Murphy C. J., Langmuir, 2004, 20(15), 6414—6420 |
| [10] | Nikoobakht B., El⁃Sayed M. A., Chem. Mater., 2003, 15(10), 1957—1962 |
| [11] | Zheng J., Cheng X., Zhang H., Bai X., Ai R., Shao L., Wang J., Chem. Rev., 2021, 121(21), 13342—13453 |
| [12] | Kelly K. L., Coronado E., Zhao L. L., Schatz G. C., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(3), 668—677 |
| [13] | Kravets V. G., Kabashin A. V., Barnes W. L., Grigorenko A. N., Chem. Rev., 2018, 118(12), 5912—5951 |
| [14] | Noginov M. A., Zhu G., Belgrave A. M., Bakker R., Shalaev V. M., Nature, 2009, 460(7259), 1110—1112 |
| [15] | Sun W., Shen J., Zhao Z., Arellano N., Rettner C., Tang J., Cao T., Zhou Z., Ta T., Streit J. K., Fagan J. A., Schaus T., Zheng M., Han S. J., Shih W. M., Maune H. T., Yin P., Science, 2020, 368(6493), 874—877 |
| [16] | Varghese B., Cheong F. C., Sindhu S., Yu T., Lim C. T., Valiyaveettil S., Sow C. H., Langmuir, 2006, 22(19), 8248—8252 |
| [17] | Malaquin L., Kraus T., Schmid H., Delamarche E., Wolf H., Langmuir, 2007, 23(23), 11513—11521 |
| [18] | Zhou Y., Zhou X., Park D. J., Torabi K., Brown K. A., Jones M. R., Zhang C., Schatz G. C., Mirkin C. A., Nano Lett., 2014, 14(4), 2157—2161 |
| [19] | Qi X., Pérez L. A., Mendoza⁃Carreño J., Garriga M., Alonso M. I., Mihi A., Nat. Commun., 2025, 16(1), 1687 |
| [20] | Zhao M., Chen Y., Wang K., Zhang Z., Streit J. K., Fagan J. A., Tang J., Zheng M., Yang C., Zhu Z., Sun W., Science, 2020, 368(6493), 878—881 |
| [21] | Schuknecht F., Kołątaj K., Steinberger M., Liedl T., Lohmueller T., Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 7192 |
| [22] | Xie M., Fang W., Qu Z., Hu Y., Zhang Y., Chao J., Shi J., Wang L., Wang L., Tian Y., Fan C., Liu H., Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 1745 |
| [23] | Liu N., Liedl T., Chem. Rev., 2018, 118(6), 3032—3053 |
| [24] | Kauranen M., Zayats A. V., Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6(11), 737—748 |
| [25] | Krasavin A.V., Ginzburg P., Zayats A.V., Laser Photonics Rev., 2018, 12(1), 1700082 |
| [26] | Ciracì C., Poutrina E., Scalora M., Smith D. R., Phys. Rev. B, 2012, 86(11), 115451 |
| [27] | Cui X., Lai Y., Ai R., Wang H., Shao L., Chen H., Zhang W., Wang J., Adv. Opt. Mater., 2020, 8(23), 2001173 |
| [28] | Celebrano M., Wu X., Baselli M., Großmann S., Biagioni, P., Locatelli A., De Angelis C., Cerullo G., Osellame R., Hecht B., Duò L., Ciccacci F., Finazzi M., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2015, 10(5), 412—417 |
| [29] | Wang Y., Peng Z., de Wilde Y., Lei D., Nanophotonics, 2024, 13(18), 3337—3346 |
| [30] | Li G. C., Lei D., Qiu M., Jin W., Lan S., Zayats A. V., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 4326 |
| [31] | Chang D. E., Vuletić V., Lukin M. D., Nat. Photonics, 2014, 8(9), 685—694 |
| [32] | Kern C., Zürch M., Spielmann C., Nanophotonics, 2015, 4(3), 303—323 |
| [33] | Tim B., Błaszkiewicz P., Kotkowiak M., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 23(1), 291 |
| [34] | Wang H. L., You E. M., Panneerselvam R., Ding S. Y., Tian Z. Q., Light Sci. Appl., 2021, 10(1), 161 |
| [35] | Ding W., Xia Y., Song H., Li T., Yang D., Dong A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202401945 |
| [36] | Sobhani A., Knight M. W., Wang Y., Zheng B., King N. S., Brown L. V., Fang Z., Nordlander P., Halas N. J., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4(1), 1643 |
| [37] | Feng L., Huo P., Liang Y., Xu T., Adv. Mater. 2020, 32(27), 1903787 |
| [38] | Wang B., Yu P., Wang W., Zhang X., Kuo H., Xu H., Wang Z. M., Adv. Opt. Mater., 2021, 9(7), 2001520 |
| [39] | Heilpern T., Manjare M., Govorov A. O., Wiederrecht G. P., Gray S. K., Harutyunyan H., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 1853 |
| [40] | Khurgin J. B., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2015, 10(1), 2—6 |
| [41] | Khurgin J. B., Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(2), 453—471 |
| [42] | Halas N. J., Lal S., Chang W. S., Link S., Nordlander P., Chem. Rev., 2011, 111(6), 3913—3961 |
| [43] | Xu Z., Li S., Yin X., Zhao H., Liu L., Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 6098 |
| [44] | Boriskina S. V., Cooper T. A., Zeng L., Ni G., Tong J. K., Tsurimaki Y., Huang Y., Meroueh L., Mahan G., Chen G., Adv. Opt. Photonics, 2017, 9(4), 775 |
| [45] | Kolomenski A., Kolomenskii A., Noel J., Peng S., Schuessler H., Appl. Opt., 2009, 48(30), 5683 |
| [46] | Trügler A., Tinguely J. C., Krenn J. R., Hohenau A., Hohenester U., Phys. Rev. B, 2011, 83(8), 081412 |
| [47] | Guo Z., Huang Q., Wang C., Gao P., Zhang W., Zhao Z., Yan L., Luo X., Plasmonics, 2014, 9(1), 103—110 |
| [48] | Ciracì C., Vidal⁃Codina F., Yoo D., Peraire J., Oh S. H., Smith D. R., ACS Photonics, 2020, 7(4), 908—913 |
| [49] | Gittinger M., Höflich K., Smirnov V., Kollmann H., Lienau C., Silies M., Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(2), 401—412 |
| [50] | Huang J. S., Nat. Commun., 2010, 1, 150 |
| [51] | Whitesides G. M., Grzybowski B., Science, 2002, 295(5564), 2418—2421 |
| [52] | Rao A., Roy S., Jain V., Pillai P. P., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15(21), 25248—25274 |
| [53] | Bishop K. J. M., Wilmer C. E., Soh S., Grzybowski B. A., Small, 2009, 5(14), 1600—1630 |
| [54] | Zhang H., Kinnear C., Mulvaney P., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(18), 1904551 |
| [55] | Jambhulkar S., Ravichandran D., Zhu Y., Thippanna V., Ramanathan A., Patil D., Fonseca N., Thummalapalli S. V., Sundaravadivelan B., Sun A., Xu W., Yang S., Kannan A. M., Golan Y., Lancaster J., Chen L., Joyee E. B., Song K., Small, 2024, 20(6), 2306394 |
| [56] | Zhang S. Y., Regulacio M. D., Han M. Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(7), 2301 |
| [57] | Boles M. A., Engel M., Talapin D. V., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(18), 11220—11289 |
| [58] | Dong A., Chen J., Vora P. M., Kikkawa J. M., Murray C. B., Nature, 2010, 466(7305), 474—477 |
| [59] | Bigioni T. P., Lin X. M., Nguyen T. T., Corwin E. I., Witten T. A., Jaeger H. M., Nat. Mater., 2006, 5(4), 265—270 |
| [60] | Schulz F., Pavelka O., Lehmkühler F., Westermeier F., Okamura Y., Mueller N. S., Reich S., Lange H., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 3821 |
| [61] | Cheng W., Campolongo M. J., Cha J. J., Tan S. J., Umbach C. C., Muller D. A., Luo D., Nat. Mater., 2009, 8(6), 519—525 |
| [62] | Santos P. J., Gabrys P. A., Zornberg L. Z., Lee M. S., Macfarlane R. J., Nature, 2021, 591(7851), 586—591 |
| [63] | Macfarlane R. J., Lee B., Jones M. R., Harris N., Schatz G. C., Mirkin C. A., Science, 2011, 334(6053), 204—208 |
| [64] | Lin H., Lee S., Sun L., Spellings M., Engel M., Glotzer S. C., Mirkin C. A., Science, 2017, 355(6328), 931—935 |
| [65] | Zhou W., Li Y., Je K., Vo T., Lin H., Partridge B. E., Huang Z., Glotzer S. C., Mirkin C. A., Science, 2024, 383(6680), 312—319 |
| [66] | Park D. J., Zhang C., Ku J. C., Zhou Y., Schatz G. C., Mirkin C. A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2015, 112(4), 977—981 |
| [67] | Zhou X., Yao D., Hua W., Huang N., Chen X., Li L., He M., Zhang Y., Guo Y., Xiao S., Bian F., Liang H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2020 , 117(11) 5617—5623 |
| [68] | Yao D., Zhang Y., Zhou X., Sun X., Liu X., Zhou J., Jiang W., Hua W., Liang H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2023, 120(18), e2219034120 |
| [69] | Ding B., Deng Z., Yan H., Cabrini S., Zuckermann R. N., Bokor J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(10), 3248—3249 |
| [70] | Liu W., Halverson J., Tian Y., Tkachenko A. V., Gang O., Nat. Chem., 2016, 8(9), 867—873 |
| [71] | Urban M. J., Dutta P. K., Wang P., Duan X., Shen X., Ding B., Ke Y., Liu N., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(17), 5495—5498 |
| [72] | Lan X., Lu X., Shen C., Ke Y., Ni W., Wang Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(1), 457—462 |
| [73] | Mastroianni A. J., Claridge S. A., Alivisatos A. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(24), 8455—8459 |
| [74] | Kuzyk A., Schreiber R., Fan Z., Pardatscher G., Roller E. M., Högele A., Simmel F. C., Govorov A. O., Liedl T., Nature, 2012, 483(7389), 311—314 |
| [75] | Kuzyk A., Yang Y., Duan X., Stoll S., Govorov A. O., Sugiyama H., Endo M., Liu N., Nat. Commun., 2016, 7(1), 10591 |
| [76] | Kuzyk A., Urban M. J., Idili A., Ricci F., Liu N., Sci. Adv., 2017, 3(4), e1602803 |
| [77] | Kuzyk A., Schreiber R., Zhang H., Govorov A. O., Liedl T., Liu N., Nat. Mater., 2014, 13(9), 862—866 |
| [78] | Zhan P., Wen T., Wang Z., He Y., Shi J., Wang T., Liu X., Lu G., Ding B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(11), 2846—2850 |
| [79] | Zhang Y., Chao J., Liu H., Wang F., Su S., Liu B., Zhang L., Shi J., Wang L., Huang W., Wang L., Fan C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(28), 8036—8040 |
| [80] | Niu R., Song C., Gao F., Fang W., Jiang X., Ren S., Zhu D., Su S., Chao J., Chen S., Fan C., Wang L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(21), 11695—11701 |
| [81] | Luo X., Chem. Sci., 2020, 11(19), 4911—4921 |
| [82] | Edwardson T. G. W., Nat. Chem., 2016, 8, 162—170 |
| [83] | Liu Y., Zeng T., Liu C., Fang X., Li S., Cao X., Lu C., Yang H., Nano Lett., 2023, 23(24), 11569—11577 |
| [84] | Zhu W., Satterthwaite P. F., Jastrzebska⁃Perfect P., Brenes R., Niroui F., Sci. Adv., 2022, 8(43), eabq4869 |
| [85] | Flauraud V., Mastrangeli M., Bernasconi G. D., Butet J., Alexander D. T. L., Shahrabi E., Martin O. J. F., Brugger J., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12(1), 73—80 |
| [86] | Kraus T., Malaquin L., Schmid H., Riess W., Spencer N. D., Wolf H., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2007, 2(9), 570—576 |
| [87] | Lin Q. Y., Mason J. A., Li Z., Zhou W., O’Brien M. N., Brown K. A., Jones M. R., Butun S., Lee B., Dravid V. P., Aydin K., Mirkin C. A., Science, 2018, 359(6376), 669—672 |
| [88] | Zhou W., Liu Z., Huang Z., Lin H., Samanta D., Lin Q. Y., Aydin K., Mirkin C. A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2020, 117(35), 21052—21057 |
| [89] | Hung A. M., Micheel C. M., Bozano L. D., Osterbur L. W., Wallraff G. M., Cha J. N., Nature Nanotech, 2010, 5(2), 121—126 |
| [90] | Michelson A., Shani L., Kahn J. S., Redeker D. C., Lee I., DeOlivares K. R., Kisslinger K., Tiwale N., Yan H., Pattammattel A., Nam Y., Pribiag V. S., Gang O., Sci. Adv., 2025, 11, eadt5620 |
| [91] | Frisk Kockum A., Miranowicz A., de Liberato S., Savasta S., Nori F., Nat. Rev. Phys., 2019, 1(1), 19—40 |
| [92] | Mueller N. S., Okamura Y., Vieira B. G. M., Juergensen S., Lange H., Barros E. B., Schulz F., Reich S., Nature, 2020, 583(7818), 780—784 |
| [93] | Wang D., Guan J., Hu J., Bourgeois M. R., Odom T. W., Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52(11), 2997—3007 |
| [94] | Borah R., Ninakanti R., Bals S., Verbruggen S. W., Sci. Rep., 2022, 12(1), 15738 |
| [95] | Kauranen M., Zayats A. V., Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6(11), 737—748 |
| [96] | Chen H., Jiang Z., Hu H., Kang B., Zhang B., Mi X., Guo L., Zhang C., Li J., Lu J., Yan L., Fu Z., Zhang Z., Zheng H., Xu H., Nat. Photonics., 2022, 16(9), 651—657 |
| [97] | Zhang Y., Xu D. D., Tanriover I., Zhou W., Li Y., López⁃Arteaga R., Aydin K., Mirkin C. A., Nat. Photonics, 2024, 19(1), 20—27 |
| [98] | Wang Y., Peng Z., de Wilde Y., Lei D., Nanophotonics, 2024, 13(18), 3337—3346 |
| [99] | Dong Z., Asbahi M., Lin J., Zhu D., Wang Y. M., Hippalgaonkar K., Chu H. S., Goh W. P., Wang F., Huang Z., Yang J. K. W., Nano Lett., 2015, 15(9), 5976—5981 |
| [100] | Melikyan A., Alloatti L., Muslija A., Hillerkuss D., Schindler P. C., Li J., Palmer R., Korn D., Muehlbrandt S., van Thourhout D., Chen B., Dinu R., Sommer M., Koos C., Kohl M., Freude W., Leuthold J., Nat. Photonics, 2014, 8(3), 229—233 |
| [101] | Haffner C., Chelladurai D., Fedoryshyn Y., Josten A., Baeuerle B., Heni W., Watanabe T., Cui T., Cheng B., Saha S., Elder D. L., Dalton L. R., Boltasseva A., Shalaev V. M., Kinsey N., Leuthold J., Nature, 2018, 556(7702), 483—486 |
| [102] | Shi J., Guo Q., Shi Z., Zhang S., Xu H., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 119(13), 130501 |
| [103] | Gür F. N., McPolin C. P. T., Raza S., Mayer M., Roth D. J., Steiner A. M., Löffler M., Fery A., Brongersma M. L., Zayats A. V., König T. A. F., Schmidt T. L., Nano Lett., 2018, 18(11), 7323—7329 |
| [104] | Wang P., Huh J., Lee J., Kim K., Park K. J., Lee S., Ke Y., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(29), 1901364 |
| [105] | Wang P., Huh J. H., Park H., Yang D., Zhang Y., Zhang Y., Lee J., Lee S., Ke Y., Nano Lett., 2020, 20(12), 8926—8932 |
| [106] | Mayer M., Potapov P. L., Pohl D., Steiner A. M., Schultz J., Rellinghaus B., Lubk A., König T. A. F., Fery A., Nano Lett., 2019, 19(6), 3854—3862 |
| [107] | Roller E. M., Besteiro L. V., Pupp C., Khorashad L. K., Govorov A. O., Liedl T., Nat. Phys., 2017, 13(8), 761—765 |
| [108] | Wang N., Wang Q., Huang Y., Curr. Appl. Phys., 2021, 27, 66—72 |
| [109] | Willets K. A., Van Duyne R. P., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2007, 58(1), 267—297 |
| [110] | Tim B., Błaszkiewicz P., Kotkowiak M., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 23(1), 291 |
| [111] | Guerrini L., Graham D., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(21), 7085 |
| [112] | Zhang Y. J., Ze H., Fang P. P., Huang Y. F., Kudelski A., Fernández⁃Vidal J., Hardwick L. J., Lipkowski J., Tian Z. Q., Li J. F., Nat. Rev. Methods Primers, 2023, 3(1), 36 |
| [113] | Yang J., Wang H., Zhu Z., Yue M., Yang W., Zhang X., Ruan X., Guan Z., Yang Z., Cai W., Wu Y., Fan F., Dong J., Zhang H., Xu H., Tian Z., Li J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(5), e202112749 |
| [114] | Funck T., Nicoli F., Kuzyk A., Liedl T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(41), 13495—13498 |
| [115] | Zhou C., Xin L., Duan X., Urban M. J., Liu N., Nano Lett., 2018, 18(11), 7395—7399 |
| [116] | Liu Z., Dong J., Pan J., Zhou C., Fan C., Wang Q., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2021, 37(4), 914—918 |
| [117] | Huang Y., Nguyen M. K., Natarajan A. K., Nguyen V. H., Kuzyk A., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(51), 44221—44225 |
| [118] | Liu F., Jiang Q., Liu Q., Li N., Han Z., Liu C., Wang Z., Jiao Y., Sun J., Ding B., CCS Chem., 2021, 3(3), 985—993 |
| [119] | Liu M., Wang F., Mao X., Wang L., Tian Y., Fan C., Li Q., Nat. Protoc., 2021, 16, 383—404 |
| [120] | Fan Z., Mao X., Zhu M., Hu X., Li M., Huang L., Li J., Maimaiti T., Zuo X., Fan C., Li Q., Liu M., Tian Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2025, 64(1), e202413244 |
| [121] | Xie X., Hu X., Li Q., Yin M., Song H., Hu J., Wang L., Fan C., Chen N., Nano Lett., 2020, 20(7), 5228—5235 |
| [122] | Tikhomirov G., Petersen P., Qian L., Nature, 2017, 552(7683), 67—71 |
| [123] | Zhang H., Kinnear C., Mulvaney P., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(18), 1904551 |
| [124] | Wang Y. W., Li D., Liang W. K., Sun Y. H., Jiang L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4), 1213—1224 |
| 王雅雯, 李东, 梁文凯, 孙迎辉, 江林. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4), 1213—1224 | |
| [125] | Li D., Sun Y. H., Wang Z. S., Huang J., Lü N., Jiang L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2), 221—227 |
| 李东, 孙迎辉, 王中舜, 黄晶, 吕男, 江林. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2), 221—227 | |
| [126] | Khanikaev A. B., Alù A., Nat. Commun., 2024, 15(1), 931 |
| [127] | Hashemi A., Zakeri M. J., Jung P. S., Blanco⁃Redondo A., APL Photonics, 2025, 10(1), 010903 |
| [1] | 李晓莉, 黄亮, 段红娟, 张力, 张海军. 石墨烯负载Pt/Co双金属纳米颗粒催化剂的制备及催化制氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1662. |
| [2] | 韩天昊, 梁福鑫, 杨振忠. 尺寸比例可调的Au-Ni双金属纳米颗粒的制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(11): 1921. |
| [3] | 李文绮, 赵万国, 周兴赟, 苏丽, 张海军, 鲁礼林, 张少伟. Pt/Ni/Fe三金属纳米颗粒的制备及催化制氢活性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(10): 2164. |
| [4] | 张邦文, 谢长生, 胡军辉, 王辉虎, 桂阳海. 金属纳米粒子在聚合物中的磁致排列──实验及分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(11): 2131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||