

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 20240345.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240345
蒋龑1, 陈妍琳2, 宋高瑜3, 陈炎炎4, 白晶1, 朱莹娣3( ), 李娟3(
), 李娟3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-08
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-07-28
通讯作者:
朱莹娣,李娟
E-mail:zhuyingdi@him.cas.cn;lijuan@him.cas.cn
基金资助:
JIANG Yan1, CHEN Yanlin2, SONG Gaoyu3, CHEN Yanyan4, BAI Jing1, ZHU Yingdi3( ), LI Juan3(
), LI Juan3( )
)
Received:2024-07-08
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-07-28
Contact:
ZHU Yingdi, LI Juan
E-mail:zhuyingdi@him.cas.cn;lijuan@him.cas.cn
Supported by:摘要:
细菌蛋白质组成分析对于了解其生物学、 生理学及其与环境的相互作用至关重要. 质谱是用于蛋白质分析的最有力工具之一, 在蛋白质的分子量确定、 表达水平测量及结构修饰分析等研究中不可或缺. 本文比较了蛋白质指纹质谱、 自上而下蛋白质组学和自下而上蛋白质组学等3种广泛使用的质谱方法在细菌蛋白成分分析中的表现. 结果表明, 自下而上蛋白质组学提供了最高的蛋白覆盖率, 同时也在不同菌种之间显示出最大的蛋白质图谱重合度. 相比之下, 蛋白质指纹质谱显示出最高的检测再现性以及菌种区分或鉴定的高效性. 自上而下蛋白组学检测到的细菌蛋白质数量明显少于自下而上蛋白质组学, 但其可以与蛋白质指纹质谱兼容(二者均偏向于检测高丰度、 高稳定和高亲水性的核糖体蛋白质), 在菌种鉴定的同时为蛋白标志物的 发现提供重要手段. 本文对基于质谱的蛋白质组成分析方法进行了比较, 为特定分析目标的方法选择提供了指导意见. 这将对于细菌感染诊断、抗生素耐受性分析和抗生素作用靶点发现等多个领域的研究具有重要价值.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
蒋龑, 陈妍琳, 宋高瑜, 陈炎炎, 白晶, 朱莹娣, 李娟. 细菌的蛋白质组成分析. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240345.
JIANG Yan, CHEN Yanlin, SONG Gaoyu, CHEN Yanyan, BAI Jing, ZHU Yingdi, LI Juan. Bacterial Protein Profiling. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(11): 20240345.
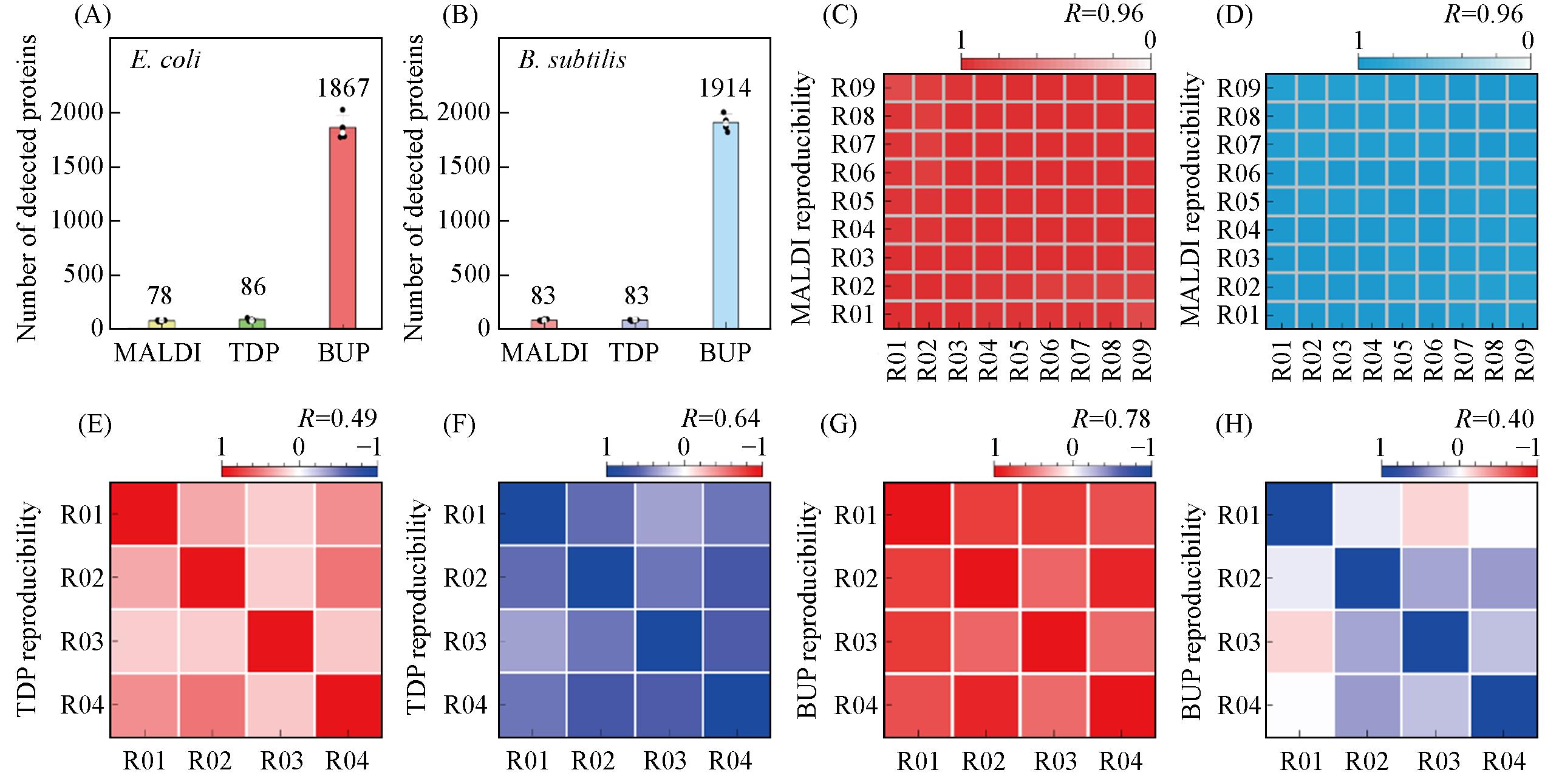
Fig.2 Investigation of protein coverage and detection reproducibility(A) Numbers of proteins or protein peaks detected from E. coli by MALDI fingerprinting(MALDI), top-down proteomics(TDP) and bottom-up proteomics(BUP); the average number was displayed for each approach; (B) numbers of proteins or protein peaks detected from B. subtilis by using the three protein profiling approaches; (C) detection reproducibility for nine repetition tests of E. coli by using MALDI approach; (D) detection reproducibility for nine repetition tests of B. subtilis by using MALDI approach; (E) detection reproducibility for four repetition tests of E. coli by using TDP approach; (F) detection reproducibility for four repetition tests of B. subtilis by using TDP approach; (G) detection reproducibility for four repetition tests of E. coli by using BUP approach; (H) detection reproducibility for four repetition tests of B. subtilis by using BUP approach.
| MALDI(m/z) | TDP precursormass | Protein entry name | Gene ID | Subcellularlocation | Isoelectricpoint | Instability index | Aliphaticindex | GRAVY | Detected by BUP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6404 | 6406.60 | P0AG51_RL30 | rpmD | Cytoplasm | 10.96 | 38.72 | 102.59 | -0.137 | YES |
| 6849 | 6848.53 | P0AAZ7_YCAR | ycaR | Cytoplasm | 4.31 | 36.22 | 105.39 | -0.127 | YES |
| 7264 | 7268.98 | P0A7M6_RL29 | rpmC | Cytoplasm | 9.98 | 50.27 | 102.22 | -0.657 | YES |
| 7861 | 7865.92 | P0A7M9_RL31 | rpmE | Cytoplasm | 9.46 | 48.68 | 57.00 | -0.649 | NO |
| 8107 | 8113.28 | P69222_IF1 | infA | Cytoplasm | 9.23 | 36.00 | 91.83 | -0.354 | NO |
| 8354 | 8344.10 | P68206_YJBJ | yjbJ | Cytoplasm/Periplasm | 5.64 | 38.38 | 15.60 | -2.432 | NO |
| 8871 | 8869.83 | P0A7M2_RL28 | rpmB | Cytoplasm | 11.42 | 36.21 | 77.87 | -0.650 | YES |
| 9213 | 9219.99 | P0ACF4_DBHB | hupB | Cytoplasm/Periplasm | 9.69 | 16.40 | 92.44 | -0.042 | YES |
| 9525 | 9529.19 | P0ACF0_DBHA | hupA | Cytoplasm/Periplasm | 9.57 | 15.88 | 91.22 | -0.228 | NO |
| 10124 | 10131.47 | P0ADZ4_RS15 | rpsO | Cytoplasm | 10.40 | 46.76 | 90.91 | -0.673 | NO |
| 10676 | 10685.76 | P68919_RL25 | rplY | Cytoplasm | 9.60 | 31.89 | 91.28 | -0.392 | YES |
| 11196 | 11192.22 | P0ADZ0_RL23 | rplW | Cytoplasm | 9.94 | 21.46 | 97.40 | -0.373 | YES |
| 12203 | 11208.28 | P60624_RL24 | rplX | Cytoplasm | 10.21 | 9.01 | 89.81 | -0.405 | YES |
| 12638 | 12645.59 | P0AD49_YFIA | raiA | Cytoplasm | 6.18 | 47.48 | 90.62 | -0.535 | YES |
| 12753 | 12761.93 | P0C018_RL18 | rplR | Cytoplasm | 10.42 | 32.35 | 86.92 | -0.395 | YES |
| 12971 | 12960.23 | P0A7S9_RS13 | rpsM | Cytoplasm | 10.78 | 38.74 | 96.75 | -0.424 | YES |
| 13522 | 13518.11 | P0AF93_RIDA | ridA | Cytoplasm | 5.36 | 40.34 | 97.56 | 0.086 | NO |
| 14343 | 14355.66 | P0AG44_RL17 | rplQ | Cytoplasm | 11.05 | 45.90 | 79.29 | -0.565 | NO |
| 14942 | 14957.31 | P02413_RL15 | rplO | Cytoplasm | 11.18 | 43.69 | 87.43 | -0.252 | YES |
| 15385 | 15398.99 | P0ACF8_HNS | hns | Cytoplasm | 5.44 | 40.47 | 82.70 | -0.751 | NO |
| 17547 | 17569.35 | P0A7J3_RL10 | rplJ | Cytoplasm | 9.04 | 28.74 | 94.21 | 0.045 | NO |
| 18745 | 18761.12 | P0AG55_RL6 | rplF | Cytoplasm | 9.71 | 17.04 | 91.93 | -0.227 | NO |
Table 1 Properties of proteins assigned on the MALDI fingerprintsof E. coli
| MALDI(m/z) | TDP precursormass | Protein entry name | Gene ID | Subcellularlocation | Isoelectricpoint | Instability index | Aliphaticindex | GRAVY | Detected by BUP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6404 | 6406.60 | P0AG51_RL30 | rpmD | Cytoplasm | 10.96 | 38.72 | 102.59 | -0.137 | YES |
| 6849 | 6848.53 | P0AAZ7_YCAR | ycaR | Cytoplasm | 4.31 | 36.22 | 105.39 | -0.127 | YES |
| 7264 | 7268.98 | P0A7M6_RL29 | rpmC | Cytoplasm | 9.98 | 50.27 | 102.22 | -0.657 | YES |
| 7861 | 7865.92 | P0A7M9_RL31 | rpmE | Cytoplasm | 9.46 | 48.68 | 57.00 | -0.649 | NO |
| 8107 | 8113.28 | P69222_IF1 | infA | Cytoplasm | 9.23 | 36.00 | 91.83 | -0.354 | NO |
| 8354 | 8344.10 | P68206_YJBJ | yjbJ | Cytoplasm/Periplasm | 5.64 | 38.38 | 15.60 | -2.432 | NO |
| 8871 | 8869.83 | P0A7M2_RL28 | rpmB | Cytoplasm | 11.42 | 36.21 | 77.87 | -0.650 | YES |
| 9213 | 9219.99 | P0ACF4_DBHB | hupB | Cytoplasm/Periplasm | 9.69 | 16.40 | 92.44 | -0.042 | YES |
| 9525 | 9529.19 | P0ACF0_DBHA | hupA | Cytoplasm/Periplasm | 9.57 | 15.88 | 91.22 | -0.228 | NO |
| 10124 | 10131.47 | P0ADZ4_RS15 | rpsO | Cytoplasm | 10.40 | 46.76 | 90.91 | -0.673 | NO |
| 10676 | 10685.76 | P68919_RL25 | rplY | Cytoplasm | 9.60 | 31.89 | 91.28 | -0.392 | YES |
| 11196 | 11192.22 | P0ADZ0_RL23 | rplW | Cytoplasm | 9.94 | 21.46 | 97.40 | -0.373 | YES |
| 12203 | 11208.28 | P60624_RL24 | rplX | Cytoplasm | 10.21 | 9.01 | 89.81 | -0.405 | YES |
| 12638 | 12645.59 | P0AD49_YFIA | raiA | Cytoplasm | 6.18 | 47.48 | 90.62 | -0.535 | YES |
| 12753 | 12761.93 | P0C018_RL18 | rplR | Cytoplasm | 10.42 | 32.35 | 86.92 | -0.395 | YES |
| 12971 | 12960.23 | P0A7S9_RS13 | rpsM | Cytoplasm | 10.78 | 38.74 | 96.75 | -0.424 | YES |
| 13522 | 13518.11 | P0AF93_RIDA | ridA | Cytoplasm | 5.36 | 40.34 | 97.56 | 0.086 | NO |
| 14343 | 14355.66 | P0AG44_RL17 | rplQ | Cytoplasm | 11.05 | 45.90 | 79.29 | -0.565 | NO |
| 14942 | 14957.31 | P02413_RL15 | rplO | Cytoplasm | 11.18 | 43.69 | 87.43 | -0.252 | YES |
| 15385 | 15398.99 | P0ACF8_HNS | hns | Cytoplasm | 5.44 | 40.47 | 82.70 | -0.751 | NO |
| 17547 | 17569.35 | P0A7J3_RL10 | rplJ | Cytoplasm | 9.04 | 28.74 | 94.21 | 0.045 | NO |
| 18745 | 18761.12 | P0AG55_RL6 | rplF | Cytoplasm | 9.71 | 17.04 | 91.93 | -0.227 | NO |
| MALDI(m/z) | TDP precursormass | Proteinentry name | Gene ID | Subcellularlocation | Isoelectricpoint | Instability index | Aliphaticindex | GRAVY | Detected by BUP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3342 | 3342.72 | P02968_FLA | hag | Cytoplasm | 6.24 | 27.62 | 82.82 | -0.513 | YES |
| 4376 | 4377.46 | O32107_YUID | yuiD | Membrane | 8.39 | 31.42 | 120.00 | 0.382 | YES |
| 4769 | 4774.53 | P80868_EFG | fusA | Cytoplasm | 8.25 | 48.35 | 76.00 | -0.511 | YES |
| 5042 | 5039.81 | O32111_YUZG | yuzG | Membrane/Secreted | 9.40 | 27.87 | 129.35 | 0.548 | NO |
| 5431 | 5427.16 | P24469_C550 | cccA | Membrane | 6.37 | 19.70 | 77.17 | -0.549 | YES |
| 6099 | 6089.51 | O05522_TATAY | tatAy | Membrane/Secreted | 6.18 | 30.93 | 95.96 | -0.258 | YES |
| 6508 | 6502.85 | P21476_RS19 | rpsS | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.11 | 48.28 | 64.57 | -0.740 | YES |
| 6640 | 6641.39 | P23308_SINI | sinI | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 6.26 | 55.83 | 73.68 | -0.804 | NO |
| 6809 | 6807.46 | C0H3Y1_YHZD | yhzD | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 5.79 | 13.70 | 83.28 | -0.461 | NO |
| 7012 | 7009.60 | P70994_4OT | ywhB | Cytoplasm | 5.37 | 59.42 | 75.32 | -0.644 | YES |
| 7116 | 7116.98 | P37815_ATPL | atpE | Membrane | 6.05 | 14.25 | 145.14 | 1.274 | YES |
| 7368 | 7360.61 | P32081_CSPB | cspB | Cytoplasm | 4.54 | 18.56 | 66.87 | -0.337 | YES |
| 7445 | 7438.68 | O03223_RL31 | rpmE | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 9.21 | 35.10 | 47.27 | -0.689 | YES |
| 7715 | 7708.26 | P12873_RL29 | rpmC | Cytoplasm | 10.10 | 34.04 | 96.21 | -0.626 | YES |
| 8255 | 8247.24 | O31718_RPOY | rpoY | Cytoplasm | 4.81 | 50.16 | 83.19 | -0.616 | YES |
| 8546 | 8539.41 | O32119_YUTI | yutI | Cytoplasm | 4.34 | 47.47 | 116.96 | 0.200 | YES |
| 8840 | 8832.90 | P21475_RS18 | rpsR | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 11.04 | 43.37 | 76.58 | -0.639 | YES |
| 9209 | 9201.90 | P05657_RL27 | rpmA | Membrane/Secreted | 10.32 | 11.28 | 57.79 | -0.809 | YES |
| 9470 | 9462.29 | P21477_RS20 | rpsT | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 10.94 | 30.28 | 77.84 | -0.714 | YES |
| 9886 | 9878.28 | P08821_DBH1 | hupA | Cytoplasm | 8.96 | 29.52 | 82.83 | -0.485 | YES |
| 10451 | 10445.56 | P21476_RS19 | rpsS | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.11 | 48.28 | 64.57 | -0.740 | YES |
| 10952 | 10943.59 | P28015_SP5G | spoVG | Cytoplasm | 5.25 | 26.40 | 83.40 | -0.479 | YES |
| 11150 | 11163.36 | P0CI78_RL24 | rplX | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.04 | 16.40 | 77.38 | -0.644 | YES |
| MALDI(m/z) | TDP precursormass | Proteinentry name | Gene ID | Subcellularlocation | Isoelectricpoint | Instability index | Aliphaticindex | GRAVY | Detected by BUP |
| 11536 | 11527.33 | P21471_RS10 | rpsJ | Cytoplasm | 9.79 | 48.41 | 99.41 | -0.460 | YES |
| 11591 | 11585.06 | P0C174_GPSB | gpsB | Cytoplasm | 5.72 | 50.84 | 85.51 | -0.853 | YES |
| 12463 | 12451.83 | P42060_RL22 | rplV | Cytoplasm | 10.73 | 31.93 | 97.61 | -0.244 | YES |
| 12622 | 12611.85 | P02394_RL7 | rplL | Cytoplasm | 4.56 | 44.34 | 114.31 | 0.115 | YES |
| 12972 | 12960.98 | P46899_RL18 | rplR | Cytoplasm | 10.11 | 19.12 | 87.92 | -0.370 | YES |
| 13157 | 13146.12 | P12875_RL14 | rplN | Cytoplasm | 9.94 | 31.75 | 96.56 | -0.137 | YES |
| 13390 | 13378.60 | O31742_RL19 | rplS | Cytoplasm | 10.97 | 41.84 | 98.17 | -0.475 | YES |
| 13652 | 13647.71 | P20282_RS13 | rpsM | Cytoplasm | 11.07 | 42.95 | 96.61 | -0.720 | YES |
| 14213 | 14210.74 | P21470_RS9 | rpsI | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.60 | 40.42 | 87.85 | -0.512 | YES |
| 15286 | 15271.55 | P35137_PPIB | ppiB | Cytoplasm | 5.53 | 20.21 | 59.30 | -0.364 | YES |
| 16380 | 16364.70 | P70974_RL13 | rplM | Cytoplasm | 9.87 | 15.64 | 80.07 | -0.632 | YES |
| 17631 | 17611.78 | P21467_RS5 | rpsE | Cytoplasm | 9.92 | 34.39 | 108.61 | -0.001 | YES |
| 17770 | 17754.49 | P21469_RS7 | rpsG | Cytoplasm | 10.81 | 45.66 | 98.17 | -0.621 | YES |
| 19385 | 19366.40 | P46898_RL6 | rplF | Cytoplasm | 9.49 | 31.26 | 87.49 | -0.501 | YES |
Table 2 Properties of proteins assigned on the MALDI fingerprintsof B. subtilis
| MALDI(m/z) | TDP precursormass | Proteinentry name | Gene ID | Subcellularlocation | Isoelectricpoint | Instability index | Aliphaticindex | GRAVY | Detected by BUP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3342 | 3342.72 | P02968_FLA | hag | Cytoplasm | 6.24 | 27.62 | 82.82 | -0.513 | YES |
| 4376 | 4377.46 | O32107_YUID | yuiD | Membrane | 8.39 | 31.42 | 120.00 | 0.382 | YES |
| 4769 | 4774.53 | P80868_EFG | fusA | Cytoplasm | 8.25 | 48.35 | 76.00 | -0.511 | YES |
| 5042 | 5039.81 | O32111_YUZG | yuzG | Membrane/Secreted | 9.40 | 27.87 | 129.35 | 0.548 | NO |
| 5431 | 5427.16 | P24469_C550 | cccA | Membrane | 6.37 | 19.70 | 77.17 | -0.549 | YES |
| 6099 | 6089.51 | O05522_TATAY | tatAy | Membrane/Secreted | 6.18 | 30.93 | 95.96 | -0.258 | YES |
| 6508 | 6502.85 | P21476_RS19 | rpsS | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.11 | 48.28 | 64.57 | -0.740 | YES |
| 6640 | 6641.39 | P23308_SINI | sinI | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 6.26 | 55.83 | 73.68 | -0.804 | NO |
| 6809 | 6807.46 | C0H3Y1_YHZD | yhzD | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 5.79 | 13.70 | 83.28 | -0.461 | NO |
| 7012 | 7009.60 | P70994_4OT | ywhB | Cytoplasm | 5.37 | 59.42 | 75.32 | -0.644 | YES |
| 7116 | 7116.98 | P37815_ATPL | atpE | Membrane | 6.05 | 14.25 | 145.14 | 1.274 | YES |
| 7368 | 7360.61 | P32081_CSPB | cspB | Cytoplasm | 4.54 | 18.56 | 66.87 | -0.337 | YES |
| 7445 | 7438.68 | O03223_RL31 | rpmE | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 9.21 | 35.10 | 47.27 | -0.689 | YES |
| 7715 | 7708.26 | P12873_RL29 | rpmC | Cytoplasm | 10.10 | 34.04 | 96.21 | -0.626 | YES |
| 8255 | 8247.24 | O31718_RPOY | rpoY | Cytoplasm | 4.81 | 50.16 | 83.19 | -0.616 | YES |
| 8546 | 8539.41 | O32119_YUTI | yutI | Cytoplasm | 4.34 | 47.47 | 116.96 | 0.200 | YES |
| 8840 | 8832.90 | P21475_RS18 | rpsR | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 11.04 | 43.37 | 76.58 | -0.639 | YES |
| 9209 | 9201.90 | P05657_RL27 | rpmA | Membrane/Secreted | 10.32 | 11.28 | 57.79 | -0.809 | YES |
| 9470 | 9462.29 | P21477_RS20 | rpsT | Cytoplasm/Secreted | 10.94 | 30.28 | 77.84 | -0.714 | YES |
| 9886 | 9878.28 | P08821_DBH1 | hupA | Cytoplasm | 8.96 | 29.52 | 82.83 | -0.485 | YES |
| 10451 | 10445.56 | P21476_RS19 | rpsS | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.11 | 48.28 | 64.57 | -0.740 | YES |
| 10952 | 10943.59 | P28015_SP5G | spoVG | Cytoplasm | 5.25 | 26.40 | 83.40 | -0.479 | YES |
| 11150 | 11163.36 | P0CI78_RL24 | rplX | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.04 | 16.40 | 77.38 | -0.644 | YES |
| MALDI(m/z) | TDP precursormass | Proteinentry name | Gene ID | Subcellularlocation | Isoelectricpoint | Instability index | Aliphaticindex | GRAVY | Detected by BUP |
| 11536 | 11527.33 | P21471_RS10 | rpsJ | Cytoplasm | 9.79 | 48.41 | 99.41 | -0.460 | YES |
| 11591 | 11585.06 | P0C174_GPSB | gpsB | Cytoplasm | 5.72 | 50.84 | 85.51 | -0.853 | YES |
| 12463 | 12451.83 | P42060_RL22 | rplV | Cytoplasm | 10.73 | 31.93 | 97.61 | -0.244 | YES |
| 12622 | 12611.85 | P02394_RL7 | rplL | Cytoplasm | 4.56 | 44.34 | 114.31 | 0.115 | YES |
| 12972 | 12960.98 | P46899_RL18 | rplR | Cytoplasm | 10.11 | 19.12 | 87.92 | -0.370 | YES |
| 13157 | 13146.12 | P12875_RL14 | rplN | Cytoplasm | 9.94 | 31.75 | 96.56 | -0.137 | YES |
| 13390 | 13378.60 | O31742_RL19 | rplS | Cytoplasm | 10.97 | 41.84 | 98.17 | -0.475 | YES |
| 13652 | 13647.71 | P20282_RS13 | rpsM | Cytoplasm | 11.07 | 42.95 | 96.61 | -0.720 | YES |
| 14213 | 14210.74 | P21470_RS9 | rpsI | Cytoplasm/Membrane | 10.60 | 40.42 | 87.85 | -0.512 | YES |
| 15286 | 15271.55 | P35137_PPIB | ppiB | Cytoplasm | 5.53 | 20.21 | 59.30 | -0.364 | YES |
| 16380 | 16364.70 | P70974_RL13 | rplM | Cytoplasm | 9.87 | 15.64 | 80.07 | -0.632 | YES |
| 17631 | 17611.78 | P21467_RS5 | rpsE | Cytoplasm | 9.92 | 34.39 | 108.61 | -0.001 | YES |
| 17770 | 17754.49 | P21469_RS7 | rpsG | Cytoplasm | 10.81 | 45.66 | 98.17 | -0.621 | YES |
| 19385 | 19366.40 | P46898_RL6 | rplF | Cytoplasm | 9.49 | 31.26 | 87.49 | -0.501 | YES |
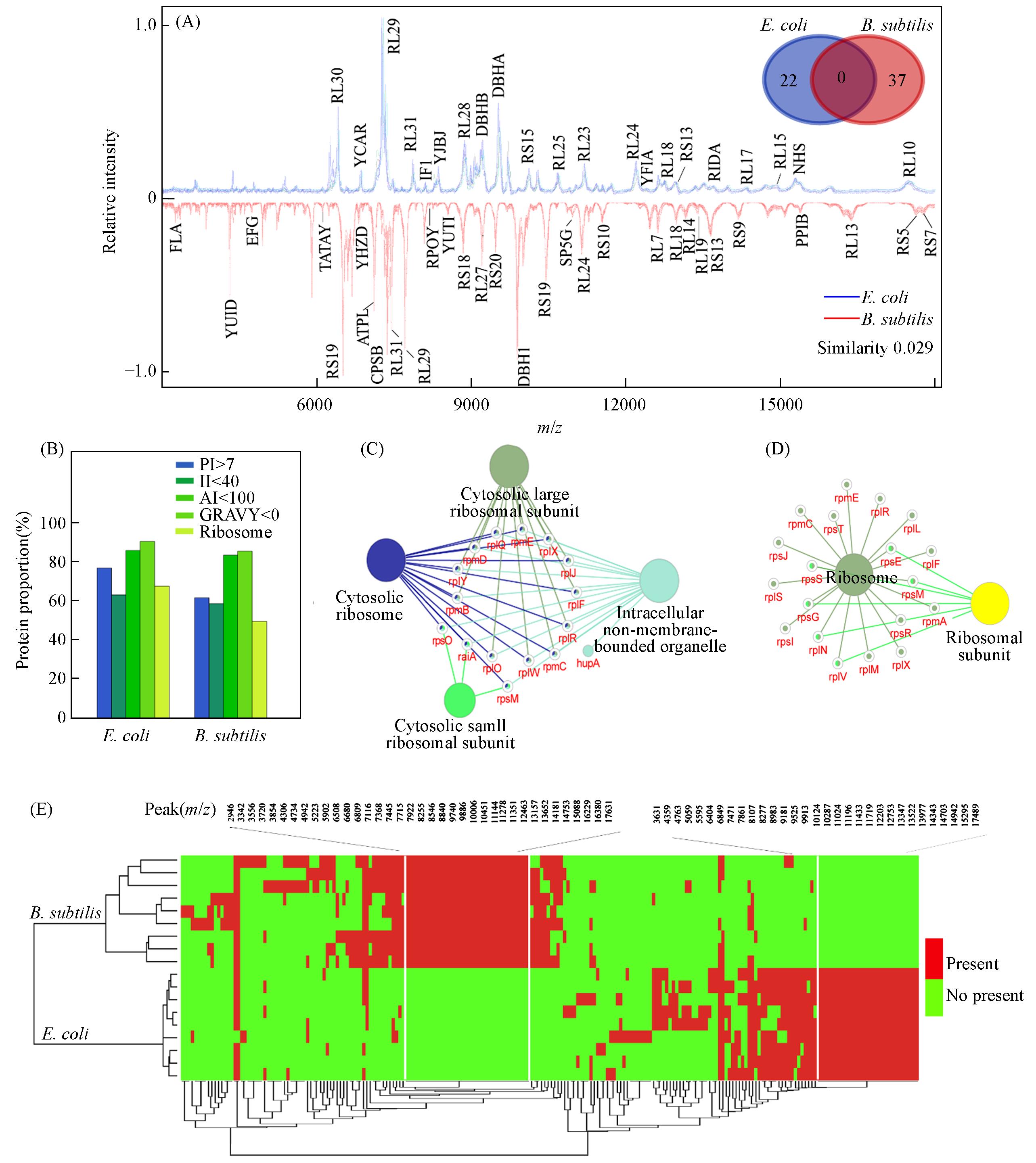
Fig.3 Correlation between MALDI and TDP protein profiles(A) MALDI protein fingerprints of E. coli and B. subtilis, with protein identity labeled on the main peaks. The protein identity was tentatively assigned through matching the fingerprint peak masses to the protein(or protein fragment) masses measured by TDP; insert: fingerprint peak numbers detected from E. coli and B. subtilis with protein identity assigned; (B) investigation of the properties of proteins assigned on the MALDI fingerprints of E. coli and B. subtilis. The investigated properties include isoelectric point(PI), instability index(II), aliphatic index(AI), grand average of hydropathy(GRAVY), and if the proteins were ribosomal proteins; (C) biological functional analysis of the proteins assigned for E. coli using ClueGO system; (D) biological functional analysis of the proteins assigned for B. subtilis using ClueGO system; gene ontology(GO) terms are represented as nodes, with node size representing the enrichment significance; only the most significant terms were labeled, with the exhibition of representative enriched pathway(P < 0.05) interactions among the main targets; (E) a deep hierarchical clustering analysis of the MALDI fingerprints using cosine correlation distance function and average linkage, correlated with the peak presence profile. The peaks exclusively detected from E. coli and B. subtilis were listed.
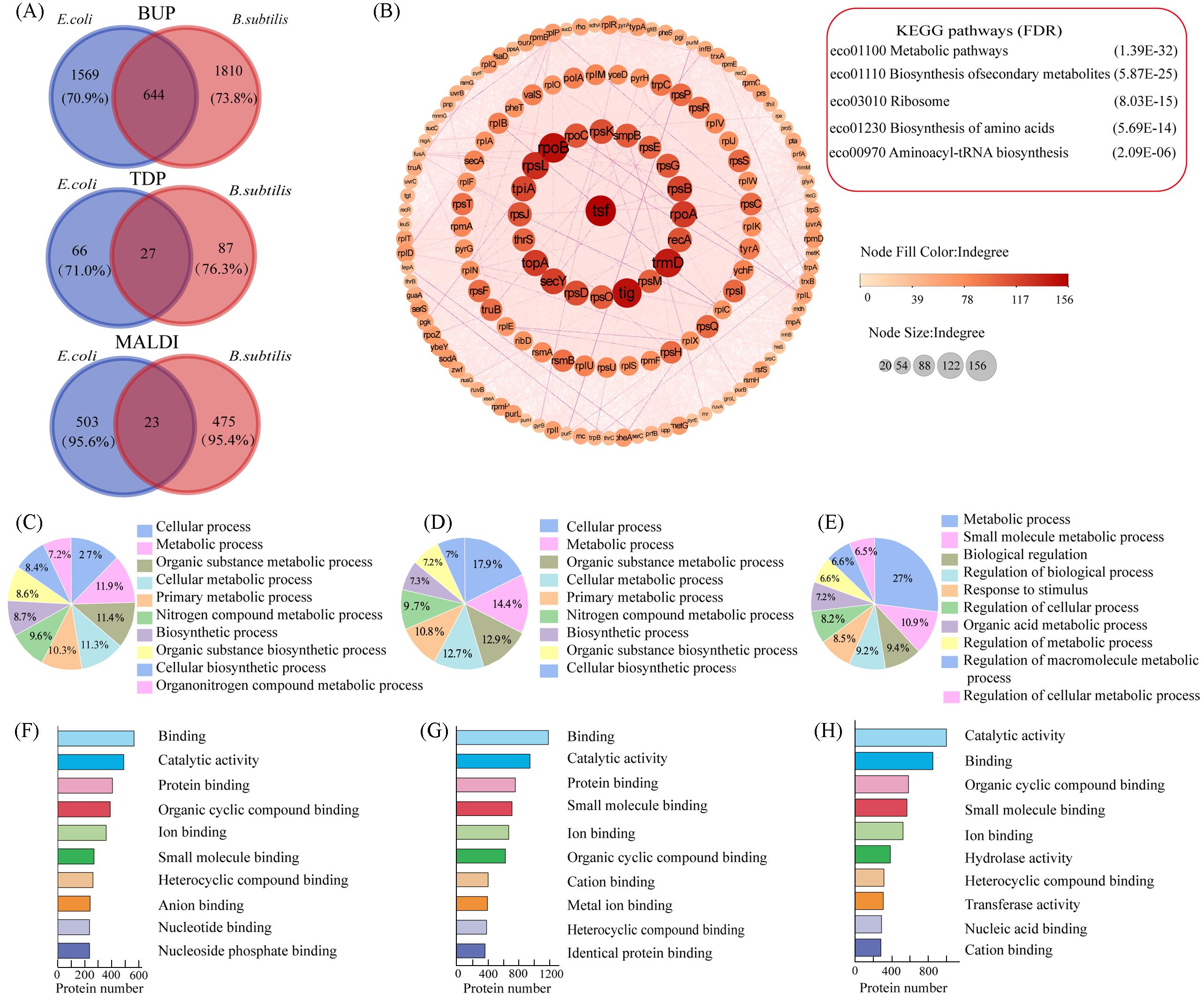
Fig.5 BUP profile exhibited the largest overlap between bacterial species(A) Counts of species-common and species-specific proteins or protein peaks detected from E. coli and B. subtilis using MALDI, TDP and BUP respectively; (B) the protein-protein interaction network of the BUP species-common proteins, constructed using the String database and Cytoscape with an indegree score threshold of 30; (C—E) top ten significantly enriched biological processes(BPs) from the species-common proteins(C), E. coli-specific proteins(D) and B. subtilis-specific proteins(E) detected by BUP; (F—H) top ten significantly enriched molecular functions(MFs) from the species-common proteins(F), E. coli-specific proteins(G) and B. subtilis-specific proteins(H) detected by BUP. P-value lower than 0.05 indicated a significant enrichment.
| 1 | Zhao X., Bi H. Y., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2022, 70(24), 7525—7534 |
| 2 | Yang K. B., Cameranesi M., Gowder M., Martinez C., Shamovsky Y., Epshtein V., Hao Z. T., Nguyen T., Nirenstein E., Shamovsky I., Rasouly A., Nudler E., Nature, 2023, 622(7981), 180—187 |
| 3 | Chirania P., Holwerda E. K., Giannone R. J., Liang X. Y., Poudel S., Ellis J. C., Bomble Y. J., Hettich R. L., Lynd L. R., Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 3870 |
| 4 | Schwenzer A. K., Kruse L., Jooss K., Neususs C., Proteomics, 2024, 24(3-4), e2300135 |
| 5 | Zhou F., Johnston M. V., Electrophoresis, 2005, 26(7/8), 1383—1388 |
| 6 | Lee P. Y., Saraygord⁃Afshari N., Low T. Y., J. Chromatogr. A, 2020, 1615, 460763 |
| 7 | Rebecca W., Scheller C., Krebs F., Wätzig H., Oltmann‐Norden I., Electrophoresis, 2020, 42(3), 206—218 |
| 8 | Zhu Y. D., Qiao L., Prudent M., Bondarenko A., Gasilova N., Möller S. B., Lion N., Pick H., Gong T. Q., Chen Z. X., Yang P. Y., Lovey L. T., Girault H. H., Chem. Sci., 2016, 7(5), 2987—2995 |
| 9 | Toby T. K., Fornelli L., Srzentic K., DeHart C. J., Levitsky J., Friedewald J., Kelleher N. L., Nat. Protoc., 2019, 14(1), 119—152 |
| 10 | Dupree E. J., Jayathirtha M., Yorkey H., Mihasan M., Petre B. A., Darie C. C., Proteomes, 2020, 8(3), 8030014 |
| 11 | Gibson B., Wilson D. J., Feil E., Eyre⁃Walker A., Proc. Biol. Sci., 2018, 285(1880), 20180789 |
| 12 | Du M. G., Yuan Z. N., Werneburg G. T., Henderson N. S., Chauhan H., Kovach A., Zhao G. P., Johl J., Li H. L., Thanassi D. G., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 5207 |
| 13 | Nefedov A. V., Mitra I., Brasier A. R., Sadygov R. G., J. Proteome Res., 2011, 10(9), 4150—4157 |
| 14 | van Doorn J., Ly A., Marsman M., Wagenmakers E. J., J. Appl. Statist., 2020, 47(16), 2984—3006 |
| 15 | Jaskolla T. W., Karas M., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2011, 22(6), 976—988 |
| 16 | Zhu Y. D., Pick H., Gasilova N., Li X. Y., Lin T. E., Laeubli H. P., Zippelius A., Ho P. C., Girault H. H., Chem, 2019, 5(5), 1318—1336 |
| 17 | Yu C. S., Lin C. J., Hwang J. K., Prot. Sci., 2004, 13(5), 1402—1406 |
| 18 | Bindea G., Mlecnik B., Hackl H., Charoentong P., Tosolini M., Kirilovsky A., Fridman W. H., Pagès F., Trajanoski Z., Galon J., Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(8), 1091—1093 |
| 19 | Fromm S. A., O'Connor K. M., Purdy M., Bhatt P. R., Loughran G., Atkins J. F., Jomaa A., Mattei S., Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 1095 |
| 20 | Ishihama Y., Schmidt T., Rappsilber J., Mann M., Hartl F. U., Kerner M. J., Frishman D., BMC Genom., 2008, 9, 102 |
| 21 | Zundel M. A., Basturea G. N., Deutscher M. P., RNA, 2009, 15(5), 977—983 |
| 22 | Fedyukina D. V., Jennaro T. S., Cavagnero S., J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289(10), 6740—6750 |
| 23 | Shannon P., Markiel A., Ozier O., Baliga N. S., Wang J. T., Ramage D., Amin N., Schwikowski B., Ideker T., Genom. Res., 2003, 13(11), 2498—2504 |
| 24 | Burnett B. J., Altman R. B., Ferrao R., Alejo J. L., Kaur N., Kanji J., Blanchard S. C., J. Biol. Chem., 2013, 288(19), 13917—13928 |
| 25 | Houry W., Protein Sci., 2021, 30, 24—25 |
| 26 | Rungsirivanich P., Inta A., Tragoolpua Y., Thongwai N., Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 16561 |
| 27 | de Crécy⁃Lagard V., Ross R. L., Jaroch M., Marchand V., Eisenhart C., Brégeon D., Motorin Y., Limbach P. A., Biomolecules, 2020, 10(7), 977 |
| [1] | 侯泽金, 李荣其, 李健, 冯怡宁, 靳茜茜, 孙俊红, 曹洁. 基于GC-MS和机器学习的深静脉血栓形成预测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(9): 20240199. |
| [2] | 石倩, 刘冬梅, 方小泥, 刘宝红. 基于基质辅助激光解析质谱的高通量酪氨酸酶活性及抑制剂分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240330. |
| [3] | 闫勇杰, 高文博, 鲁晨辉, 杨成, 徐姝婷. 基于微萃取-纳喷雾质谱技术的纳升脑脊液中咖啡多酚的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240327. |
| [4] | 张磊, 申华莉. 标志物研究中常用蛋白组学质谱方法的定量准确性评估[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240311. |
| [5] | 靳莹, 张俊杰, 张毅欣, 袁悦, 韩珍珍. 外泌体分离和蛋白质组学分析的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240305. |
| [6] | 胡宇虹, 俞相明, 宋丽丽, 邢清和, 周峰. DEEP SEQ方法检测新生儿毛干蛋白质组动态变化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240326. |
| [7] | 范智瑞, 方群, 杨奕. 基于质谱的单细胞蛋白质组学分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240294. |
| [8] | 许霞, 秦伟达, 李若萌, 王倩倩, 刘宁, 李功玉. 深度覆盖蛋白质组学质谱分析: 细胞蛋白提取方法的评估[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240344. |
| [9] | 续红妹, 王梁臣, 闵乾昊. 面向小分子检测的MALDI MS基质研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240285. |
| [10] | 黄玉滢, 于成鲲, 刘斯奇, 任艳. 利用无标记单细胞蛋白质组学方法构建小鼠外周血单个核细胞的细胞图谱[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240355. |
| [11] | 刘思盈, 粟雯, 周仲燕, 杨治渝, 裴华夫, 何芷茹, 王娜, 岳磊. 温度控制的泛素/三磷酸腺苷相互作用的电喷雾质谱研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240382. |
| [12] | 沈枫林, 冯兆莹, 方静, 张磊, 刘晓慧, 周新文. 基于质谱的单细胞分辨的空间蛋白质组学新技术研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240299. |
| [13] | 霍志远, 周金萍, 马秀敏, 周严, 黄琳. 基于质谱的单细胞多组学分析技术研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240389. |
| [14] | 曹婷, 舒伟康, 万晶晶. 等离子体复合材料辅助小分子代谢物的质谱半定量分析及鉴定[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240325. |
| [15] | 张怡涵, 滑天宇, 侯士姣, 张洋洋, 殷丹, 姬向波, 张岩皓, 裴聪聪, 张书胜. 尖端Fe2O3纳米棒驱动的高性能质谱分析用于构建PM2.5暴露鼠的代谢指纹图谱[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240376. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||