

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 20230151.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230151
宋欣1,2( ), 高申正1, 许善磊1, 徐浩1, 周鑫杰1, 朱梦冰1, 郝儒林1, 朱卫国1(
), 高申正1, 许善磊1, 徐浩1, 周鑫杰1, 朱梦冰1, 郝儒林1, 朱卫国1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-30
出版日期:2023-09-10
发布日期:2023-05-18
通讯作者:
宋欣,朱卫国
E-mail:xin.song@cczu.edu.cn;zwg18@126.com
基金资助:
SONG Xin1,2( ), GAO Shenzheng1, XU Shanlei1, XU Hao1, ZHOU Xinjie1, ZHU Mengbing1, HAO Rulin1, ZHU Weiguo1(
), GAO Shenzheng1, XU Shanlei1, XU Hao1, ZHOU Xinjie1, ZHU Mengbing1, HAO Rulin1, ZHU Weiguo1( )
)
Received:2023-03-30
Online:2023-09-10
Published:2023-05-18
Contact:
SONG Xin, ZHU Weiguo
E-mail:xin.song@cczu.edu.cn;zwg18@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
本体异质结(BHJ)有机太阳能电池(OSC)因具有可溶液制备、 绿色无毒及可柔性化等特点而被视为具有广阔应用前景的太阳能电池技术之一. 活性层内部的纳米形貌是决定器件性能和工作稳定性的关键因素之一. 基于此, 研究者先后开发了热退火、 溶剂退火和溶剂添加剂等形貌优化方法. 然而, 上述处理方式不能与大面积印刷工艺兼容, 而且不利于器件内部形貌和性能的稳定性, 因此寻找简单高效的形貌调控手段是OSC研究的热点. 近年来, 挥发固体添加剂因其独特的分子特性, 能够与给受体分子间形成较强的相互作用力, 被认为是提升OSC能量转换效率(PCE)和稳定性的发展方向. 本文系统总结了非卤素及卤素型挥发固体添加剂调控OSC形貌和光伏性能的研究现状, 深入讨论了挥发固体添加剂优化活性层形貌的不同机理, 包括分子间吸附能、 给体与受体的相互作用、 晶体成核和生长等; 分析了挥发固体添加剂策略所面临的挑战和未来的发展趋势.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
宋欣, 高申正, 许善磊, 徐浩, 周鑫杰, 朱梦冰, 郝儒林, 朱卫国. 挥发固体添加剂调控有机太阳能电池性能的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230151.
SONG Xin, GAO Shenzheng, XU Shanlei, XU Hao, ZHOU Xinjie, ZHU Mengbing, HAO Rulin, ZHU Weiguo. Progress on the Efficiency Regulation of Organic Solar Cells by Volatile Solid Additives. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(9): 20230151.
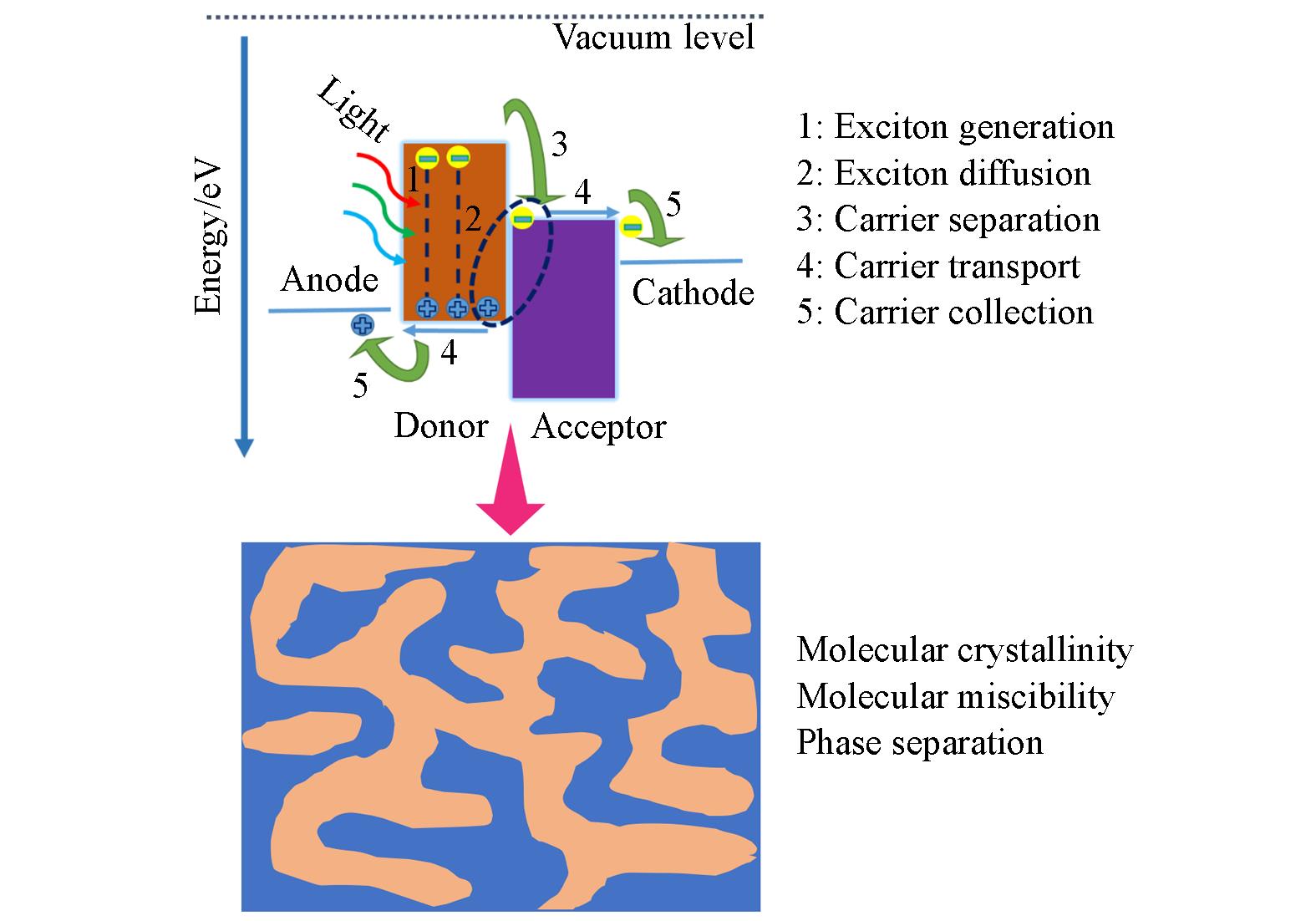
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the optoelectronic conversion process of organic solar cells(A) and the donor∶acceptor blend morphology of the active layer in OSC devices(B)
| Donor∶Acceptor | Additive | JSC/(mA∙cm-2) | VOC/V | FF(%) | PCE(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM7∶IT⁃4F | SA⁃1 | 20.6 | 0.87 | 77.0 | 13.8 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6 | An | 25.9 | 0.84 | 77.8 | 17.0 | [ |
| PTQ10∶m⁃BTP⁃PhC6∶PC71BM | CN+DTT | 26.99 | 0.87 | 80.6 | 18.89 | [ |
| PBQ6∶PYF⁃T⁃o | DTT | 25.12 | 0.89 | 76.6 | 17.06 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6 | Fc | 26.71 | 0.84 | 76.0 | 17.40 | [ |
| PTzBI⁃dF∶Y6⁃BO | NT | 27.35 | 0.84 | 76.45 | 17.45 | [ |
| PM6∶L8⁃BO | SAD⁃2 | 26.73 | 0.889 | 79.32 | 18.85 | [ |
| PBDB⁃T∶TTC8⁃O1⁃4F | DIO+DMON | 23.0 | 0.82 | 70.3 | 13.3 | [ |
| PBDB⁃T∶ITIC | BP⁃BP | 19.31 | 0.88 | 70.2 | 11.9 | [ |
| PM6∶L8⁃BO | 2⁃HM | 27.1 | 0.875 | 79.4 | 18.85 | [ |
| PM6∶PY⁃DT | 2⁃MN | 23.84 | 0.95 | 76.4 | 17.32 | [ |
Table 1 Typical device photovoltaic performance based on non-halogen volatile solid additives
| Donor∶Acceptor | Additive | JSC/(mA∙cm-2) | VOC/V | FF(%) | PCE(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM7∶IT⁃4F | SA⁃1 | 20.6 | 0.87 | 77.0 | 13.8 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6 | An | 25.9 | 0.84 | 77.8 | 17.0 | [ |
| PTQ10∶m⁃BTP⁃PhC6∶PC71BM | CN+DTT | 26.99 | 0.87 | 80.6 | 18.89 | [ |
| PBQ6∶PYF⁃T⁃o | DTT | 25.12 | 0.89 | 76.6 | 17.06 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6 | Fc | 26.71 | 0.84 | 76.0 | 17.40 | [ |
| PTzBI⁃dF∶Y6⁃BO | NT | 27.35 | 0.84 | 76.45 | 17.45 | [ |
| PM6∶L8⁃BO | SAD⁃2 | 26.73 | 0.889 | 79.32 | 18.85 | [ |
| PBDB⁃T∶TTC8⁃O1⁃4F | DIO+DMON | 23.0 | 0.82 | 70.3 | 13.3 | [ |
| PBDB⁃T∶ITIC | BP⁃BP | 19.31 | 0.88 | 70.2 | 11.9 | [ |
| PM6∶L8⁃BO | 2⁃HM | 27.1 | 0.875 | 79.4 | 18.85 | [ |
| PM6∶PY⁃DT | 2⁃MN | 23.84 | 0.95 | 76.4 | 17.32 | [ |
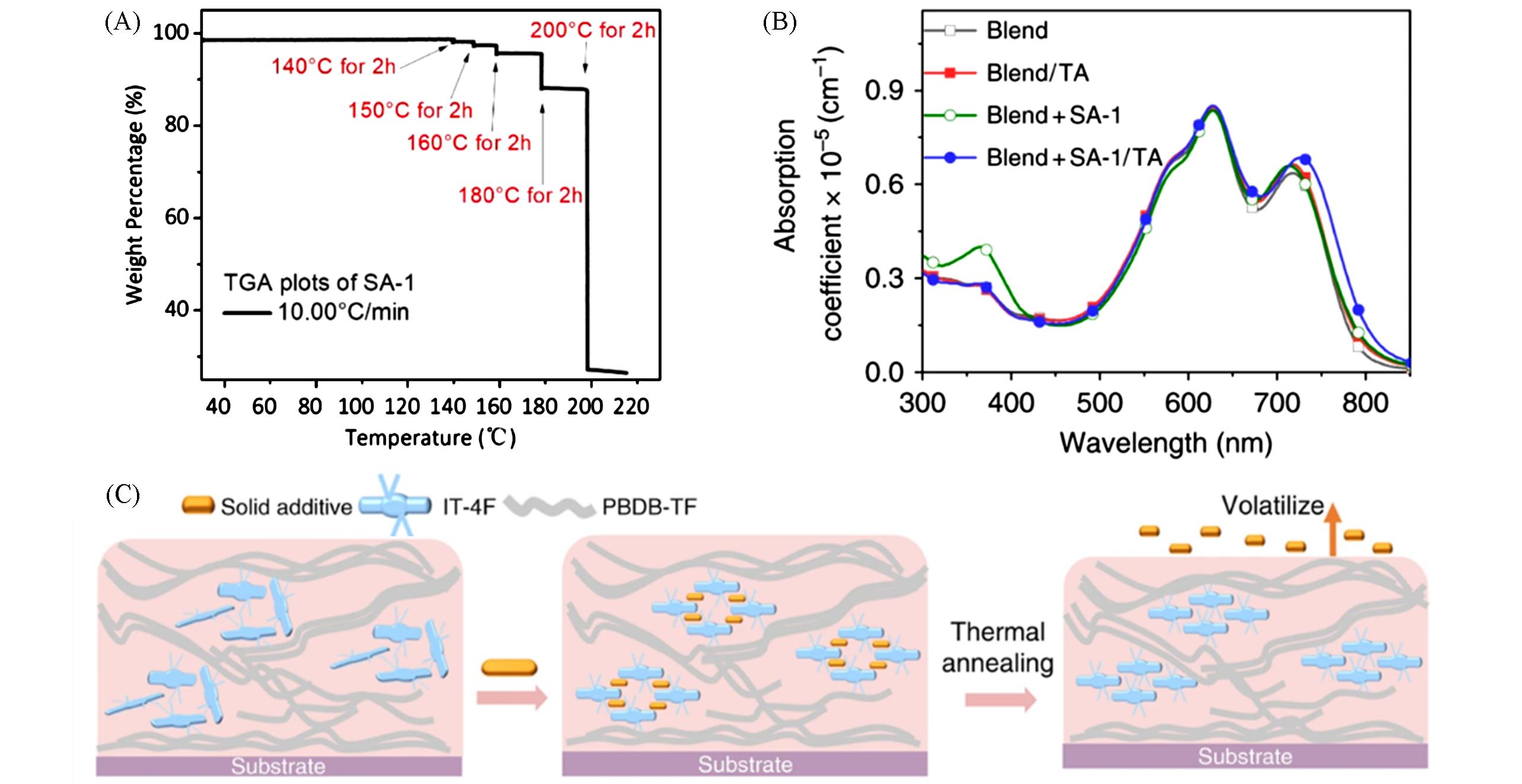
Fig.3 TGA curve of SA⁃1 solid(A), absorption spectra of SA⁃1 in blend system with or without thermal annealing treatment(B) and schematic diagram of the basic process evolution of solid additives in PBDB⁃TF∶IT⁃4F blend system(C)[35]Copyright 2018, Springer Nature.
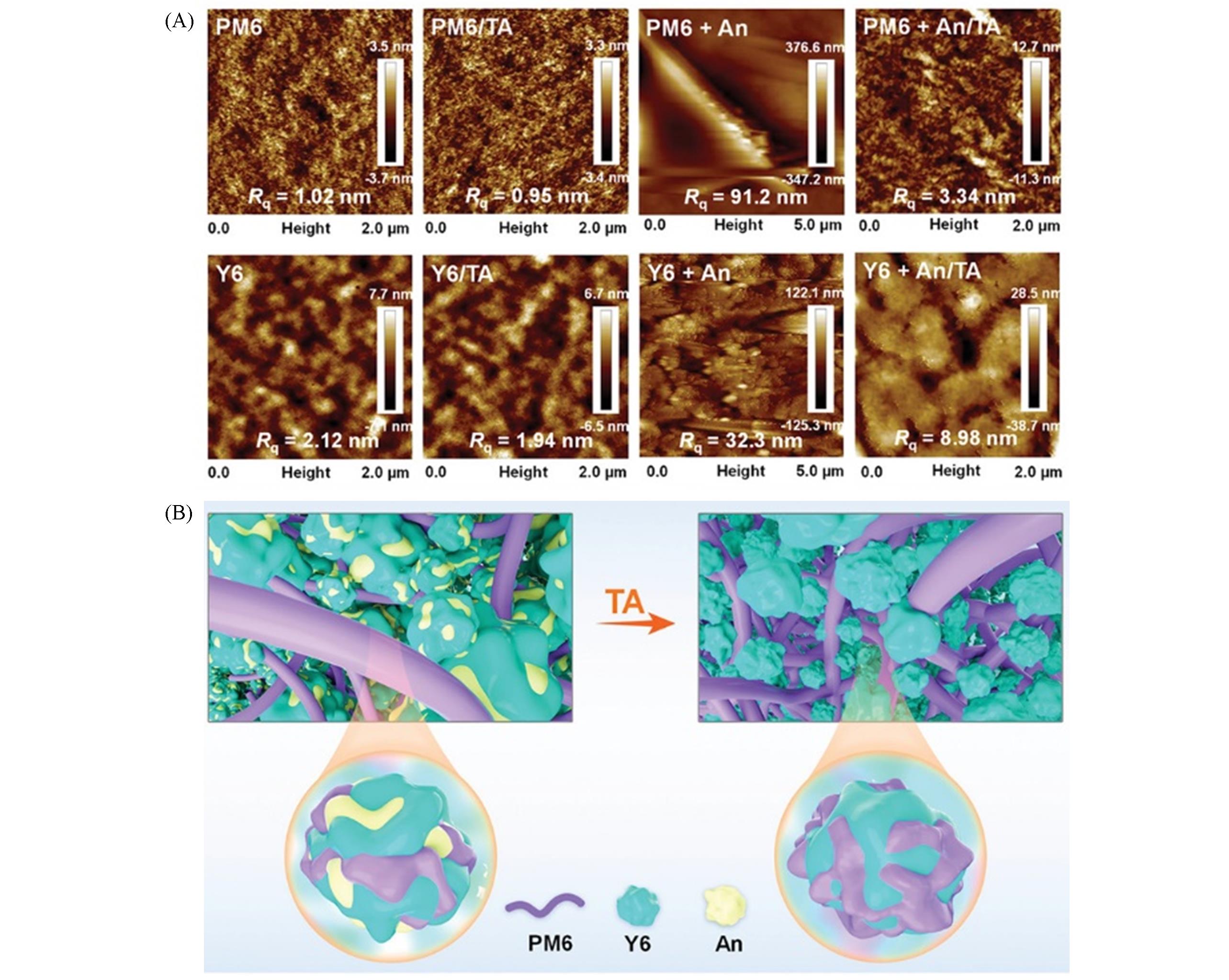
Fig.4 AFM images of PM6 andY6, PM6/TA, PM6+An, PM6+An/TA(A) and the working mechanism of An solid additive in PM6∶Y6 blend system(B)[36]Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH.
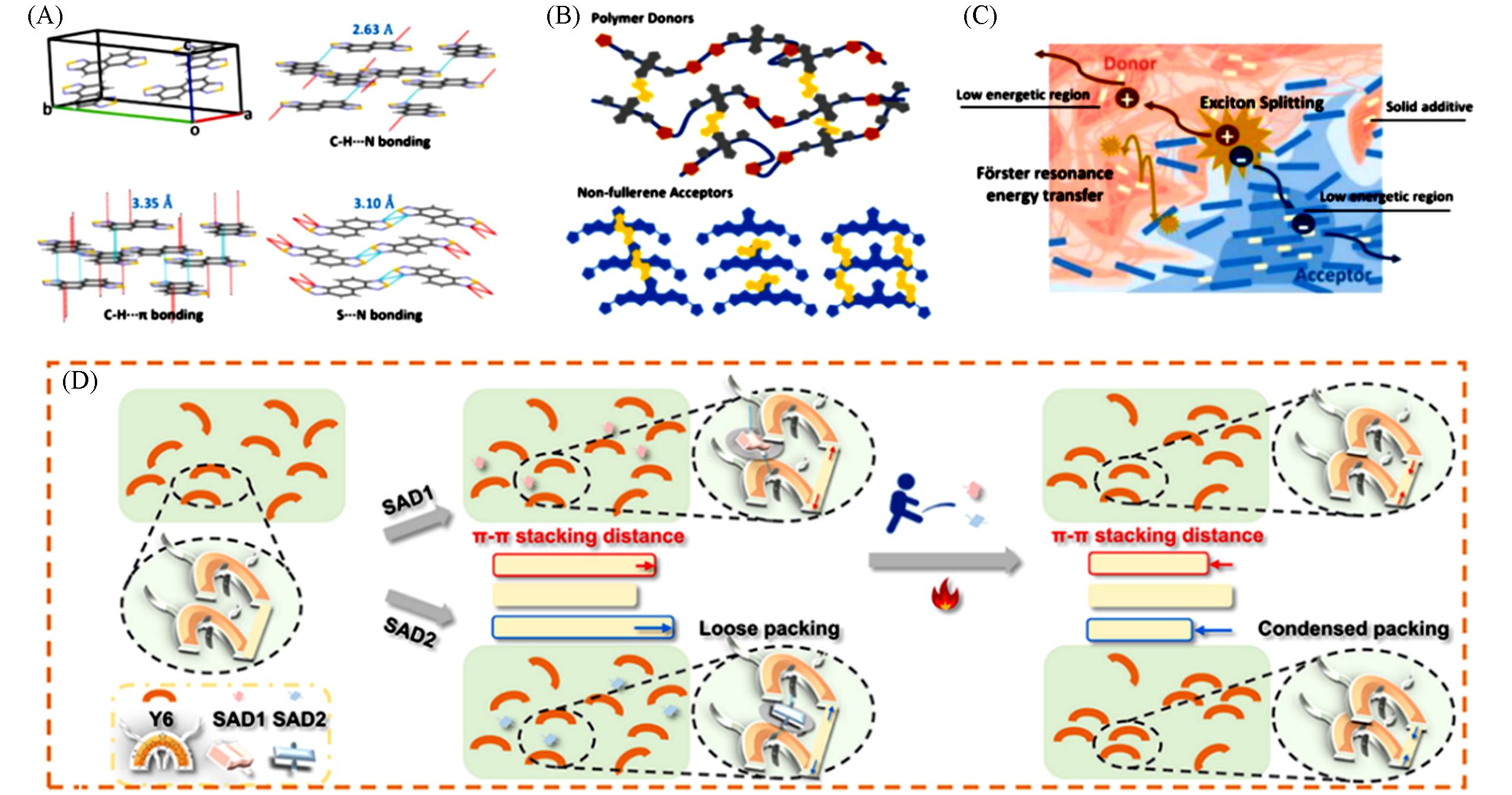
Fig.5 Molecular self⁃assembly evolution of NT solid(A), ideal structural configuration of non⁃fullerene Y6 molecules with NT molecules(B), schematic diagram of photoelectric conversion of blend film after the introduction of NT molecules(C)[40], the schematic diagram of working mechanism SAD⁃2 operation(D)[41](C) Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH;(D) Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society.
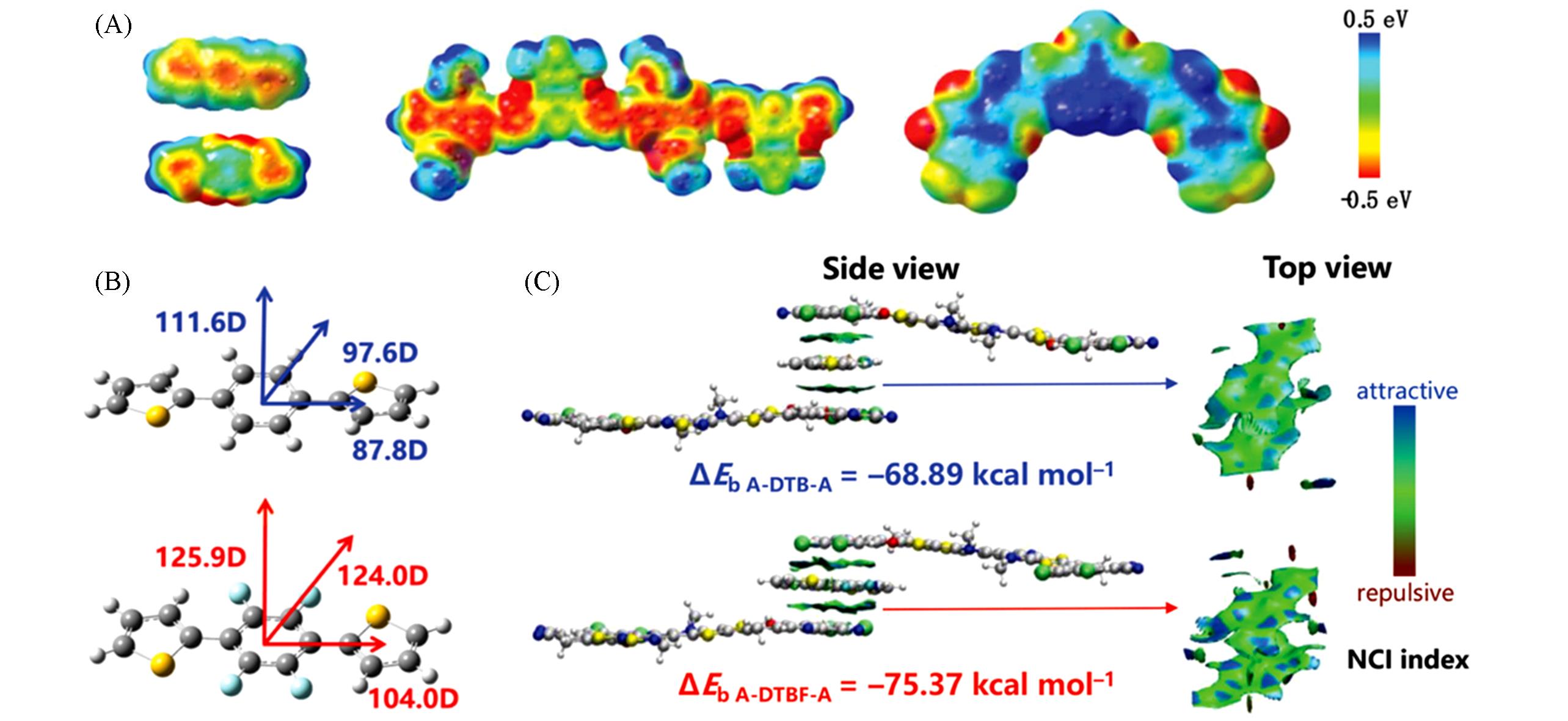
Fig.7 ESP distributions of DTBF, PM6, BO⁃4Cl(A), the four⁃pole moment direction of the DTBF(B) and Non⁃covalent interactions(NCI) by reduced density gradient analysis between BO4Cl and DTB or DTBF(C)[46]Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH.
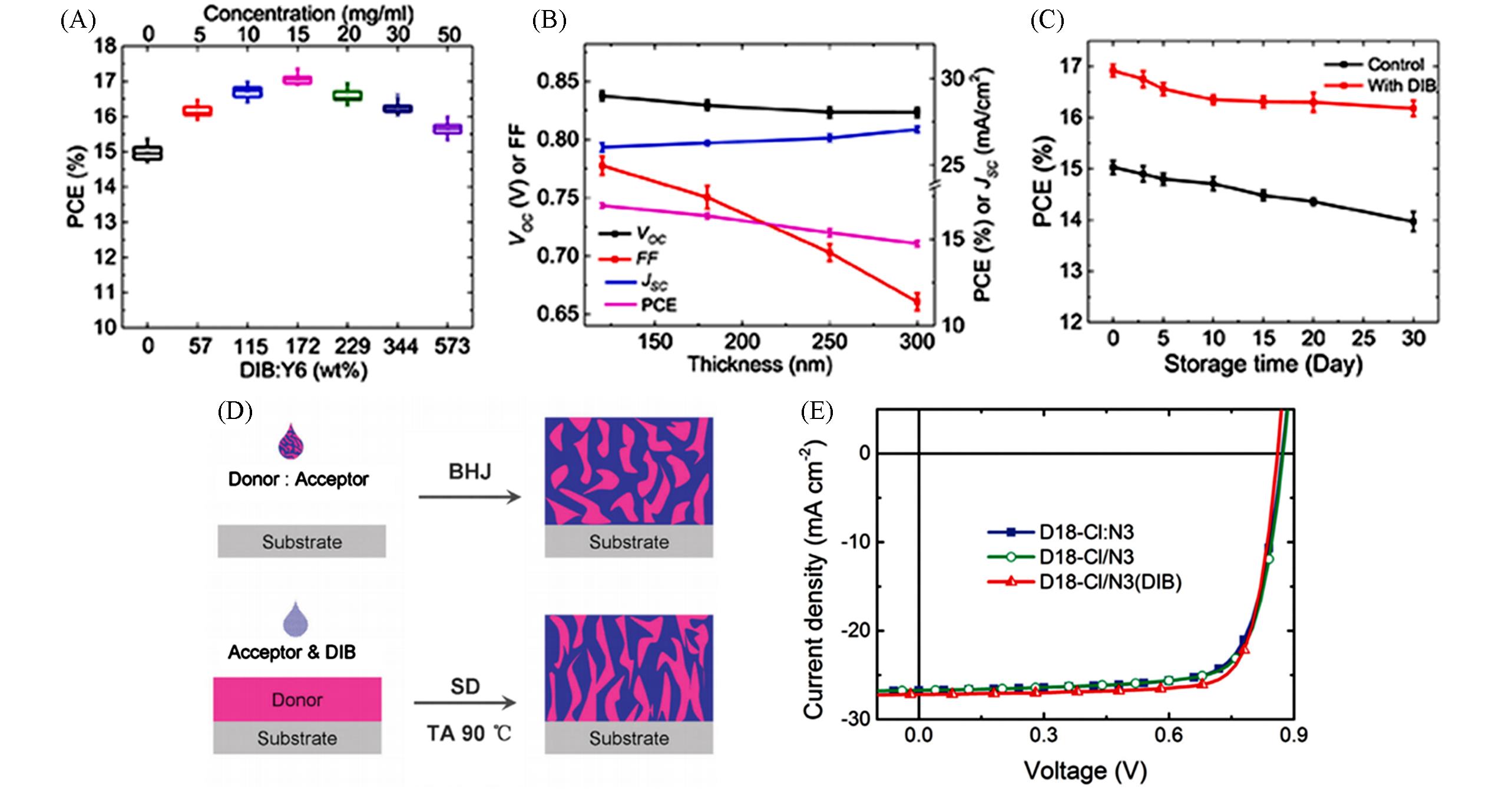
Fig.8 Device efficiency attenuation curve over additive concentration(A), the device performance variation with the varied active layer thickness(B), stored PCE values for time variation(C)[49], the device Pseudo⁃bilayer device preparation flowchart(D)and J⁃V curve of a pseudo⁃bilayer device(E)[50](C) Copyright 2021, Elsevier;(E) Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH.
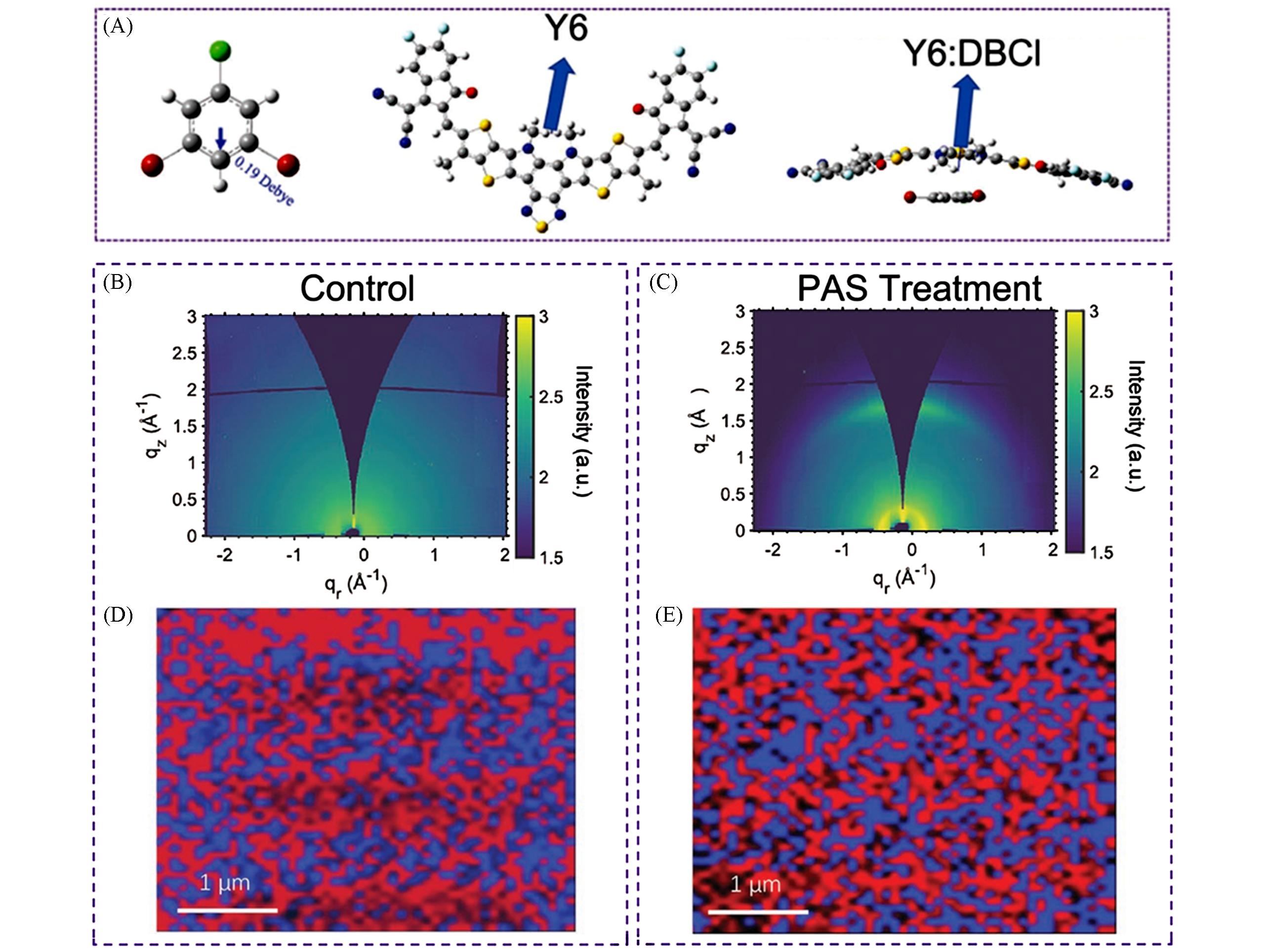
Fig.9 Molecular dipole direction of DBCl, Y6 and DBCl∶Y6 dimer(A), GIWAXS pattern of blend film without(B) and film with(C) DBCl additive, conforcal Raman mapping pattern of blend film without(D) and with(E) DBCl additive[52]Copyright 2022, Wiley⁃VCH.
| Donor∶Acceptor | Additive | JSC/(mA∙cm-2) | VOC/V | FF(%) | PCE(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM6∶BO4Cl | DTBF | 26.2 | 0.85 | 77.0 | 17.1 | [ |
| PM6/BTP⁃eC9 | FBT | 26.68 | 0.84 | 79.52 | 17.7 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6 | A3 | 26.5 | 0.82 | 76.05 | 16.5 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6∶ICBA | DIB | 26.5 | 0.84 | 79.62 | 17.72 | [ |
| D18⁃Cl/N3 | DIB | 27.18 | 0.86 | 78.8 | 18.42 | [ |
| D18⁃Cl∶L8⁃BO | DIB | 26.6 | 0.92 | 75.6 | 18.7 | [ |
| PM6∶L8⁃BO | DBCl | 25.9 | 0.89 | 80.2 | 18.5 | [ |
| PBQx⁃TF∶eC9⁃2Cl | DCBB | 27.2 | 0.879 | 80.4 | 19.2 | [ |
| PM6∶BTP⁃eC9 | TCB | 27.88 | 0.861 | 80.69 | 19.31 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6⁃BO | INB⁃F | 26.5 | 0.82 | 76.7 | 16.7 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6⁃BO | INB⁃5F | 27.7 | 0.82 | 75.1 | 16.7 | [ |
Table 2 Typical device photovoltaic performance based on halogen volatile solid additives
| Donor∶Acceptor | Additive | JSC/(mA∙cm-2) | VOC/V | FF(%) | PCE(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM6∶BO4Cl | DTBF | 26.2 | 0.85 | 77.0 | 17.1 | [ |
| PM6/BTP⁃eC9 | FBT | 26.68 | 0.84 | 79.52 | 17.7 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6 | A3 | 26.5 | 0.82 | 76.05 | 16.5 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6∶ICBA | DIB | 26.5 | 0.84 | 79.62 | 17.72 | [ |
| D18⁃Cl/N3 | DIB | 27.18 | 0.86 | 78.8 | 18.42 | [ |
| D18⁃Cl∶L8⁃BO | DIB | 26.6 | 0.92 | 75.6 | 18.7 | [ |
| PM6∶L8⁃BO | DBCl | 25.9 | 0.89 | 80.2 | 18.5 | [ |
| PBQx⁃TF∶eC9⁃2Cl | DCBB | 27.2 | 0.879 | 80.4 | 19.2 | [ |
| PM6∶BTP⁃eC9 | TCB | 27.88 | 0.861 | 80.69 | 19.31 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6⁃BO | INB⁃F | 26.5 | 0.82 | 76.7 | 16.7 | [ |
| PM6∶Y6⁃BO | INB⁃5F | 27.7 | 0.82 | 75.1 | 16.7 | [ |
| 1 | Guo Y. T., Chen Z. Y., Ge Z. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(7), 20230084 |
| 郭赟彤, 陈振宇, 葛子义. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7), 20230084 | |
| 2 | Zhang Y. Q., Zhu X. Y., Miao J. H., Liu J., Wang L. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(7), 20230068 |
| 张永倩, 朱小玉, 苗俊辉, 刘俊, 王利祥. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7), 20230068 | |
| 3 | Guo X. G., Zhou N. J., Lou S. J., Smith J., Tice D. B., Hennek J. W., Ortiz R. P., Navarrete J. T. L., Li S. Y., Strzalka J., Chen L. X., Chang R. P. H., Facchetti A., Marks T. J., Nat. Photonics, 2013, 7(10), 825—833 |
| 4 | An Q. S., Zhang F. J., Zhang J., Tang W. H., Deng Z. B., Hu B., Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9(2), 281—322 |
| 5 | Yan T. T., Song W., Huang J. M., Peng R. X., Huang L. K., Ge Z. Y., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(39), 1902210 |
| 6 | Xie Y. P., Yang F., Li Y. X., Uddin M. A., Bi P. Q., Fan B. B., Cai Y. H., Hao X. T., Woo H. Y., Li W. W., Liu F., Sun Y. M., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(38), 1803045 |
| 7 | Yue Q. H., Liu W. Y., Zhu X. Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(27), 11613—11628 |
| 8 | Zhang G. Y., Zhao J. B., Chow P. C. Y., Jiang K., Zhang J. Q., Zhu Z. L., Zhang J., Huang F., Yan H., Chem. Rev., 2018, 118(7), 3447—3507 |
| 9 | Chen H. Y., Hou J. H., Zhang S. Q., Liang Y. Y., Yang G. W., Yang Y., Yu L. P., Wu Y., Li G., Nat. Photonics, 2009, 3(11), 649—653 |
| 10 | Li G., Zhu R., Yang Y., Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6(3), 153—161 |
| 11 | Xu X. P., Jing W. W., Meng H. F., Guo Y. Y., Yu L. Y., Li R. P., Peng Q., Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2208997 |
| 12 | Zhu L., Zhang M., Xu J. Q., Li C., Yan J., Zhou G. Q., Zhong W. K., Hao T. Y., Song J. L., Xue X. N., Zhou Z. C., Zeng R., Zhu H. M., Chen C. C.., MacKenzie R. C. I., Zou Y. C., Nelson J., Zhang Y. M., Sun Y. M., Liu F., Nat. Mater., 2022, 21(6), 656—663 |
| 13 | Bi P. Q., Wang J. Q., Cui Y., Zhang J. Q., Zhang T., Chen Z. H., Qiao J. W., Dai J. B., Zhang S. Q., Hao X. T., Wei Z. X., Hou J. H., Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 202210865 |
| 14 | Zheng Z., Wang J. Q., Bi P. Q., Ren J. Z., Wang Y. F., Yang Y., Liu X. Y., Zhang S. Q., Hou J. H., Joule, 2022, 6(1), 171—184 |
| 15 | Yuan J., Zhang Y. Q., Zhou L. Y., Zhang G. C., Yip H. L., Lau T. K., Lu X. H., Zhu C., Peng H. J., Johnson P. A., Leclerc M., Cao Y., Ulanski J., Li Y. F., Zou Y. P., Joule, 2019, 3(4), 1140—1151 |
| 16 | Song X., Gasparini N., Nahid M. M., Paleti S. H. K., Wang J. L., Ade H., Baran D., Joule, 2019, 3(3), 846—857 |
| 17 | Hou J. H., Inganäs O, Friend R. H., Gao F., Nat. Mater., 2018, 17(2), 119—128 |
| 18 | Li C., Zhou J. D., Song J. L., Xu J. Q., Zhang H. T., Zhang X. N., Guo J., Zhu L., Wei D. H., Han G. C., Min J., Zhang Y., Xie Z. Q., Yi Y. P., Yan H., Gao F., Liu F., Sun Y. M., Nat. Energy, 2021, 6(6), 605—613 |
| 19 | Rivnay J., Mannsfeld S. C. B., Miller C. E., Salleo A., Toney M. F., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(10), 5488—5519 |
| 20 | Liao H. C., Hou C. C., Chang C. Y., Jao M. H., Darling S. B., Su W. F., Mater. Today, 2013, 16(9), 326—336 |
| 21 | Yang D., Löhrer F. C., Körstgens V., Schreiber A., Bernstorff S., Buriak J. M., Müller⁃Buschbaum P., ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4(2), 464—470 |
| 22 | Bi Z. Z., Naveed H. B., Wu H. B., Zhang C. K., Zhou X. B., Wang J., Wang M., Wu X. H., Zhu Q. L., Zhou K., Chen K., Wang C., Tang Z., Ma W., Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(18), 2103735 |
| 23 | Meng H. F., Liao C. T., Deng M., Xu X. P., Yu L. Y., Peng Q., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(41), 22554—22561 |
| 24 | Peng W. H., Lin Y. B., Jeong S. Y., Firdaus Y., Genene Z., Nikitaras A., Tsetseris L, Whoo H. Y., Zhu W. G., Anthopoulos T. D., Wang E. G., Chem. Mater., 2021, 33(18), 7254—7262 |
| 25 | Zhuang W. L., Wang S. H., Tao Q., Ma W., Berggren M., Fabiano S., Zhu W. G., Wang E. G., Macromolecules, 2021, 54(2), 970—980 |
| 26 | Xia H. Zhang Y., Deng W. Y., Liu K., Xia X. X., Su C. J., Jeng U. S., Zhang M., Huang J. M., Huang J. W., Yan C. Q., Wong W. Y., Lu X. H., Zhu W. G., Li G., Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(10), 2107659 |
| 27 | Li X. J., Luo S. W., Sun H. L., Sung H. H. Y., Yu H., Liu T., Xiao Y. Q., Bai F. J., Pan M. G., Lu X. H., Williams I. D., Guo X. G., Li Y. F., Yan H., Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14(8), 4555—4563 |
| 28 | Liu W. Y., Sun S. M., Xu S. J., Zhang H., Zheng Y. Q., Wei Z. X., Zhu X. Z., Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(18), 2200337 |
| 29 | Song X., Sun P., Sun D. W., Xu Y. C., Liu Y., Zhu W. G., Nano Energy, 2022, 91, 106678 |
| 30 | Jiang Y. Y., Sun L. L., Jiang F. Y., Xie C., Hu L., Dong X. Y., Qin F., Liu T. F., Hu L., Jiang X. S., Zhou, Y. H., Mater. Horiz., 2019, 6(7), 1438—1443 |
| 31 | Zheng Y. Q., Chen Y. J., Cao Y. H., Huang F., Guo Y. L., Zhu X. Z., ACS Mater. Lett., 2022, 4(5), 882—890 |
| 32 | Fu Y. W., Wang L., Guo C. A. H., Li D. H., Cai J. L., Zhou B. J., Chen C., Liu C. H., Liu D., Li W., Wang T., ACS Mater. Lett., 2022, 4(10), 2009—2018 |
| 33 | Liang Q. J., Li W. C., Lu H. D., Yu Z. H., Zhang X. Y., Dong Q. J., Song C. P., Miao Z. C., Liu J. A., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2023, 6(1), 31—50 |
| 34 | Ma Y. F., Zhang Y. M., Zhang H. L., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10(7), 2364—2374 |
| 35 | Yu R. N., Yao H. F., Hong L., Qin Y. P., Zhu J., Cui Y., Li S. S., Hou J. H., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 4645 |
| 36 | Fan H. Y., Yang H., Wu Y., Yildiz O., Zhu X. M., Marszalek T., Blom P. W. M., Cui C. H., Li Y. F., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(37), 2103944 |
| 37 | Bao S. N., Yang H., Fan H. Y., Zhang J. Q., Wei Z. X., Cui C. H., Li Y. F., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(48), 2105301 |
| 38 | Hu K., Zhu C., Ding K., Qin S. C., Lai W. B., Du J. Q., Zhang J. Q., Wei Z. X., Li X. J., Zhang Z. J., Meng L., Ade H., Li Y. F., Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15(10), 4157—4166 |
| 39 | Ye L. L., Cai Y. H., Li C., Zhu L., Xu J. Q., Weng K. K., Zhang K. N., Huang M. F., Zeng M., Li T. F., Zhou E. J., Tan S. T., Hao X. T., Yi Y. P., Liu F., Wang Z. H., Zhan X. W., Sun Y. M., Energy Environ. Sci., 2020, 13(12), 5117—5125 |
| 40 | Zhang D. F., Li Y. F., Li M. J., Zhong W. K., Heumüller T., Li N., Ying L., Brabec C. J., Huang F., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 23(39), 2205338 |
| 41 | Li C. Q., Gu X. B., Chen Z. H., Han X., Yu N., Wei Y. N., Gao J. H., Chen H., Zhang M., Wang A., Zhang J. Q., Wei Z. X., Peng Q., Tang Z., Hao X. T., Zhang X., Huang H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(32), 14731—14739 |
| 42 | Ding Y. Q., Zhang X., Feng H. R., Ke X., Meng L. X., Sun Y. N., Guo Z. Q., Cai Y., Jiao C. C., Wan X. J., Li C. X., Zheng N., Xie Z. Q., Chen Y. S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(24), 27425—27432 |
| 43 | Fan P., Sun W. J., Zhang X. H., Wu Y., Hu Q., Zhang Q., Yu J. S., Russell T. P., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(8), 2008699 |
| 44 | Yang X., Li B., Zhang X. L., Li S. Y., Zhang Q. L., Yuan L., Ko D. H., Ma W. L., Yuan J. Y., Adv. Mater., 2023, doi: 10.1002/ adma.202301604 |
| 45 | Song J. L., Li Y., Cai Y. H., Zhang R., Wang S. J., Xin J. M., Han L. L., Wei D. H., Ma W., Gao F., Sun Y. M., Matter, 2022, 5(11), 4047—4059 |
| 46 | Yu R. N., Yao H. F., Xu Y., Li J. Y., Hong L., Zhang T., Cui Y., Peng Z. X., Gao M. Y., Ye L., Tan Z. A., Hou J. H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(18), 2010535 |
| 47 | Oh J., Jung S., Kang S. H., Park G., Jeong M., Kim S., Lee S., Kim W., Lee B., Lee S. M., Yang C., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(38), 20606—20615 |
| 48 | Fu J. H., Chen S. S., Yang K., Jung S. W. O., Lv J., Lan L. K., Chen H. Y., Hu D. Q., Yang Q. G., Duan T. N., Kan Z. P., Yang C. D., Sun K., Lu S. R., Xiao Z. Y., Li Y. F., iScience, 2020, 23(3), 100965 |
| 49 | Fu J. H., Chen H. Y., Huang P. H., Yu Q. Q., Tang H., Chen S. S., Jung S., Sun K., Yang C., Lu S. R., Kan Z. P., Xiao Z. Y., Li G., Nano Energy, 2021, 84, 105862 |
| 50 | Qin J. Q., Yang Q. G., Oh J., Chen S. S., Odunmbaku G. O., Ouedraogo N. A. N., Yang C., Sun K., Lu S. R., Adv. Sci., 2022, 9(9), 2105347 |
| 51 | Cai G. L., Chen Z., Xia X. X., Li Y. H., Wang J. Y., Liu H., Sun P. P., Li C., Ma R. J., Zhou Y. Q., Chi W. J., Zhang J. Q., Zhu H. M., Xu J. B., Yan H., Zhan X. W., Lu X. H., Adv. Sci., 2022, 9(14), 2200578 |
| 52 | Song X., Zhang K., Guo R. J., Sun K., Zhou Z. X., Huang S. L., Huber L., Reus M., Zhou J. G., Schwartzkopf M., Roth S. V., Liu W. Z., Liu Y., Zhu W. G., Müller⁃Buschbaum P., Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(20), 2200907 |
| 53 | Wang J. Q., Wang Y. F., Bi P. Q., Chen Z. H., Qiao J. W., Li J. Y., Wang W. X., Zheng Z., Zhang S. Q., Hao X. T., Hou J. H., Adv. Mater., 2023, 2301583 |
| 54 | Fu J. H., Fong P. W. K., Liu H., Huang C. S., Lu X. H., Lu S. R., Abdelsamie M., Kodalle T., Sutter⁃Fella C. M., Yang Y., Li G., Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 1760 |
| 55 | Zhang X., Cai J. L., Guo C. H., Li D. H., Du B. C., Zhuang Y., Cheng S. L., Wang L., Liu D., Wang T., Small, 2021, 17(35), 2102558 |
| 56 | Cai J. L., Wang H., Zhang X., Li W., Li D. H., Mao Y. C., Du B. C., Chen M. X., Zhuang Y., Liu D., Qin H. L., Zhao Y., Smith J. A., Kilbride R. C., Parnell A. J., Jones R. A. L., Lidzey D. G., Wang T., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(8), 4230—4238 |
| [1] | 李伟, 陈宸, 刘丹, 王涛. 非富勒烯电子受体多尺度分子聚集体[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230160. |
| [2] | 马伊帆, 张雅敏, 甘胜民, 张昱琛, 费贤, 王汀, 张则琪, 巩雪柱, 张浩力. 基于宽带隙小分子给体第三组分的三元有机光伏器件[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230170. |
| [3] | 张丽婷, 仇丁丁, 张建齐, 吕琨, 魏志祥. 具有热退火提升器件VOC特性的Z构型A⁃DA'D⁃A结构受体[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230164. |
| [4] | 李耀凯, 关诗陶, 左立见, 陈红征. 高性能半透明有机太阳能电池的实现途径[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230166. |
| [5] | 吴济发, 吴汉平, 袁琳, 彭小彬. 协同富勒烯和非富勒烯受体提高卟啉全小分子三元有机太阳能电池的性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230136. |
| [6] | 宋亚男, 游祖豪, 王旭, 刘瑶. 电活性紫罗烯有机光伏界面材料的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230167. |
| [7] | 王家成, 蔡贵龙, 张亚静, 王嘉宇, 路新慧, 占肖卫, 陈兴国. 侧链的简单调制使近红外吸收的非富勒烯受体实现更高的短路电流密度[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230163. |
| [8] | 张立福, 王新康, 陈义旺. 用平衡相容性和相分离的新策略提高有机太阳电池效率[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230177. |
| [9] | 李浩, 杨晨熠, 李佳尧, 张少青, 侯剑辉. 基于受体1-受体2型聚合物给体的高效有机太阳能电池[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230157. |
| [10] | 施世领, 蒋寒曦, 涂雪杨, 鲜开虎, 韩德霞, 李艳如, 姚翔, 叶龙, 费竹平. 基于芳环取代酰亚胺端基的非富勒烯受体材料的合成与光伏性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230182. |
| [11] | 郭子琦, 焦灿灿, 吴思敏, 孟令贤, 孙延娜, 柯鑫, 万相见, 陈永胜. 小分子给体桥联单元烷基链取代位置对光伏器件性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230180. |
| [12] | 张伟超, 杨朔, 李世麟, 张莹玉, 张渊, 张弘, 周惠琼. β-丙氨酸作为有机太阳能电池双重修饰添加剂的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230185. |
| [13] | 杨航, 凡晨岭, 崔乃哲, 李肖肖, 张雯婧, 崔超华. 添加剂和溶剂退火协同优化制备高性能厚膜有机太阳能电池[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(9): 20230162. |
| [14] | 张亿, 单通, 王焱, 钟洪亮. 以锗为桥接原子的受体材料及其在有机太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230050. |
| [15] | 何韦, 陈飞, 李鸿祥, 王嘉宇, 秦家强, 崔宁博, 严岑琪, 程沛. 基于三氟苯甲酸自组装阳极界面层的高性能有机太阳能电池[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||