

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (11): 3247.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210509
收稿日期:2021-07-16
出版日期:2021-11-10
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
袁荃
E-mail:yuanquan@whu.edu.cn
基金资助:
XI Jing, CHEN Na, YANG Yanbing, YUAN Quan( )
)
Received:2021-07-16
Online:2021-11-10
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
YUAN Quan
E-mail:yuanquan@whu.edu.cn
摘要:
长余辉纳米材料具有独特的发光性质, 能在激发光关闭后持续发光. 通过收集激发光关闭后的长余辉发光信号可以有效消除背景信号的干扰. 此外, 长余辉材料在成像时无需原位激发, 可以减少生物体系的组织自发荧光和光散射干扰, 提高生物成像和检测的灵敏度. 由于这种独特的光学特性, 长余辉纳米材料在生物传感/生物成像以及疾病治疗等领域被广泛应用. 近年来, 为满足疾病相关生物标志物的体外检测及体内生物成像的应用要求, 控制合成发光性能优异、 生物相容性好的长余辉纳米材料成为研究热点.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
席京, 陈娜, 杨雁冰, 袁荃. 长余辉纳米材料的控制合成及在疾病诊断中的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3247.
XI Jing, CHEN Na, YANG Yanbing, YUAN Quan. Recent Progress in Controlled Synthesis of Persistent Luminescence Nanomaterials for Diagnosis Applications. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3247.
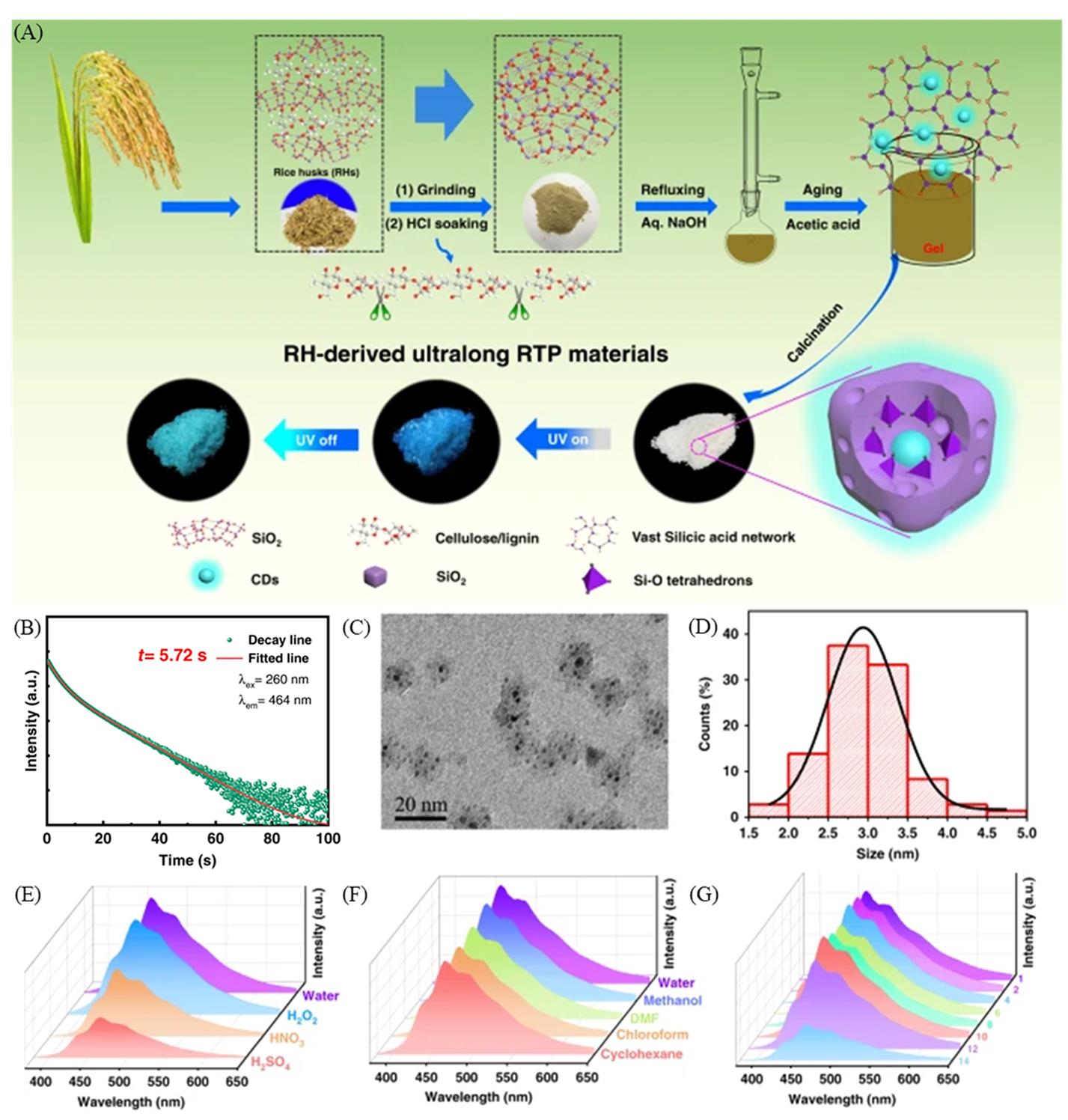
Fig.1 Schematic of the overall process for fabrication of the carbon dots confined by SiO2(A), persistent luminescence decay and fitting curve(red line) of the emission bands at 464?nm with 260?nm excitation(B), HRTEM image of the as synthesized carbon dots confined by SiO2(C), size distribution histogram of the carbon dots confined by SiO2(D), phosphorescence spectra of the untreated carbon dots confined by SiO2 oxidized by H2O2(30%, mass fraction), concentrated HNO3(30%, mass fraction), or H2SO4(98%, mass fraction)(E), phosphorescence spectra of the carbon dots confined by SiO2 in solvents with diffe? rent polarities(F), phosphorescence spectra of the carbon dots confined by SiO2 under pH values from 1.0 to 14.0(G)[39]Copyright 2020, Springer Nature.
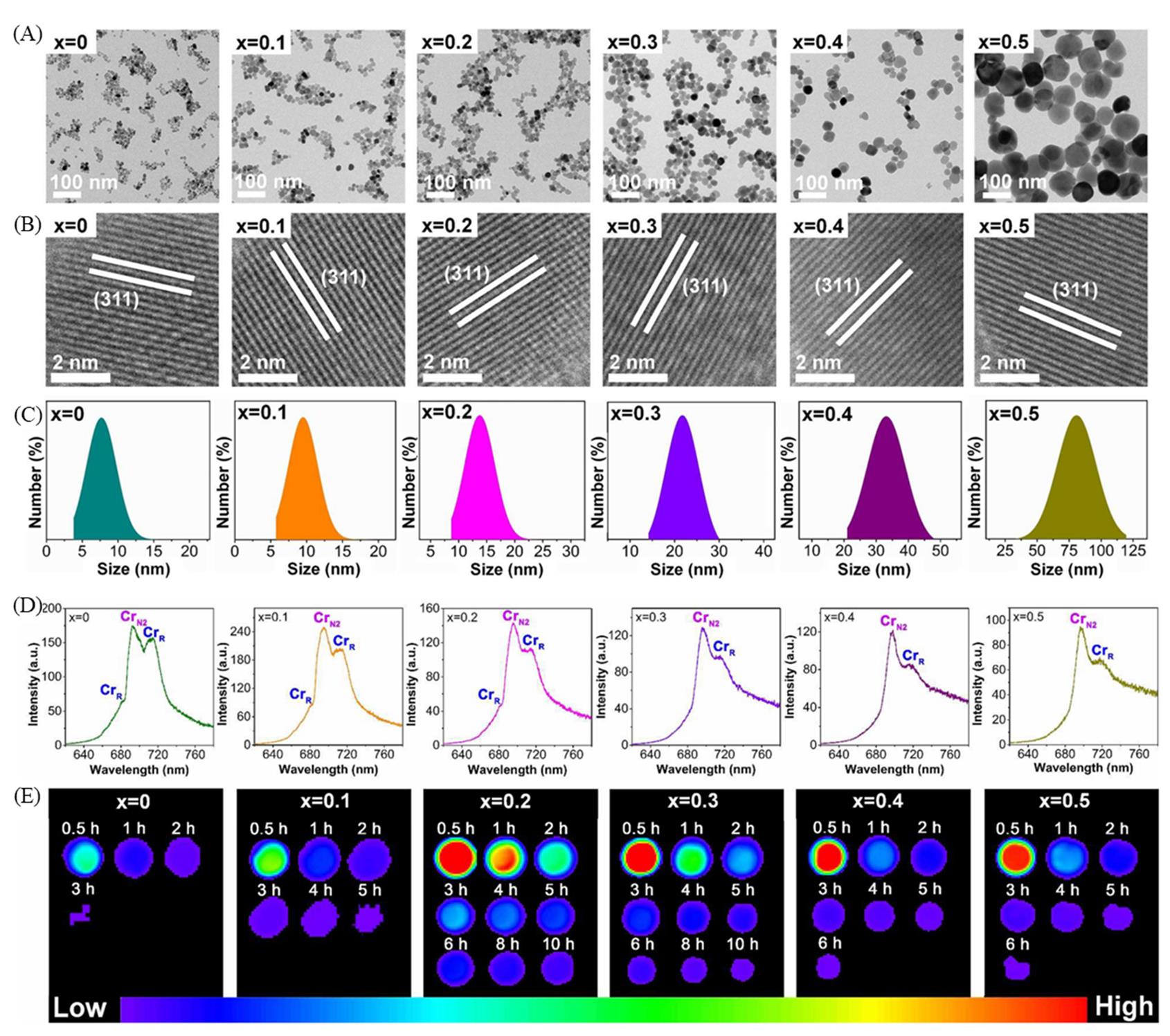
Fig.2 TEM images(A), HRTEM images(B), size distributions(C), photoluminescence spectrum(D), and persistent luminescence decay images(E) of the Zn1+xGa2-2xGexO4:Cr3+ nanoparticles when x increases from 0 to 0.5[9]Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
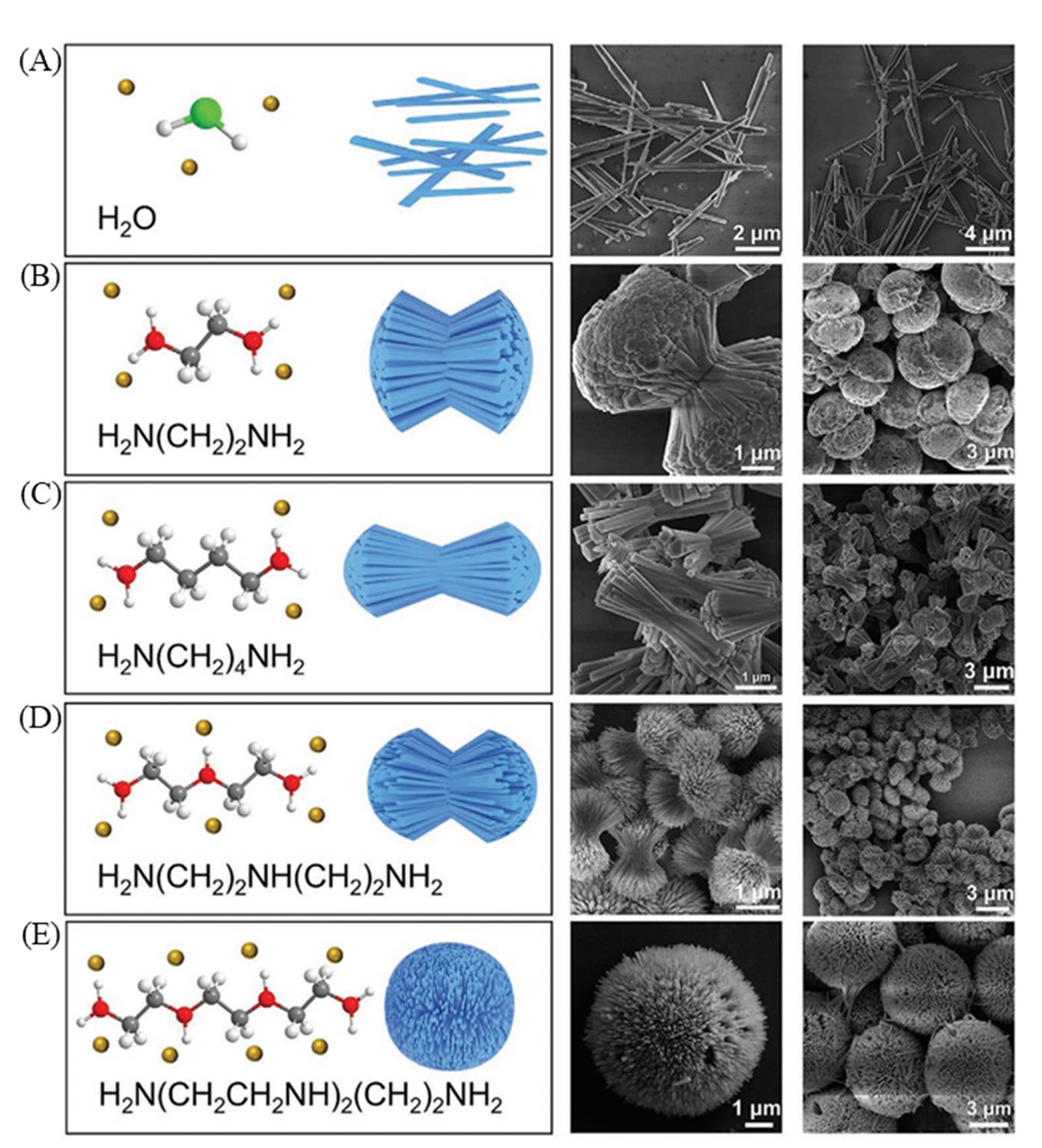
Fig.3 The structure of the used ligand, the schematic illustration, and SEM images of Zn2GeO4:Mn2+ persistent luminescence materials synthesized with pure water(A), ethylenediamine/water(B), butanediamine/water(C), diethylenetriamine/water(D), and triethylenetetramine/water(E)[41]Copyright 2021, John Wiley and Sons.
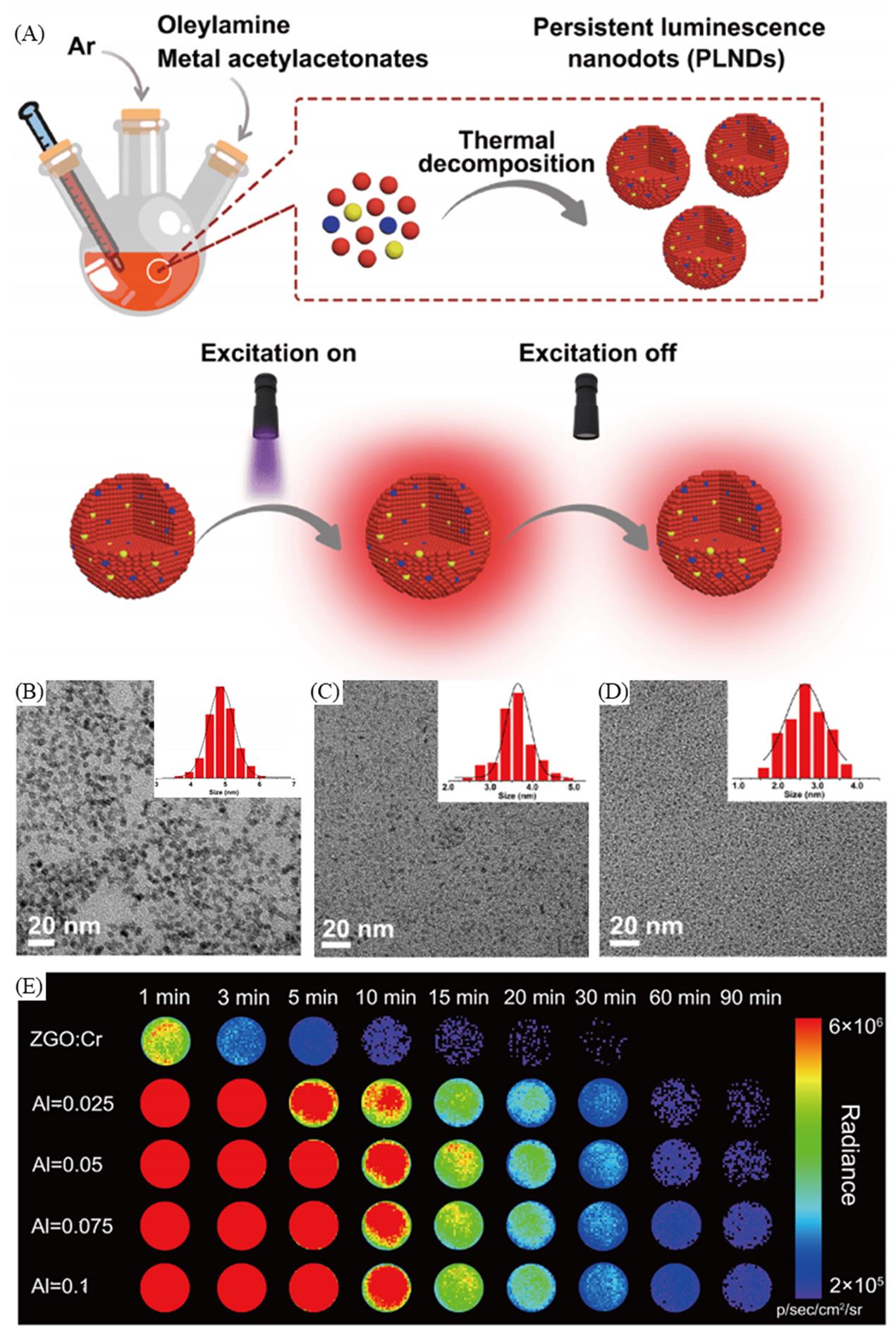
Fig.4 Schematic of the process for fabrication of the persistent luminescence nanoparticles via a thermal decomposition method(A), TEM images and size distribution of ZnGa2O4:Al3+, Cr3+(B), ZnS:Cr3+(C), CaF2(D), persistent luminescence decay images of ZnGa2O4:Cr3+(ZGO:Cr) andZnGa2O4:Al3+, Cr3+(E)[40]Copyright 2020, Springer Nature.
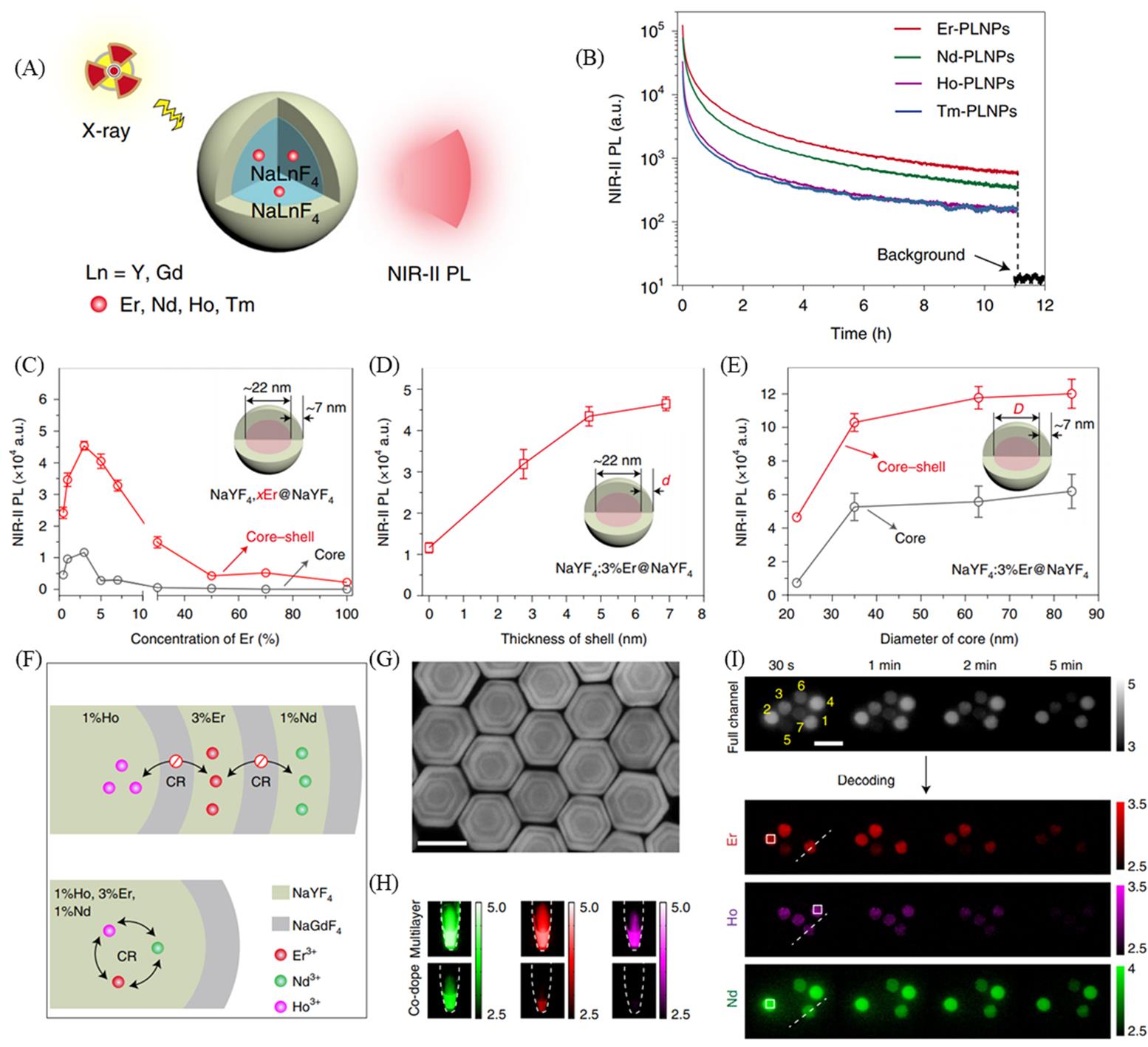
Fig.5 Schematic of X?ray?activated persistent luminescence generated in lanthanide?doped persistent luminescence nanoparticles(PLNPs)(A), persistent luminescence decay curves of typical lanthanide?doped PLNPs(B), influence of activator concentration(C), shell thickness(D), core diameter(E) on the NIR?II persistent luminescence intensity of Er?doped PLNPs, schematic of Ln?doped PLNPs with multilayered(top) and co?doped(bottom) configurations(CR refers to cross?relaxation)(F), high?angle annular dark?field?scanning transmission electron microscopy(G) and NIR?II persistent luminescence images after X?ray irradiation ceases(H) of the multilayered Er/Nd/Ho?doped PLNPs, persistent luminescence coding by different multilayered PLNPs, NIR?II persistent luminescence images were acquired in all three(Nd3+, Ho3+ and Er3+) channels covered with mimic tissue(1% Intralipid) over time(I)[30]Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.
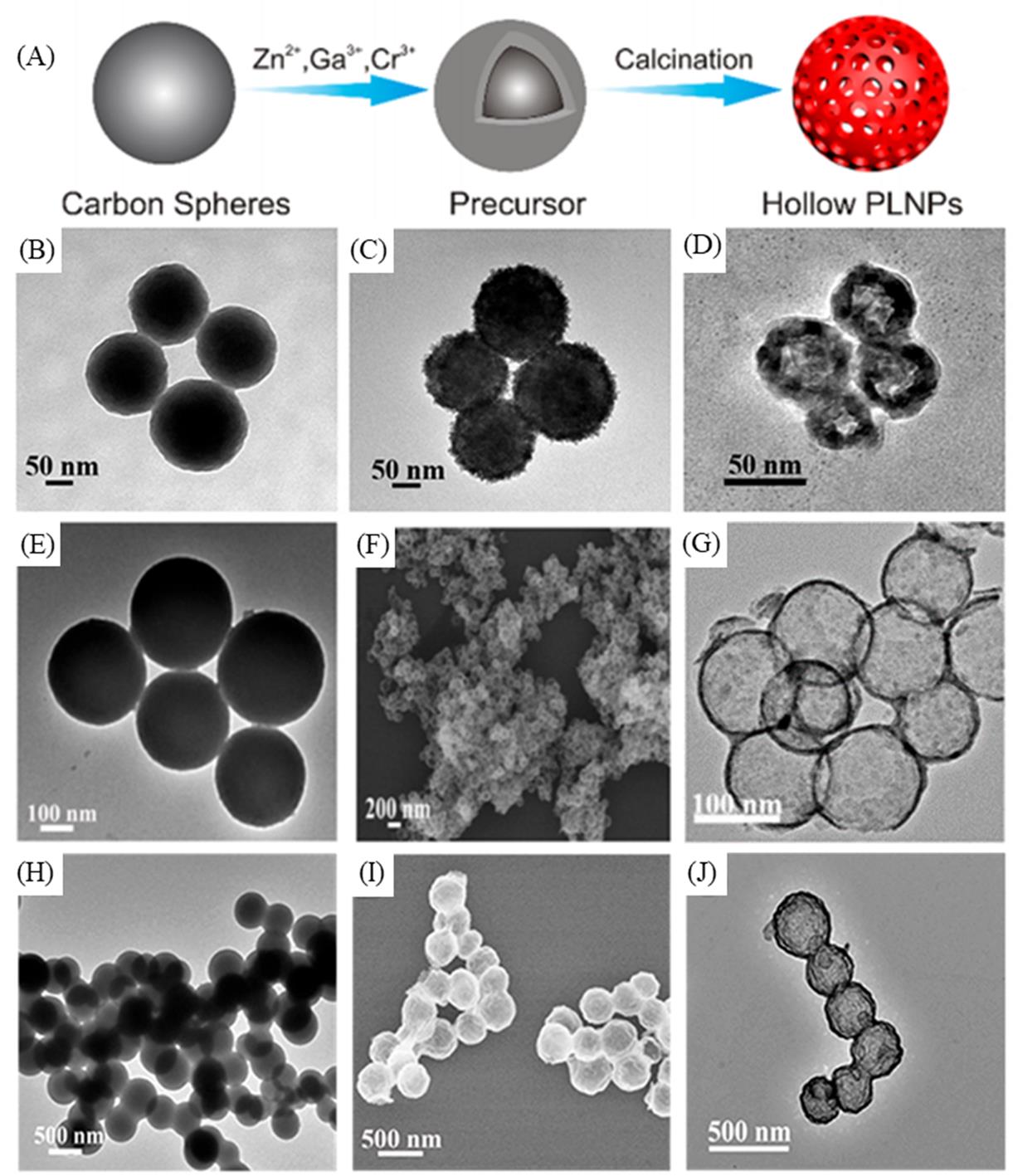

Fig.6 Schematic of the process for fabrication of hollow ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ persistent luminescence nanoparticles(PLNPs)(A), TEM images of the original carbon spheres(B), carbon spheres labeled by precursor ions(C), the hollow PLNPs(D) corresponding to the PLNPs with a size of ca. 50 nm, TEM images of the original carbon spheres(E), carbon spheres labeled by precursor ions(F), the hollow PLNPs(G) corresponding to the PLNPs with a size of ca. 100 nm, TEM images of the original carbon spheres(H), carbon spheres labeled by precursor ions(I), the hollow PLNPs(J) corresponding to the PLNPs with a size of ca. 250 nm[14]Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
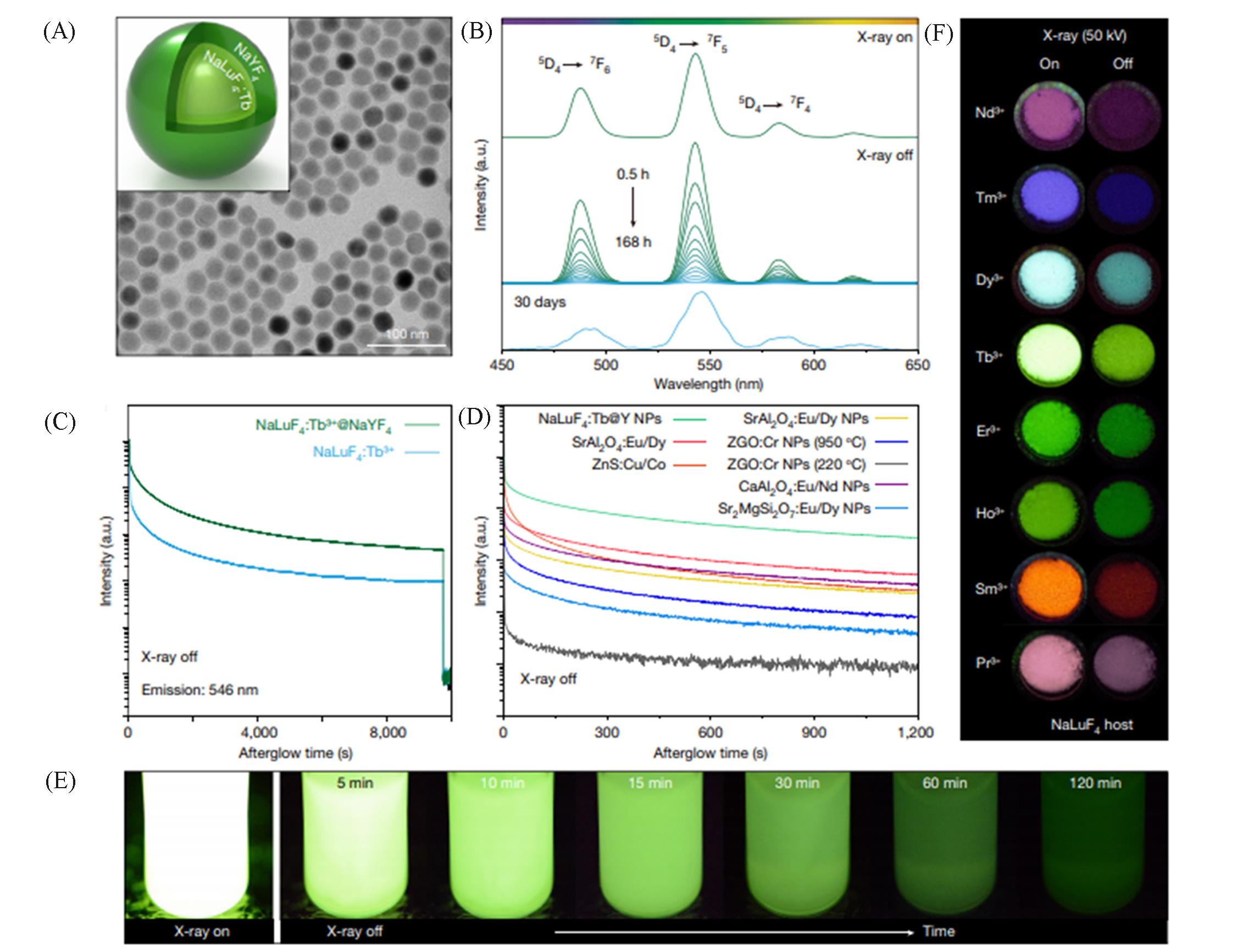
Fig.7 Schematic and TEM image of NaLuF4:Tb3+@NaYF4 nanocrystals(A), phosphorescence spectra of the NaLuF4:Tb3+@NaYF4 nanocrystals, recorded after cessation of X?rays(50 kV) for 0.5—168 h or 30 days(B), phosphorescence decay curve of NaLuF4:Tb3+ and NaLuF4:Tb3+@NaYF4 nanocrystals, monitored at 546 nm after X?rays(50 kV) cessation(C), comparison of phosphorescence decay profiles of various phosphors after cessation of X?ray(50 kV) excitation(NPs refer to nanoparticles)(D), persistent luminescence photographs of NaLuF4:Tb3+@NaYF4 nanocrystals dispersed in 1 mL cyclohexane, and X?ray was set at a voltage of 70 kV with a tube current of 1 mA(E), phosphorescence decay of NaLuF4 nanocrystals doped with various activators(Nd3+, Tm3+, Dy3+, Tb3+, Er3+, Ho3+, Sm3+ and Pr3+)(a.u. refers to arbitrary units)(F)[52]Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.
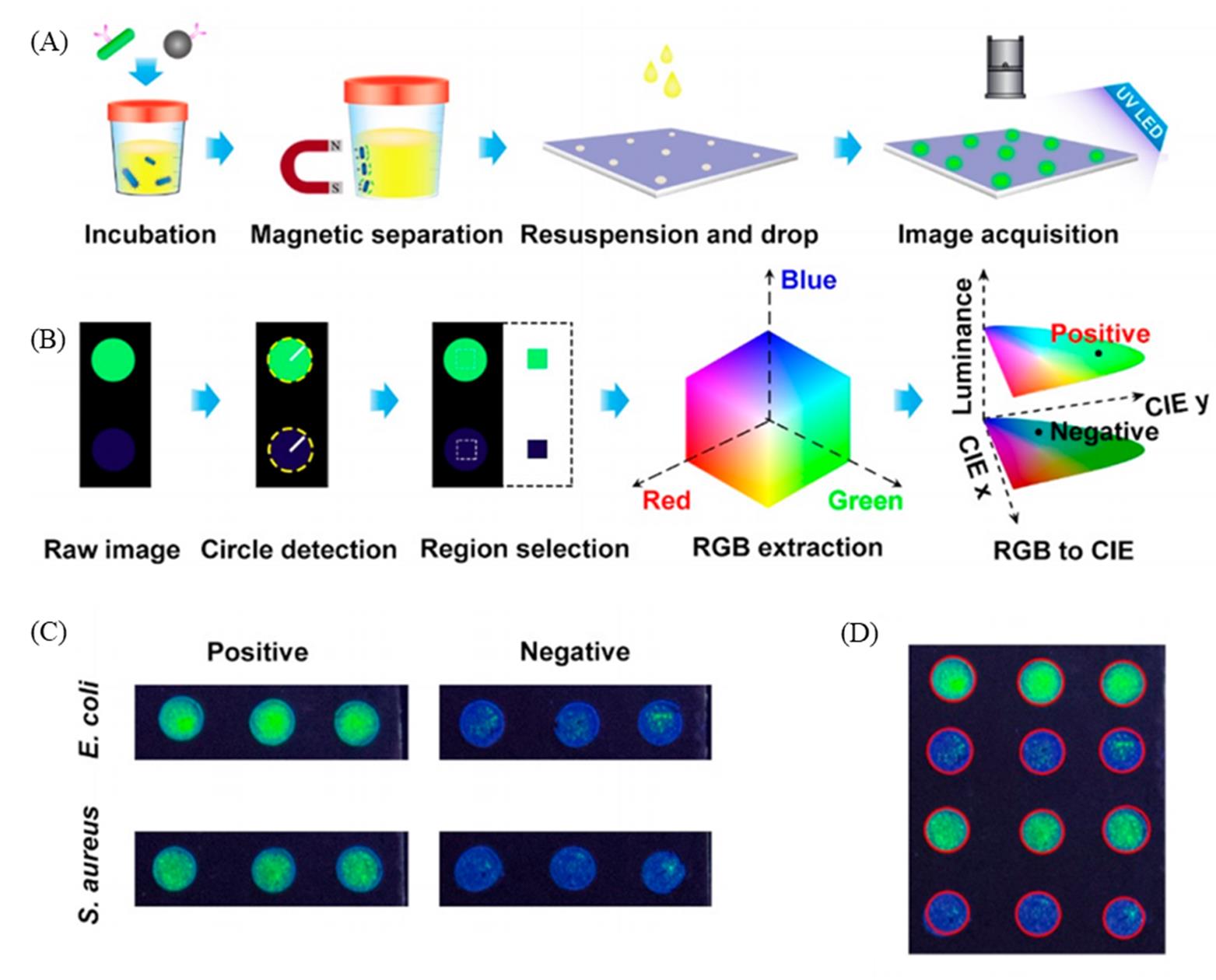
Fig.8 Schematic illustration of process of immunoluminescence assay supported by photonic crystal?based biochips(A), workflow of immunoluminescence image analysis by Python algorithm(B), raw images of PC dots, where positive samples and negative samples were dropped on the biochip when detecting E. coli and S. aureus(C), recognition results of photonic crystal dots by image algorithm(D)[25]Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
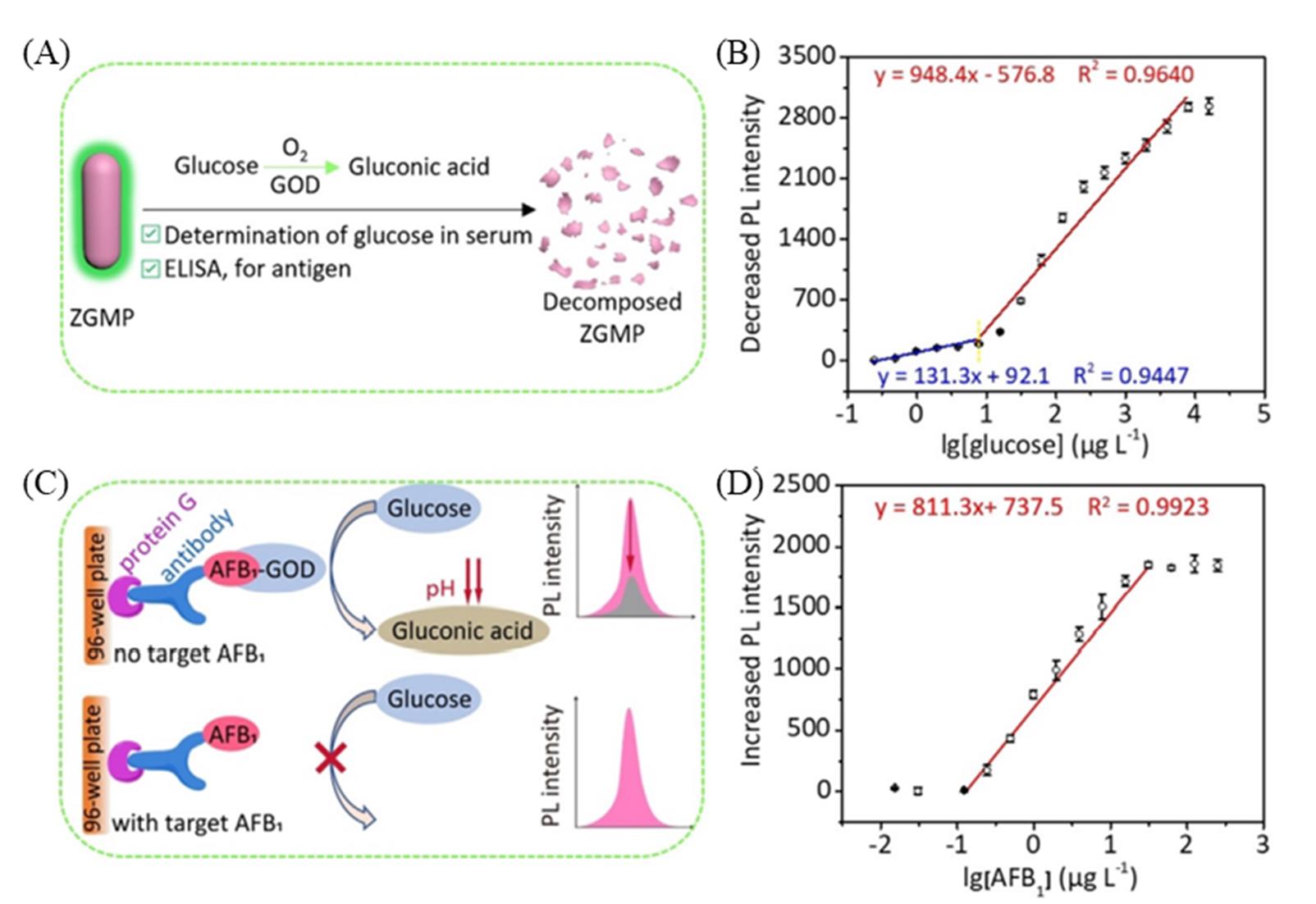
Fig.10 Schematic of the luminescent biodetector for the determination of glucose based on pH?responsive persistent luminescence of ZnGa2O4:Mn2+,Pr3+(A), plot of the decreased PL intensity of ZGMP at 535 nm against lg[glucose](B), schematic illustration of the competitive enzyme?linked immunosorbent assay for AFB1 determination based on GOD?catalyzed glucose oxidation and pH?responsive persistent luminescence of ZGMP(C), plot of the decreased PL intensity of ZGMP at 535 nm against lg[AFB1](D)[29]Copyright 2020, John Wiley and Sons.
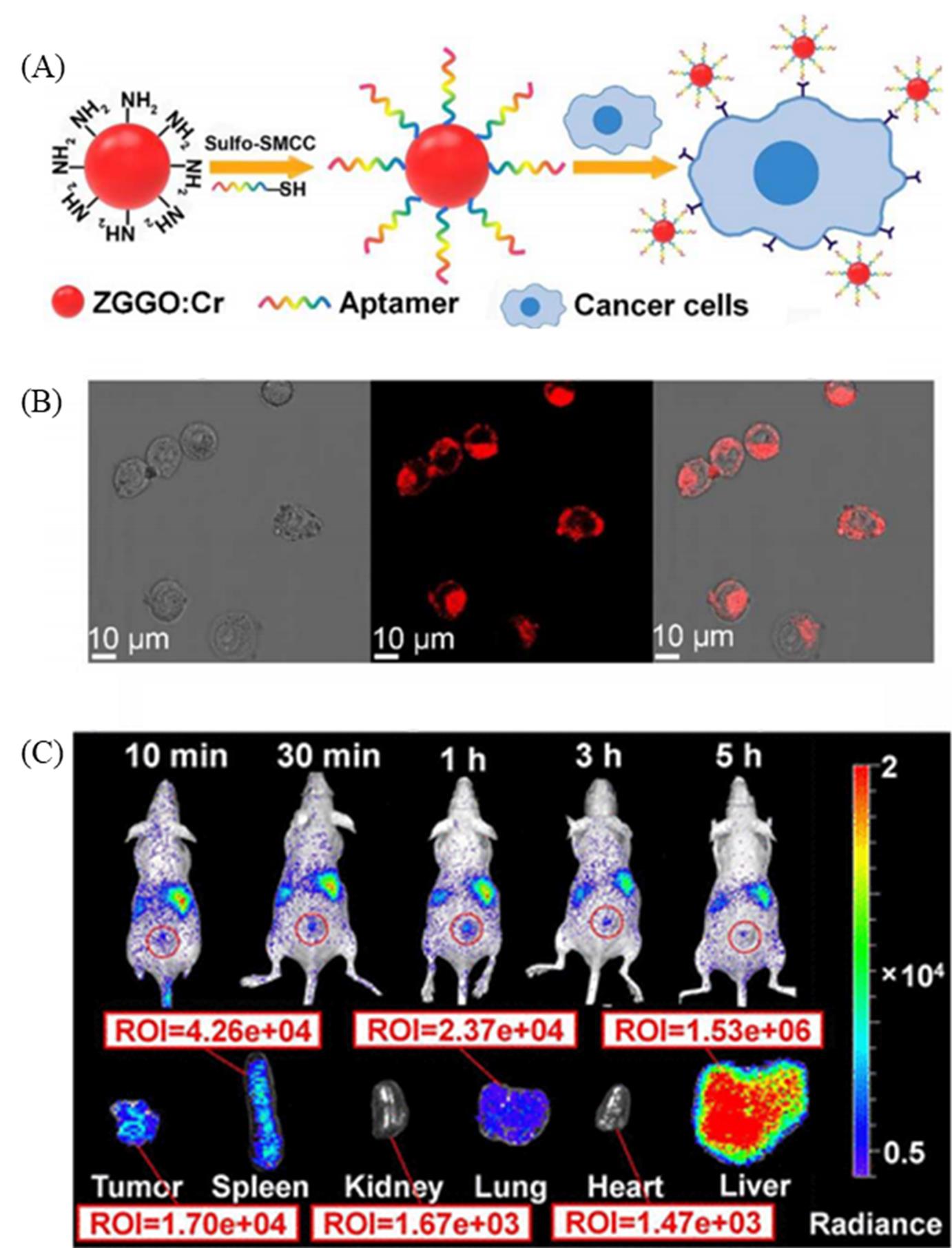
Fig.11 Schematic illustration of construction of aptamer labeled Zn1.2Ga1.6Ge0.2O4:Cr3+ probe for target recognition of cancer cells(A), confocal microscopy images of 4T1 cells incubated with aptamer labeled Zn1.2Ga1.6Ge0.2O4:Cr3+ nanoparticles(B), in vivo and in vitro luminescent images of 4T1 tumor?bearing mice after intravenous injection of aptamer labeled Zn1.2Ga1.6Ge0.2O4:Cr3+ nanoparticles(C)[9]Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
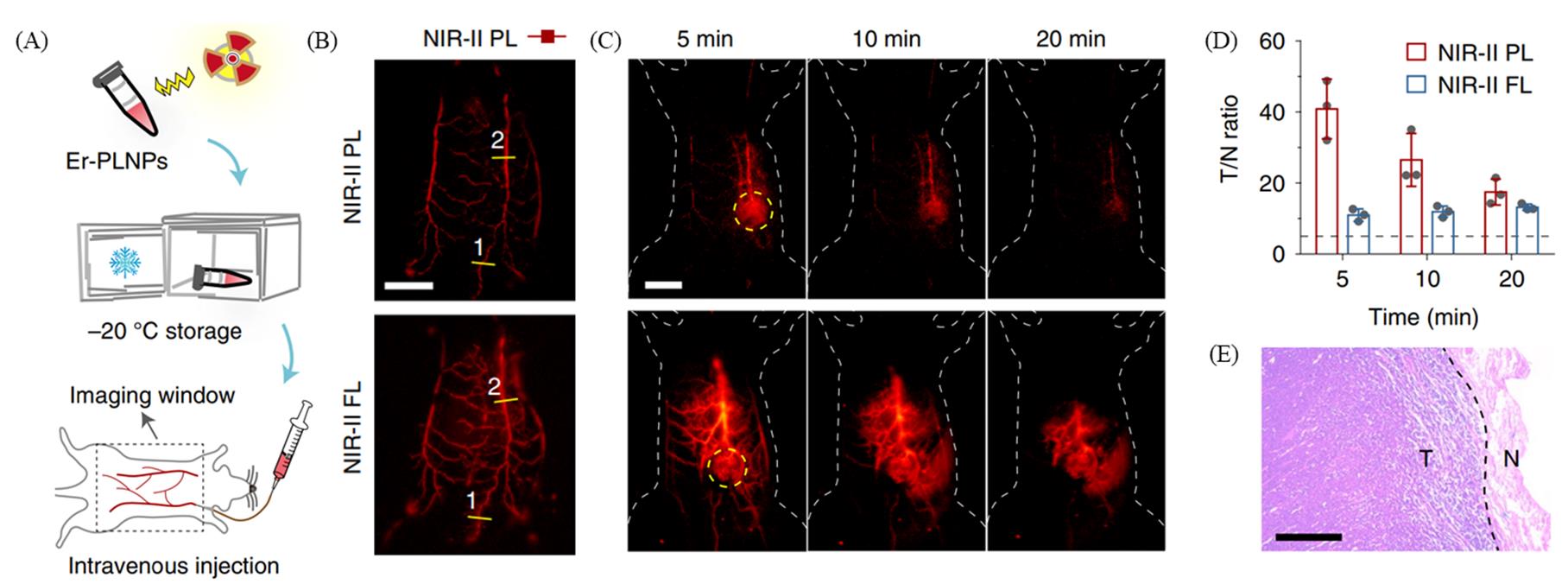
Fig.12 Schematic illustration of process of NIR?II persistent luminescence imaging of blood vessels(A), NIR?II persistent luminescence(top) and NIR?II fluorescence(bottom) images of blood vessels in a living mouse after intravenous injection of NaYF4:3%Er3+@NaYF4 at 10?s postinjection(B), NIR?II persistent luminescence(top) and NIR?II fluorescence(bottom) images of tumors on living mice after multiple injections of NaYF4:3%Er3+@NaYF4(scale bar: 1?cm)(C), tumor?to?normal tissue ratios of the tumors shown in (C), and the black dashed line demarcates the Rose criterion(D), the haematoxylin and eosin staining results of the removed tumor(scale bar: 400 μm)(E)[30]Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.
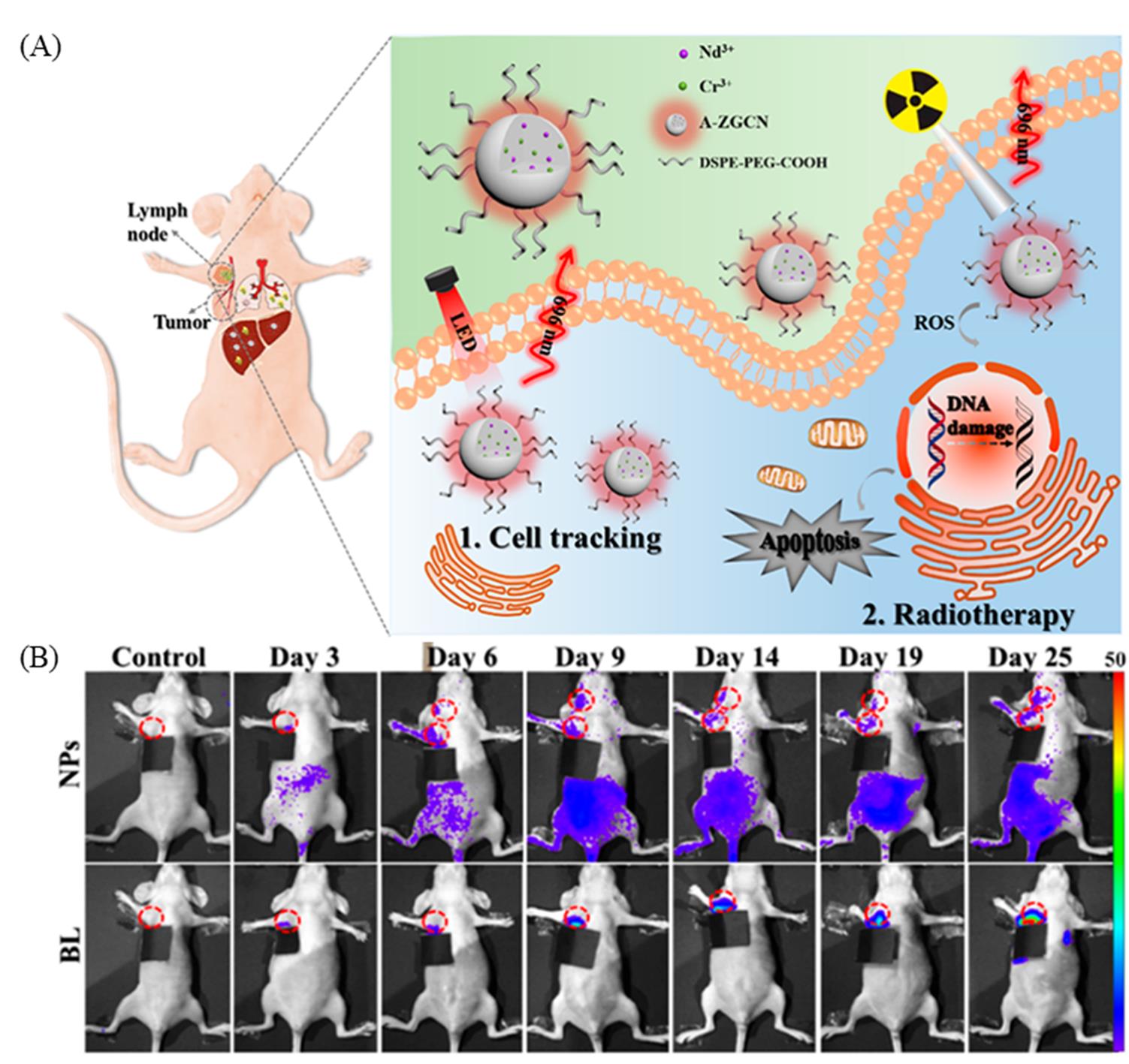
Fig.13 Schematic illustration of in vivo tracking of breast cancer cells and radiotherapy to inhibit tumor metastasis by ZnGa2O4:Cr3+,Nd3+ nanoparticles(A), in vivo persistent luminescence and bioluminescence images of nude mice at different time points after the transplantation of ZnGa2O4:Cr3+,Nd3+ nanoparticles and luciferase labeled breast cancer cells and the lymph nodes being highlighted by red circles(B)[80]Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Matsuzawa T., Aoki Y., Takeuchi N., Murayama Y., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143, 2670—2673 |
| 2 | Li Y., Gecevicius M., Qiu J. R., J. Cheminformatics, 2016, 45, 2090—2136 |
| 3 | Pan Z., Lu Y. Y., Liu F., Nat. Mater., 2011, 11, 58—63 |
| 4 | Wang J., Ma Q., Wang Y., Shen H., Yuan Q., Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 6204—6218 |
| 5 | de Chermont Q., Chaneac C., Seguin J., Pelle F., Maitrejean S., Jolivet J. P., Gourier D., Bessodes M., Scherman D., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007,104, 9266—9271 |
| 6 | Li N., Li Y., Han Y., Pan W., Zhang T., Tang B., Anal. Chem., 2014,86, 3924—3930 |
| 7 | Zhang K. Y., Yu Q., Wei H., Liu S., Zhao Q., Huang W., Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 1770—1839 |
| 8 | Wang Y., Li Z., Lin Q., Wei Y., Yuan Q., ACS Sensors, 2019, 4, 2124—2130 |
| 9 | Wang J., Ma Q., Hu X. X., Liu H., Zheng W., Chen X., Yuan Q., Tan W., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 8010—8017 |
| 10 | Liang L., Chen N., Jia Y., Ma Q., Wang J., Yuan Q., Tan W., Nano Res., 2019, 12, 1279—1292 |
| 11 | Lin Q., Li Z., Yuan Q., Chinese Chem. Lett., 2019, 30, 1547—1556 |
| 12 | Sun S. K., Wu J. C., Wang H., Zhou L., Zhang C., Cheng R., Kan D., Zhang X., Yu C., Biomaterials, 2019,218, 119328 |
| 13 | Sun S. K., Wang H. F., Yan X. P., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 1131—1143 |
| 14 | Wang J., Li J., Yu J., Zhang H., Zhang B., ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 4246—4258 |
| 15 | Song L., Li P. P., Yang W., Lin X. H., Liang H., Chen X. F., Liu G., Li J., Yang H. H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1707496 |
| 16 | Wu B. Y., Yan X. P., Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 3903—3906 |
| 17 | Wu B. Y., Wang H., Chen J., Yan X. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 686—688 |
| 18 | Tang Y., Song H., Su Y., Lv Y., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 11876—11884 |
| 19 | Xu J., Tanabe S., J. Lumin., 2018, 205, 581—620 |
| 20 | Liu J., Lécuyer T., Séguin J., Mignet N., Scherman D., Viana B., Richard C., Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev., 2019, 138, 193—210 |
| 21 | Zhou Z., Li Y., Peng M., Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 399, 125688 |
| 22 | Thomas L., Eliott T., Gonzalo R. G., Thomas M., Bruno V., Johanne S., Nathalie M., Daniel S., Cyrille R., Theranostics, 2016, 6, 2488—2524 |
| 23 | Abdukayum A., Yang C. X., Zhao Q., Chen J. T., Yan X. P., Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 4096—4101 |
| 24 | Bessière A., Sharma S. K., Basavaraju N., Priolkar K. R., Binet L., Viana B., Bos A., Maldiney T., Richard C., Scherman D., Chem. Mater.,2014, 26, 1365—1373 |
| 25 | Liu H., Li Z., Shen R., Li Z., Yang Y., Yuan Q., Nano Lett., 2021, 21, 2854—2860 |
| 26 | Shi L., Zheng W., Miao H., Liu H., Zhao Y., Microchim. Acta, 2020, 187, 615 |
| 27 | Wang J., Ma Q., Zheng W., Liu H., Yin C., Wang F., Chen X., Yuan Q., Tan W., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 8185—8191 |
| 28 | Zhang L., Lei J., Liu J., Ma F., Ju H., Biomaterials, 2015, 67, 323—334 |
| 29 | Li J., Huang X., Zhao X., Chen L. J., Yan X. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 2398—2405 |
| 30 | Pei P., Chen Y., Sun C., Fan Y., Yang Y., Liu X., Lu L., Zhao M., Zhang H., Zhao D., Liu X., Zhang F., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16, 1011—1018 |
| 31 | Abdukayum A., Chen J. T., Zhao Q., Yan X. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 14125—14133 |
| 32 | Zhao H., Shu G., Zhu J., Fu Y., Gu Z., Yang D., Biomaterials 2019,217, 119332 |
| 33 | Zhang Y., Huang R., Lin Z., Song J., Wang X., Guo Y., Song C., Yu Y., J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 686, 407—412 |
| 34 | Teston E., Richard S., Maldiney T., Lièvre N., Wang G. Y., Motte L., Richard C., Lalatonne Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2015, 21, 7350—7354 |
| 35 | Liu J., Lecuyer T., Seguin J., Mignet N., Scherman D., Viana B., Richard C., Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev., 2019, 138, 193—210 |
| 36 | Zhao B., Zhu Q., Sun X., Li J. G., Ceram. Int., 2021,47, 17000 |
| 37 | Zhang H., Fu X., Niu S., Qin X., J. Lumin., 2008, 128, 1348—1352 |
| 38 | Duan X., Yi L., Huang S., Integr. Ferroelectr., 2020, 210, 74—82 |
| 39 | Sun Y., Liu S., Sun L., Wu S., Hu G., Pang X., Smith A. T., Hu C., Zeng S., Wang W., Liu Y., Zheng M., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 5591 |
| 40 | Lv X., Chen N., Wang J., Yuan Q., Sci. China Mater., 2020, 63, 1808—1817 |
| 41 | Li Z., Wang J., Shen R., Chen N., Qin X., Wang W., Yuan Q., Small, 2021, 17, 2100562 |
| 42 | Lin X. H., Song L., Chen S., Chen X. F., Wei J. J., Li J., Huang G., Yang H. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 41181—41187 |
| 43 | Li Z., Zhang Y., Wu X., Huang L., Li D., Fan W., Han G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015,137, 5304—5307 |
| 44 | Hu S., Li Z., Luo Q., Ma Q., Chen N., Fu L., Wang J., Yang R., Yuan Q., Cryst. Growth Des., 2019, 19, 2322—2328 |
| 45 | Fu L., Wang J., Chen N., Ma Q., Lu D., Yuan Q., Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 6660—6663 |
| 46 | Lan N. M. C. H., Thang C. X., Pham V. H., Kien P. T., Minh V. T. N., Tam T. T. H., Optik, 2019, 199, 163310 |
| 47 | Zou R., Huang J., Shi J. P., Lin H., Zhang X., Wong K. L., Zhang H., Jin D., Wang J., Su Q., Nano Res., 2017, 10, 2070—2082 |
| 48 | Glais E., Pellerin M., Castaing V., Alloyeau D., Touati N., Viana B., Chaneac C., RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 41767—41774 |
| 49 | Beke D., Nardi M. V., Bortel G., Timpel M., Czigany Z., Pasquali L., Chiappini A., Bais G., Rudolf M., Zalka D., Bigi F., Rossi F., Bencs L., Pekker A., Markus B. G., Salviati G., Saddow S. E., Kamaras K., Simon F., Gali A., Chem. Mater., 2021, 33, 2457—2465 |
| 50 | Wang H. F., Chen X., Feng F., Ji X., Zhang Y., Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 8923—8929 |
| 51 | Lee S. S., Zhu H., Contreras E. Q., Prakash A., Puppala H. L., Colvin V. L., Chem. Mater., 2012, 24, 424—432 |
| 52 | Ou X., Qin X., Huang B., Zan J., Wu Q., Hong Z., Xie L., Bian H., Yi Z., Chen X., Wu Y., Song X., Li J., Chen Q., Yang H., Liu X., Nature, 2021, 590, 410—415 |
| 53 | Li L., Pandey A., Werder D. J., Khanal B. P., Pietryga J. M., Klimov V. I., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 1176—1179 |
| 54 | Wei X., Huang X., Zeng Y., Jing L., Gao M., ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 12113—12124 |
| 55 | Shi J., Sun X., Li J., Man H., Shen J., Yu Y., Zhang H., Biomaterials, 2015, 37, 260—270 |
| 56 | Li Z. J., Shi J. P., Zhang H. W., Sun M., Opt. Express., 2014, 22, 10509—10518 |
| 57 | Li Z., Zhang Y., Xiang W., Wu X., Wu X., Maudgal R., Zhang H., Han G., Adv. Sci., 2015, 2, 1500001 |
| 58 | Li Z. J., Zhang Y. J., Zhang H. W., Fu H. X., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2013, 176, 48—54 |
| 59 | Shi J. P., Sun M., Sun X., Zhang H. W., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016,4, 7845—7851 |
| 60 | Zou R., Gao Y., Zhang Y., Jiao J., Wang J., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2021, 13, 9667—9680 |
| 61 | Shi J. P., Fu H. X., Sun X., Shen J., Zhang H. W., J. Mater. Chem. B,2015, 3, 635—641 |
| 62 | Dai W. B., Lei Y. F., Ye S., Song E. H., Chen Z., Zhang Q. Y., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016, 4, 1842—1852 |
| 63 | Li Z., Yu N., Zhou J., Li Y., Zhang Y., Huang L., Huang K., Zhao Y., Kelmar S., Yang J., Han G., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2003881 |
| 64 | Feng Y., Liu R., Zhang L., Li Z., Su Y., Lv Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2019, 11, 44978—44988 |
| 65 | Sanad M., Rayan D. A., Rashad M. M., Opt. Quant. Electron., 2019, 51, 192 |
| 66 | Cheng B., Zhang Z., Han Z., Xiao Y., Lei S., Crystengcomm, 2011, 13, 3545—3550 |
| 67 | Boiko V., Dai Z., Markowska M., Leonelli C., Hreniak D., Sci. Rep., 2021, 11, 141 |
| 68 | Mandl G. A., van der Heggen D., Cooper D. R., Joos J. J., Seuntjens J., Smet P. F., Capobianco J. A., Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 20759—20766 |
| 69 | Moon J. W., Kim J. S., Park J. H., Ivanov I. N., Phelps T. J., Acta Biomater., 2019, 97, 557—564 |
| 70 | Elsagh M., Rajabi M., Amini E., J. Mater. Sci⁃Mater. El., 2014, 25, 1612—1619 |
| 71 | Srivastava B. B., Kuang A., Mao Y. B., Chem. Commun., 2015,51, 7372—7375 |
| 72 | Zhao Y., Zheng F., Shi L., Liu H., Ke W., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2019, 11, 40669—40676 |
| 73 | Zhang Y., Huang R., Lin Z., Song J., Wang X., Guo Y., Song C., Yu Y., J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 686, 407—412 |
| 74 | Feng F., Chen X., Li G., Song L., Hong Z., Wang H. F., ACS Sensors, 2018, 3, 1846—1854 |
| 75 | Li J., Yang C., Wang W. L., Yan X. P., Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 14931—14937 |
| 76 | Yang S. H., Zhang H. Y., Huang C. C., Tsai Y. Y., Liao S. M., Appl. Phys. A: Mater., 2021, 127, 588 |
| 77 | Li N., Diao W., Han Y., Pan W., Zhang T., Tang B., Chem. Eur. J., 2014, 20, 16488—16491 |
| 78 | Liu J. L., Zhao X., Chen L. J., Pan L. M., Yan X. P., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93, 7348—7354 |
| 79 | Zhao H., Liu C., Gu Z., Dong L., Li F., Yao C., Yang D., Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 252—260 |
| 80 | Liu H., Ren F., Zhou X., Ma C., Wang T., Zhang H., Sun Q., Li Z., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91, 15064—15072 |
| 81 | Li Y. J., Yang C. X., Yan X. P., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90, 4188—4195 |
| 82 | Liu J. M., Zhang D. D., Fang G. Z., Wang S., Biomaterials, 2018, 165, 39—47 |
| [1] | 曹舒杰, 李泓君, 管文丽, 任梦田, 周传政. 硫代磷酸酯寡聚核苷酸的立体控制合成研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220304. |
| [2] | 江博文, 陈敬轩, 成永华, 桑微, 寇宗魁. 单原子材料在电化学生物传感中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220334. |
| [3] | 王君旸, 刘争, 张茜, 孙春燕, 李红霞. DNA银纳米簇在功能核酸荧光生物传感器中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [4] | 孙雪峰, 热娜古丽·阿不都热合曼, 杨通胜, 杨倩婷. Cr,In共掺杂MgGa2O4小尺寸近红外长余辉纳米颗粒的制备及发光性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210850. |
| [5] | 徐梦祎, 黄雪雯, 李小杰, 魏玮, 刘晓亚. “串珠状”复合纳米组装体修饰丝网印刷电极构建的生物传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1768. |
| [6] | 王博东, 潘美辰, 卓颖. 二氧化硅纳米颗粒表面原位还原银纳米簇电化学发光传感界面的构建与分子识别[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [7] | 王庆, 何雨秋, 王富安. 多功能脱氧核酶用于生物医学分析的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3334. |
| [8] | 张嘉懿, 丁臻尧, 王丹丹, 陈礼平, 封心建. 基于多孔金结构的三相界面酶电极的制备及高效电化学酶传感性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3167. |
| [9] | 袁中文, 贺利贞, 陈填烽. 单原子催化剂的生物医学应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(12): 2690. |
| [10] | 李慧圆, 雷春阳, 黄燕, 聂舟. 荧光蛋白结构改造及其生物传感应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2324. |
| [11] | 张怡萌, 张慧欣, 刘洋. 外泌体生物分析及其临床应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2306. |
| [12] | 苏高鸣, 沈瑞晨, 谈洁, 袁荃. 长余辉荧光粉在光催化系统中的应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2404. |
| [13] | 郑姗, 刘洋, 陈飘飘, 邢怡晨, 黄朝表. 基于PbS QDs/TiO2 NPs构建新型谷胱甘肽光电化学传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9): 1866. |
| [14] | 周羽婷, 汤玉娇, 邵爽, 戴诗岩, 程圭芳, 何品刚, 方禹之. 构象转换型传感器对汞、 铅、 锶离子的同时检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1621. |
| [15] | 贾宏亮, 赵建伟, 秦丽溶, 赵敏. 基于镍丝负载氧化镍纳米片的尿酸生物传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(2): 240. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||