

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 895.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130766
• 高分子化学 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2013-08-06
出版日期:2014-04-10
发布日期:2014-02-27
作者简介:联系人简介: 邱学青, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事木质素资源化利用的应用基础研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
ZHOU Haifeng, YANG Dongjie, QIU Xueqing*( ), WU Xiaolei
), WU Xiaolei
Received:2013-08-06
Online:2014-04-10
Published:2014-02-27
Contact:
QIU Xueqing
E-mail:cexqqiu@scut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
在室温及水溶液体系中, 采用辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)对亚硫酸法制浆造纸废液的副产物木质素磺酸钠(木钠)进行改性, 通过凝胶渗透色谱、 电位滴定、 红外光谱和核磁共振波谱等表征了HRP改性木钠的结构. 结果表明, HRP可以有效聚合木钠大分子, 调节HRP的用量, 得到不同分子量的木钠产品, 当HRP浓度为6 g/L时, 可使木钠分子量增大155%. HRP可氧化木钠分子上的酚羟基变成苯氧自由基, 该自由基可直接交联, 也可转移到酚羟基的邻位或对位再发生聚合作用, 其聚合方式主要为β-O-4'及β-β'连接. HRP改性还可使木钠磺化度增加27%. 采用静电逐层自组装技术研究了HRP改性对木钠吸附特征的影响, 结果表明, 经HRP改性后, 木钠在平板上的吸附量增大; 对TiO2浆体的分散稳定性能也得到改善, 这主要是因为分子量增大, 空间位阻作用增强; 磺化度增大, 静电排斥作用增强, 从而使TiO2颗粒更好地分散在水中.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
周海峰, 杨东杰, 邱学青, 伍晓蕾. 辣根过氧化物酶改性木质素磺酸钠的结构特征及吸附分散性能. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(4): 895.
ZHOU Haifeng, YANG Dongjie, QIU Xueqing, WU Xiaolei. Structural Characterization, Adsorption and Dispersion Properties of Sodium Lignosulfonate by Horseradish Peroxidase Incubation†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 895.
| Sample | Concentration of HRP/(g·L-1) | Incubation time/h | 10-3 Mn | 10-4 Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D748 | 0 | 0 | 4.8 | 1.40 | 2.92 |
| SL | 0 | 0 | 2.7 | 0.99 | 3.69 |
| HRP-SL 1 | 0.2 | 12 | 2.9 | 1.13 | 3.96 |
| HRP-SL 2 | 0.5 | 12 | 3.3 | 1.42 | 4.25 |
| HRP-SL 3 | 1 | 12 | 3.5 | 1.63 | 4.62 |
| HRP-SL 4 | 3 | 12 | 3.8 | 1.90 | 5.03 |
| HRP-SL 5 | 6 | 12 | 4.6 | 2.50 | 5.47 |
| HRP-SL 6 | 1 | 0.33 | 3.5 | 1.61 | 4.58 |
| HRP-SL 7 | 1 | 0.67 | 3.5 | 1.63 | 4.60 |
| HRP-SL 8 | 1 | 1.0 | 3.6 | 1.65 | 4.63 |
| HRP-SL 9 | 1 | 36 | 3.6 | 1.66 | 4.63 |
| HRP-SL 10 | 6 | 0.33 | 4.6 | 2.48 | 5.45 |
| HRP-SL 11 | 6 | 0.67 | 4.5 | 2.49 | 5.48 |
| HRP-SL 12 | 6 | 1.0 | 4.6 | 2.51 | 5.47 |
| HRP-SL 13 | 6 | 36 | 4.6 | 2.52 | 5.49 |
Table 1 Reaction conditions and molecular weight distribution of SL by HRP incubation
| Sample | Concentration of HRP/(g·L-1) | Incubation time/h | 10-3 Mn | 10-4 Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D748 | 0 | 0 | 4.8 | 1.40 | 2.92 |
| SL | 0 | 0 | 2.7 | 0.99 | 3.69 |
| HRP-SL 1 | 0.2 | 12 | 2.9 | 1.13 | 3.96 |
| HRP-SL 2 | 0.5 | 12 | 3.3 | 1.42 | 4.25 |
| HRP-SL 3 | 1 | 12 | 3.5 | 1.63 | 4.62 |
| HRP-SL 4 | 3 | 12 | 3.8 | 1.90 | 5.03 |
| HRP-SL 5 | 6 | 12 | 4.6 | 2.50 | 5.47 |
| HRP-SL 6 | 1 | 0.33 | 3.5 | 1.61 | 4.58 |
| HRP-SL 7 | 1 | 0.67 | 3.5 | 1.63 | 4.60 |
| HRP-SL 8 | 1 | 1.0 | 3.6 | 1.65 | 4.63 |
| HRP-SL 9 | 1 | 36 | 3.6 | 1.66 | 4.63 |
| HRP-SL 10 | 6 | 0.33 | 4.6 | 2.48 | 5.45 |
| HRP-SL 11 | 6 | 0.67 | 4.5 | 2.49 | 5.48 |
| HRP-SL 12 | 6 | 1.0 | 4.6 | 2.51 | 5.47 |
| HRP-SL 13 | 6 | 36 | 4.6 | 2.52 | 5.49 |
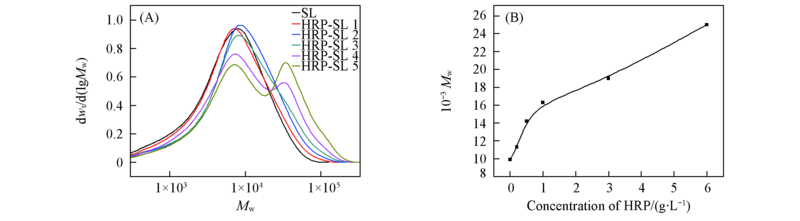
Fig.1 Effect of concentration of HRP on molecular weight distribution of SL by HRP incubation (A) Molecular weight distribution; (B) relationship of molecular weight and concentration of HRP.
| Sample | Concentration of phenolic group/(mmol·g-1) | Concentration of sulfonic group/(mmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| SL | 2.35 | 1.30 |
| HRP-SL 6 | 1.72 | 1.42 |
| HRP-SL 7 | 1.70 | 1.43 |
| HRP-SL 8 | 1.74 | 1.42 |
| HRP-SL 3 | 1.70 | 1.44 |
| HRP-SL 9 | 1.71 | 1.41 |
| HRP-SL 10 | 1.33 | 1.64 |
| HRP-SL 11 | 1.32 | 1.63 |
| HRP-SL 12 | 1.32 | 1.61 |
| HRP-SL 5 | 1.34 | 1.64 |
| HRP-SL 13 | 1.32 | 1.65 |
Table 2 Phenolic and sulfonic group content of SL by HRP incubation
| Sample | Concentration of phenolic group/(mmol·g-1) | Concentration of sulfonic group/(mmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| SL | 2.35 | 1.30 |
| HRP-SL 6 | 1.72 | 1.42 |
| HRP-SL 7 | 1.70 | 1.43 |
| HRP-SL 8 | 1.74 | 1.42 |
| HRP-SL 3 | 1.70 | 1.44 |
| HRP-SL 9 | 1.71 | 1.41 |
| HRP-SL 10 | 1.33 | 1.64 |
| HRP-SL 11 | 1.32 | 1.63 |
| HRP-SL 12 | 1.32 | 1.61 |
| HRP-SL 5 | 1.34 | 1.64 |
| HRP-SL 13 | 1.32 | 1.65 |
| Peak intensity ratio | Assignment | SL | HRP-SL 3 | HRP-SL 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A3436/A1512 | OH stretching in phenolic and aliphatic structures | 1.588 | 1.430 | 1.347 |
| A2937/A1512 | C—H vibration in —CH3 and —CH2 | 1.002 | 0.987 | 0.969 |
| A2850/A1512 | C—H vibration in CH3O— | 0.962 | 0.947 | 0.770 |
| A1703/A1512 | C=O vibration in unconjugated ketone, carbonyl and ester groups | 0.812 | 0.846 | 0.861 |
| A1604/A1512 | Aromatic skeleton vibrations | 1.242 | 1.181 | 1.174 |
| A1462/A1512 | C—H deformations band of asymmetric methyl and methylene | 0.948 | 0.921 | 0.872 |
| A1421/A1512 | Aromatic skeleton vibrations combined with C—H in plane deformations | 0.995 | 0.996 | 0.989 |
| A1366/A1512 | Aliphatic C—H stretching in methyl groups and phenolic hydroxyl | 0.961 | 0.906 | 0.842 |
| A1164/A1512 | G ring plus C—O stretching | 1.686 | 1.437 | 1.318 |
| A1076/A1512 | S ring and C—O stretching | 1.409 | 1.302 | 1.264 |
| A1044/A1512 | S=O stretching | 1.576 | 1.703 | 1.824 |
Table 3 IR bands assignment of SL and the ratio of characteristic peak at 1512 cm-1
| Peak intensity ratio | Assignment | SL | HRP-SL 3 | HRP-SL 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A3436/A1512 | OH stretching in phenolic and aliphatic structures | 1.588 | 1.430 | 1.347 |
| A2937/A1512 | C—H vibration in —CH3 and —CH2 | 1.002 | 0.987 | 0.969 |
| A2850/A1512 | C—H vibration in CH3O— | 0.962 | 0.947 | 0.770 |
| A1703/A1512 | C=O vibration in unconjugated ketone, carbonyl and ester groups | 0.812 | 0.846 | 0.861 |
| A1604/A1512 | Aromatic skeleton vibrations | 1.242 | 1.181 | 1.174 |
| A1462/A1512 | C—H deformations band of asymmetric methyl and methylene | 0.948 | 0.921 | 0.872 |
| A1421/A1512 | Aromatic skeleton vibrations combined with C—H in plane deformations | 0.995 | 0.996 | 0.989 |
| A1366/A1512 | Aliphatic C—H stretching in methyl groups and phenolic hydroxyl | 0.961 | 0.906 | 0.842 |
| A1164/A1512 | G ring plus C—O stretching | 1.686 | 1.437 | 1.318 |
| A1076/A1512 | S ring and C—O stretching | 1.409 | 1.302 | 1.264 |
| A1044/A1512 | S=O stretching | 1.576 | 1.703 | 1.824 |
| δ | Assignment | Amount(DMSO-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL | HRP-SL 5 | ||
| 7.75—7.20 | Aromatic protons in positions C-2 and C-6 with C=O group | 1.05 | 1.16 |
| 7.20—6.80 | H2, H5, H6 in guaiacyl units(G) | 1.00 | 0.83 |
| 6.80—6.20 | H2, H6 in syringyl units(S) | 0.56 | 0.51 |
| 5.75—5.25 | Hα, Hβ in β-β' structures | 0.89 | 1.06 |
| 5.00—4.75 | Hα in β-O-4' structures | 0.73 | 0.95 |
| 4.75—4.07 | Hβ, Hγ in β-O-4' structures | 2.74 | 4.69 |
| 4.00—3.50 | H in methoxyls | 5.66 | 3.57 |
| 3.20—2.90 | 0.61 | 0.76 | |
| 2.56—2.44 | DMSO | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 2.40—2.10 | H in aromatic acetates | 0.50 | 0.58 |
| 1.95—1.85 | H in aliphatic acetates | 0.19 | 0.27 |
| 1.60—0.70 | Aliphatic H | 1.29 | 2.27 |
Table 4 Signal assignment in 1H NMR spectra of SL and results for quantification of functional groups(DMSO signal intensity as reference)
| δ | Assignment | Amount(DMSO-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL | HRP-SL 5 | ||
| 7.75—7.20 | Aromatic protons in positions C-2 and C-6 with C=O group | 1.05 | 1.16 |
| 7.20—6.80 | H2, H5, H6 in guaiacyl units(G) | 1.00 | 0.83 |
| 6.80—6.20 | H2, H6 in syringyl units(S) | 0.56 | 0.51 |
| 5.75—5.25 | Hα, Hβ in β-β' structures | 0.89 | 1.06 |
| 5.00—4.75 | Hα in β-O-4' structures | 0.73 | 0.95 |
| 4.75—4.07 | Hβ, Hγ in β-O-4' structures | 2.74 | 4.69 |
| 4.00—3.50 | H in methoxyls | 5.66 | 3.57 |
| 3.20—2.90 | 0.61 | 0.76 | |
| 2.56—2.44 | DMSO | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 2.40—2.10 | H in aromatic acetates | 0.50 | 0.58 |
| 1.95—1.85 | H in aliphatic acetates | 0.19 | 0.27 |
| 1.60—0.70 | Aliphatic H | 1.29 | 2.27 |
| [1] | Ouyang X. P., Ke L. X., Qiu X. Q., Guo Y. X., Pang Y. X., J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 2009, 30(1), 1—6 |
| [2] | Qiu X. Q., Kong Q., Zhou M. S., Yang D. J., J. Phys. Chem. B,2010, 114(48), 15857—15861 |
| [3] | Yang D. J., Qiu X. Q., Pang Y. X., Zhou M. S., J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 2008, 29(9), 1296—1303 |
| [4] | Zhou M. S., Qiu X. Q., Yang D. J., Lou H. M., J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 2006, 27(6), 851—856 |
| [5] | Yan M. F., Qiu X. Q., Yang D. J., Hu W. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2008, 29(11), 2312—2316 |
| (严明芳, 邱学青, 杨东杰, 胡文莉. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(11), 2312—2316) | |
| [6] | Qiu X. Q., Lou H. M., Yang D. J., Pang Y. X., Fine Chem., 2005, 22(3), 161—167 |
| (邱学青, 楼宏铭, 杨东杰, 庞煜霞. 精细化工, 2005, 22(3), 161—167) | |
| [7] | Kobayashi S., Uyama H., Kimura S., Chem. Rev., 2001, 101(12), 3793—3818 |
| [8] | Veitch N. C., Phytochemistry, 2004, 65(3), 249—259 |
| [9] | Choi Y. J., Chae H. J., Kim E. Y., J. Biosci. Bioeng., 1999, 88(4), 368—373 |
| [10] | Guerra A., Ferraz A., Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2001, 28(4), 308—313 |
| [11] | Dordick J. S., Marletta M. A., Klibanov A. M., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2004, 30(1), 31—36 |
| [12] | Blinkovsky A. M., Dordick J. S., J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 1993, 31(7), 1839—1846 |
| [13] | Liu J., Li L., Cheng J., Wang L., Ye L., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2001, 81(10), 2408—2418 |
| [14] | Tobimatsu Y., Takano T., Kamitakahara H., Nakatsubo F., J. Wood Chem. Technol., 2008, 28(2), 69—83 |
| [15] | Saake B., Argyropoulos D.S., Beinhoff O., Faix O., Phytochemistry,1996, 43(2), 499—507 |
| [16] | Cathala B., Saake B., Faix O., Monties B., J. Chromatogr. A,2003, 1020(2), 229—239 |
| [17] | Boerjan W., Ralph J., Baucher M., Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2003, 54(1), 519—546 |
| [18] | Sasaki S., NishidaT., Tsutsumi Y., Kondo R., FEBS Lett., 2004, 562(1), 197—201 |
| [19] | Tobimatsu Y., Takano T., Kamitakahara H., Nakatsubo F., J. Wood Sci., 2010, 56(3), 233—241 |
| [20] | Grönqvist S., Viikari L., Niku-Paavola M. L., Orlandi M., Canevali C., Buchert J., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005, 67(4), 489—494 |
| [21] | Zhou H. F., Yang D. J., Wu X. L., Qiu X. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(1), 218—224 |
| (周海峰, 杨东杰, 伍晓蕾, 邱学青. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(1), 218—224) | |
| [22] | Yang D.J., Zhou H. F., Xie S. Q., Wu X. L., Qiu X. Q.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2013, (2), 232—240 |
| (杨东杰, 周海峰, 谢绍朐, 伍晓蕾, 邱学青. 高分子学报, 2013, (2), 232—240) | |
| [23] | Childs R. E., Bardsley W. G., Biochem. J., 1975, 145(1), 93 |
| [24] | Qiu X.Q., Wu Y., Deng Y. H., Yang D. J., Ouyang X. P., Yi C. H.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2010, (6), 699—704 |
| (邱学青, 吴渊, 邓永红, 杨东杰, 欧阳新平, 易聪华. 高分子学报, 2010, (6), 699—704) | |
| [25] | De Sousa F., Reimann A., BjöRklund Jansson M., Nilberbrant N., The 11th International Symposium on Wood and Pulping Chemistry(ISWPC), Nice France,2001, 3, 649—653 |
| [26] | Li P. W., Yang D. J., Lou H. M., Qiu X. Q., Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2008, 36(5), 524—529 |
| (李朋伟, 杨东杰, 楼宏铭, 邱学青. 燃料化学学报, 2008, 36(5), 524—529) | |
| [27] | Yang D. J., Qiu X. Q., Zhou M. S., Lou H. M., Energy Convers. Manage., 2007, 48(9), 2433—2438 |
| [28] | Matsushita Y., Yasuda S., Bioresour. Technol., 2005, 96(4), 465—470 |
| [29] | Martínez A., Almendros G., González-Vila F., Fründ R., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 1999, 15(1), 41—48 |
| [30] | Tejado A., Pena C., Labidi J., Echeverria J., Mondragon I., Bioresour. Technol., 2007, 98(8), 1655—1663 |
| [31] | Yuan T. Q., He J., Xu F., Sun R. C., Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 2009, 94(7), 1142—1150 |
| [32] | Sun R., Mott L., Bolton J., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1998, 46(2), 718—723 |
| [33] | Boeriu C. G., Bravo D., Gosselink R. J. A., van Dam J. E. G., Ind. Crop. Prod., 2004, 20(2), 205—218 |
| [34] | Shao L., Qiu J., Feng H., Liu M., Zhang G., An J., Gao C., Liu H., Synth. Met., 2009, 159(17), 1761—1766 |
| [35] | Nugroho Prasetyo E., Kudanga T., Østergaard L., Rencoret J., Gutiérrez A., Del Río J.C., Ignacio Santos J., Nieto L., Jiménez-Barbero J., Martínez A. T., Bioresour. Technol., 2010, 101(14), 5054—5062 |
| [36] | Jahan M. S., Chowdhury D., Islam M. K., Moeiz S., Bioresour. Technol., 2007, 98(2), 465—469 |
| [37] | Kubo S., Kadla J. F., Macromolecules,2004, 37(18), 6904—6911 |
| [38] | Balakshin M., Capanema E., Chen C. L., Gratzl J., Kirkman A., Gracz H., J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym., 2001, 13(1), 1—16 |
| [39] | Toledano A., Serrano L., Garcia A., Mondragon I., Labidi J., Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 157(1), 93—99 |
| [40] | Deng Y. H., Wu Y., Feng X. J., Ouyang X. P., Yang D. J., Qiu X. Q., Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2010, 38(11), 74—79 |
| (邓永红, 吴渊, 冯鑫佳, 欧阳新平, 杨东杰, 邱学青. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(11), 74—79) | |
| [41] | Boisvert J. P., Persello J., Castaing J. C., Cabane B., Colloids Surf., A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects,2001, 178(1), 187—198 |
| [42] | Farrokhpay S., Morris G. E., Fornasiero D., Self P., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2004, 274(1), 33—40 |
| [43] | Yi C. H., Qiu X. Q., Yang D. J., Lou H. M., CIESC Journal,2009, 60(4), 959—964 |
| (易聪华, 邱学青, 杨东杰, 楼宏铭. 化工学报, 2009, 60(4), 959—964) | |
| [44] | Yi C.H., Study of Corrosion Inhibition Performances of Lignosulfonate and Its Action Mechanism, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2005 |
| (易聪华. 木质素磺酸盐的缓蚀性能及作用机理研究, 广州: 华南理工大学, 2005) | |
| [45] | Guo W.Y., Yang D. J., Li R., Qiu X. Q.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2012, (9), 988—996 |
| (郭闻源, 杨东杰, 李荣, 邱学青. 高分子学报, 2012, (9), 988—996) | |
| [46] | Ye D. Z., Jiang X. C., Xia C., Liu L., Zhang X., Carbohydr. Polym., 2012, 89, 876—882 |
| [47] | Chen R., Kokta B. V., Valade J. L., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1980, 25, 2211—2220 |
| [1] | 朱浩天, 金美秀, 唐文思, 苏芳, 李阳光. 过渡金属-联咪唑-Dawson型钨磷酸盐杂化化合物的酶固定化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220328. |
| [2] | 高霞,潘会宾,乔成芳,陈凤英,周元,杨文华. 基于多级孔金属有机骨架构筑HRP固定化酶反应器及其染料降解应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(7): 1591. |
| [3] | 滕渝,杨绍明,柏朝朋,张剑. 基于多壁碳纳米管增敏材料的辣根过氧化物酶分子印迹电化学传感器的制备及对H2O2的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(1): 78. |
| [4] | 范宏亮, 张涛, 金伟, 金钦汉. 基于脱氧核酶的无标记端粒酶检测新方法[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4): 625. |
| [5] | 周明松, 王文利, 杨东杰, 邱学青. 木质素磺酸钠在氧化铁表面的吸附驱动力[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1828. |
| [6] | 周明松, 王文利, 杨东杰, 邱学青. 木质素磺酸钠在氧化铁表面的吸附驱动力[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1822. |
| [7] | 屈建莹, 康世平, 娄童芳, 杜学萍. 基于聚乙烯醇离子液体负载HRP修饰石墨烯/纳米金复合膜的过氧化氢生物传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(9): 2097. |
| [8] | 石虎, 程珊珊, 艾洪奇. 质子化作用对Aβ1—16单体结构特征和聚集机理的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(5): 1214. |
| [9] | 周海峰, 杨东杰, 伍晓蕾, 邱学青. 漆酶改性木质素磺酸钠的结构表征及吸附特征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(1): 218. |
| [10] | 严明芳, 邱学青, 杨东杰, 胡文莉. 木质素磺酸盐的分离提纯[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(11): 2312. |
| [11] | 王新平, 陈志方, 倪华钢, 沈之荃. 端羟基化聚苯乙烯的表面性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(9): 1747. |
| [12] | 汪矫宁, 任吉存. 毛细管电泳流动注射化学发光检测辣根过氧化物酶及其在免疫分析中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(S1): 171. |
| [13] | 李利东, 王齐, 范志强. 铁系后过渡金属催化剂/不同铝氧烷体系制备具有双峰分子量分布的聚乙烯[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(9): 1777. |
| [14] | 张娟, 徐静娟, 陈洪渊. 基于SiO2纳米粒子固定辣根过氧化物酶的生物传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(4): 614. |
| [15] | 王雁峰, 潘继伦, 俞耀庭. 开环棉籽糖分子内交联血红蛋白及其戊二醛的二次交联[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(10): 1845. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||