

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2026, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 20250293.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250293
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Guangjie1, WANG Lei1, TIAN Yanqing1,2( )
)
Received:2025-10-15
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2025-12-07
Contact:
TIAN Yanqing
E-mail:tianyq@sustech.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SONG Guangjie, WANG Lei, TIAN Yanqing. Visual Detection of Shrimp Freshness via Colorimetric Sensors[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2026, 47(1): 20250293.
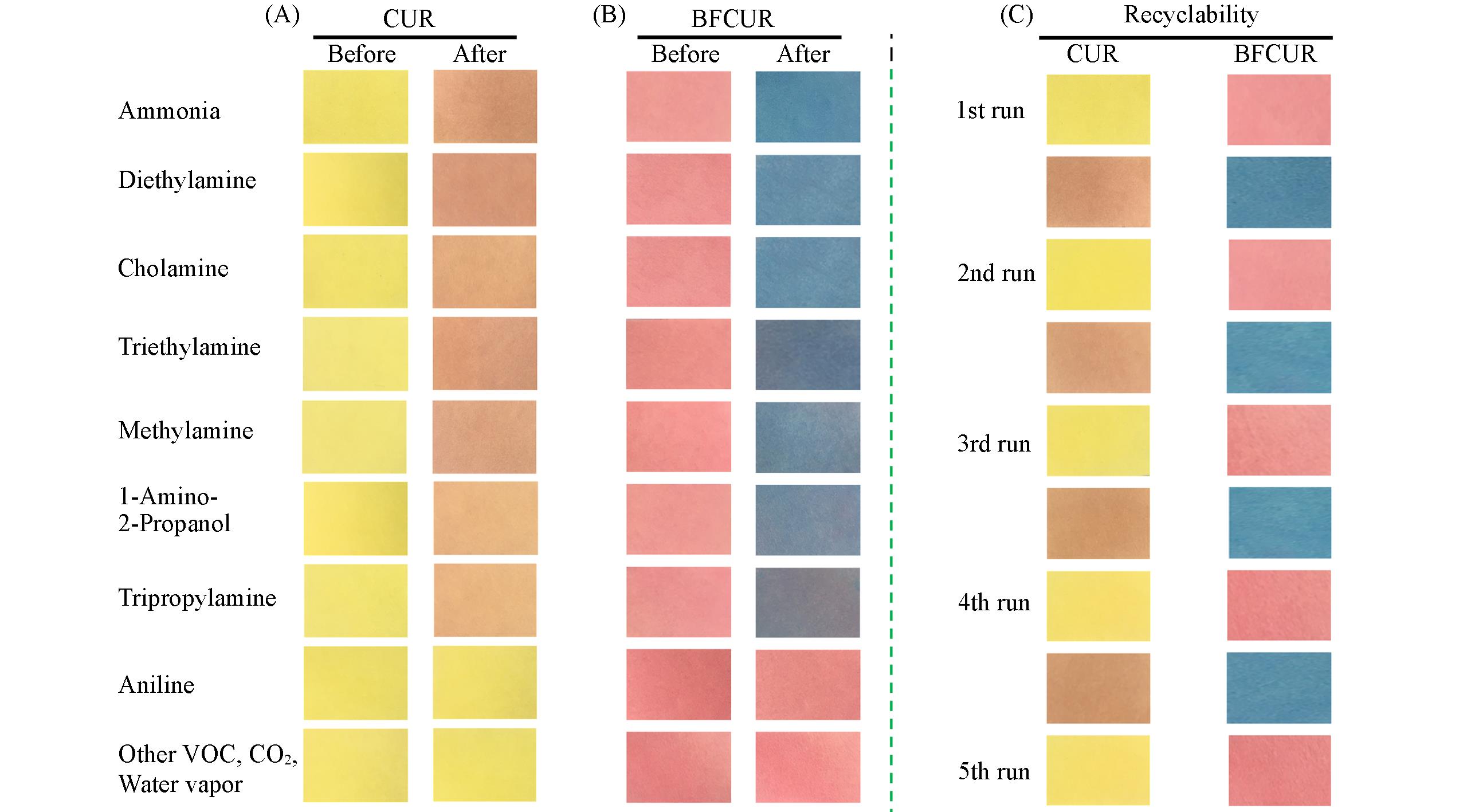
Fig.1 Visual color changes of CUR⁃loaded filter paper strips(A) and BFCUR⁃loaded filter paper strips(B) after exposure to ammonia or volatile amines vapors, visual color changes of CUR⁃loaded filter paper strips(C) and BFCUR⁃loaded filter paper strips(D) after repeated exposure to ammonia vapor and degassing
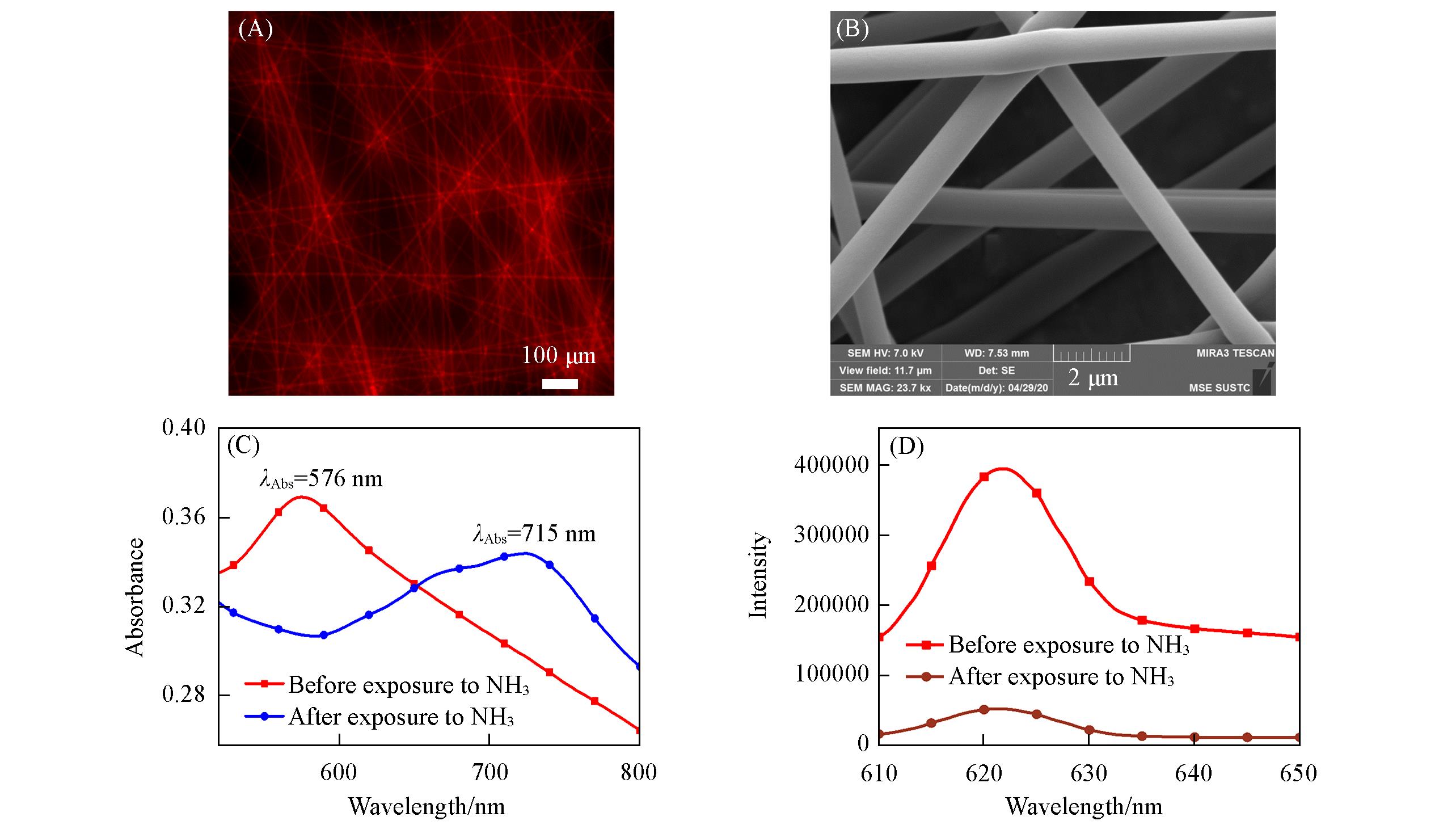
Fig.2 Fluorescence microscopy images of BFCUR⁃ENFs(A), SEM images of BFCUR⁃ENFs(B), UV spectra of BFCUR⁃ENFs before and after exposure to ammonia(C) and fluorescence emission spectra of BFCUR⁃ENFs before and after exposure to ammonia(D)
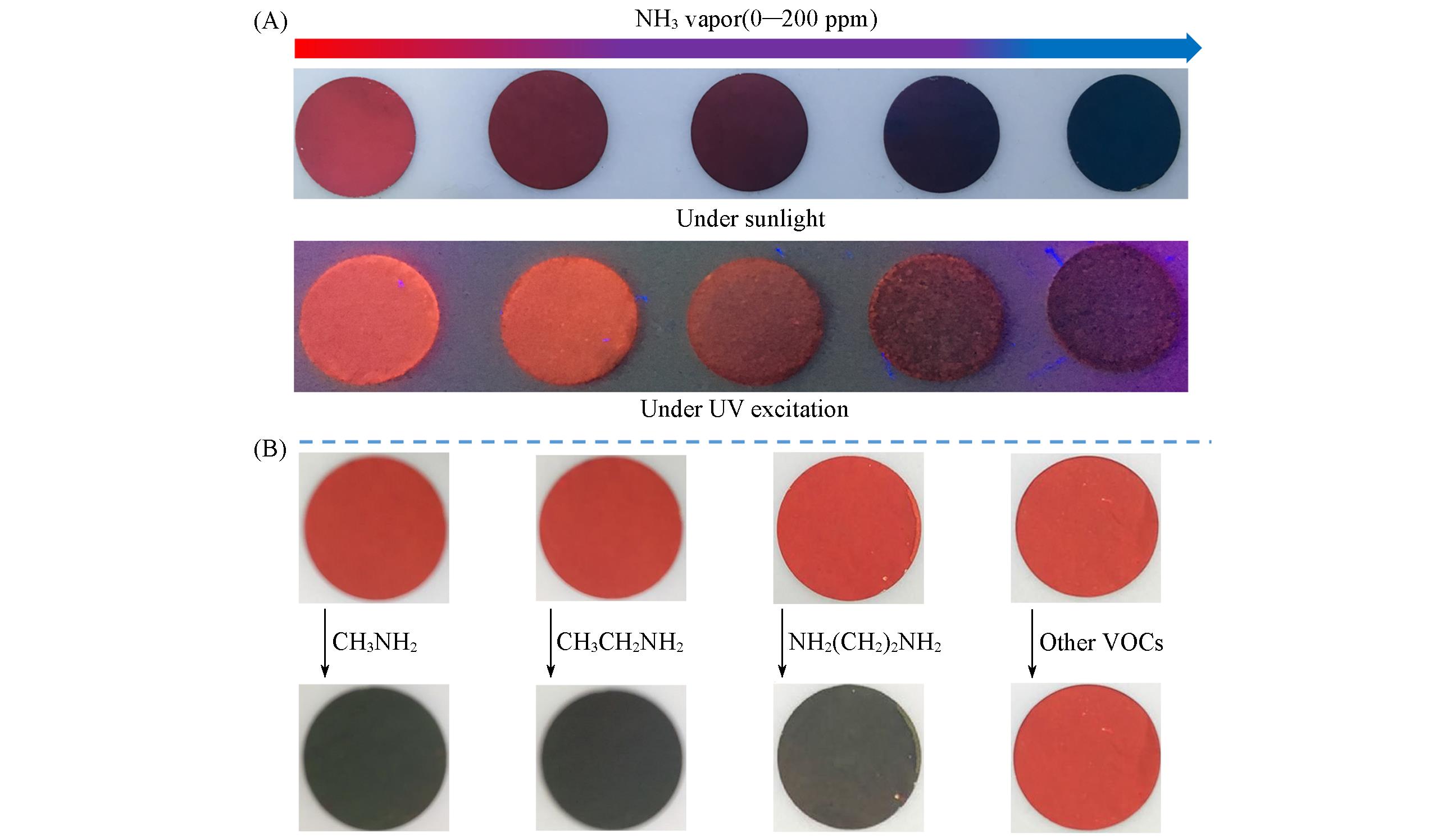
Fig.3 Color changes of BFCUR⁃ENF sensors(A) After exposure to different concentrations of ammonia vapor under sunlight and UV light excitation(365 nm);(B) after exposure to methylamine, ethylamine and ethylenediamine, other VOCs depicted in the figure include the following: n-hexane, toluene, chloroform, tetrahydrofuran, acetone, and methanol.
| [1] | Snyder A. B., Worobo R. W., J. Food Protect., 2018, 81(6), 1035―1040 |
| [2] | Thomas S. W., Joly G. D., Swager T. M., Chem. Rev., 2007, 107(4), 1339―1386 |
| [3] | Shang C., Gang W., He M., Chang X., Yu F. J. S., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2016, 241, 1316―1323 |
| [4] | Vinci G., Antonelli M. L., Food Control, 2002, 13(8), 519―524 |
| [5] | Ruiz⁃Capillas C., Gillyon C. M., Horner W. F. A., Eur. Food Res. Technol., 2000, 210(6), 434―436 |
| [6] | Bene A., Fornage A., Luisier J. L., Pichler P., Villettaz J. C., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2001, 72(2), 184―187 |
| [7] | Rull-Barrull J., d'Halluin M., Le Grognec E., Felpin F. X., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(12), 2525―2528 |
| [8] | Tsumura S., Enoki T., Ooyama Y., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(72), 10144―10147 |
| [9] | Tsien R. Y., Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 1989, 12, 227―253 |
| [10] | Hu Y., Han T., Yan N., Liu J., Liu X., Wang W. X., Lam J. W. Y., Tang B. Z., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(31), 1902240 |
| [11] | Yang M. H., Zhang M., Jia M. Y., Nat. Prod. Rep., 2023, 40(3), 628―645 |
| [12] | Agius N., Magri D. C., Nat. Prod. Commun., 2024, 19(9), 1934578 |
| [13] | Chen Q. M., Han Y. Y., Wang Y. L., Wang S., Wei J., Jiao T. H., Chen X. M., Yuan S. F., Li D., Chen Q. S., Food Chem., 2025, 465, 141945 |
| [14] | Qin W., Zhang P. F., Li H., Lam J. W. Y., Cai Y. J., Kwok R. T. K., Qian J., Zheng W., Tang B. Z., Chem. Sci., 2018, 9(10), 2705―2710 |
| [15] | Huang X., Zou X., Zhao J., Shi J., Li Z., Shen T., Int. J. Food Sci. Technol., 2015, 50(1), 203―209 |
| [16] | de Silva S. A., Loo K. C., Amorelli B., Pathirana S. L., Nyakirang'ani M., Dharmasena M., Demarais S., Dorcley B., Pullay P., Salih Y. A., J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15(27/28), 2791―2795 |
| [17] | Huang M. T., Lou Y. R., Ma W., Newmark H. L., Reuhl K. R., Conney A. H., Cancer Res., 1994, 54(22), 5841―5847 |
| [18] | Hatcher H., Planalp R., Cho J., Tortia F. M., Torti S. V., Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2008, 65(11), 1631―1652 |
| [19] | Ding D., Li K., Liu B., Tang B. Z., Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46(11), 2441―2453 |
| [20] | Kuswandi B., Jayus, Larasati T. S., Abdullah A., Heng L. Y., Food Anal. Method, 2012, 5(4), 881―889 |
| [21] | Jiang S. J.,Qiu J. B.,Lin B. N.,Guo H. Y.,Yang F. F., Spectrochimica Acta Part A―Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2020, 229, 117916 |
| [22] | Maeng B., Kim S., An H., Jung D., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2023, 394, 134420 |
| [23] | Sudhesh P., Sruthi S., Jose M., Vyshnavi K., Aiswarya P., Manu R., Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1), 18961. |
| [24] | Wei X. Y., Liu Z., Fang H. L., Cui Z. Y., He S., Shao W., Polymer, 2025, 319, 16896 |
| [25] | Kaur N., Chopra S., Singh G., Raj P., Bhasin A., Sahoo S. K., Kuwar A., Singh N., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, 6(30), 4872―4902 |
| [26] | Kumar V., Kim K. H., Kumar P., Jeon B. H., Kim J. C., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2017, 342, 80―105 |
| [27] | Rochat S., Swager T. M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(37), 9792―9796 |
| [28] | Xue P. C., Xu Q. X., Gong P., Qian C., Ren A. M., Zhang Y., Lu R., Chem. Commun., 2013, 49(52), 5838―5840 |
| [29] | Hu Y., Han T., Yan N., Liu J., Liu X., Wang W. X., Lam J. W. Y., Tang B. Z., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(31), 1902240 |
| [30] | Gao M., Li S., Lin Y., Geng Y., Ling X., Wang L., Qin A., Tang B. Z., ACS Sensors, 2015, 1(2), 179―184 |
| [31] | Zsila F., Bikadi Z., Simonyi M., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2004, 2(20), 2902―2910 |
| [32] | Pourreza N., Golmohammadi H., Talanta, 2015, 131, 136―141 |
| [33] | Moussa Z., Chebl M., Patra D., J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 2017, 173, 307―317 |
| [34] | Song G. J., Jiang D., Wu J. C., Sun X. Z., Deng M. Y., Wang L., Hao C. X., Shi J. Y., Liu H. T., Tian Y. Q., Chen M. W., Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 440, 135979 |
| [35] | Xue J. J., Wu T., Dai Y. Q., Xia Y. N., Chem. Rev., 2019, 119(8), 5298―5415 |
| [36] | Jia R., Tian W., Bai H., Zhang J., Wang S., Zhang J., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 795―803 |
| [37] | Zhai L., Liu M., Xue P., Sun J., Gong P., Zhang Z., Sun J., Lu R., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 4(34), 7939―7947 |
| [38] | Park H. J., Kim W. J., Lee H. K., Lee D. S., Shin J. H., Jun Y., Yun Y. J., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2018, 257, 846―852 |
| [39] | Lang C., Fang J., Shao H., Ding X., Lin T., Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 11108 |
| [1] | WANG Dandan, CHEN Liping, FENG Xinjian. Three-phase Enzymatic Reaction Interface Based on 3D Branched TiO2 Nanoarrays for High Performance Photoelectrochemical Sensing [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2026, 47(1): 189. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yuwei, DU Yihao, ZHANG Yantu, LI Yunyun. Cataluminescent Sensing of 1,2-Epoxypropane Using Dy₂O₃/La₂O₃ Rare Earth Composite Oxides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(8): 20250108. |
| [3] | REN Shufang, GUO Tong, WANG Zihan, LIU Yahui, CHEN Yu, ZENG Junling. Construction of Molecular Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on 2D Ti3C2T x Nanosheet/Conductive Kochen Black Composite Polymethacrylic Acid and the Detection of Dopamine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(7): 20250040. |
| [4] | LUO Kui, LIN Jiaxi, LI Jianping. Development of a Glycosyl-imprinted Sensor and Rapid Detection of PD-L1 Positive Exosomes in Breast Cancer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(5): 20240524. |
| [5] | LI Jingsong, YANG Sirui, SUN Shimin, LI Zhongbo, ZHANG Lijun. Preparation and Performance Study of Fiber-based Organic Electrochemical Transistor Glucose Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(5): 20240431. |
| [6] | WANG Congcong, ZHOU Hengbo, REN Lifang, SHEN Shigang, MA Huichun, DONG Jiangxue. Dual-emission Carbon Dots Work with Smartphones to Build Portable Fluorescence Colorimetric Sensors for Ag+ and Cu2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(4): 20240422. |
| [7] | YANG Yanmei, RAN Yuqing, WANG Cun. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide Terbium Complex Electrochemiluminescence Material and Sensitive Detection of Tetracycline [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(3): 20240361. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiang, LYU Haiyan, LYU Baoqiang, LYU Xiaoming, LI E, XU Chunli, SU Xiaodong. Nanosheet FeSe-based Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid Detection of Trace Nitrite Ions in Fracturing Flowback Fluid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(11): 20250140. |
| [9] | ZHENG Delun, ZHANG Ruilong. Construction of an Ultrasensitive AFP Photoelectrochemical Analysis Based on the Efficient Carrier Separation Capability of p-n Heterojunction CuO/TiO2 Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(8): 20240183. |
| [10] | WEI Chaoxian, LI Nansheng, PANG Yuanhao, ZHANG Yun, JIN Wenying, YUAN Yali. Synthesis of Carbon Nanopolymers Based on Deep Eutectic Strategy for Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of a Variety of Biological Small Molecules [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(7): 20240103. |
| [11] | CHEN Yating, WANG Peng, GUO Baoying, FU Siyun, LIU Wanning, CHEN Shuyi, SHI Yu, CAI Songliang, ZHENG Shengrun, FAN Jun, ZHANG Weiguang. Assembly of Functionalized MIL-101(Cr)-loaded Quartz Crystal Microbalance Gas Sensors for Formic Acid Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(6): 20240031. |
| [12] | MA Qinzheng, WANG Wei, LIANG Xuting. Graphene⁃gold Nanomaterial Modified Electrode for the Detection of L-Tyrosine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(4): 20230521. |
| [13] | CHEN Xiaoping, WANG Xutan, LIU Ning, WANG Qingxiang, NI Jiancong, YANG Weiqiang, LIN Zhenyu. MOFs-based Microfluidic Chips for Real-time Online Determination of Multiple Heavy Metal Ions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(2): 20230395. |
| [14] | LI Jiahui, ZHANG Jian, YAN Long, FENG Yun, ZHANG Jiali, LIU Yongxin, YANG Shaoming. Preparation and Detection Performance of Norfloxacin Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(12): 20240322. |
| [15] | LI Shixuan, MENG Hua, YIN Xuehu, YI Jinfei, MA Lihong, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, YANG Wenrong, PANG Pengfei. A Double-Chamber Enzymatic Biofuel Cells-based Self-powered Glucose Biosensor Based on Graphene/Gold Nanoparticles/Titanium Carbide Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(12): 20240301. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||