

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 28.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190572
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xinghuo,TANG Jun( ),YANG Yingwei(
),YANG Yingwei( )
)
Received:2019-11-05
Online:2020-01-10
Published:2019-12-17
Contact:
Jun TANG,Yingwei YANG
E-mail:chemjtang@jlu.edu.cn;ywyang@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Xinghuo,TANG Jun,YANG Yingwei. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles-Based Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems Gated by Polymers †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 28.
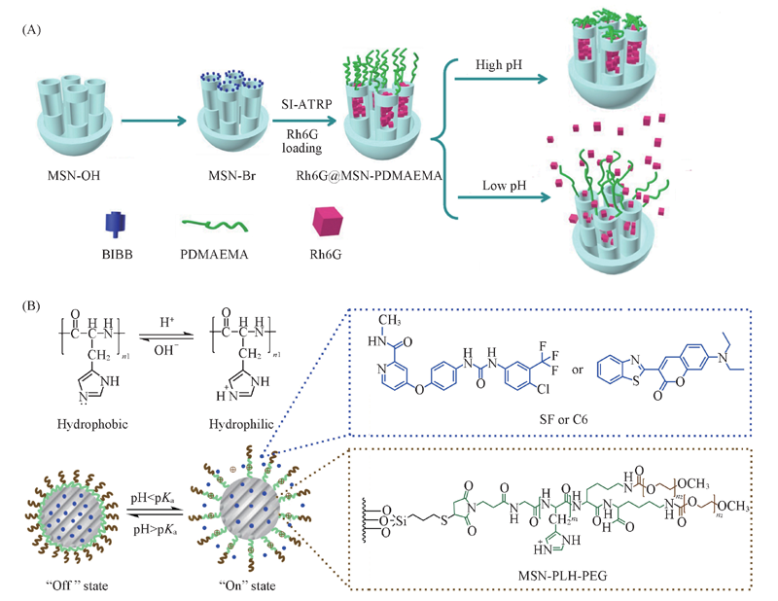
Fig.3 Schematic representation of the preparation process of Rh6G-loaded PDMAEMA-grafted MSN(Rh6G@MSN-PDMAEMA) via SI-ATRP and its pH-responsive behavior[60](A) and illustration of the pH-responsive drug delivery system of MSNs-PLH-PEG[64](B) (A) Copyright 2016, MDPI; (B) copyright 2017, Elsevier Ltd.
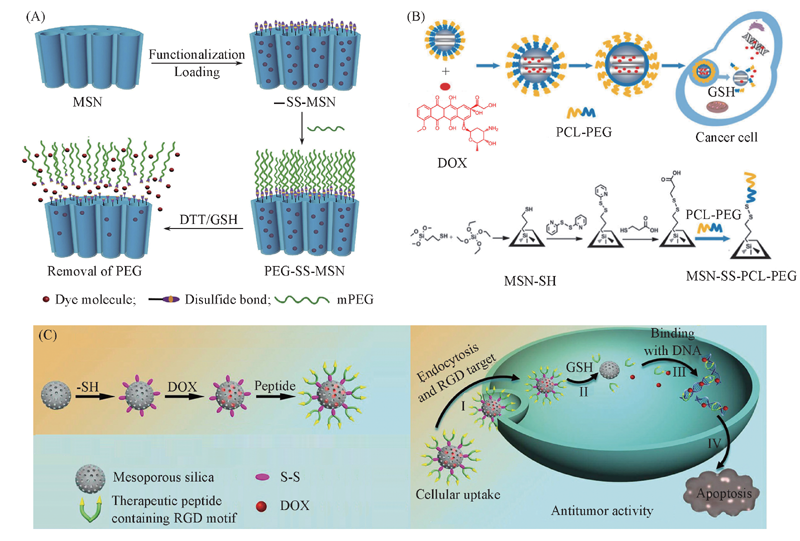
Fig.4 Redox-responsive cargo release systems based onmPEG brushes decorated MSNs[69](A), PEG-PCL brushes-functionalized MSNs(MSN-SS-PCL-PEG)[71](B) and therapeutic peptides-gated MSNs(DOX@TTSTMSN)[72](C) (A) Copyright 2015, Elsevier Ltd. (B) copyright 2013, Royal Society of Chemistry; (C) copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry.
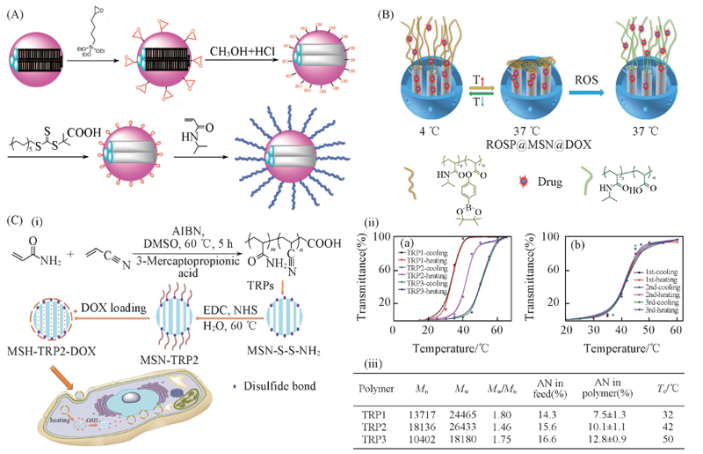
Fig.5 Drug loading and release triggered by temperature (A) Schematic illustration of PNIPAAm grafting onto the surface of MSNs for drug delivery[73]; (B) schematic illustration of dual-responsive MSNs gated byPNIPAAm-PBAPAR [77]; (C) UCST TRP-modified MSN system: (i) schematic illustration of the preparation and intracellular uptake; (ii) turbidity curve of TRP1, TRP2, and TRP3(1%) in PBS; (iii) characterization of TRP1, TRP2 and TRP3 of different UCSTs[79]. (A) Copyright 2008, American Chemical Society; (B) copyright 2018, Elsevier Ltd.; (C) copyright 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry.
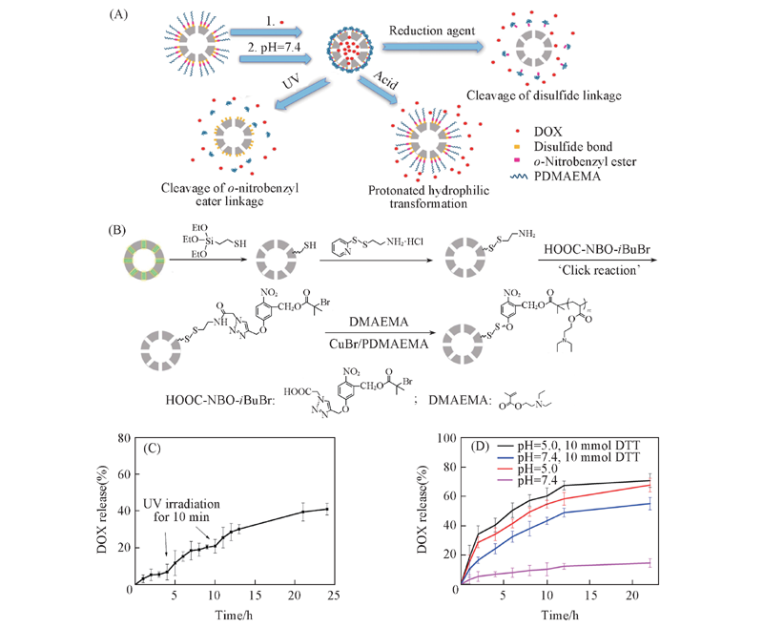
Fig.6 Drug loading and release triggered by light[84] (A) Schematic representation for the structure of HMSNs-PDEAEMA and the different mechanisms of triggered release; (B) synthetic route of tripleresponsive HMSNs-PDEAEMA via SI-ATRP. in vitro DOX release profiles of HMSNs@DOX; (C) triggered by UV light at pH=7.4; (D) at 37 ℃ under different pH values without and with DTT. Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
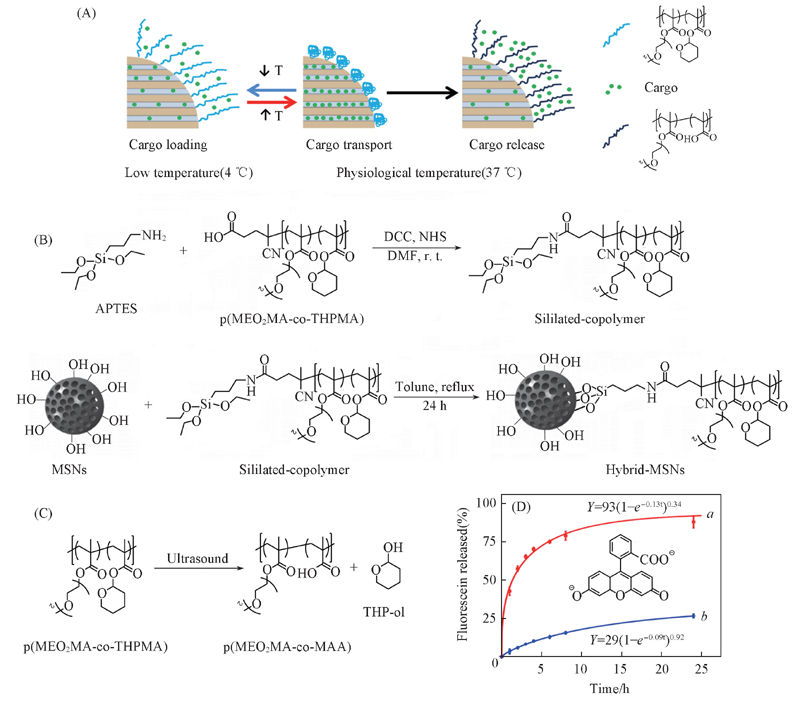
Fig.7 Drug loading and release triggered by ultrasound[88] (A) Schematic illustration of the temperature/ultrasound dual-responsiveness; (B) synthetic route to PMEO2MA-PTHPMA-MSN; (C) ultrasound-triggered bond cleavage of PMEO2MA-PTHPMA into PMEO2MA-PMAA and tetrahydropyranol(THP-ol); (D) release profile of fluorescein from hybrid-MSNs in PBS uponultrasound treatment(10 min and 1.3 MHz, 100 W)(a) and without ultrasound(b). Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
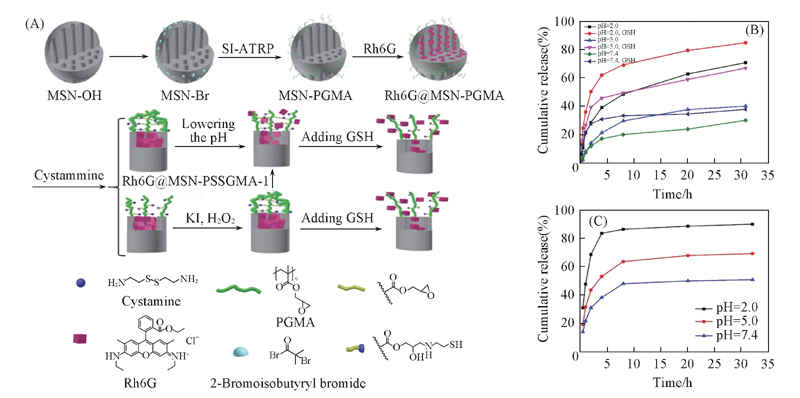
Fig.8 Covalent bond cross-linked polymer networks served as gatekeepers (A) Schematic illustration ofthe synthetic route of MSN-PGMA and cystamine cross-linked PGMA networks on MSNs and Rh6G release in response to pH and GSH; (B) release profiles of cross-linked PSSGMA in PBS buffers of different pH values; (C) release profiles of polymer brushes PSGMA in PBS buffers of different pH values[91]. Copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry.
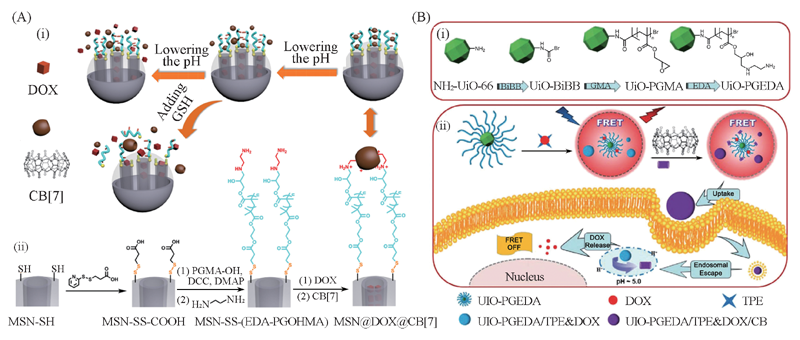
Fig.9 Non-covalent bond cross-linked polymer networks served as gatekeepers (A) Schematic diagram of (i) pH and GSH dual-responsive dynamic cross-linked supramolecular networks on MSNs; (ii) synthetic route of MSN-SS-(EDA-PGOHMA) and its assembly with CB[7][100]. (B) Schematic illustration of (i) the preparation of polymer brush decorated MOFs; (ii) drug release behavior of the MOF-based nanoparticles[101]. (A) Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.
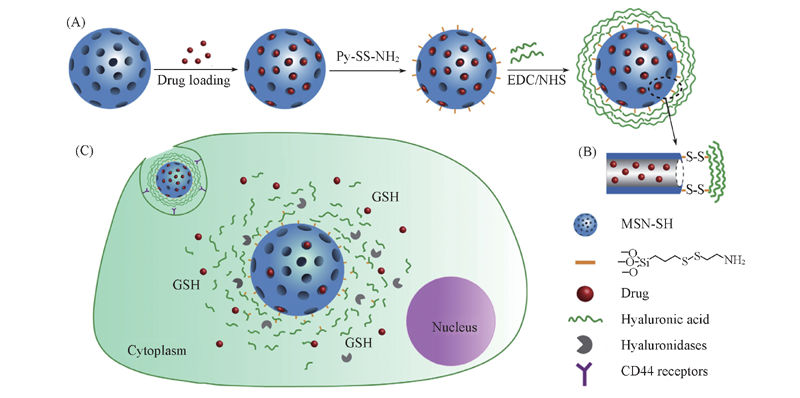
Fig.10 Schematic illustration of the preparation of MSN-SS-HA and its dual-stimuli responsive drug delivery[102] (A) Synthesis of drug-loaded MSN-SS-HA; (B) magnified image of pore structure upon grafting of HA; (C) cell uptake through CD44 receptor-mediated interaction. Copyright 2015, Elsevier Ltd.
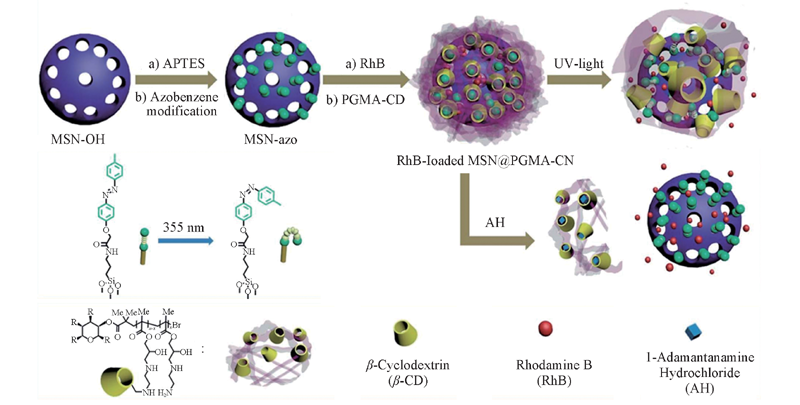
Fig.11 Schematic representation of the preparation process of RhB-loaded MSN@PGMA-CD and its cargo release in response to UV light or competitive binding[104] Copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry.
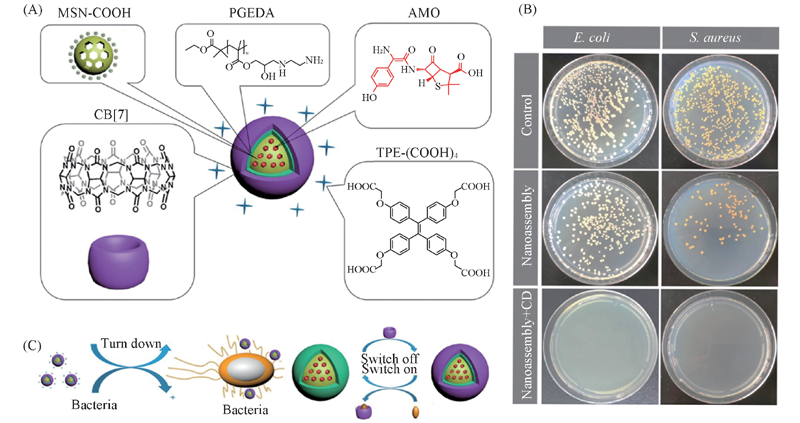
Fig.12 Schematic representation of nanoassembly constructed via LBL assembly(A), colony forming units(CFU) for S. aureus and E. coli treated with nanoassembly before and after addition of adamantaneamine(AD) on LB agar plate(B) and illustration of drug release triggered by addition of AD(C)[106] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
| [1] |
Mura S., Nicolas J., Couvreur P., Nat. Mater., 2013,12(11), 991— 1003
doi: 10.1038/nmat3776 URL pmid: 24150417 |
| [2] |
Wu M. X., Yang Y. W., Adv. Mater., 2017,29(23), 1606134
doi: 10.1002/adma.201606134 URL |
| [3] |
Wen J., Yang K., Liu F., Li H., Xu Y., Sun S., Chem. Soc.Rev., 2017,46(19), 6024— 6045
doi: 10.1039/c7cs00219j URL pmid: 28848978 |
| [4] |
Sun Y. L ., Yang Y. W.,Chen D. X.,Wang G.,Zhou Y.,Wang C. Y.,Stoddart J. F.,. Small, 2013,9(19), 3224— 3229
doi: 10.1002/smll.201300445 URL |
| [5] |
Sun Y. L ., Zhou Y.,Li Q. L.,Yang Y.W ., Chem. Commun., 2013,49(79), 9033— 9035
doi: 10.1039/c3cc45216f URL pmid: 23982479 |
| [6] |
Jamal W. A ., Kostarelos K., Acc. Chem. Res., 2011,44(10), 1094— 1104
doi: 10.1021/ar200105p URL pmid: 21812415 |
| [7] |
Deng C., Jiang Y., Cheng R., Meng F., Zhong Z ., Nano Today, 2012,7(5), 467— 480
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2012.08.005 URL |
| [8] |
Karthik S., Puvvada N., Kumar B. N ., Rajput S.,Pathak A.,Mandal M.,Singh N. D., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013,5(11), 5232— 5238
doi: 10.1021/am401059k URL pmid: 23730930 |
| [9] |
Kresge C. T ., Leonowicz M. E.,Roth W. J.,Vartuli J. C.,Beck J. S.,. Nature, 1992,359, 710— 712
doi: 10.1038/359710a0 URL |
| [10] |
Beck J. S ., Vartuli J. C.,Roth W. J.,Leonowicz M. E.,Kresge C. T.,Schmitt K. D.,Chu C. T. W.,Olson D. H.,Sheppard E. W.,McCullen S. B.,Higgins J. B.,Schlenker J. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992,114(6), 10834— 10843
doi: 10.1021/ja00053a020 URL |
| [11] |
Wang X., Tan L. L ., Li X.,Song N.,Li Z.,Hu J. N.,Cheng Y. M.,Wang Y.,Yang Y. W., Chem. Commun., 2016,52(95), 13775— 13778
doi: 10.1039/c6cc08241f URL pmid: 27824167 |
| [12] |
Li X., Han J., Wang X., Zhang Y., Jia C., Qin J., Wang C., Wu J. R ., Fang W.,Yang Y. W., Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3(1), 103— 110
doi: 10.1039/C8QM00509E URL |
| [13] |
Li Q. L ., Sun Y.,Ren L.,Wang X.,Wang C.,Li L.,Yang Y. W.,Yu X.,Yu J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(35), 29314— 29324
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b09330 URL pmid: 30091897 |
| [14] |
Wang X., Tan L. L ., Li X.,Song N.,Li Z.,Hu J. N.,Cheng Y. M.,Wang Y.,Yang Y. W., Chem. Commun., 2016,52(95), 13775— 13778
doi: 10.1039/c6cc08241f URL pmid: 27824167 |
| [15] |
Song N., Yang Y. W ., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015,44(11), 3474— 3504
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00243e URL pmid: 25904466 |
| [16] |
Li H., Tan L. L ., Jia P.,Li Q. L.,Sun Y. L.,Zhang J.,Ning Y. Q.,Yu J.,Yang Y. W., Chem. Sci., 2014,5(7), 2804— 2808
doi: 10.1039/c4sc00198b URL |
| [17] |
Tan L. L ., Li H.,Zhou Y.,Zhang Y.,Feng X.,Wang B.,Yang Y. W.,. Small, 2015,11(31), 3807— 3813
doi: 10.1002/smll.201500155 URL pmid: 25919865 |
| [18] |
Li Z., Song N., Yang Y. W ., . Matter, 2019,1(2), 345— 368
doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(99)01310-2 URL pmid: 10905718 |
| [19] |
Wu M. X ., Yan H. J.,Gao J.,Cheng Y.,Yang J.,Wu J. R.,Gong B. J.,Zhang H. Y.,Yang Y. W., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(40), 34655— 34663
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b13758 URL pmid: 30226739 |
| [20] |
Zhang L., Bei H. P ., Piao Y.,Wang Y.,Yang M.,Zhao X.,. Chem Phys Chem, 2018,19(16), 1956— 1964
doi: 10.1002/cphc.201800018 URL pmid: 29575338 |
| [21] |
Wu M. X ., Wang X.,Yang Y. W., Chem. Rec., 2017,18(1), 45— 54
doi: 10.1002/tcr.201700036 URL pmid: 28675576 |
| [22] |
Tan L. L ., Li S., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2019,40(17), 1800879
doi: 10.1002/marc.201800879 URL pmid: 30817069 |
| [23] |
Wang P., Chen S., Cao Z., Wang G., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2017,9(34), 29055— 29062
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b07468 URL pmid: 28795557 |
| [24] |
Hamner K. L ., Alexander C. M.,Coopersmith K.,Reishofer D.,Provenza C.,Maye M. M.,. ACS Nano, 2013,7(8), 7011— 7020
doi: 10.1021/nn402214e URL pmid: 23899347 |
| [25] |
Wei H., Cheng S. X ., Zhang X. Z.,Zhuo R. X., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2009,34(9), 893— 910
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.05.002 URL |
| [26] |
Xia J., Li T., Lu C., Xu H ., Macromolecules, 2018,51(19), 7435— 7455
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b01597 URL |
| [27] |
Majewski A. P ., Schallon A.,Jerome V.,Freitag R.,Muller A. H.,Schmalz H., Biomacromolecules, 2012,13(3), 857— 866
doi: 10.1021/bm2017756 URL |
| [28] |
Sirsi S. R ., Borden M. A., Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2014,72, 3— 14
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.12.010 URL pmid: 24389162 |
| [29] |
Yang Y. W ., Sun Y. N.,Song N., Acc. Chem. Res., 2014,47(7), 1950— 1960
doi: 10.1021/ar500022f URL pmid: 24635353 |
| [30] |
Tukappa A., Ultimo A., de la Torre C.,Pardo T.,Sancenon F.,Martinez-Manez R.,. Langmuir, 2016,32(33), 8507— 8515
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01715 URL pmid: 27468799 |
| [31] |
Aznar E., Oroval M., Pascual L., Murguia J. R ., Martinez-Manez R.,Sancenon F., Chem. Rev., 2016,116(2), 561— 718
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00456 URL pmid: 26730615 |
| [32] |
Stuart M. A ., Huck W. T.,Genzer J.,Muller M.,Ober C.,Stamm M.,Sukhorukov G. B.,Szleifer I.,Tsukruk V. V.,Urban M.,Winnik F.,Zauscher S.,Luzinov I.,Minko S., Nat. Mater., 2010,9(2), 101— 113
doi: 10.1038/nmat2614 URL pmid: 20094081 |
| [33] |
Schmaljohann D ., Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2006,58(15), 1655— 1670
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2006.09.020 URL pmid: 17125884 |
| [34] |
Siegwart D. J ., Oh J. K.,Matyjaszewski K., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2012,37(1), 18— 37
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.08.001 URL pmid: 23525884 |
| [35] |
Xu F. J ., Yang W. T., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2011,36(9), 1099— 1131
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.11.005 URL |
| [36] |
Matyjaszewski K ., Macromolecules, 2012,45(10), 4015— 4039
doi: 10.1021/ma3001719 URL |
| [37] |
Matyjaszewski K., Xia J., Chem. Rev., 2001,101(9), 2921— 2990
doi: 10.1021/cr940534g URL pmid: 11749397 |
| [38] |
Moad G., Rizzardo E., Thang S. H ., . Polymer, 2008,49(5), 1079— 1131
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2007.11.020 URL |
| [39] | Moad G., Rizzardo E., Thang S. H ., Aust.J. Chem., 2005,58(6), 379— 410 |
| [40] | Moad G., Rizzardo E., Thang S. H ., Aust.J. Chem., 2012,65(8), 985— 1076 |
| [41] | Zhou H., Jiang W., An N., Zhang Q., Xiang S., Wang L., Tang J., RSC Adv ., 2015,5(53), 42728— 42735 |
| [42] | Wang X., Yun W., Jiang W., Wang D., Zhang L., Tang J., RSC Adv ., 2017,7(16), 9926— 9932 |
| [43] |
Zhang B., Wang X., Zhu A., Ma K., Lv Y., Wang X., An Z ., Macromolecules, 2015,48(21), 7792— 7802
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b01893 URL |
| [44] |
Wang X. H ., Wu M. X.,Jiang W.,Yuan B. L.,Tang J.,Yang Y. W.,. Macromolecules, 2018,51(3), 716— 723
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b02650 URL |
| [45] |
Wanner V., Dullaart A., Bock A. K, Zweck A ., Nat. Biotechnol., 2006,24(10), 1211— 1217
doi: 10.1038/nbt1006-1211 URL pmid: 17033654 |
| [46] |
Li X., Han J., Qin J., Sun M., Wu J., Lei L., Li J., Fang L., Yang Y. W ., Chem. Commun., 2019,55(94), 14099— 14102
doi: 10.1039/c9cc07115f URL pmid: 31641718 |
| [47] | Wu M. X ., Gao J.,Wang F.,Yang J.,Song N.,Jin X.,Mi P.,Tian J.,Luo J.,Liang F.,Yang Y. W.,. Small, 2018,14(17), 34655— 34663 |
| [48] |
Yang J., Dai D., Lou X., Ma L., Wang B., Yang Y. W ., . Theranostics, 2020,10(2), 615— 629
doi: 10.7150/thno.40066 URL pmid: 31903141 |
| [49] |
Wang X., Yang J., Sun X., Yu H., Yan F., Meguellati K., Cheng Z., Zhang H., Yang Y. W ., Chem. Commun., 2018,54(92), 12990— 12993
doi: 10.1039/c8cc08168a URL pmid: 30387478 |
| [50] |
Lin C. T ., Lee S. Y.,Keh E. S.,Dong D. R.,Huang H. M.,Shih Y. H., J. Oral Rehabil., 2000,27(11), 919— 926
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2000.00573.x URL pmid: 11106982 |
| [51] |
Huang P., Chen Y., Lin H., Yu L., Zhang L., Wang L., Zhu Y., Shi J ., Biomaterials, 2017,125, 23— 37
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.02.018 URL pmid: 28226244 |
| [52] |
Lu N., Fan W., Yi X., Wang S., Wang Z., Tian R., Jacobson O., Liu Y., Yung B. C ., Zhang G.,Teng Z.,Yang K.,Zhang M.,Niu G.,Lu G.,Chen X.,. ACS Nano, 2018,12(2), 1580— 1591
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b08103 URL pmid: 29384652 |
| [53] |
Mekaru H., Yoshigoe A., Nakamura M., Doura T., Tamanoi F., ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2019,2(1), 479— 488
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b02023 URL |
| [54] |
Moghaddam S. P. H ., Yazdimamaghani M.,Ghandehari H., J. Controlled Release, 2018,282, 62— 75
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.04.032 URL pmid: 29679666 |
| [55] |
Cardone R. A ., Casavola V.,Reshkin S. J., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2005,5(10), 786— 795
doi: 10.1038/nrc1713 URL pmid: 16175178 |
| [56] |
Lobb E. J ., Ma I.,Billingham N. C.,Armes S. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001,123(32), 7913— 7914
doi: 10.1021/ja003906d URL pmid: 11493068 |
| [57] |
Liu S., Billingham N. C ., Armes S. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001,40(12), 2328— 2331
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010618)40:12<2328::AID-ANIE2328>3.0.CO;2-M URL |
| [58] |
Lee A. S ., Gast A. P.,. Macromolecules, 1999,32(13), 4302— 4310
doi: 10.1021/ma981865o URL |
| [59] |
Sun J. T ., Hong C. Y.,Pan C. Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010,114(29), 12481— 12486
doi: 10.1021/jp103982a URL |
| [60] |
Zhou H., Wang X., Tang J., Yang Y. W ., . Polymers, 2016,8(8), 277
doi: 10.3390/polym8080277 URL |
| [61] |
Huang L., Liu M., Mao L., Xu D., Wan Q., Zeng G., Shi Y., Wen Y., Zhang X., Wei Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017,412, 571— 577
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.026 URL |
| [62] |
Zhou K., Wang Y., Huang X., Luby-Phelps K., Sumer B. D ., Gao J., Angew. Chem.,Int. Ed., 2011,50(27), 6109— 6114
doi: 10.1002/anie.201100884 URL pmid: 21495146 |
| [63] |
Wang Y., Zhou K., Huang G., Hensley C., Huang X., Ma X., Zhao T., Sumer B. D ., DeBerardinis R. J.,Gao J., Nat. Mater., 2014,13(2), 204— 212
doi: 10.1038/nmat3819 URL pmid: 24317187 |
| [64] |
Mu S., Liu Y., Wang T., Zhang J., Jiang D., Yu X., Zhang N., Acta Biomater., 2017,63, 150— 162
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.050 URL pmid: 28873341 |
| [65] |
Tian B., Liu S., Wu S., Lu W., Wang D., Jin L., Hu B., Li K., Wang Z., Quan Z., Colloids Surf. B, 2017,154, 287— 296
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.03.024 URL |
| [66] |
Saito G., Swanson J. A ., Lee K. D., Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2003,55(2), 199— 215
doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00179-5 URL pmid: 12564977 |
| [67] |
Lai C. Y ., Trewyn B. G.,Jeftinija D. M.,Jeftinija K.,Xu S.,Jeftinija S.,Lin V. S. Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003,125(15), 4451— 4459
doi: 10.1021/ja028650l URL pmid: 12683815 |
| [68] |
Rowan S. J ., Cantrill S. J.,Cousins G. R. L.,Sanders J. K. M.,Stoddart J. F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2002,41(6), 898— 952
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020315)41:6&lt;898::aid-anie898&gt;3.0.co;2-e URL pmid: 12491278 |
| [69] |
Wang Y., Han N., Zhao Q., Bai L., Li J., Jiang T., Wang S., Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 2015,72, 12— 20
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2015.02.008 URL pmid: 25701727 |
| [70] |
Wang Y., Cui Y., Huang J., Di D., Dong Y., Zhang X., Zhao Q., Han N., Gao Y., Jiang T., Wang S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015,356, 1282— 1288
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.151 URL |
| [71] |
He H., Kuang H., Yan L., Meng F., Xie Z., Jing X., Huang Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013,15(34), 14210— 14218
doi: 10.1039/c3cp51947c URL pmid: 23880907 |
| [72] |
Xiao D., Hu J. J ., Zhu J. Y.,Wang S. B.,Zhuo R. X.,Zhang X. Z.,. Nanoscale, 2016,8(37), 16702— 16709
doi: 10.1039/c6nr04784j URL pmid: 27714082 |
| [73] |
Hong C. Y ., Li X.,Pan C. Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008,112(39), 15320— 15324
doi: 10.1021/jp805028z URL |
| [74] |
Chung P. W ., Kumar R.,Pruski M.,Lin V. S. Y., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2008,18(9), 1390— 1398
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v18:9 URL |
| [75] |
Yang Y., Yan X., Cui Y., He Q., Li D., Wang A., Fei J., Li J ., J. Mater. Chem., 2008,18(47), 5731— 5737
doi: 10.1039/b811573g URL |
| [76] |
You Y. Z ., Kalebaila K. K.,Brock S. L.,Oupicky D., Chem. Mater., 2008,20(10), 3354— 3359
doi: 10.1021/cm703363w URL |
| [77] |
Yu F., Wu H., Tang Y., Xu Y., Qian X., Zhu W., Int. J. Pharm., 2018,536(1), 11— 20
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.11.025 URL pmid: 29146540 |
| [78] |
Shu Y., Song R., Zhang A., Huang J., Chen M., Wang J ., Talanta, 2018,181, 278— 285
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.018 URL pmid: 29426513 |
| [79] |
Hei M., Wang J., Wang K., Zhu W., Ma P. X ., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5(48), 9497— 9501
doi: 10.1039/c7tb02429k URL pmid: 29250331 |
| [80] |
Ji W., Li N., Chen D., Qi X., Sha W., Jiao Y., Xu Q., Lu J ., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2013,1(43), 5942— 5949
doi: 10.1039/c3tb21206h URL |
| [81] |
Lai J., Mu X., Xu Y., Wu X., Wu C., Li C., Chen J., Zhao Y., Chem. Commun., 2010,46(39), 7370— 7372
doi: 10.1039/c0cc02914a URL pmid: 20820679 |
| [82] |
Xing Q., Li N., Chen D., Sha W., Jiao Y., Qi X., Xu Q., Lu J ., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2(9), 1182— 1189
doi: 10.1039/c3tb21269f URL |
| [83] |
Mei X., Yang S., Chen D., Li N., Li H., Xu Q., Ge J., Lu J., Chem. Commun., 2012,48(80), 10010— 10012
doi: 10.1039/c2cc33995a URL pmid: 22946093 |
| [84] |
Zhang Y., Ang C. Y ., Li M.,Tan S. Y.,Qu Q.,Luo Z.,Zhao Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015,7(32), 18179— 18187
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b05893 URL pmid: 26221866 |
| [85] |
Yang J., Shen D., Zhou L., Li W., Li X., Yao C., Wang R., El-Toni A. M ., Zhang F.,Zhao D., Chem. Mater., 2013,25(15), 3030— 3037
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.05.003 URL pmid: 26048790 |
| [86] |
Brantley J. N ., Wiggins K. M.,Bielawski C. W.,. Science, 2011,333, 1606— 1609
doi: 10.1126/science.1210923 URL |
| [87] |
Wang J., Pelletier M., Zhang H., Xia H., Zhao Y ., Langmuir, 2009,25(22), 13201— 13205
doi: 10.1021/la9018794 URL pmid: 19572509 |
| [88] |
Paris J. L ., Cabanas M. V.,Manzano M.,Vallet-Regi M.,. ACS Nano, 2015,9(11), 11023— 11033
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04378 URL pmid: 26456489 |
| [89] |
Sun H., Kabb C. P ., Sims M. B.,Sumerlin B. S., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2019,89, 61— 75
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.09.006 URL |
| [90] |
Sun J. T ., Piao J. G.,Wang L. H.,Javed M.,Hong C. Y.,Pan C. Y., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2013,34(17), 1387— 1394
doi: 10.1002/marc.201300477 URL pmid: 23881541 |
| [91] |
Zhou H., Wang X., Tang J., Yang Y. W., Polym. Chem., 2016,7(12), 2171— 2179
doi: 10.1039/C6PY00045B URL |
| [92] |
Xu F. J ., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2018,78, 56— 91
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.09.003 URL |
| [93] |
Li R. Q ., Wu Y.,Zhi Y.,Yang X.,Li Y.,Du J.,Xu F. J., Adv. Mater., 2016,28(33), 7204— 7212
doi: 10.1002/adma.201602319 URL pmid: 27297033 |
| [94] |
Li R. Q ., Hu Y.,Yu B. R.,Zhao N. N.,Xu F. J., Bioconjugate Chem., 2014,25(1), 155— 164
doi: 10.1021/bc400467h URL |
| [95] |
Li C., Yang Y. W ., Liang Z. X.,Wu G. L.,Gao H., Polym. Chem., 2013,4(16), 4366— 4374
doi: 10.1039/c3py00573a URL |
| [96] |
Benaglia M., Alberti A., Giorgini L., Magnoni F., Tozzi S., Polym. Chem., 2013,4(1), 124— 132
doi: 10.1039/C2PY20646C URL |
| [97] |
Li Q. L ., Gu W. X.,Gao H.,Yang Y. W., Chem. Commun., 2014,50(87), 13201— 13215
doi: 10.1039/c4cc03036b URL pmid: 24894023 |
| [98] |
Chen C., Sun W., Yao W., Wang Y., Ying H., Wang P., RSC Adv., 2018,8(37), 20862— 20871
doi: 10.1039/C8RA03163K URL |
| [99] |
Yan X., Wang F., Zheng B., Huang F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012,41(18), 6042— 6065
doi: 10.1039/c2cs35091b URL pmid: 22618080 |
| [100] |
Li Q. L ., Xu S. H.,Zhou H.,Wang X.,Dong B.,Gao H.,Tang J.,Yang Y. W., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015,7(51), 28656— 28664
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b10534 URL pmid: 26633741 |
| [101] |
Chen S., Chen Q., Dong S., Ma J., Yang Y. W ., Chen L.,Gao H., Macromol. Biosci., 2018,18(12), 1800317
doi: 10.1002/mabi.201800317 URL pmid: 30334359 |
| [102] |
Zhao Q., Liu J., Zhu W., Sun C., Di D., Zhang Y., Wang P., Wang Z., Wang S ., Acta Biomaterialia, 2015,23, 147— 156
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.05.010 URL pmid: 25985912 |
| [103] |
Lin J. T ., Liu Z. K.,Zhu Q. L.,Rong X. H.,Liang C. L.,Wang J.,Ma D.,Sun J.,Wang G. H., Colloids Surf. B, 2017,155, 41— 50
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.04.002 URL pmid: 28407530 |
| [104] |
Li Q. L ., Wang L.,Qiu X. L.,Sun Y. L.,Wang P. X.,Liu Y.,Li F.,Qi A. D.,Gao H.,Yang Y. W., Polym. Chem., 2014,5(10), 3389— 3395
doi: 10.1039/c4py00041b URL |
| [105] |
Wu Y., Xu Z., Sun W., Yang Y., Jin H., Qiu L., Chen J., Chen J., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2019,103, 109831
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.109831 URL pmid: 31349481 |
| [106] |
Li Q., Wu Y., Lu H., Wu X., Chen S., Song N., Yang Y. W ., Gao H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017,9(11), 10180— 10189
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b00873 URL pmid: 28244730 |
| [107] |
Moreno-Villaecija M. A ., Sedo-Vegara J.,Guisasola E.,Baeza A.,Regi M. V.,Nador F.,Ruiz-Molina D., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(9), 7661— 7669
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b08584 URL pmid: 28960952 |
| [1] | WANG Huan, SUO Jinquan, WANG Chunyan, WANG Runwei. Glucose Oxidase Immobilization with Amino Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Its Application in Glucose Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1731. |
| [2] | REN Yushuang, GUO Yuanyuan, LIU Xueyi, SONG Jie, ZHANG Chuan. Platinum(Ⅳ) Prodrug-grafted Phosphorothioate DNA and Its Self-assembled Nanostructure for Targeted Drug Delivery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1721. |
| [3] | ZHAO Yu, CAO Wanqing, LIU Yang. Recent Advances in Polymeric Nano-sized Carrier Systems † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 909. |
| [4] | WANG Dagui, CHEN Yajie, JIAN Qi, GAO Pengcheng, XIA Fan. Research Advance of Polymer Anti-fouling Coatings [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2638. |
| [5] | Minwen JIANG,Chenhui YIN,Sheng LI,Xiaoli LI. Synthesis of DOPO-based Cyclotriphosphazene Macromolecule Flame Retardant and Its Performance in Flame-retarded Epoxy Resin † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2615. |
| [6] | FENG Wenya, QIAO Juan, QI Li, LI Zhiwei. Sepatation of Antipyretic Analgesics by CapillaryElectrochromatography with Block Copolymer Coating† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1640. |
| [7] | LI Yang, ZHU Ye, MENG Long, WEI Wei, LUO Jing, LIU Xiaoya. Preparation and Properties of Antibacterial Coating with Redox-responsive Drug Releasing Function Based on Macromolecule Self-assembly Colloidal Particle† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1326. |
| [8] | GAO Lei, WANG Qing, YANG Xiaohai, WANG Kemin, DENG Peng, ZHANG Hua, LI Zhiping. Aptamer-capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Myoglobin Detection† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 187. |
| [9] | QIU Linzi, WANG Guirong, PAN Yan, WANG Yiwen, LI Xinqing, DENG Linhong, Mark Bradley, ZHANG Rong. Polymer Coatings for Purification and Long-term Culture of Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1897. |
| [10] | YANG Nianwang, CHEN Tao, FU Jiajun. Controlled Release of Corrosion Inhibitor from Intelligent Nanocontainers Based on Acid and Base Dual-responsive† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 971. |
| [11] | SUN Yu-Long, YANG Ying-Wei, WU Wei, ZHANG Sean Xiao-An. Supramolecular Nanovalve Systems Based on Macrocyclic Synthetic Receptors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(08): 1635. |
| [12] | WANG Yong-Hong, HE Xiao-Xiao, WANG Ke-Min, SU Jing, CHEN Zhi-Feng, YAN Gen-Ping. Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Biosensor Based on Ru(bpy)32+ Doped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(06): 1162. |
| [13] | CAO Jie, HE Ding-Geng, HE Xiao-Xiao, WANG Ke-Min, ZHAO Ying-Xiang. Preparation of a pH-Responsive Carrier Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Its Application for Controlled Release [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(05): 914. |
| [14] | HU Jia-Wei, SHEN Ye-Hua, QIN Wei-Jie, ZHANG Yang-Jun, Qian Xiao-Hong. Preparation of Multi-layer Open Capillary Immobilized Enzyme Reactor and Its Application in Digestion of Proteins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(02): 268. |
| [15] | CHEN Jia-Mei, WU Chuan-Bin, LU Tong-Bu*. Application of Supramolecular Chemistry on Pharmaceutical Cocrystals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9): 1996. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||