

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 1326.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170703
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yang, ZHU Ye, MENG Long, WEI Wei, LUO Jing, LIU Xiaoya*( )
)
Received:2017-11-06
Online:2018-06-10
Published:2018-06-10
Contact:
LIU Xiaoya
E-mail:lxy@jiangnan.edu.cn
Supported by:TrendMD:
LI Yang, ZHU Ye, MENG Long, WEI Wei, LUO Jing, LIU Xiaoya. Preparation and Properties of Antibacterial Coating with Redox-responsive Drug Releasing Function Based on Macromolecule Self-assembly Colloidal Particle†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1326.
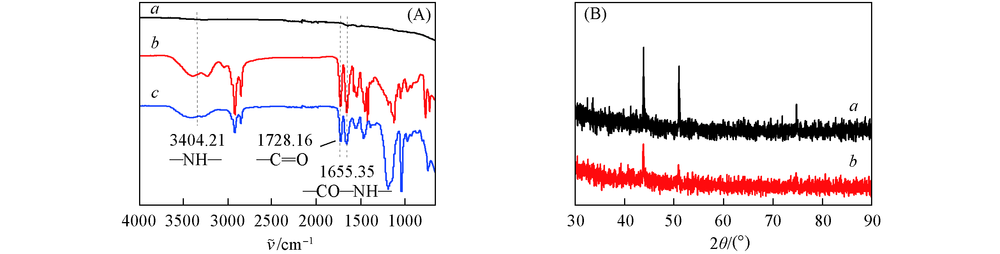
Fig.3 ATR-FTIR spectra(A) and XRD patterns(B) for bare 316L stainless steel and PCTM-loaded PPDM CPs coated 316L stainless steel (A) a. 316L stainless steel; b. PCTM copolymer; c. PCTM coating. (B) a. 316L stainless steel; b. PCTM coating.
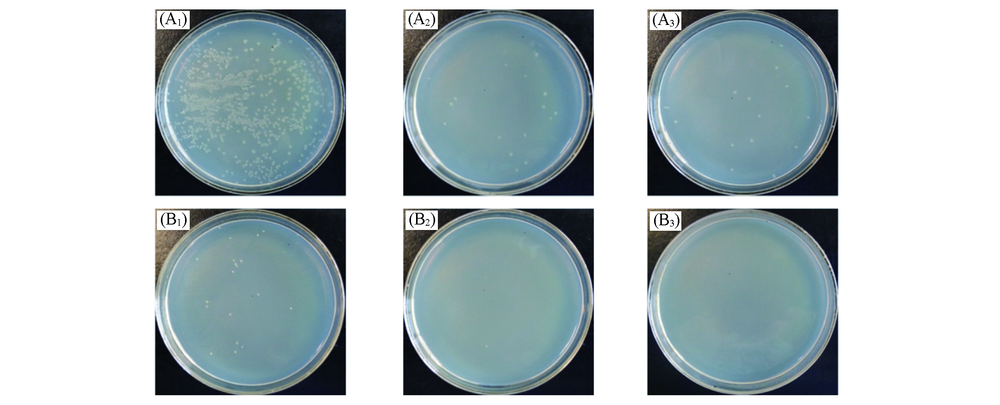
Fig.7 Bacterial culture of E. coli(A1—A3) and S. aureus(B1—B3) after being treated on bare(A1, B1), PPDM CPs coated(A2, B2) and PCTM-loaded PPDM CPs(A3, B3) coated 316L stainless steel for 24 h
| [1] | Fu J. H., Ji J., Yuan W. Y., Shen J. C., Biomaterials, 2005, 26(33), 6684—6692 |
| [2] | Yan S. J., Shi H. C., Song L. J., Wang X. H., Liu L., Luan S. F., Yang Y. M., Yin J. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(37), 24471—24481 |
| [3] | Li Z. F., Huang W. J., Liu M., Journal of Chongqing Institute of Technology, 2006, 20(5), 42—46 |
| (李兆峰, 黄伟九, 刘明. 重庆工学院学报, 2006, 20(5), 42—46) | |
| [4] | Sydowplum G., Tabrizian M., Materials Science & Technology, 2013, 24(9), 1127—1143 |
| [5] | Lin B., Li C. Y., Zhu Y., Huang H. L., Chinese Journal of Bone and Joint Injury, 2007, 22(7), 553—555 |
| (林斌, 李春艳, 朱勇, 黄惠丽. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007 22(7), 553—555) | |
| [6] | Ruan H. J., Fan C. Y., Liu S., Zheng X. B., Chinese Journal of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, 2011, 25(6), 668—672 |
| (阮洪江, 范存义, 刘生, 郑学斌. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011, 25(6), 668—672) | |
| [7] | Wang B. L., Xu Q. W., Ye Z., Liu H. H., Lin Q. K., Nan K. H., Li Y. Z., Wang Y., Qi L., Chen H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(40), 27207—27217 |
| [8] | Celine F. D., Emilie F., Tiziana S. L., Fabrice F., Christine J., Cecile V. D., Joseph M., Anne S. D., Christophe D., Langmuir, 2012, 28(18), 7233—7241 |
| [9] | Shady F., Oren A., Natalia L., Stanislav R., Nurit B., Abraham J.D., Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2015, 128, 608—613 |
| [10] | Anne V., Barbara T., Kevin D., Dereck K., Georg M. G., Mathias U., Langmuir, 2016, 32(5), 1347—1359 |
| [11] | Zhao C. L., Hou P., Ni J. H., Han P., Chai Y. M., Zhang X. N., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(8), 5093—5103 |
| [12] | Du W. X., Yang J., Sang Y. X., Zhang L. L., Zhao N., Xu K., Cheng X. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3), 346—354 |
| (杜文修, 杨娟, 桑玉祥, 张莉莉, 赵难, 徐凯, 程晓农. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(3), 346—354) | |
| [13] | Chen X. J., Hou D. D., Wang L., Zhang Q., Zou J. H., Sun G., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(40), 22394—22403 |
| [14] | Yu L., Mu R. H., Li L., Liang F., Yao L., Su L., International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2016, 498(1/2), 195—204 |
| [15] | Wang Y., Hong C. Y., Pan C. Y., Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14(5), 1444—1451 |
| [16] | Wu L. Y., Zhang L. P., Shi G., Ni C. H., Materials Science and Engineering C, 2016, 61, 278—285 |
| [17] | Zuo C., Dai X. Y., Zhao S. J., Liu X. N., Ding S. L., Ma L. W., Liu M. Z., Wei H., ACS Macro Lett., 2016, 5(7), 873—878 |
| [18] | Lin C., Lou B., Zhao J., Jin R., Zhao P., Lic J. B., Ren J., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016, 4, 902—909 |
| [19] | Giovanni L. B., Marco F., Francesca C., Yan Y., Enrico F., Subramanian K., Christoph H., Joseph J. R., Stella T., Andreas F., Frank C., Nadia Z., Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 6261—6270 |
| [20] | Han Y., Li J. J., Zan M. H., Luo S. Z., Ge Z. S., Liu S. Y., Polym. Chem., 2014, 5, 3707—3718 |
| [21] | Wang R. Y., He X. J., Gao Y., Zhang X. Y., Yao X. H., Tang B., Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 75, 7—15 |
| [22] | Han H., Wu J. F., Christopher W. A., Masato M., Jiang X. M., Masami K., Chen Z., Xi C. W., Kuroda K., Langmuir, 2011, 27(7), 4010—4019 |
| [23] | Alexander W. J., David A. F., Macromolecules, 2012, 45(6), 2699—2708 |
| [24] | Niren M., Jean C., Nelson F., Allan S. H., Patrick S. S., Bioconjugate Chem., 2003, 14(2), 412—419 |
| [25] | Bulmus V., Woodward M., Lin L., Murthy N. R., Stayton P., Hoffman A., Journal of Controlled Release, 2003, 23, 105—120 |
| [26] | Sun J. D., Zhu Y., Meng L., Wei W., Li Y., Liu X. Y., Zheng Y. F., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015, 3, 1667—1676 |
| [27] | He M. Y., Alicia P., Julie C. K., Katharina F., Cynthia A. R., Chu C. C., Biomacromolecules, 2016, 17(2), 523—537 |
| [28] | Sun J. D., Zhu Y., Meng L., Chen P., Shi T. T., Liu X. Y., Zheng Y. F., Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 45, 387—398 |
| [29] | Shi T. T., Sun J. D., Zhu Y., Meng L., Wei W., Liu X. Y., Jounral of Functional Materials, 2017, 5, 5042—5047 |
| (石甜甜, 孙家娣, 朱叶, 孟龙, 魏玮, 刘晓亚. 功能材料2017, 5, 5042—5047) | |
| [30] | Ding M. H., Wang B. L., Li L., Zheng Y. F., Surf. Coat. Technol., 2010, 204, 2519—2526 |
| [31] | Yao C., Zhou B., Wang Y. H., Wen Z. L., Preparation Method of Intelligent Antibacterial Coating with Polypeptide, CN 201510823695.8,2015-11-24 |
| (姚琛, 周宾, 王怡红, 温智理. 一种智能抗菌多肽涂层的制备方法, CN 201510823695.8, 2015-11-24) | |
| [32] | Wang L. R., Li H., Chen S., Nie C. X., Cheng C., Zhao C. S., ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2015, 1(11), 1183—1193 |
| [33] | Zhang R. B., Lu J. R., Liu J. B., Mu J. B., Yang X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8), 1521—1529 |
| (张瑞波, 卢俊瑞, 刘金彪, 穆江蓓, 杨旭云. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(8), 1521—1529) |
| [1] | FAN Xiaoyong, ZHU Yongqiang, WU Yan, ZHANG Shuai, XU Lei, GOU Lei, LI Donglin. Three-dimensional Porous Sn-Zn Alloy Towards Uniform Zn Plating/stripping [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210861. |
| [2] | CHEN Feng, CHENG Na, ZHAO Jianwei, SONG Yitian, SUN Yanyan, LOU Xinli, TONG Xiayan. Electrodeposition Mechanism and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopic Effect of Nano-sized Silver Layer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1891. |
| [3] | SUN Qiangqiang, CAO Baoyue, ZHOU Chunsheng, ZHANG Guochun, WANG Zenglin. Enhancing Hydrogen Evolution Performance of a Regular Cube NiCu Nanocrystalline Electrocatalyst Fabricated by Normal Pluse Electrodeposition † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1287. |
| [4] | FU Kefei, LIAN Huiting, WEI Xiaofeng, SUN Xiangying, LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin-based Impedance Sensor for Recognition of L-Cysteine † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 706. |
| [5] | SUN Weixin, LIU Jia, WANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Yimiao, JIN Lei, ZHOU Jianzhang, YANG Fangzu, WU Deyin, TIAN Zhongqun. Preparation of Platinum-modified Uniform Gold Nanopillar Electrodes and Photoelectrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2788. |
| [6] | LI Chong,CHENG Zhongjun,AN Maozhong. Fabrication of Robust Underwater Superoleophobic Copper Mesh with Tunable Oil Adhesion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 125. |
| [7] | SUN Jie, MING Tingyun, QIAN Huixuan, ZHANG Manke, TAN Yong. Electrochemical Behavior of Copper Electrodeposition in BMIMPF6 Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1497. |
| [8] | XU Liang, LIN Youqin, CHEN Xu, LU Yanluo, YANG Wensheng. Electrodeposition of Platinum Nanoparticles on MgAl-layered Double Hydroxide Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode for Electrochemical Glucose Biosensor† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 442. |
| [9] | XU Die, SHEN Xiaohua, LI Huanhuan, DU Yuanchun, HU Jiawen. Ag Through-void Arrays Prepared by Template Electrodeposition and Their Refractive Index Sensing Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2511. |
| [10] | WANG Yaoqiong, RAN Xiuzhi, GAO Huanfang, LI Li, WEI Zidong. Improvement Performance of Dye-sensitized Solar Cells with Pt/Ti Counter Electrode Prepared by Electrodeposition-displacement† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 1988. |
| [11] | XIN Hua, CHEN Libo, SHI Hongyan, SONG Wenbo, LIU Tiemei. Electrodeposition of Nanostructured Cu Electrode and Its Glucose Assay Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 482. |
| [12] | DAN Yuanyuan, ZHANG Li, CHEN Lizhuang, YUE Huijuan, LIN Haibo, LU Haiyan. Preparation of PbO2+nano-WO3 Composite Electrode on Ti Substrate by Composite Electrodeposition and Its Oxygen Evolution Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(12): 2632. |
| [13] | CHENG Kui, YANG Fan, YAN Peng, CAO Dianxue, YIN Jinling, WANG Guiling. Preparation of Co3O4 Nanosheet Supported on Ni Foam and Its Catalytic Performance for H2O2 Electroreduction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1): 110. |
| [14] |
HASIMU Yushanjiang, LIU Ruiquan, MI Hongyu.
Electrodeposition Behavior of Chromium in Ionic Liquid [BMIM]P |
| [15] | SUN Xiu-Yu, LI Zong-Mu, XU Fa-Qiang, CHENG Ying-Zhi, XUE Li. X-Ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism Study on the Fe-group Magnetic Films by Electrodeposition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12): 2628. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||