

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 1993.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180169
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Lei1, LUO Yongchun1,2,*( ), DENG Anqiang1, JIANG Wanting1
), DENG Anqiang1, JIANG Wanting1
Received:2018-03-04
Online:2018-09-07
Published:2018-06-11
Contact:
LUO Yongchun
E-mail:luoyc@lut.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Lei,LUO Yongchun,DENG Anqiang,JIANG Wanting. Hydrogen Storage and Electrochemical Properties of the Mg-free A2B7-type La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 Alloys with Superlattice Structure†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1993.
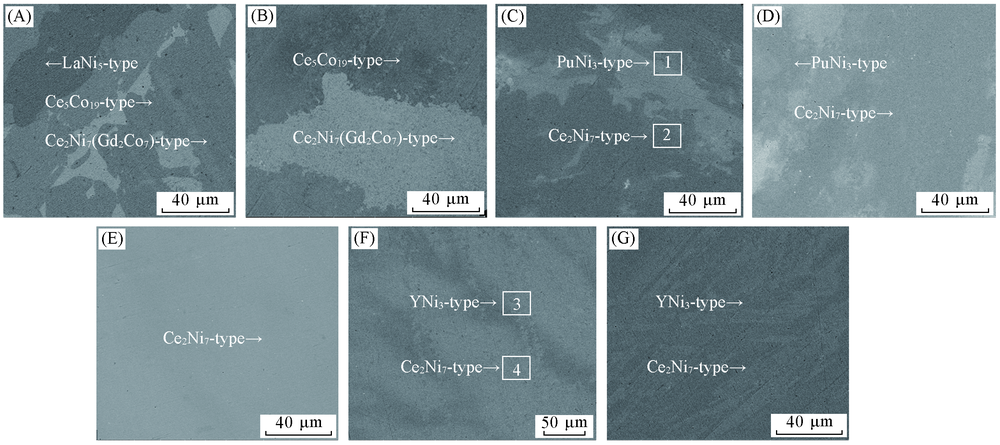
Fig.1 Back scattered SEM images of the annealed La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1(x=0—1) alloys (A) x=0; (B) x=0.25; (C) x=0.50; (D) x=0.67; (E) x=0.75; (F) x=0.85; (G) x=1.00.
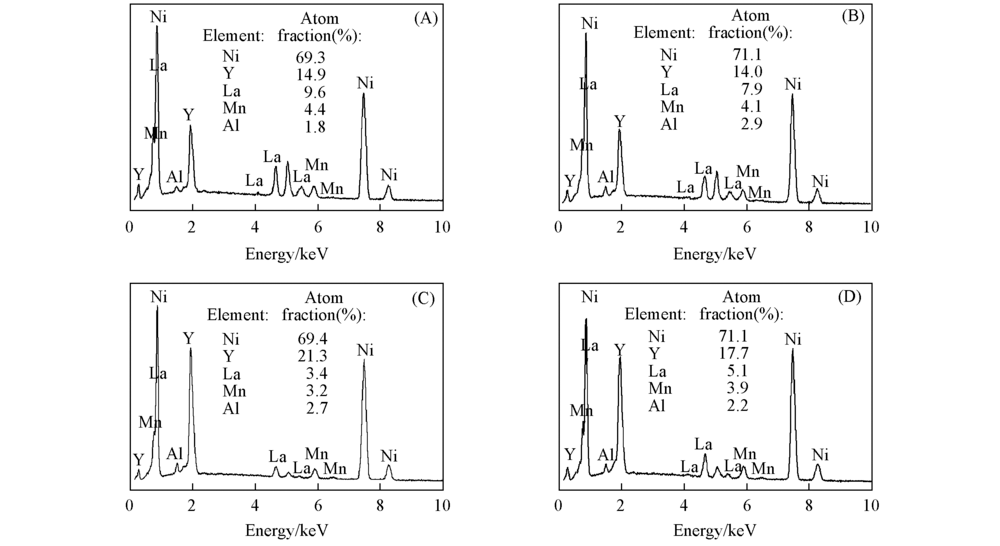
Fig.2 EDS results for different regions of the annealed La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 alloys(x=0.5, 0.85) in Fig.1 (A) Area 1 of x=0.50; (B) area 2 of x=0.50; (C) area 3 of x=0.85; (D) area 4 of x=0.85.
| x | Normal composition | Chemical compositions by ICP, w(%) | Stoichiometric B/A ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | Y | Ni | Mn | Al | |||
| 0 | LaNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 40.80 | 0 | 54.42 | 3.14 | 1.64 | 3.52 |
| 0.25 | La0.75Y0.25Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 31.01 | 6.48 | 58.67 | 2.93 | 0.91 | 3.56 |
| 0.50 | La0.5Y0.5Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 21.67 | 14.10 | 60.53 | 2.66 | 0.94 | 3.54 |
| 0.67 | La0.33Y0.67Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 14.49 | 19.35 | 62.74 | 2.56 | 0.87 | 3.56 |
| 0.75 | La0.25Y0.75Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 10.84 | 22.35 | 63.34 | 2.54 | 0.92 | 3.45 |
| 0.85 | La0.15Y0.85Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 6.28 | 25.70 | 64.66 | 2.41 | 0.94 | 3.53 |
| 1.00 | YNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 0 | 31.51 | 65.14 | 2.71 | 0.93 | 3.44 |
Table 1 Chemical compositions of the annealed alloys La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 by ICP analysis
| x | Normal composition | Chemical compositions by ICP, w(%) | Stoichiometric B/A ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | Y | Ni | Mn | Al | |||
| 0 | LaNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 40.80 | 0 | 54.42 | 3.14 | 1.64 | 3.52 |
| 0.25 | La0.75Y0.25Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 31.01 | 6.48 | 58.67 | 2.93 | 0.91 | 3.56 |
| 0.50 | La0.5Y0.5Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 21.67 | 14.10 | 60.53 | 2.66 | 0.94 | 3.54 |
| 0.67 | La0.33Y0.67Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 14.49 | 19.35 | 62.74 | 2.56 | 0.87 | 3.56 |
| 0.75 | La0.25Y0.75Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 10.84 | 22.35 | 63.34 | 2.54 | 0.92 | 3.45 |
| 0.85 | La0.15Y0.85Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 6.28 | 25.70 | 64.66 | 2.41 | 0.94 | 3.53 |
| 1.00 | YNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 | 0 | 31.51 | 65.14 | 2.71 | 0.93 | 3.44 |
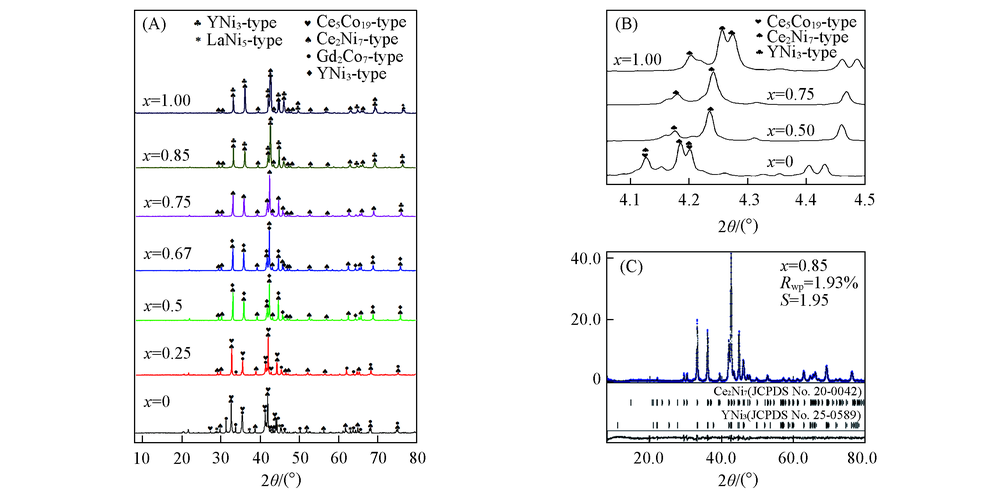
Fig.3 XRD patterns of the annealed La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1(x=0—1.00) alloys(A, B) and Rietveld refinement XRD profile of the La0.15Y0.85Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 alloy(C)
| x | Phase type | Space group | Lattice parameter | Phase abundance, w(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | c/a | V/nm3 | ||||||||
| 0 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5060 | 2.4586 | 4.859 | 0.545154 | 39.56 | ||||
| Gd2Co7-type | R | 0.5001 | 3.6326 | 7.264 | 0.786796 | 18.24 | |||||
| Ce5Co19-type | R | 0.4952 | 4.9093 | 9.914 | 1.042585 | 17.64 | |||||
| LaNi5-type | P6/mmm(191) | 0.5013 | 0.3987 | 0.795 | 0.086771 | 24.56 | |||||
| 0.25 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5049 | 2.4521 | 4.857 | 0.541352 | 48.26 | ||||
| Gd2Co7-type | R | 0.5000 | 3.6320 | 7.264 | 0.786351 | 10.38 | |||||
| Ce5Co9-type | R | 0.4948 | 4.8743 | 9.851 | 1.033480 | 41.36 | |||||
| 0.50 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5021 | 2.4393 | 4.858 | 0.532569 | 81.03 | ||||
| PuNi3-type | R | 0.5000 | 2.4350 | 4.870 | 0.527193 | 18.97 | |||||
| 0.67 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5015 | 2.4332 | 4.852 | 0.530880 | 86.61 | ||||
| PuNi3-type | R | 0.5000 | 2.4350 | 4.870 | 0.529966 | 13.39 | |||||
| 0.75 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5003 | 2.4303 | 4.858 | 0.526807 | 100.00 | ||||
| 0.85 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.4977 | 2.4223 | 4.867 | 0.519630 | 62.54 | ||||
| YNi3-type | R | 0.4986 | 2.4223 | 4.948 | 0.521511 | 37.46 | |||||
| 1.00 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.4965 | 2.4237 | 4.882 | 0.517426 | 56.72 | ||||
| YNi3-type | R | 0.4978 | 2.4361 | 4.894 | 0.522800 | 43.28 | |||||
Table 2 Characteristics of phase structures and lattice parameters of the annealed alloys La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1
| x | Phase type | Space group | Lattice parameter | Phase abundance, w(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | c/a | V/nm3 | ||||||||
| 0 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5060 | 2.4586 | 4.859 | 0.545154 | 39.56 | ||||
| Gd2Co7-type | R | 0.5001 | 3.6326 | 7.264 | 0.786796 | 18.24 | |||||
| Ce5Co19-type | R | 0.4952 | 4.9093 | 9.914 | 1.042585 | 17.64 | |||||
| LaNi5-type | P6/mmm(191) | 0.5013 | 0.3987 | 0.795 | 0.086771 | 24.56 | |||||
| 0.25 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5049 | 2.4521 | 4.857 | 0.541352 | 48.26 | ||||
| Gd2Co7-type | R | 0.5000 | 3.6320 | 7.264 | 0.786351 | 10.38 | |||||
| Ce5Co9-type | R | 0.4948 | 4.8743 | 9.851 | 1.033480 | 41.36 | |||||
| 0.50 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5021 | 2.4393 | 4.858 | 0.532569 | 81.03 | ||||
| PuNi3-type | R | 0.5000 | 2.4350 | 4.870 | 0.527193 | 18.97 | |||||
| 0.67 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5015 | 2.4332 | 4.852 | 0.530880 | 86.61 | ||||
| PuNi3-type | R | 0.5000 | 2.4350 | 4.870 | 0.529966 | 13.39 | |||||
| 0.75 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.5003 | 2.4303 | 4.858 | 0.526807 | 100.00 | ||||
| 0.85 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.4977 | 2.4223 | 4.867 | 0.519630 | 62.54 | ||||
| YNi3-type | R | 0.4986 | 2.4223 | 4.948 | 0.521511 | 37.46 | |||||
| 1.00 | Ce2Ni7-type | P63/mmc(194) | 0.4965 | 2.4237 | 4.882 | 0.517426 | 56.72 | ||||
| YNi3-type | R | 0.4978 | 2.4361 | 4.894 | 0.522800 | 43.28 | |||||
| x | Hydriding capacity at 8 MPa, w(%) | Plateau pressure/MPa | Hydrogen capacity at 8 MPa, w(%) | Hydrogen capacity at 0.1 MPa, w(%) | △H 0—/ (kJ·mol-1 H2) | △S 0—/(J· K-1·mol-1 H2) | Hf | Sf | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The 1st cycle | The 3rd cycle | Abs. | Des. | |||||||
| 0 | 1.522 | 1.271 | 0.173 | 0.052 | 1.024 | 0.603 | -38.26 | 96.29 | 0.52 | 3.66 |
| 0.25 | 1.485 | 1.119 | 0.218 | 0.037 | 0.983 | 0.573 | -35.80 | 108.10 | 0.77 | 4.52 |
| 0.50 | 1.530 | 1.389 | 0.026 | 0.009 | 1.418 | 1.122 | -34.25 | 77.22 | 0.46 | 1.10 |
| 0.67 | 1.442 | 1.444 | 0.054 | 0.031 | 1.425 | 1.128 | -33.75 | 91.59 | 0.24 | 1.66 |
| 0.75 | 1.489 | 1.434 | 0.044 | 0.033 | 1.435 | 1.216 | -34.19 | 78.11 | 0.12 | 0.88 |
| 0.85 | 1.528 | 1.513 | 0.094 | 0.046 | 1.490 | 0.804 | -33.10 | 80.12 | 0.32 | 1.26 |
| 1.00 | 1.465 | 1.444 | 0.097 | 0.057 | 1.432 | 0.749 | -32.91 | 79.21 | 0.22 | 1.59 |
Table 3 Hydriding absorption and hydrogen storage thermodynamic properties of the La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 alloys
| x | Hydriding capacity at 8 MPa, w(%) | Plateau pressure/MPa | Hydrogen capacity at 8 MPa, w(%) | Hydrogen capacity at 0.1 MPa, w(%) | △H 0—/ (kJ·mol-1 H2) | △S 0—/(J· K-1·mol-1 H2) | Hf | Sf | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The 1st cycle | The 3rd cycle | Abs. | Des. | |||||||
| 0 | 1.522 | 1.271 | 0.173 | 0.052 | 1.024 | 0.603 | -38.26 | 96.29 | 0.52 | 3.66 |
| 0.25 | 1.485 | 1.119 | 0.218 | 0.037 | 0.983 | 0.573 | -35.80 | 108.10 | 0.77 | 4.52 |
| 0.50 | 1.530 | 1.389 | 0.026 | 0.009 | 1.418 | 1.122 | -34.25 | 77.22 | 0.46 | 1.10 |
| 0.67 | 1.442 | 1.444 | 0.054 | 0.031 | 1.425 | 1.128 | -33.75 | 91.59 | 0.24 | 1.66 |
| 0.75 | 1.489 | 1.434 | 0.044 | 0.033 | 1.435 | 1.216 | -34.19 | 78.11 | 0.12 | 0.88 |
| 0.85 | 1.528 | 1.513 | 0.094 | 0.046 | 1.490 | 0.804 | -33.10 | 80.12 | 0.32 | 1.26 |
| 1.00 | 1.465 | 1.444 | 0.097 | 0.057 | 1.432 | 0.749 | -32.91 | 79.21 | 0.22 | 1.59 |
| x | Na | Cmax(mA·h/g) | S100(%) | HRD900(%) | I0/ (mA·g-1) | 1010D0/ (cm2·s-1) | Ecorr/V | icorr/ (mA·cm-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 mA/g | 300 mA/g | ||||||||
| 0 | 2 | 211.3 | 152.3 | 92.1 | 64.5 | 321.8 | 0.91 | -0.916 | 6.69 |
| 0.25 | 2 | 184.2 | 137.6 | 95.5 | 74.4 | 267.9 | 1.01 | -0.919 | 6.57 |
| 0.50 | 1 | 376.1 | 340.6 | 75.6 | 75.6 | 249.0 | 1.32 | -0.915 | 6.74 |
| 0.67 | 2 | 376.3 | 335.3 | 85.1 | 83.4 | 248.3 | 1.71 | -0.912 | 5.81 |
| 0.75 | 1 | 381.6 | 347.2 | 80.3 | 85.7 | 274.3 | 2.56 | -0.912 | 6.29 |
| 0.85 | 2 | 350.4 | 297.5 | 52.6 | 75.4 | 235.4 | 1.58 | -0.927 | 8.75 |
| 1.00 | 1 | 307.2 | 164.1 | 22.1 | 68.1 | 51.9 | 0.94 | -0.935 | 8.74 |
Table 4 Electrochemical properties of La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 alloy electrodes
| x | Na | Cmax(mA·h/g) | S100(%) | HRD900(%) | I0/ (mA·g-1) | 1010D0/ (cm2·s-1) | Ecorr/V | icorr/ (mA·cm-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 mA/g | 300 mA/g | ||||||||
| 0 | 2 | 211.3 | 152.3 | 92.1 | 64.5 | 321.8 | 0.91 | -0.916 | 6.69 |
| 0.25 | 2 | 184.2 | 137.6 | 95.5 | 74.4 | 267.9 | 1.01 | -0.919 | 6.57 |
| 0.50 | 1 | 376.1 | 340.6 | 75.6 | 75.6 | 249.0 | 1.32 | -0.915 | 6.74 |
| 0.67 | 2 | 376.3 | 335.3 | 85.1 | 83.4 | 248.3 | 1.71 | -0.912 | 5.81 |
| 0.75 | 1 | 381.6 | 347.2 | 80.3 | 85.7 | 274.3 | 2.56 | -0.912 | 6.29 |
| 0.85 | 2 | 350.4 | 297.5 | 52.6 | 75.4 | 235.4 | 1.58 | -0.927 | 8.75 |
| 1.00 | 1 | 307.2 | 164.1 | 22.1 | 68.1 | 51.9 | 0.94 | -0.935 | 8.74 |
| [1] | Cuevas F., Joubert J. M., Latroche M., Percheron-Guégan A., Appl. Phys. A, 2001, 72(2), 225—238 |
| [2] | Ouyang L. Z., Huang J. L., Wang H., Liu J. W., Zhu M., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2017, 200, 164—178 |
| [3] | Young K. H., Ng K., Bendersky L., Batteries, 2016, 2(1), 2—15 |
| [4] | Gao Z. J., Kang L., Luo Y. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(9), 2035—2042 |
| (高志杰, 康龙, 罗永春. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(9), 2035—2042) | |
| [5] | Kohno T., Yoshida H., Kawashima F., Inaba T., Sakai I., Yamamoto M., Kanda M., J. Alloys Compd., 2000, 311, L5—L7 |
| [6] | Yasuoka S., Magari Y., Murata T., Tanaka T., Ishida J., Nakamura H., Nohma T., Kihara M., Baba Y., Teraoka H., J. Power Sources, 2006, 156(2), 662—666 |
| [7] | Liu J. J., Han S. M., Li Y., Zhang L., Zhao Y. M., Yang S. Q., Liu B. Z., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(44), 20261—20275 |
| [8] | Denys R. V., Riabov A. B., Yartys V. A., Sato M., Delaplane R. G., J. Solid State Chem., 2008, 181(4), 812—821 |
| [9] | Crivello J. C., Zhang J., Latroche M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(51), 25470—25478 |
| [10] | Gal L., Charbonnier V., Zhang J., Goubault L., Bernard P., Latroche M., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(47), 17017—17020 |
| [11] | Iwase K., Mori K., Terashita N., Tashiro S., Suzuki T., J. Solid State Chem., 2016, 247, 142—146 |
| [12] | Subramanian P. R., Smith J. F., Metall. Trans. B, 1985, 16(3), 577—584 |
| [13] | Nagasaki S., Hirabayashi M., Binary Alloy Phase-Diagrams, Translated by Liu A. S., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2004, 119—220 |
| (刘安生[译]. 二元合金状态图集, 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2004, 119—220) | |
| [14] | Shrivastava D., Sanyal S. P., Indian J. Phys., 2016, 9(2), 183—196 |
| [15] | Baddour-Hadjean R., Meyer L., Pereira-Ramos J. P., Latroche M., Percheron-Guegan A., Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46(15), 2385—2393 |
| [16] | Berezovets V. V., Denys R. V., Ryabov O. B., Zavaliil I. Y., Mater Sci., 2007, 43(4), 499—507 |
| [17] | Charbonnier V., Zhang J. X., Monnier J., Goubault L., Bernard P., Magén C., Serin V., Latroche M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(22), 12218—12225 |
| [18] | Charbonnier V., Monnier J., Zhang J. X., Paul-Boncour V., Joiret S., Puga B., Goubault L., Bernard P., Latroche M., J. Power Sources, 2016, 326, 146—155 |
| [19] | Yan H. Z., Xiong W., Wang L., Li B. Q., Li J., Zhao X., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 42(4), 2257—2264 |
| [20] | Xiong W., Yan H. Z., Wang L., Zhao X., Li J., Li B Q., Wang Y., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(22), 15319—15327 |
| [21] | Wang H., Luo Y. C., Deng A. Q., Zhao L., Jiang W. T., J. Inorg. Mater., 2018, 33(4), 434—440 |
| (王浩, 罗永春, 邓安强, 赵磊, 姜婉婷. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4), 434—440) | |
| [22] | Young R. A., Cryst. Res. Technol., 1993, 210(8), 252—254 |
| [23] | Zhang L., Han S. M., Li Y., Yang S. Q., Zhao X., Liu J. J., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, 161(12), A1844—A1850 |
| [24] | Aoki K., Masumoto T., J. Alloys Compd., 1995, 231(1/2), 20—28 |
| [25] | Zhang J., Zhou G. Y., Chen G. R., Latroche M., Percheron-Guégan A., Sun D. L., Acta Mater., 2008, 56(19), 5388—5394 |
| [26] | Zhang Q. A., Chen Z. L., Li Y. T., Fang F., Sun D. L., Ouyang L. Z., Zhu M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(9), 4719—4727 |
| [27] | Senohl H., Yonei T., Takeshita H., Nobuhiko T., Takeichi N., Tanaka H., Kuriyama N., Mater. Trans., 2005, 46(2), 152—154 |
| [28] | Li S., Lan C., Hong H., Deng X. X., Chen W., Chen D. M., Yang K., J. Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2008, 42(3), 359—363 |
| (李慎, 兰程, 宏辉, 邓小霞, 陈伟, 陈德敏, 杨柯. 西安交通大学学报, 2008, 42(3), 359—363) | |
| [29] | Luo G., Hu X. C., Li S. L., Chen W., Han X. B., Chen J. P., Chen D. M., Yang K., Rare Metal Mat. Eng., 2012, 41(10), 1693—1699 |
| [30] | Liu J. J., Li Y., Han D., Yang S. Q., Chen X. C., Zhang L. Han. S. M., J. Power Sources, 2015, 300, 77—86 |
| [31] | Enomoto M., Ohata Y., Uchida H., J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 580(Suppl. 1), S3—S5 |
| [1] | BAI Yanqun,WANG Cunguo,LI Xue,FAN Wenqi,SONG Penghao,GU Yuanchun,LIU Faqian,LIU Guangye. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of S@C Composite Material with High Capacity and Ordered Alignment of Channels † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1306. |
| [2] | DENG Anqiang,LUO Yongchun,XIA Yuanhua,PENG Sihui,MA Weiqin,ZHAO Xudong,YANG Yang,HOU Xiaodong. Effect of Annealing Treatment on Structure and Electrochemical Properties of New Mg-free Y0.7La0.3Ni3.25Al0.1Mn0.15 Hydrogen Storage Alloys † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 145. |
| [3] | CHEN Yaoyan,ZHAO Xin,WANG Zhe,DONG Jie,ZHANG Qinghua. Effects of Preparation Conditions on the Morphologies, Structures and Electrochemical Properties of MXene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1249. |
| [4] |
ZHANG Bo, HE Jun, HUA Zhengshen, WANG Xin, PENG Huifen.
Effect of S |
| [5] | WANG Xue, YANG Lili, WANG Chunzhong, CHEN Gang, WEI Yingjin. Preparation and Characterizations of Zn-doped Li1.13Ni0.3-xMn0.57ZnxO2 Cathode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 733. |
| [6] | KUANG Daizhi, FENG Yonglan, YU Jiangxi, ZHANG Fuxing, JIANG Wujiu, PENG Yan, ZHU Xiaoming, TAN Yuxing. Microwave Assisted Solid-state Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Properties of the Coordination Polymer Constructed from Tricyclohexyltin Hydroxide and o-Ferrocenylcarbonyl Benzoic Acid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1629. |
| [7] | ZHAO Jia, SUN Huabing, LIU Lingyan, CHANG Weixing, LI Jing. Synthesis, Characterization and Potential Electrochemical Properties of Novel Mn-Re Dinuclear Complexes Containing N-Heterocyclic Carbene-carbon Disulfide Ligands† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1): 68. |
| [8] | SUN Hong-Dan, HE Shi-Ci, XIA Bing-Bo, FANG Guo-Qing, LIU Wei-Wei, QIU Guang-Chao, ZHANG Qian, KANEKO Shingo, ZHENG Jun-Wei, LI De-Cheng. Preparation, Structure and Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.5-xAl2xMn1.5-xO4(0≤2x≤0.15) by Spray-Dry Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5): 1059. |
| [9] | KE Chuan, CAI Fang-Gong, YANG Feng, CHENG Cui-Hua, ZHAO Yong. Preparation and Photoelectrical Properties of CuS/TiO2 Nanotube Heterojunction Arrays [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2): 423. |
| [10] | LIU Wei-Wei, KANEKO Shingo, FANG Guo-Qing, SUN Hong-Dan, XIA Bing-Bo, ZHENG Jun-Wei, LI De-Cheng. Structure and Electrochemical Properties of xLi[Li1/3Mn2/3] O2-(1-x)LiNi5/12Mn5/12Co2/12O2(0≤x≤0.8) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2395. |
| [11] | WANG Huan-Feng, GAO Yan-Ying, JIANG Qian-Qian, MA Cong, WANG Xing-Yao. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Characteristics of Cathode Materials Li3V2(PO4)3/C [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10): 2326. |
| [12] | GAO Zhi-Jie, KANG Long, LUO Yong-Chun. Influence of Magnesium Content on Structure and Performance of A2B7-type RE-Mg-Ni Hydrogen Storage Alloys [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(09): 2035. |
| [13] | GU Ning-Yu, AO He, PEI Jian-Jun. Preparation and Characterization of Composite Polymer Electrolytes Containing Surface-modified Nano Silica [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(06): 1295. |
| [14] | SU Zhi*, XU Mao-Wen, YE Shi-Hai, WANG Yong-Long. Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Monoclinic Layered Structure LiMn0.97Al0.03O2-x(PO4)x Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(2): 247. |
| [15] | ZHANG Liang-Tang, SONG Jie, CAI Min-Zhen, XU Fu-Chun, WU Sun-Tao*, ....... Structure and Electrochemical Performance of Copper Doped Vanadium Oxide Thin Films Deposited by RF Magnetron Sputtering [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(5): 971. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||