

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 1018.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170557
Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Rui*, LI Yunpeng, TU Ruixiang, SONG Bo, GUO Yu
Received:2017-08-14
Online:2018-04-22
Published:2018-04-22
Contact:
GUO Rui
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GUO Rui,LI Yunpeng,TU Ruixiang,SONG Bo,GUO Yu. Corrosion Inhibition of 3-Butyl-5,5-dimethyhydantoin Imidazole Ammonium Salt on Q235 Steel in HCl Solution†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 1018.
| Temperature/℃ | Solution | Ecorr/mV | jcorr/(μA·cm-2) | ba/(mV·dec-1) | bc/(mV·dec-1) | ηie(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Blank | -442.5 | 265.26 | 116.81 | 64.41 | |
| BDMHI | -419.9 | 23.18 | 111.12 | 74.23 | 91.3 | |
| 35 | Blank | -449.5 | 343.24 | 105.49 | 72.05 | |
| BDMHI | -424.5 | 39.61 | 117.71 | 79.69 | 88.4 | |
| 45 | Blank | -449.6 | 411.25 | 116.28 | 104.67 | |
| BDMHI | -442.0 | 78.09 | 100.35 | 78.30 | 81.0 | |
| 55 | Blank | -450.3 | 502.37 | 101.40 | 85.38 | |
| BDMHI | -449.7 | 112.90 | 103.52 | 68.84 | 77.5 |
Table 1 Polarization parameters of Q235 steel in 6% HCl solution in the absence and presence of 1.0 g/L BDMHI at different temperatures*
| Temperature/℃ | Solution | Ecorr/mV | jcorr/(μA·cm-2) | ba/(mV·dec-1) | bc/(mV·dec-1) | ηie(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Blank | -442.5 | 265.26 | 116.81 | 64.41 | |
| BDMHI | -419.9 | 23.18 | 111.12 | 74.23 | 91.3 | |
| 35 | Blank | -449.5 | 343.24 | 105.49 | 72.05 | |
| BDMHI | -424.5 | 39.61 | 117.71 | 79.69 | 88.4 | |
| 45 | Blank | -449.6 | 411.25 | 116.28 | 104.67 | |
| BDMHI | -442.0 | 78.09 | 100.35 | 78.30 | 81.0 | |
| 55 | Blank | -450.3 | 502.37 | 101.40 | 85.38 | |
| BDMHI | -449.7 | 112.90 | 103.52 | 68.84 | 77.5 |
| Temperature/℃ | Solution | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rct/(Ω·cm2) | n | Cdl/(μF·cm-2) | ηie(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Blank | 0.4866 | 30.2 | 0.9433 | 216.0 | |
| BDMHI | 0.5674 | 326.8 | 0.8703 | 168.9 | 90.76 | |
| 35 | Blank | 0.5475 | 19.4 | 0.9352 | 215.8 | |
| BDMHI | 0.5310 | 163.5 | 0.8886 | 169.0 | 88.13 | |
| 45 | Blank | 0.5357 | 13.9 | 0.9351 | 214.5 | |
| BDMHI | 0.5171 | 74.8 | 0.8615 | 178.1 | 81.42 | |
| 55 | Blank | 0.4602 | 8.7 | 0.9338 | 217.4 | - |
| BDMHI | 0.4160 | 39.2 | 0.8832 | 186.2 | 77.81 |
Table 2 Simulative electrochemical parameters for Q235 steel in 6% HCl solution in the absence and in the presence of 1.0 g/L BDMHI at different temperatures*
| Temperature/℃ | Solution | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rct/(Ω·cm2) | n | Cdl/(μF·cm-2) | ηie(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Blank | 0.4866 | 30.2 | 0.9433 | 216.0 | |
| BDMHI | 0.5674 | 326.8 | 0.8703 | 168.9 | 90.76 | |
| 35 | Blank | 0.5475 | 19.4 | 0.9352 | 215.8 | |
| BDMHI | 0.5310 | 163.5 | 0.8886 | 169.0 | 88.13 | |
| 45 | Blank | 0.5357 | 13.9 | 0.9351 | 214.5 | |
| BDMHI | 0.5171 | 74.8 | 0.8615 | 178.1 | 81.42 | |
| 55 | Blank | 0.4602 | 8.7 | 0.9338 | 217.4 | - |
| BDMHI | 0.4160 | 39.2 | 0.8832 | 186.2 | 77.81 |
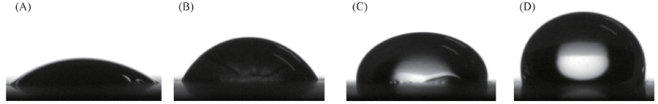
Fig.7 Contact angles for Q235 steel after 24 h immersion at 25 ℃ in 6% HCl solution in the absence(A) and presence of 0.2 g/L(B), 0.6 g/L(C) and 1.0 g/L(D) BDMHI
| ρ(BDMHI)/(g·L-1) | CA/(°) | γs/(mJ·m-2) | ρ(BDMHI)/(g·L-1) | CA/(°) | γs/(mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 32.8 | 62.87 | 0.6 | 96.7 | 24.79 |
| 0.2 | 61.3 | 46.44 | 1.0 | 112.0 | 16.94 |
Table 3 Contact angles and surface energy for Q235 steel after 24 h immersion at 25 ℃ in 6% HCl solution in the absence and in the presence of BDMHI
| ρ(BDMHI)/(g·L-1) | CA/(°) | γs/(mJ·m-2) | ρ(BDMHI)/(g·L-1) | CA/(°) | γs/(mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 32.8 | 62.87 | 0.6 | 96.7 | 24.79 |
| 0.2 | 61.3 | 46.44 | 1.0 | 112.0 | 16.94 |
| Temperature/K | Slope | R2 | K/mol-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 1.00400 | 0.99953 | 3.642 | -30.283 | -42.66 | -41.53 |
| 308 | 0.99648 | 0.99911 | 2.090 | -29.879 | -42.66 | -41.50 |
| 318 | 0.98819 | 0.99903 | 1.377 | -29.741 | -42.66 | -40.63 |
| 328 | 0.86603 | 0.99955 | 0.725 | -28.926 | -42.66 | -41.87 |
Table 4 Thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of BDMHI on Q235 steel surface at different temperatures
| Temperature/K | Slope | R2 | K/mol-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 1.00400 | 0.99953 | 3.642 | -30.283 | -42.66 | -41.53 |
| 308 | 0.99648 | 0.99911 | 2.090 | -29.879 | -42.66 | -41.50 |
| 318 | 0.98819 | 0.99903 | 1.377 | -29.741 | -42.66 | -40.63 |
| 328 | 0.86603 | 0.99955 | 0.725 | -28.926 | -42.66 | -41.87 |
| Molecule | EHOMO/eV | ELUMO/eV | ΔE/eV | ΔE1/eV | ΔE2/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDMHI+ | -7.849 | -5.871 | 1.978 | 1.939 | 7.599 |
| Fe | -7.810 | -0.250 |
Table 5 Frontier orbital energies of BDMHI+ and Fe*
| Molecule | EHOMO/eV | ELUMO/eV | ΔE/eV | ΔE1/eV | ΔE2/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDMHI+ | -7.849 | -5.871 | 1.978 | 1.939 | 7.599 |
| Fe | -7.810 | -0.250 |
| Atom | Atom | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C13 | 0.010 | C1 | -0.006 |
| C15 | -0.012 | C3 | 0.049 |
| N10 | -0.007 | C5 | 0.057 |
| N12 | 0.005 | C7 | -0.008 |
| O17 | 0.233 | N2 | 0.056 |
| O18 | 0.197 | N4 | 0.028 |
Table 6 Fukui index values for BDMHI+
| Atom | Atom | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C13 | 0.010 | C1 | -0.006 |
| C15 | -0.012 | C3 | 0.049 |
| N10 | -0.007 | C5 | 0.057 |
| N12 | 0.005 | C7 | -0.008 |
| O17 | 0.233 | N2 | 0.056 |
| O18 | 0.197 | N4 | 0.028 |
| [1] | Li C.N., Surf. Tech., 2016, 45(8), 80—86(李从妮. 表面技术, 2016, 45(8), 80—86) |
| [2] | Zhan F.T., Yang Z., Lu Z. F., Hu Y. P., Pan Y., Chen Y. F., Xiao C. L., Zhang T., Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9), 1116—1121 |
| (战风涛, 杨震, 吕志凤, 胡以朋, 潘原, 陈彦飞, 肖常林, 张婷. 石油学报, 2015, 36(9), 1116—1121) | |
| [3] | Guo R., Cheng M., Yang J.Y., Li H. L., Liu A.Y., Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2017, 36, 336—342 |
| (郭睿, 程敏, 杨江月, 李欢乐, 刘爱玉. 化工进展, 2017, 36, 336—342) | |
| [4] | Hu S.Q., Hu J. C., Fan C. C., Mi S. Q., Zhang J., Guo W. Y., Acta Phys. Chim.Sin., 2010, 26(8), 2163—2170 |
| (胡松青, 胡建春, 范成成, 米思奇, 张军, 郭文跃. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26(8), 2163—2170) | |
| [5] | Liu M., Tian Y., Fu J., Xu H.F., Chem. [J]. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12), 2228—2235 |
| (刘明, 田颖, 傅杰, 徐洪峰. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(12), 2228—2235) | |
| [6] | Liu X., Okafor P.C., Zheng Y. G., Corros. Sci., 2009, 51, 744—751 |
| [7] | Zhang J., Du M., Yu H.H., Wang N., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2009, 25(3), 525—531 |
| (张静, 杜敏, 于会华, 王宁. 物理化学学报, 2009, 25(3), 525—531) | |
| [8] | Liu F.G., Du M., Zhang J., Qiu M., Corros. Sci., 2009, 51, 102—109 |
| [9] | Guo R., Li Y.P., Ma L., Wang Y. Y., Fine Chem., 2018, 35(2), 201—206 |
| (郭睿, 李云鹏, 马兰, 王映月.精细化工, 2018, 35(2), 201—206 | |
| [10] | Zarrouk A., Zarrok H., Ramli Y., Bouachrine M., Hammouti B., Sahibed D.A., Bentiss F., [J]. Mol. Liq., 2016, 222, 239—252 |
| [11] | Zhao J.M., Chen G. H., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 69, 247—255 |
| [12] | Wang T.Y., Zou C. J., Li D. X., Chen Z. L., Liu Y., Li X. K., Li M., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2015, 31(12), 2294—2302 |
| (王太杨, 邹长军, 李代禧, 陈正隆, 刘圆, 李小可, 李明. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(12), 2294—2302) | |
| [13] | Qian B., Wang J., Zheng M., Hou B.R., Corros. Sci., 2013, 75, 184—192 |
| [14] | Wang B., Du M., Zhang J., Gao C.[J]., Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, 353—361 |
| [15] | Zhang J., Gong X.L., Yu H H., Du M., Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, 3324—3330 |
| [16] | Feng L., Zhang S.T., Yan S., Xu S. Y., Chen S. J., Int. [J]. Eletrochem. Sci., 2017, 12, 1915—1928 |
| [17] | Ahamad I., Pradad R., Quraishi M.A., Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, 1472—1481 |
| [18] | Amar H., Benzakour J., Derja A., Villemin D., Moreau B., Braisaz T., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 252, 6162—6172 |
| [19] | Song W.W., Zhang J., Du M., Acta Chim. Sin., 2011, 69(16), 1851—1857 |
| (宋伟伟, 张静, 杜敏. 化学学报, 2011, 69(16), 1851—1857) | |
| [20] | Liu N.N., Sun J. L., Xia L., Zeng Y. F., Acta Phys. Sin., 2013, 62(20), 203102 |
| (刘娜娜, 孙建林, 夏垒, 曾颖峰. 物理学报, 2013, 62(20), 203102) | |
| [21] | Li X.B., Liu Y., J. Mater. Eng., 2008, 4, 74—80(李小兵, 刘莹. 材料工程, 2008, 4, 74—80) |
| [22] | Zhang W.W., Ma R., Li S., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(5), 827—837 |
| [23] | Zhao J.M., Zhang M. L., Tie Z. W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2017, 33(1), 100—106 |
| [24] | Liu Y.M., Shi J. Y., Lu Q. Q., Guo Y. Z., Chen R. Q., Yin D. C., Mater. Rev., 2013, 27(6), 123—129 |
| (刘永明, 施建宇, 鹿芹芹, 郭云珠, 陈瑞卿, 尹大川. 材料导报, 2013, 27(6), 123—129) | |
| [25] | He X.K., Jiang Y. M., Li C., Wang W. C., Hou B. L., Wu L. Y., Corros. Sci., 2014, 83, 124—136 |
| [26] | Okafor P.C., Zheng Y. G., Corros. Sci., 2009, 51, 850—859 |
| [27] | Xu Q.J., Li C. X., Zhou G. D., Zhu L. J., Lin C. [J]., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2009, 25(1), 86—90 |
| (徐群杰, 李春香, 周国定, 朱律均, 林昌健. 物理化学学报, 2009, 25(1), 86—90) | |
| [28] | Liu Z., Li B.R., Pan Y. X., Shi K., Wang W. C., Chem. [J]. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4), 669—677 |
| (刘志, 李炳睿, 潘艳雄, 石凯, 王伟财. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(4), 669—677) | |
| [29] | Zhang W.W., Ma R., Liu H. H., Liu Y., Li S., Niu L., [J]. Mol. Liq., 2016, 222, 671—679 |
| [30] | Lian B.J., Shi Z. M., Xu H., Zhao Q. F., Wang M. L., Jiang Y. Y., Hu S. Q., Surf. Tech., 2015, 44(12),19—22 |
| (廉兵杰, 石泽民, 徐慧, 赵起锋, 王木立, 姜云瑛, 胡松青. 表面技术, 2015, 44(12), 19—22) | |
| [31] | Guo R., Cheng M., Li X.F., Wang C., Zhen J. B., Fine. Chem., 2017, 34(1), 109—113 |
| (郭睿, 程敏, 李晓芳, 王超, 甄建斌. 精细化工, 2017, 34(1), 109—113) | |
| [32] | He X.K., Hou B. L., Jiang Y. M., Li C., Wu L. Y., Acta Metall. Sin., 2013, 49(8), 1017—1024 |
| (何新快, 侯柏龙, 江雨妹, 李晨, 吴璐烨. 金属学报, 2013, 49(8), 1017—1024) | |
| [33] | Obot I.B., Macdonald D. D., Gasem Z. M., Corros. Sci., 2015, 99, 1—30 |
| [34] | Khaled K.F., Electrochim Acta, 2008, 53, 3484—3492 |
| [35] | Fouda A.S., Ellithy A. S., Corros. Sci., 2009, 51, 868—875 |
| [36] | Ji Y., Xu B., Gong W.N., Zhang X. Q., Jin X. D., Ning W. B., Meng Y., Yang W. Z., Chen Y. Z., [J]. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2016, 66, 301—312 |
| [37] | Zhang K.G., Xu B., Yang W. Z., Yin X. S., Liu Y., Chen Y. Z., Corros. Sci., 2015, 90, 284—295 |
| [1] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [2] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [3] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, JIANG Wei, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Activation of Biochar from Cattail and the VOCs Adsorption Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [4] | MENG Xianglong, YANG Ge, GUO Hailing, LIU Chenguang, CHAI Yongming, WANG Chunzheng, GUO Yongmei. Synthesis of Nano-zeolite and Its Adsorption Performance for Hydrogen Sulfide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [5] | CHEN Xiaolu, YUAN Zhenyan, ZHONG Yingchun, REN Hao. Preparation of Triphenylamine Based PAF-106s via Mechanical Ball Milling and C2 Hydrocarbons Adsorption Property [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [6] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [7] | ZHENG Meiqi, MAO Fangqi, KONG Xianggui, DUAN Xue. Layered Double Hydroxides as Sorbent for Remediation of Radioactive Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [8] | TIAN Xiaokang, ZHANG Qingsong, YANG Shulin, BAI Jie, CHEN Bingjie, PAN Jie, CHEN Li, WEI Yen. Porous Materials Inspired by Microbial Fermentation: Preparation Method and Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [9] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [10] | MA Jianxin, LIU Xiaodong, XU Na, LIU Guocheng, WANG Xiuli. A Multi-functional Zn(II) Coordination Polymer with Luminescence Sensing, Amperometric Sensing, and Dye Adsorption Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| [11] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [12] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, SONG Fujiao, ZHU Ting, HUANG Weiqiu, ZHONG Jing, CHEN Ruoyu. Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption Properties of Hollow Carbon Nanospheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1704. |
| [13] | WANG Longjie, FAN Hongchuan, QIN Yu, CAO Qiue, ZHENG Liyan. Research Progress of Metal-organic Frameworks in the Field of Chemical Separation and Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [14] | YAN Yanhong, WU Simin, YAN Yilun, TANG Xihao, CAI Songliang, ZHENG Shengrun, ZHANG Weiguang, GU Fenglong. Sulfonic Acid-functionalized Spherical Covalent Organic Framework with Ultrahigh Capacity for the Removal of Cationic Dyes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 956. |
| [15] | HU Xueyi, HAN Lulu, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei. Admicelles and Adsolubilization of Extended Surfactants on Alumina [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 843. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||