

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 2185.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170314
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Nan, ZHAO Huanxi, LI Jing, WANG Nan, YU Bohao, YUE Hao*( ), YU Shanshan*(
), YU Shanshan*( )
)
Received:2017-05-18
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-10-10
Contact:
YUE Hao,YU Shanshan
E-mail:yuehao001@aliyun.com;yushanshan001@aliyun.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Nan, ZHAO Huanxi, LI Jing, WANG Nan, YU Bohao, YUE Hao, YU Shanshan. Transformation of Total Notoginsenosides by Recombinant Endocellulase Fpendo5A†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2185.
| Peak No. | Compd. | tR/min | Molecular formula | MS(calcd. mass), m/z | 106 Error | MS/MS fragment ions of [M-H]-(mass accuracy < 5×10-6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ra1 | 21.74 | C58H98O26 | 1209.6242 (1209.6274) | 2.7 | 1077.5839[M-H-Xyl ]-, 945.5418[M-H-Xyl-Ara(p)]-, 783.4874[M-H-Xyl-Ara-Glu]-, 621.4336[M-H-Xyl-Ara-GlcGlc]-, 459.5418[M-H-Xyl-Ara-GlcGlcGlc]-, 323.0862[GlcGlc-H]- |
| 2 | Rb1 | 22.67 | C54H92O23 | 1107.5957 (1107.5976) | 1.7 | 945.5294[M-H-Glc]-, 783.4787[M-H-GlcGlc]-,621.4295[M-H-GlcGlcGlc]-, 459.33790[M-H-GlcGlcGlcGlc]-, 323.0832[GlcGlc-H]- |
| 3 | Rc | 24.01 | C53H90O22 | 1077.5851 (1077.5875) | 2.2 | 945.5193[M-H-Ara(f)]-, 783.4760[M-H-Ara-Glc]-, 621.4169[M-H-Ara-GlcGlc]-, 459.3660[M-H-Ara-GlcGlcGlc]- |
| 4 | Rb2 | 24.93 | C53H90O22 | 1077.5851 (1077.5812) | 3.6 | 945.5348[M-H-Ara(p)]-, 783.4898[M-H-Ara-Glc]-, 621.4365[M-H-Ara-GlcGlc]-, 459.3852[M-H-Ara-GlcGlcGlc]- |
| 5 | Rd | 25.76 | C48H82O18 | 945.5428 (945.5462) | 3.6 | 783.7832[M-H-Glc]-, 621.5318[M-H-GlcGlc]-, 459.5767[M-H-GlcGlcGlc]-, 323.3125[GlcGlc-H]- |
| 6 | Gyp ⅩⅦ | 26.57 | C48H82O18 | 945.5428 (945.5437) | 0.95 | 783.4615[M-H-Glc]-, 621.4111[M-H-GlcGlc]-, 459.9876[M-H-GlcGlcGlc]- |
| 7 | CMC1 | 28.28 | C47H80O17 | 915.5323 (915.5348) | 2.7 | 783.1984[M-H-Ara(f)]-, 621.6952[M-H-Ara-Glc]-, 459.4832[M-H-Ara-GlcGlc]- |
| 8 | F2 | 29.11 | C42H72O13 | 783.4900 (783.4870) | 3.8 | 621.3217[M-H-Glc]-, 459.1521[M-H-GlcGlc]- |
| 9 | Rg3 | 30.83 | C42H72O13 | 783.4900 (783.4933) | 4.2 | 621.4223[M-H-Glc]-, 459.3791[M-H-GlcGlc]- |
| 10 | Rh2 | 33.66 | C36H62O8 | 621.4372 (621.4347) | 4.0 | 459.3563[M-H-Glc]- |
Table1 Analysis results obtained by RRLC/Q-TOF MS
| Peak No. | Compd. | tR/min | Molecular formula | MS(calcd. mass), m/z | 106 Error | MS/MS fragment ions of [M-H]-(mass accuracy < 5×10-6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ra1 | 21.74 | C58H98O26 | 1209.6242 (1209.6274) | 2.7 | 1077.5839[M-H-Xyl ]-, 945.5418[M-H-Xyl-Ara(p)]-, 783.4874[M-H-Xyl-Ara-Glu]-, 621.4336[M-H-Xyl-Ara-GlcGlc]-, 459.5418[M-H-Xyl-Ara-GlcGlcGlc]-, 323.0862[GlcGlc-H]- |
| 2 | Rb1 | 22.67 | C54H92O23 | 1107.5957 (1107.5976) | 1.7 | 945.5294[M-H-Glc]-, 783.4787[M-H-GlcGlc]-,621.4295[M-H-GlcGlcGlc]-, 459.33790[M-H-GlcGlcGlcGlc]-, 323.0832[GlcGlc-H]- |
| 3 | Rc | 24.01 | C53H90O22 | 1077.5851 (1077.5875) | 2.2 | 945.5193[M-H-Ara(f)]-, 783.4760[M-H-Ara-Glc]-, 621.4169[M-H-Ara-GlcGlc]-, 459.3660[M-H-Ara-GlcGlcGlc]- |
| 4 | Rb2 | 24.93 | C53H90O22 | 1077.5851 (1077.5812) | 3.6 | 945.5348[M-H-Ara(p)]-, 783.4898[M-H-Ara-Glc]-, 621.4365[M-H-Ara-GlcGlc]-, 459.3852[M-H-Ara-GlcGlcGlc]- |
| 5 | Rd | 25.76 | C48H82O18 | 945.5428 (945.5462) | 3.6 | 783.7832[M-H-Glc]-, 621.5318[M-H-GlcGlc]-, 459.5767[M-H-GlcGlcGlc]-, 323.3125[GlcGlc-H]- |
| 6 | Gyp ⅩⅦ | 26.57 | C48H82O18 | 945.5428 (945.5437) | 0.95 | 783.4615[M-H-Glc]-, 621.4111[M-H-GlcGlc]-, 459.9876[M-H-GlcGlcGlc]- |
| 7 | CMC1 | 28.28 | C47H80O17 | 915.5323 (915.5348) | 2.7 | 783.1984[M-H-Ara(f)]-, 621.6952[M-H-Ara-Glc]-, 459.4832[M-H-Ara-GlcGlc]- |
| 8 | F2 | 29.11 | C42H72O13 | 783.4900 (783.4870) | 3.8 | 621.3217[M-H-Glc]-, 459.1521[M-H-GlcGlc]- |
| 9 | Rg3 | 30.83 | C42H72O13 | 783.4900 (783.4933) | 4.2 | 621.4223[M-H-Glc]-, 459.3791[M-H-GlcGlc]- |
| 10 | Rh2 | 33.66 | C36H62O8 | 621.4372 (621.4347) | 4.0 | 459.3563[M-H-Glc]- |
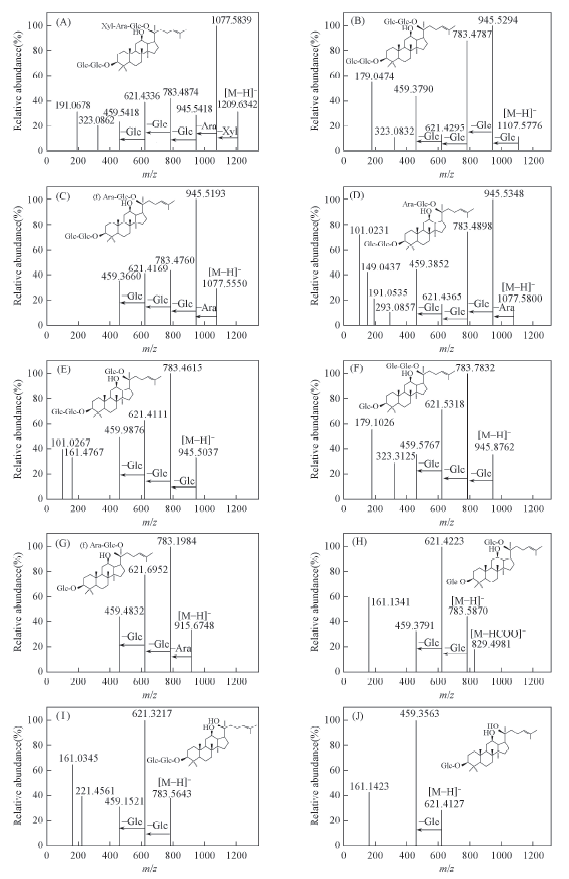
Fig.3 ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS spectra of ginsenosides in negative-ion mode(A) Ra1; (B) Rb1; (C) Rc; (D) Rb2; (E) Rd; (F) Gyp ⅩⅦ; (G) CMC1; (H) F2; (I) Rg3; (J) Rh2.
| [1] | Wang T., Guo R., Zhou G., Zhou X., Kou Z., Sui F., Li C., Tang L., Wang Z., J. Ethnopharmacol., 2016, 188, 234—258 |
| [2] | Li J., Wang R. F., Yang L., Wang Z. T., Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2015, 40(17), 3480—3487 |
| [3] | Uzayisenga R., Ayeka P. A., Wang Y., Phytother. Res., 2014, 28(4), 510—516 |
| [4] | Ng T. B., J. Pharm. Pharmaco., 2006, 28(8), 1007—1019 |
| [5] | Xie G. X., Ni Y., Su M. M., Zhang Y. Y., Zhao A. H., Gao X. F., Liu Z., Xiao P. G., Jia W., Metabolomics,2008, 4, 248—260 |
| [6] | Liu J. H., Wang X., Cai S. Q., Komatsu K., Namba T., J. Pharm. Sci., 2004, 13(4), 225—237 |
| [7] | Chen W., Dang Y. J., Zhu C., Chin. Med-UK, 2010, 5(1), 12—18 |
| [8] | Wang J. R., Yao L. F., Gao W. N., Liu Y., Yick P. W., Liu L., Jiang Z. H., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62, 9024—9034 |
| [9] | Wang L., Li Z., Zhao X., Liu W., Liu Y., Yang J., Li X., Fan X., Cheng Y., Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med., 2013, 6, 264—269 |
| [10] | Wang J. R., Yao L. F., Zhang R., Xia Y., Ma J., Ho H. M., Hu P., Hu M., Liu L., Jiang Z. H., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62, 2558—2573 |
| [11] | Kim Y. J., Yamabe N., Choi P., Lee J. W., Ham J., Kang K. S., J. Agric. Food. Chem., 2013, 61, 9185—9191 |
| [12] | Yu S. S., Zhou X. L., Li F., Xu C. C., Zheng F., Li J., Zhao H. X., Dai Y. L., Liu S. Y., Feng Y., Sci. Rep., 2016, 138(7), 225—237 |
| [13] | Quan K., Liu Q., Wan J. Y., Zhao Y. J., Guo R. Z., Alolga R. N., Li P., Qi L. W., Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 1—7 |
| [14] | Chai R. H., Jiang B. H., Zhao Y. Q., Modern Chinese Medicine, 2007, 12(9), 14—25 |
| (柴瑞华, 姜彬慧, 赵余庆. 中国现代中药, 2007, 12(9), 14—25 | |
| [15] | Wang R. F., Zheng M. M., Cao Y. D., Li H., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 99, 3433—3442 |
| [16] | Miller G., Anal. Chem., 1959, 31, 426—428 |
| [17] | Xu C. C., Yu B. H., Wang H. L., Li J., Liu S. Y., Yu S. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2), 281—289 |
| (许春春, 于渤浩, 王红蕾, 李晶, 刘淑莹, 于珊珊. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2), 281—289 ) | |
| [18] | Chen H. Y., Yao C. X., Zhang X. L., China Pharmacist, 2017, 20(3), 460—462 |
| (陈红岩, 姚晨旭, 张小龙. 中国药师, 2017, 20(3), 460—462) | |
| [19] | Dai Y. L., Yu S. S., Zhang Y., Hao Y., Zhong W., Yue H., Liu S. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7), 1396—1402 |
| (戴雨霖, 于珊珊, 张颖, 郝颖, 钟薇, 越皓, 刘淑莹. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(7), 1396—1402) | |
| [20] | Dai Y. L., Yue H., Sun C. J., Guo Y. L., Zheng F., Li J., Liu S. Y., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2015, 43(8), 1181—1186 |
| (戴雨霖, 越皓, 孙长江, 郭云龙, 郑飞, 李晶, 刘淑莹. 分析化学, 2015, 43(8), 1181—1186) | |
| [21] | He Y. F., Liu W. L., Su R., Xiu Y., Pei J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2017, 33(2), 172—178 |
| [22] | Ma Y. H., Liu Y. Y., Wei M. Y., Song F. R., Liu Z. Y., Pi Z. F., Chem. Res. Chinese Univerisities, 2015, 31(6), 914—918 |
| [23] | Domon B., Costello C. E., Glycoconj. J., 1988, 5, 397—409 |
| [24] | Perreault H., Costello C. E., J. Mass Spectrom., 1994, 29, 720—735 |
| [25] | Lee D. Y., Kim J. K., Shrestha S., Seo K. H., Lee Y. H., Noh H. J., Kim G. S., Kim G. S., Kim Y. B., Kim S. Y., Baek N. I., Molecules,2013, 18(12), 14849—14861 |
| [1] | LUO Lei, MU Xiaoqing, WU Tao, NIE Yao, XU Yan. Synthesis of Norephedrine in One Pot [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2458. |
| [2] | ZHU Ling,WANG Yuchen,ZHAO Jiangyuan,WEN Mengliang,LI Minggang,HAN Xiulin. Transformation of Ginsenoside Rb3 and C-Mx by Recombinant β-Xylosidase † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1010. |
| [3] | WANG Tianqi,YU Qiongwei,FENG Yuqi. Analysis of Imidazole Propionic Acid in Serum of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Based on NiO@SiO2 Solid-phase Extraction Coupled with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 262. |
| [4] | DU Chenhui, LI Ze, CUI Xiaofang, ZHANG Min, PEI Xiangping, ZHAN Haixian, YAN Yan. Chemical Transformation of Raw and Fermented Ziziphi Spinosae Semen Analyzed by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS/MS [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1614. |
| [5] | HAN Mingxin, LI Fangtong, ZHANG Yan, DAI Yulin, ZHENG Fei, YUE Hao. Biotransformation of Rare Protopanaxadiol Saponin by Human Intestinal Microflora† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1390. |
| [6] |
XIAO Yongkun,LIU Chunying,YU Hongshan,YI Tea-Hoo,XU Longquan,SONG Jianguo,IM Wan-Teak,SUN Changkai,JIN Fengxie.
Dynamic Biotransformation of Protopanaxadiol-ginsenosides and Preparation of Minor Ginsenosides C-K or |
| [7] | ZHAO Huanxi,WANG Qiuying,SUN Xiuli,LI Xue,MIAO Rui,WU Dongxue,LIU Shuying,XIU Yang. Discrimination of Ginseng Origins and Identification of Ginsenoside Markers Based on HPLC-MS Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 246. |
| [8] | QIAO Mengdan, LIU Shang, ZHANG Yan, LI Jing, ZHENG Fei, DAI Yulin, YUE Hao. Biotransformation of Ginsenosides in Fermented Ginseng Using UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS/MS† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 219. |
| [9] | LIU Xinru, LIU Chunying, XU Longquan, SONG Jianguo, YU Hongshan. Construction of Ginsenoside-β-glucosidase Gene Vector and Biotransformation in Pichia Pastoris† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2451. |
| [10] | LI Ruigang,ZHU Na,ZHAO Huanxi,WANG Nan,SUN Hongmei,YUE Hao,LI Jing. Effects of Ginseng Polysaccharides on the Metabolism of Ginsenoside Re in vivo and Transformation of Ginsenoside Re in vitro† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2192. |
| [11] | MIAO Rui,WU Dongxue,WANG Qiuying,ZHAO Huanxi,LI Xue,XIU Yang,LIU Shuying. Rapid Separation of Ginsenosides Based on Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2178. |
| [12] | XU Chunchun, YU Bohao, WANG Honglei, LI Jing, LIU Shuying, YU Shanshan. Transformation of Minor Ginsenoside Rd and CK by Recombinant Thermostable β-Glucosidase† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 281. |
| [13] | ZHAO Yu-Feng1,2, SONG Feng-Rui1, GUO Xin-Hua1, LIU Shu-Ying1*. Studies on the Biotransformation of Aconitine in Human Intestinal Bacteria Using Soft-ionization Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(1): 55. |
| [14] | SUN Guang-Zhi1, LI Xiang-Gao2, LIU Zhi1, WANG Ji-Yan3, ZHENG Yi-Nan2, YANG Xiu-Wei4*. Isolation and Structure Characterization of Malonyl-notoginsenoside-R4 from the Root of Panax ginseng [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(7): 1316. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yu-Feng1,2, SONG Feng-Rui1, YUE Hao1, GUO Xin-Hua1, LI Hui-Lin1, LIU Zhi-Qiang1, LIU Shu-Ying1*. Biotransformation of Deoxyaconitine of Metabolite of Aconitine by Human Intestinal Bacteria and Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(11): 2051. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||