

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 85.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160477
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Kaihong, LIN Qi, CUI Zhenggang*( ), PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong
), PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong
Received:2016-07-06
Online:2017-01-10
Published:2016-12-20
Contact:
CUI Zhenggang
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Kaihong, LIN Qi, CUI Zhenggang, PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong. pH-Responsive Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles in Combination with N-Dodecyl-β-aminopropionate†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 85.

Fig.1 Photographs of n-decane-in-water(volume ratio 1:1) emulsions stabilized by 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles solely(A), DPA solely at different concentrations(B) and their mixtures(C, D)DPA concentration(from left to right)/(mmol·L-1): (B) 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1, 3; (C), (D) 0.003, 0.006, 0.01, 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1. Taken 24 h after preparation; (D) 1 week after preparation.
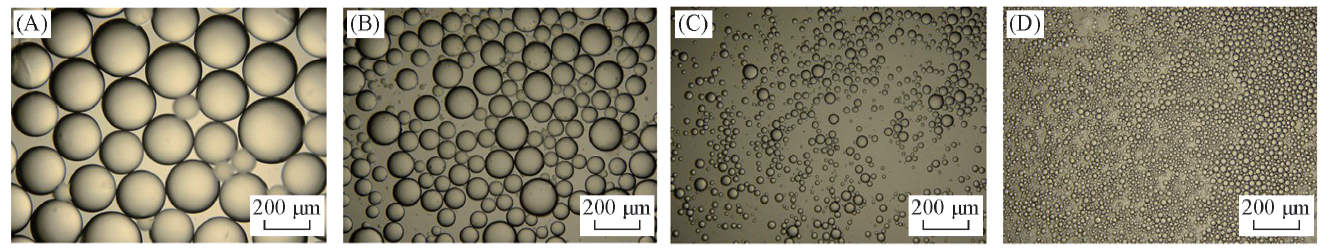
Fig.2 Optical micrographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles and DAP at different concentrations(A—C) and by DAP solely(D) taken 24 h after preparationSurfactant concentration/(mmol·L-1): (A) 0.006; (B) 0.3; (C) 0.6; (D) 1.
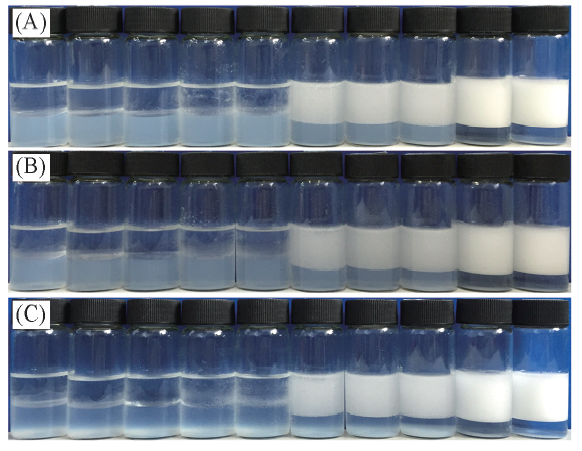

Fig.3 Photographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles and 0.06 mmol/L DAP with different aqueous pH value, taken 24 h(A), 1 week(B) and 2 months(C) after preparationAqueous pH value(from left to right): 6.77, 6.03, 5.65, 5.32, 5.14, 4.99, 4.58, 4.18, 3.63, 3.30.
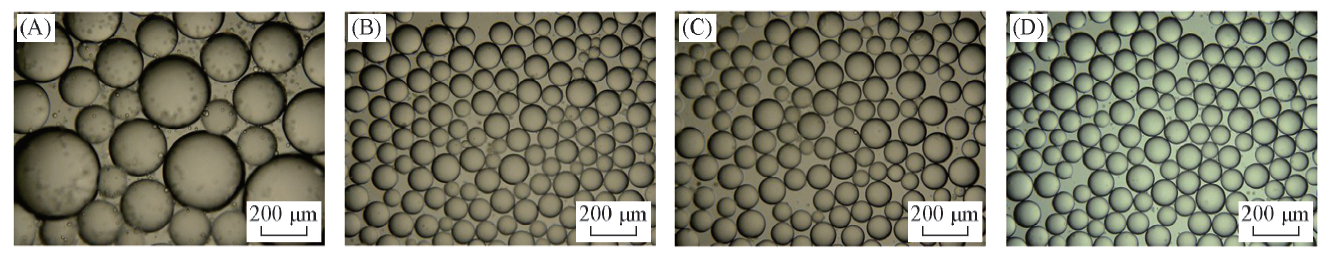
Fig.4 Optical micrographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles and 0.06 mmol/L DAP with different pH values taken 24 h(A—C) and 2 months(D) after preparationpH value: (A) 4.58; (B) 3.63; (C) 3.30; (D) 3.63.
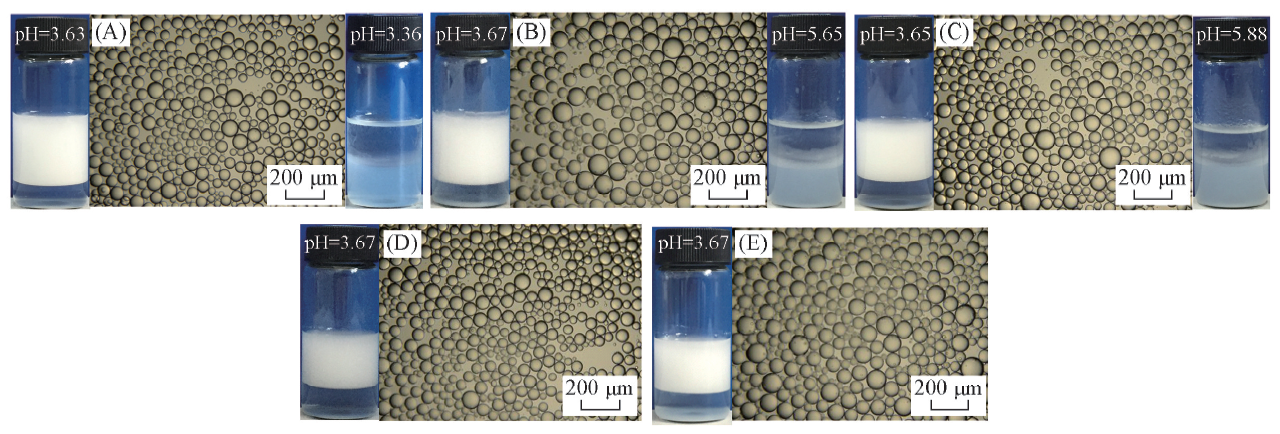

Fig.5 Photographs and micrographs(at low pH) of the n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.06 mmol/L DAP following pH alternation cycling, taken 24 h[cycle 1(A), cycle 2(B), cycle 4(C), cycle 6(D)] and 2 months(cycle 6 only, E) after homogenization(for stable emulsions) and 20 min after dropping NaOH solution with agitation(for unstable emulsions)
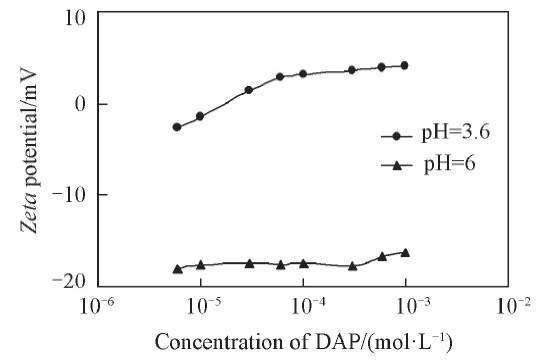
Fig.8 Zeta potential of silica nanoparticles(0.1%) dispersed in DAP aqueous solution with different pH values as a function of initial DAP concentration(25 ℃)
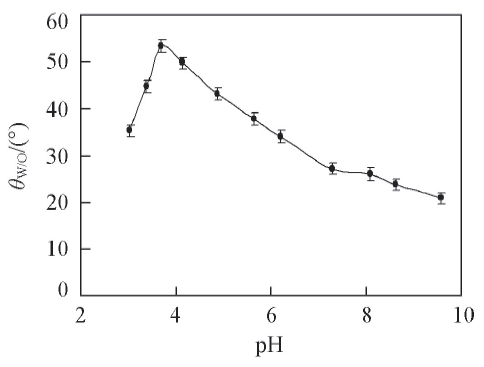
Fig.9 Contact angle of DAP aqueous solution(0.06 mmol/L) on negatively charged quartz slide as a function of pH measured by captured oil(n-decane) drop method(25 ℃)
| [1] | Aveyard R., Binks B. P., Clint J. H., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, 100, 503—546 |
| [2] | Jiang J. Z., Zhu Y., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(47), 12373—12376 |
| [3] | Li T., Zhang L., Chen Y., Guo Y. J., Du X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(4), 772—780 |
| (李涛, 张龙, 陈颖, 郭亚军, 杜雪岩. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4), 772—780) | |
| [4] | Gao Y. J., Zhang L., Hou J. J., Ma Y. B., Qiu H., Zhang W. J., Du X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(6), 1202—1207 |
| (郭亚军, 张龙, 后洁琼, 马泳波, 秋虎, 张文娟, 杜雪岩. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6), 1202—1207) | |
| [5] | Tang J. T., Quinlan P. J., Tam K. C., Soft Matter,2015, 11(18), 3512—3529 |
| [6] | Binks B. P., Murakami R., Armes S. P., Fujii S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(30), 4795—4798 |
| [7] | Zoppe J. O., Venditti R. A., Rojas O. J., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 369, 202—209 |
| [8] | Saigal T., Dong H. C., Matyjaszewski K., Tilton R. D., Langmuir,2010, 26(19), 15200—15209 |
| [9] | Tan T. T. Y., Ahsan A., Reithofer M. R., Tay S. W., Tan S. Y., Hor T. S. A., Chin J. M., Chew B. K. J., Wang X. B., Langmuir,2014, 30(12), 3448—3454 |
| [10] | Anwar N., Williams T., Grimme B., Kuehne A. J. C., ACS Macro Lett., 2013, 2(9), 766—769 |
| [11] | Liu P. W., Lu W. Q., Wang W. J., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Langmuir,2014, 30(34), 10248—10255 |
| [12] | Liang C., Liu Q. X., Xu Z. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2014, 6(9), 6898—6904 |
| [13] | Zhang Q., Yu G. Q., Wang W. J., Yuan H. M., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Langmuir,2012, 28(14), 5940—5946 |
| [14] | Su X., Jessop P. G., Cunningham M. F., Macromol., 2012, 45(2), 666—670 |
| [15] | Pinaud J., Kowal E., Cunningham M. F., Jessop P. G., ACS Macro Lett., 2012, 1(9), 1103—1107 |
| [16] | Zhang Q., Wang W. J., Lu Y. Y., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Macromol., 2011, 44(16), 6539—6545 |
| [17] | Lin S. J., Theato P., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2013, 34(14), 1118—1133 |
| [18] | Zhang Q., Yu G. Q., Wang W. J., Yuan H. M., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Macromol., 2013, 46(4), 1261—1267 |
| [19] | Quesada M., Muniesa C., Botella P., Quesada M., Muniesa C., Botella P., Chem. Mater., 2013, 25(13), 2597—2602 |
| [20] | Lam S., Blanco E., Smoukov S. K., Velikov K. P., Velev O. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(35), 13856—13859 |
| [21] | Blanco E., Lam S., Smoukov S. K., Velikov K. P., Khan S. A., Velev O. D., Langmuir,2013, 29(32), 10019—10027 |
| [22] | Morse A. J., Armes S. P., Thompson K. L., Dupin D., Fielding L. A., Mills P., Swart R., Langmuir,2013, 29(18), 5466—5475 |
| [23] | Liu H., Wang C. Y., Zou S. W., Wei Z. J., Tong Z., Langmuir,2012, 28(30), 11017—11024 |
| [24] | Fujii S., Suzaki M., Armes S. P., Dupin D., Hamasaki S., Aono K., Nakamura Y., Langmuir,2011, 27(13), 8067—8074 |
| [25] | Binks B. P., Murakami R., Armes S. P., Fujii S., Schmid A., Langmuir,2007, 23(17), 8691—8694 |
| [26] | Yi C. L., Yang Y. Q., Zhu Y., Liu N., Liu X. Y., Luo J., Jiang M., Langmuir,2012, 28(25), 9211—9222 |
| [27] | Fujii S., Okada M., Furuzone T., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 315(1), 287—292 |
| [28] | Yu D., Lin Z., Li Y., Colloid Surface A,2013, 422, 100—109 |
| [29] | Yang H., Zhou T., Zhang W., Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(29), 7455—7459 |
| [30] | Motornov M., Sheparovych R., Lupitskyy R., MacWillianms E., Hoy O., Luzinov I., Minko S., Adv. Func. Mater., 2007, 17(14), 2307—2314 |
| [31] | Yang F., Niu Q., Lan Q., Sun D., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 306(2), 285—295 |
| [32] | Amalvy J. I., Unali G. F., Li Y., Granger-Bevan S., Armes S. P., Binks B. P., Rodrigues J. A., Whiteby C. P., Langmuir,2004, 20(11), 4345—4354 |
| [33] | Morse A. J., Madsen J., Growney D. J., Armes S. P., Mills P., Swart R., Langmuir,2014, 30(42), 12509—12519 |
| [34] | Wang Z. P., Floris P. J. T. R., van Hest J. C. M., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(93), 14550—14553 |
| [35] | Nguyen B. T., Wang W. K., Saunders B. R., Benyahia L., Nicolai T., Langmuir,2015, 31(12), 3605—3611 |
| [36] | Lu J., Zhou W., Chen J., Jin Y. L., Walters K. B., Ding S. J., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(13), 9416—9424 |
| [37] | Richtering W., Langmuir, 2012, 28(50), 17218—17229 |
| [38] | Yamagami T., Kitayama Y., Okubo M., Langmuir,2014, 30(26), 7823—7832 |
| [39] | Tang J., Lee M. F. X., Zhang W., Zhao B. X., Berry R. M., Tam K. C., Biomacromolecules,2014, 15(8), 3052—3062 |
| [40] | Fujii S., Akiyama K., Nakayama S., Hamasaki S., Yusa S., Nakamura Y., Soft Matter,2015, 11(3), 572—579 |
| [41] | Rahman M. M., Chehimi M. M., Fessi H., Elaissari A., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 360(2), 556—564 |
| [42] | Brugger B., Richtering W., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19(19), 2973—2978 |
| [43] | Fameau A. L., Lam S., Velev O. D., Chem. Sci., 2013, 4(10), 3874—3881 |
| [44] | Zhou P., Liu B., Yang F. X., Wang Q., Qu X. Z., Yang Z. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(7), 1431—1436 |
| (周鹏, 刘宝, 杨福鑫, 王倩, 屈小中, 杨振忠. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(7), 1431—1436) | |
| [45] | Yan H. Q., Chen X. Q., Li J. C., Feng Y. H., Wu J. B., Ling Q., Shi Z. F., Wang X. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(5), 1018—1024 |
| (颜慧琼, 陈秀琼, 李嘉诚, 冯玉红, 伍剑博, 林强, 史载峰, 王向辉. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(5), 1018—1024) | |
| [46] | Cui Z. G., Yang L. L., Cui Y. Z., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2010, 26(7), 4717—4724 |
| [47] | Binks B. P., Rodrigues J. A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46(28), 5389—5392 |
| [48] | Cui Z. G., Cui C. F., Zhu Y., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2012, 28(1), 314—320 |
| [49] | Chen Z., Cui C. F., Cui Z. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(11), 2246—2253 |
| (陈钊, 崔晨芳, 崔正刚. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(11), 2246—2253) | |
| [50] | Zhu Y., Jiang J. Z., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Soft Matter,2014, 10(48), 9739—9745 |
| [51] | Zhu Y., Jiang J. Z., Liu K. H., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2015, 31(11), 3301—3307 |
| [52] | Zhu Y., Pei X. M., Jiang J. Z., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2015, 31(47), 12937—12943 |
| [53] | Bettayeb B., Descoteaux C., Benoit F., Chapados C., Bérubé G., J. Surfact. Deterg., 2009, 12(3), 237—247 |
| [54] | Xu H.J., Liu X. M., Cao H. X., Ma D. G., 1999, (Suppl.), 47—49 |
| (许虎君, 刘学民, 曹红霞, 马德广. 日用化学品科学, 1999, (增刊), 47—49 | |
| [55] | Worthen A. J., Foster L. M., Dong J., Bollinger J. A., Peterman A. H., Pastora L. E., Bryant S. L.,Truskett T. M., Bielawski C. W., Johnston K. P., Langmuir,2014, 30(4), 984—994 |
| [1] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [2] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [3] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, JIANG Wei, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Activation of Biochar from Cattail and the VOCs Adsorption Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [4] | MENG Xianglong, YANG Ge, GUO Hailing, LIU Chenguang, CHAI Yongming, WANG Chunzheng, GUO Yongmei. Synthesis of Nano-zeolite and Its Adsorption Performance for Hydrogen Sulfide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [5] | CHEN Xiaolu, YUAN Zhenyan, ZHONG Yingchun, REN Hao. Preparation of Triphenylamine Based PAF-106s via Mechanical Ball Milling and C2 Hydrocarbons Adsorption Property [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [6] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [7] | ZHENG Meiqi, MAO Fangqi, KONG Xianggui, DUAN Xue. Layered Double Hydroxides as Sorbent for Remediation of Radioactive Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [8] | TIAN Xiaokang, ZHANG Qingsong, YANG Shulin, BAI Jie, CHEN Bingjie, PAN Jie, CHEN Li, WEI Yen. Porous Materials Inspired by Microbial Fermentation: Preparation Method and Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [9] | MA Jianxin, LIU Xiaodong, XU Na, LIU Guocheng, WANG Xiuli. A Multi-functional Zn(II) Coordination Polymer with Luminescence Sensing, Amperometric Sensing, and Dye Adsorption Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| [10] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [11] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [12] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, SONG Fujiao, ZHU Ting, HUANG Weiqiu, ZHONG Jing, CHEN Ruoyu. Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption Properties of Hollow Carbon Nanospheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1704. |
| [13] | WANG Longjie, FAN Hongchuan, QIN Yu, CAO Qiue, ZHENG Liyan. Research Progress of Metal-organic Frameworks in the Field of Chemical Separation and Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [14] | YAN Yanhong, WU Simin, YAN Yilun, TANG Xihao, CAI Songliang, ZHENG Shengrun, ZHANG Weiguang, GU Fenglong. Sulfonic Acid-functionalized Spherical Covalent Organic Framework with Ultrahigh Capacity for the Removal of Cationic Dyes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 956. |
| [15] | HU Xueyi, HAN Lulu, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei. Admicelles and Adsolubilization of Extended Surfactants on Alumina [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 843. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||