

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 934.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131201
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Liyan1, LIU Zhifang1, QIN Qing1, CAO Yaan2, ZHENG Wenjun1,*( )
)
Received:2013-12-10
Online:2014-05-10
Published:2014-03-11
Contact:
ZHENG Wenjun
E-mail:zhwj@nankai.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Liyan, LIU Zhifang, QIN Qing, CAO Yaan, ZHENG Wenjun. Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of Anatase TiO2 Nanotubes and Their UV Light Photocatalytic Activities†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 934.
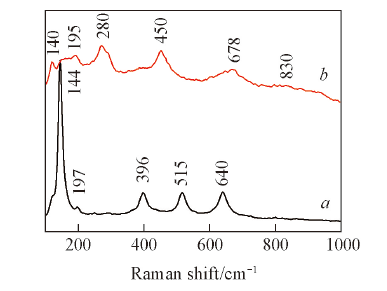
Fig.2 Raman spectra of anatase TiO2 nanotubes after calcination at 470 ℃ for 2 h(a) and hydrogen titanate nanutubes synthesized with [Bmim]OH at 180 ℃ for 24 h(b)
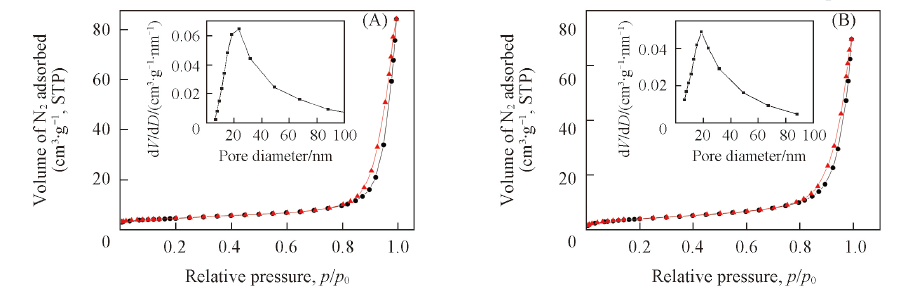
Fig.4 Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of anatase TiO2 nanotubes after calcination at 470 ℃ for 2 h(A) and hydrogen titanate nanotubes prepared with [Bmim]OH at 180 ℃ for 24 h(B)^Insets are the correspongding pore size distribution curves.
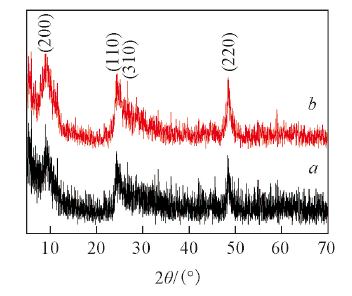
Fig.5 XRD patterns of the hydrogen titanate nanotubes obtained by hydrothermal methods at 120 ℃ for 24 h^a. Without [Bmim]OH; b. with [Bmim]OH, V(NaOH)∶V([Bmim]OH)=1∶3.
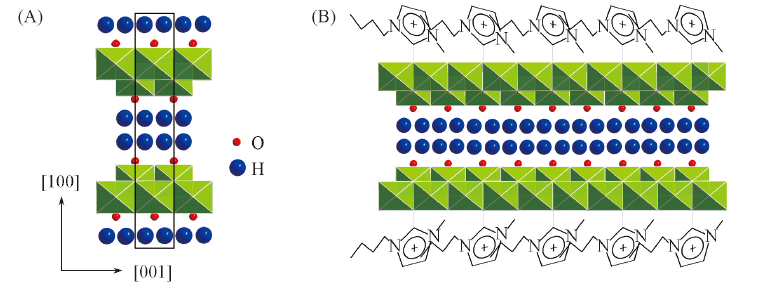
Fig.6 Representation of the crystal structure of H2Ti2O5·H2O projecting along [010] direction(A) and [Bmim]+ ions perpendicular to the (NaH)xTi2-x/4□x/4O4·H2O sheets and their self-assembly into order structures along the c axis(B)
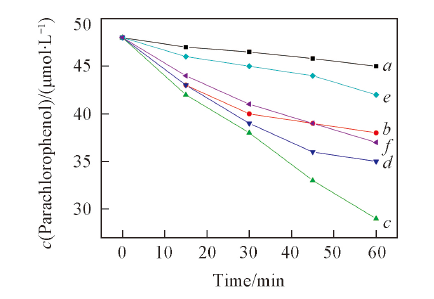
Fig.7 Photodegradation of parachlorophenol under UV-light irradiation^a. Blank; b. TiO2 nanoparticles; c. anatase TiO2 nanotubes(calcined at 470 ℃); d. hydrogen titanate nanotubes prepared with [Bmim]OH; e. hydrogen titanate nanotubes prepared without [Bmim]OH; f. anatase TiO2 nanotubes(calcined at 450 ℃).
| [1] | Fujishima A., Honda A., Nature, 1972, 238, 37—38 |
| [2] | Khan S., Al-Shahry M., Ingler W. B., Science, 2002, 297, 2243—2245 |
| [3] | Antonelli D.M., Ying J. Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 1995, 34, 2014—2019 |
| [4] | Lakshmi B. B., Dorhout P. K., Martin C. R., Chem. Mater., 1997, 9(3), 857—865 |
| [5] | Kasuga T., Hiramatsu M., Hoson A., Sekino T., Niihara K., Langmuir, 1998, 14(12), 3160—3163 |
| [6] | Zwilling V., Aucouturier M., Darque-Ceretti E., Electrochim. Acta, 1999, 45(6), 921—929 |
| [7] | Morgado Jr E., Jardim P. M., Marinkovic B. A., Rizzo F. C., de Abreu M. A. S., Zotin J. L., Araüjo A. S., Nanotechnol., 2007, 18, 495710 |
| [8] | Thorne A., Kruth A., Tunstall D., Irvine J. T. S., Zhou W. Z., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 5439—5444 |
| [9] | Quan X., Yang S., Ruan X., Zhao H., Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39, 3770—3775 |
| [10] | Zhang Z. H., Yuan Y., Shi G. Y., Fang Y. J., Liang L. H., Ding H. C., Jin L. T., Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41, 6259—6263 |
| [11] | Ortiz G. F., Hanzu I., Djenizian T., Lavela P., Tirado J. L., Knauth P., Chem. Mater., 2009, 21(1), 63—67 |
| [12] | Xu C. K., Shin P. H., Cao L. L., Wu J. M., Gao D., Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(1), 143—148 |
| [13] | Galinski M., Lewandowski A., Stepniak I., Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 51(26), 5567—5580 |
| [14] | Knang D. B., Brezesinski T. Smarsly B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 10534—10535 |
| [15] | Zheng W. J., Liu X. D., Yan Z. Y., Zhu L. J., ACS Nano, 2009, 3(1), 115—122 |
| [16] | Duan X. C., Lian J. B., Ma J. M., Kim T. I., Zheng W. J., Crystal Growth & Design, 2010, 10(10), 4449—4455 |
| [17] | Ma Z., Yu J. H., Dai S., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22(2), 261—285 |
| [18] | Chen Q., Sun Y., Duan X. C., Zheng W. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(3), 667—672 |
| (陈青, 孙嫣, 段小川, 郑文君, 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(3), 667—672) | |
| [19] | Ranu B. C., Banerjee S., Organ. Lett., 2005, 7(14), 3049—3052 |
| [20] | Cao Y. A., Shen D. F., Zhang X. T., Meng Q. J., Ma Y., Wu Z. Y., Bai Y. B., Li T. J., Yao J. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(11), 1910—1912 |
| (曹亚安, 沈东方, 张昕彤, 孟庆巨, 马颖, 吴志芸, 白玉白, 李铁津, 姚建年.高等学校化学学报, 2001,22(11), 1910—1912) | |
| [21] | Kim S. J., Yun Y. U., Oh H. J., Hong S. H., Roberts C. A., Routray K., Wachs I. E., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1(1), 130—135 |
| [22] | Mao Y. B., Wong S. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 8217—8226 |
| [23] | Hodos M., Horváth E., Haspel H., Kukovecz Á., Kónya Z., Kiricsi I., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2004, 399(4—6), 512—515 |
| [24] | Bavykin D. V., Parmon V. N., Lapkin A. A., Walsh F. C., J. Mater. Chem., 2004, 14, 3370—3377 |
| [25] | Yu J., Yu H., Cheng B., Trapalis C., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2006, 249, 135—142 |
| [26] | Qamar M., Yoon C. R., Oh H. J., Lee N. H., Park K., Kim D. H., Lee K. S., Lee W. J., Kim S. J., Catal. Today, 2008, 131, 3—14 |
| [27] | Sheng J., Hu L. H., Xu S. Y., Liu W. Q., Mo L. E., Tian H. J., Dai S. Y., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 5457—5463 |
| [28] | Morgado J. E., de Marco A. S., Moure G. T., Marinkovic B. A., Jardim P. M., Araujo A. S., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19, 665—676 |
| [29] | Hu W. B., Li L. P., Li G. S., Meng J., Tong W. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(39), 16996—17001 |
| [30] | Kiatkittipong K., Scott J., Amal R., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2011, 3(10), 3988—3996 |
| [31] | An H. Q., Zhu B. L., Li J. X., Zhou J., Wang S. R., Zhang S. M., Wu S. H., Huang W. P., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 18772—18775 |
| [32] | Fukuda K., Sasaki T., Watanabe M., Nakai I., Inaba K., Omote K., Cryst. Growth & Design, 2003, 3(3), 281—283 |
| [33] | Ma R., Bando Y., Sasaki T., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 380(5/6), 577—582 |
| [34] | Tsai C. C., Teng H. S., Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(2), 367—373 |
| [35] | Chen Q., Du G. H., Zhang S., Peng L. M., Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., 2002, 58, 587—593 |
| [36] | Dong K., Zhang S. J., Wang D. X., Yao X. Q., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110, 9775—9782 |
| [37] | Duan X. C., Kim T. I., Li D., Ma J. M., Zheng W. J., Chem. Eur. J., 2013, 19(19), 5924—5937 |
| [38] | Lian J. B., Ma J. M., Duan X. C., Kim T. I., Li H. B., Zheng W. J., Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(15), 2650—2652 |
| [39] | Pensado A. S., Padua A. A. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(37), 8683—8687 |
| [40] | Miki K., Westh P., Koga Y., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 9014—9019 |
| [1] | CUI Wei, ZHAO Deyin, BAI Wenxuan, ZHANG Xiaodong, YU Jiang. CO2 Absorption in Composite of Aprotic Solvent and Iron-based Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220120. |
| [2] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [3] | JI Shuangqi, JIN Zhao, GUAN Wenna, PAN Xiangyu, GUAN Tong. Preparation and Chromatographic Performance of Mixed-mode Silica Stationary Phase Modified by Double Cationic Ionic Liquid and Octadecyl Group [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220008. |
| [4] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [5] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [6] | ZHANG Huishuang, GAO Yanxiao, WANG Qiuxian, LI Xiangnan, LIU Wenfeng, YANG Shuting. High-low Temperature Properties of Ni-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material by Hydrothermal Synthesis with CTAB Assisted [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 819. |
| [7] | WANG Ye, ZHANG Xiaosi, SUN Lijing, LI Bing, LIU Lin, YANG Miao, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Morphology Control of SAPO Molecular Sieves under the Assistance of Organosilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 683. |
| [8] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [9] | WANG Man, WANG Xin, ZHOU Jing, GAO Guohua. Efficient Synthesis of Dimethyl Carbonate via Transesterification of Methanol and Ethylene Carbonate Catalyzed by Poly(ionic liquid)s [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3701. |
| [10] | WANG Jianyu, ZHANG Qiang, YAN Wenfu, YU Jihong. Roles of Hydroxyl Radicals in Zeolite Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 11. |
| [11] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [12] | ZHOU Molin, JIANG Xin, YI Ting, YANG Xiangguang, ZHANG Yibo. Improvement of Interface Stability Between Sulfide Solid Electrolyte Li10GeP2S12 and Lithium Metal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1810. |
| [13] | GAO Chong,YU Fengli,XIE Congxia,YU Shitao. Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Cyclic Ketones Catalyzed by Amino Alcohol Heteropoly Acid Ionic Liquid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1101. |
| [14] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| [15] | LIU Yabing,LI Mingyang,TIAN Ge,ALATENG Shaga,PEI Tonghe,NIE Jingsi. Syntheses, Structures and Catalytic Properties of Two Supramolecular Complexes Based on 2-Pyridylamine and Cluster † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 995. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||