

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 2033.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190104
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles
XIE Xin1,ZHANG Xiao1,LI Ruihan1,SONG Xiaoxiao1,2,LIU Lifen1,2,*( ),GAO Congjie1,2
),GAO Congjie1,2
Received:2019-02-16
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-09-09
Contact:
LIU Lifen
E-mail:lifenliu@zjut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XIE Xin, ZHANG Xiao, LI Ruihan, SONG Xiaoxiao, LIU Lifen, GAO Congjie. Microstructure Regulation of the Reverse Osmosis Membrane to Improve the Boron Removal Performance †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 2033.
| Membrane | Elemental composition(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | |
| TFC | 73.18 | 16.06 | 10.77 |
| TFC-ABA | 73.14 | 16.45 | 10.41 |
| TFC-PEI | 69.82 | 16.58 | 13.65 |
| TFC-PEI-ABA | 70.43 | 16.36 | 13.21 |
| Membrane | Elemental composition(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | |
| TFC | 73.18 | 16.06 | 10.77 |
| TFC-ABA | 73.14 | 16.45 | 10.41 |
| TFC-PEI | 69.82 | 16.58 | 13.65 |
| TFC-PEI-ABA | 70.43 | 16.36 | 13.21 |
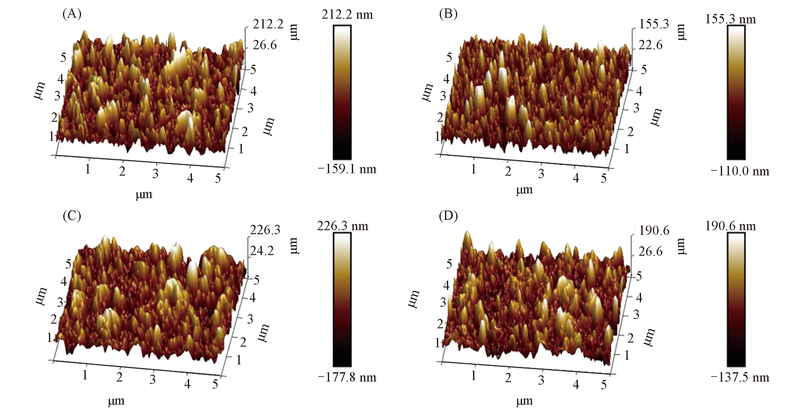
Fig.5 AFM images of TFC(A), TFC-ABA(B), TFC-PEI(C) and TFC-PEI-ABA(D) (A) Rq=58.6, Ra=46.2; (B) Rq=39.7, Ra=28.8; (C) Rq=60.9, Ra=46.8; (D) Rq=51.9, Ra=39.2.
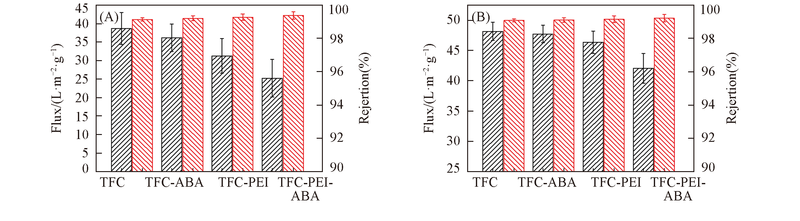
Fig.6 Separation performances of fabricated membranes under low pressure(A) and simulated seawater conditions(B) (A) 2 g/L NaCl, 15.5 MPa, pH=7.0; (B) 32 g/L NaCl, 0.005 g/L H3BO3, 55 MPa, pH=8. Flux; rejertion.
| RO membrane | Water flux/(L·m-2·h-1) | NaCl retention rate(%) | Boron retention rate(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12-RO | 42.1 | 98.1 | 87.8 | [31] |
| SRN-RO | 80.3 | 98.4 | 62.0 | [32] |
| CAI-RO | 7.7 | 90.0 | 90.6 | [33] |
| TFC-PEI-ABA | 34.2 | 99.2 | 90.3 | This work |
| RO membrane | Water flux/(L·m-2·h-1) | NaCl retention rate(%) | Boron retention rate(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12-RO | 42.1 | 98.1 | 87.8 | [31] |
| SRN-RO | 80.3 | 98.4 | 62.0 | [32] |
| CAI-RO | 7.7 | 90.0 | 90.6 | [33] |
| TFC-PEI-ABA | 34.2 | 99.2 | 90.3 | This work |
| [1] | Uemura T., Kotera K., Henmi M., Tomioka H., ,. Desalin. Water. Treat 2012, 33, 283— 288 |
| [2] | Wu L. X., Cai Z. B., Chen X. L., Liu L. F., Gao C. J., ,Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015,36( 4), 765— 771 |
| (吴丽项, 蔡志彬, 陈晓林, 刘立芬, 高从堦. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4), 765— 771) | |
| [3] |
Liu L. F., Xu D. Z., Zhang L., Gao C. J., ,Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012,33( 7), 1605— 1612
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0251-0790.2012.07.043 |
|
(刘立芬, 徐德志, 张林, 高从堦. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(7), 1605— 1612)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0251-0790.2012.07.043 |
|
| [4] | Liyanaarachchi S., Shu L., Muthukumaran S., Jegatheesan V., Baskaran K., ,. Environ. Sci. 2014, 13, 203— 214 |
| [5] | Argust P., ,. Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 1998, 66, 131— 143 |
| [6] | Nable R. O., Banuelos G. S., Paull J. G., ,. Plant Soil 1997, 193, 181— 198 |
| [7] | Meng J. Q., Yuan J., Kang Y. L., Zhang Y. F., Du Q. Y., ,. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2012, 368, 197— 207 |
| [8] | Shi Q., Men J. Q., Xu R. S., Du X. L., Zhang Y. F., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 50— 59 |
| [9] | Lee K. P., Arnot T. C., Mattia D., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1— 22 |
| [10] | Shultz S. R., Bass M., Semiat R., Freger V., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 165— 172 |
| [11] | Bernstein R., Belfer S., Freger V., ,. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3613— 3620 |
| [12] | Tang Y. P., Luo L., Thong Z. W., Chung T. S., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 434— 446 |
| [13] | Tu K. L., Nghiem L. D., Chivas A. R., ,. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 87— 101 |
| [14] | Busch M., Mickols W. E., Jons S., Redondo J., Witte J. D., ,. Water Reuse Q 2004, 13, 25— 41 |
| [15] | Shultz S., Bass M., Semiat R., Freger V., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 165— 172 |
| [16] | Kim S. H., Kwak S. Y., Suzuki T., ,. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1764— 1770 |
| [17] | Coronell O., Mariñas B. J., Zhang X., Cahill D. G., ,Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42, 5260— 5266 |
| [18] | Cahill D. G., Freger V. S., Kwak Y., ,. MRS Bull. 2008, 33, 27— 32 |
| [19] | Shultz S., Freger V ., Desalination 2018, 431, 66— 72 |
| [20] | Hu J. H., Pu Y. L., Ueda M., Zhang X., Wang L. J., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 1— 7 |
| [21] | Vincenzoa M. D., Barboiua M., Tiraferrib A., Legrand Y. M., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 71— 77 |
| [22] | Wang S. H., Zhou Y., Gao C. J., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 244— 252 |
| [23] | Zhu X. Q., Fan X. W., Ju G. N., Cheng M. J., An Q., Nie J., Shi F., ,. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8093— 8095 |
| [24] | Luan X. L., Huang T., Zhou Y., An Q., Wang Y., Wu Y. L., Li X. M., Li H. T., Shi F., Zhang Y. H., ,. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34080— 34088 |
| [25] | Amoozgar Z., Rickett T., Park J., Tuchek C., Shi R., Yeo Y., ,. Acta Biomaterialia 2012, 8, 1849— 1858 |
| [26] | Yu H. P., Zeng Z. Q., Liu H. C., Luo Y. Y., ,. Advanced Materials Research 2012, 824, 824— 829 |
| [27] | Bhat V. T., James N. R., Jayakrishnan A., ,. Polym Int. 2008, 57, 124— 132 |
| [28] | Liu L. F., Cai Z. B., Shen J. N., Wu L. X., Hoek E. M. V., Gao C. J., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 397— 409 |
| [29] | Ma D. C., Peh S. B., Han G., Chen S. B., ,. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7523— 7534 |
| [30] | Xu J., Wang Z. J., Wang X., Wang S. C ., Desalination 2015, 365, 398— 406 |
| [31] | Shultz S., Bass M., Semiat R., Freger V., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 165— 172 |
| [32] | Vincenzo M. Di., Barboiu M., Tiraferri A., Legrand Y. M., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 71— 77 |
| [33] | Hu J. H., Pu Y. L., Ueda M., Zhang X., Wang L. J., ,. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 1— 7 |
| [1] | YAN Tingting, ZHANG Na, LI Qiang, LI Zhenhua, LI Chunhui, LI Xue, YU Ru, WANG Rui, WANG Jihua, CAO Zanxia. Effects of Co-reagent for Improving the Performance of Polyamide Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2008. |
| [2] | GUO Zhaopei,LIN Lin,CHEN Jie,TIAN Huayu,CHEN Xuesi. Polyglutamic Acid Grafted Polyethylene Glycol@Calcium Carbonate Based Shielding System for Improving Polyethyleneimine Gene Transfection Efficiency † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 235. |
| [3] | XU Jianling,ZHANG Di,NIE Miaoqing,WANG Hanxi,LI Longwei. Adsorption of Cr 6+ on Polyethyleneimine-functionalized Straw Biochar from Aqueous Solution † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 155. |
| [4] | WEI Yanshan, WEI Bangzhi, HUANG Aimin, MA Lin. Membrane Structure Alteration of DOPC Liposome Induced by Interaction with Gene Carrier Polyethyleneimine† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2271. |
| [5] | YANG Chuanxiao, YU Mengwen, SONG Duoduo, SUN Xiangying. Determination of Cr(Ⅵ) by Ratiometric and Visual Fluorescence Method Based on Formaldehyde Functionalized Polyethyleneimine-rhodamine B Hydrazide System† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 852. |
| [6] | WANG Jiaona, YIN Zefang, LI Congju. Preparation and Desalination Performance of Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane Based on Electrospinning Technology† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 396. |
| [7] | LI Chong, JIA Liping, MA Rongna, JIA Wenli, WANG Huaisheng, YANG Haitao, GUO Aixiang. Simultaneous Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, Uric Acid and Tryptophan on the PEI-graphene Modified Electrode† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(7): 1282. |
| [8] | WU Lixiang, CAI Zhibin, CHEN Xiaolin, LIU Lifen, ZHU Lifang, GAO Congjie. Stability of a Novel Poly(amide-urea-imide) Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 765. |
| [9] | FAN Ying, YAO Jing*, ZHOU Jian-Ping*. Preparation of Nucleus-targeting Polyethyleneimine-dexamethasone Conjugates and Their Application for Gene Delivery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(12): 2916. |
| [10] |
LIU Qing-Zhi1*, YANG Deng-Feng1, HU Yang-Dong2.
Water and Salts Molecular Simulation of Diffusion Process in Reverse Osmosis Membrane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(3): 568. |
| [11] | HAN Su-Fang1, DUAN Ya-Jun1, WANG Yan-Ming1, ZHENG Jun-Nian2, WU Yi2, CAI Rong1, OU Lai-Liang1, KONG De-Ling1*, YU Yao-Ting1. Tumor Targeted Gene Vector Modified with G250 Monoclonal Antibody for Gene Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(5): 923. |
| [12] | WANG Xu-Peng; GAO Bao-Jiao*; GUO Jian-Feng; ZHANG Li-Ping. Preparation and Characters of Novel Support PEI/SiO2 for the Immobilization of Penicillin Acylase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(6): 1167. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||