

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 1510.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180790
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YIN Jiao, ZHANG Guoqiang*( ), YAN Lifei, JIA Dongsen, ZHENG Huayan, LI Zhong*(
), YAN Lifei, JIA Dongsen, ZHENG Huayan, LI Zhong*( )
)
Received:2018-11-21
Online:2019-07-10
Published:2019-07-12
Contact:
ZHANG Guoqiang,LI Zhong
E-mail:zgq198615@163.com;lizhong@tyut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YIN Jiao, ZHANG Guoqiang, YAN Lifei, JIA Dongsen, ZHENG Huayan, LI Zhong. Influence of Structure Evolution of CuY Catalyst During the Reaction Process on Its Catalytic Performance for Oxidative Carbonylation of Methanol†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1510.
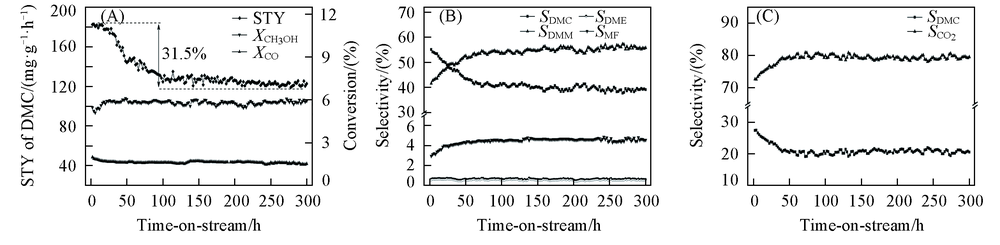
Fig.1 Space time yield(STY) of DMC, conversion(X) of CH3OH and CO as a function of time on stream(A), selectivity(S) of DMC, DMM, DME and MF based on CH3OH as a function of time on stream(B) and selectivity of DMC and CO2(C) based on CO as a function of time on stream
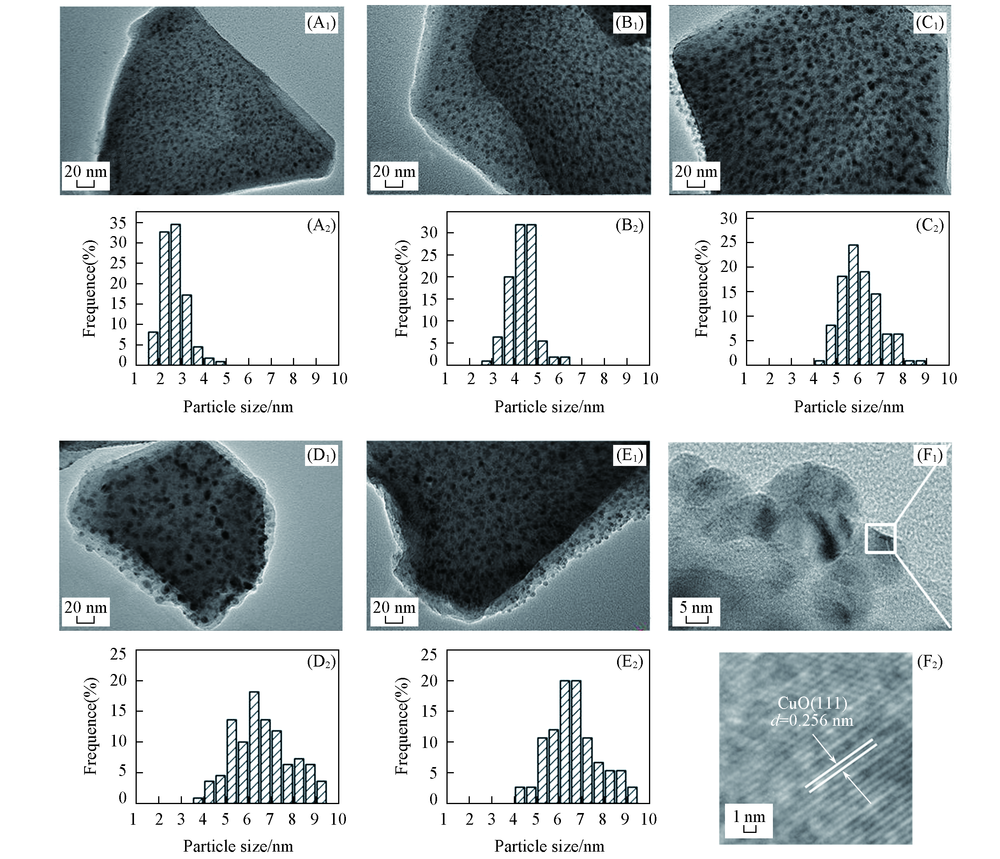
Fig.4 TEM images(A1—E1) and particle size distribution(A2—E2) of CuY(A1, A2), CuY-20 h(B1, B2), CuY-100 h(C1, C2), CuY-190 h(D1, D2), CuY-300 h(E1, E2) and HRTEM images of CuY-190 h(F1, F2)(F2) is the enlarged part of (F1).
| Sample | Dmeso/nm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuY | 685 | 632 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 1.85 |
| CuY-20 h | 632 | 582 | 0.38 | 0.26 | 1.84 |
| CuY-100 h | 626 | 577 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 1.84 |
| CuY-190 h | 608 | 560 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 1.86 |
| CuY-300 h | 612 | 557 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 1.85 |
Table 1 Textural properties of CuY catalysts
| Sample | Dmeso/nm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuY | 685 | 632 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 1.85 |
| CuY-20 h | 632 | 582 | 0.38 | 0.26 | 1.84 |
| CuY-100 h | 626 | 577 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 1.84 |
| CuY-190 h | 608 | 560 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 1.86 |
| CuY-300 h | 612 | 557 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 1.85 |
| Catalyst | Eb of C | Area percentage of surface C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu+ | Cu2++CuO | Cu+ | Cu2++CuO | |
| CuY | 933.2 | 935.6 | 49.6 | 50.4 |
| CuY-20 h | 933.5 | 935.7 | 43.2 | 56.8 |
| CuY-100 h | 933.4 | 935.6 | 41.5 | 58.5 |
| CuY-190 h | 933.9 | 935.7 | 33.4 | 66.6 |
| CuY-300 h | 933.6 | 935.7 | 33.6 | 66.4 |
Table 2 Quantitative analysis of the XPS curve-fitting of CuY catalysts
| Catalyst | Eb of C | Area percentage of surface C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu+ | Cu2++CuO | Cu+ | Cu2++CuO | |
| CuY | 933.2 | 935.6 | 49.6 | 50.4 |
| CuY-20 h | 933.5 | 935.7 | 43.2 | 56.8 |
| CuY-100 h | 933.4 | 935.6 | 41.5 | 58.5 |
| CuY-190 h | 933.9 | 935.7 | 33.4 | 66.6 |
| CuY-300 h | 933.6 | 935.7 | 33.6 | 66.4 |
| Catalyst | H2 consumption /(mmol·g-1) | CuO/Cusum(%) | Cu2+/Cusum(%) | Cu+/Cusum(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | CuO | Cu+ | ||||
| CuY | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.54 | 17.9 | 34.1 | 48.0 |
| CuY-20 h | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.40 | 31.4 | 28.9 | 39.7 |
| CuY-100 h | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 41.1 | 22.2 | 36.7 |
| CuY-190 h | 0.12 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 42.2 | 24.2 | 33.6 |
| CuY-300 h | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 41.7 | 25.1 | 33.2 |
Table 3 Quantitative analysis of the H2-TPR profiles of CuY catalysts
| Catalyst | H2 consumption /(mmol·g-1) | CuO/Cusum(%) | Cu2+/Cusum(%) | Cu+/Cusum(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | CuO | Cu+ | ||||
| CuY | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.54 | 17.9 | 34.1 | 48.0 |
| CuY-20 h | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.40 | 31.4 | 28.9 | 39.7 |
| CuY-100 h | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 41.1 | 22.2 | 36.7 |
| CuY-190 h | 0.12 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 42.2 | 24.2 | 33.6 |
| CuY-300 h | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 41.7 | 25.1 | 33.2 |
| Catalyst | Desorption capacity of NH3/(mmol·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak a+b | Peak c | Peak d | Peak c+d | Total | |
| CuY | 3.42 | 2.57 | 1.47 | 4.04 | 7.46 |
| CuY-20 h | 3.71 | 2.13 | 1.57 | 3.70 | 7.41 |
| CuY-100 h | 3.36 | 1.59 | 1.64 | 3.23 | 6.59 |
| CuY-190 h | 3.41 | 1.38 | 1.65 | 3.03 | 6.44 |
| CuY-300 h | 3.40 | 1.37 | 1.65 | 3.02 | 6.42 |
Table 4 Quantitative analysis of the NH3-TPD profiles of CuY catalysts
| Catalyst | Desorption capacity of NH3/(mmol·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak a+b | Peak c | Peak d | Peak c+d | Total | |
| CuY | 3.42 | 2.57 | 1.47 | 4.04 | 7.46 |
| CuY-20 h | 3.71 | 2.13 | 1.57 | 3.70 | 7.41 |
| CuY-100 h | 3.36 | 1.59 | 1.64 | 3.23 | 6.59 |
| CuY-190 h | 3.41 | 1.38 | 1.65 | 3.03 | 6.44 |
| CuY-300 h | 3.40 | 1.37 | 1.65 | 3.02 | 6.42 |
| [1] | Aricò F., Tundo P., Russ. Chem. Rev., 2010, 79(6), 479—489 |
| [2] | Huang S. Y., Yan B.,Wang S. P., Ma X. B., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(10), 3079—3116 |
| [3] | Ding X.S., Dong X. M., Kuang D. T., Wang S. F., Zhao X. Q., Wang Y. J., Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 240, 221—227 |
| [4] | Woo J. M., Seo J. Y., Kim H., Lee D. H.,Park Y. C., Yi C. K., Park Y. S., Moon J. H., Ultrason. Sonochem., 2018, 44, 146—151 |
| [5] | Li Y. J., Yan L. F., Zheng H. Y., Li Z., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2015, 31(12), 2315—2323 |
| (李艳娇, 阎立飞, 郑华艳, 李忠. 无机化学学报, 2015, 31(12), 2315—2323) | |
| [6] | Nam J. K. Choi M. J., Cho D. H., Suh J. K., Kim S. B., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2013, 370, 7—13 |
| [7] | King S. T., Catal. Today, 1997, 33(1—3), 173—182 |
| [8] | King S. T., J. Catal., 1996, 161(2), 530—538 |
| [9] | Zhang Y.H., Briggs D. N., de Smit E., Bell A. T., J. Catal., 2007, 251(2), 443—452 |
| [10] | Li Z., Wang R.Y., Zheng H. Y., Xie K. C., Fuel, 2010, 89(7), 1339—1343 |
| [11] | Richter M., Fait M.J. G., Eckelt R., Schneider M., Radnik J., Heidemann D., Fricke R., J. Catal., 2007, 245(1), 11—24 |
| [12] | Richter M., Fait M. J. G. Eckelt R., Schreier E., Schneider M., Pohl M. M., Fricke R., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2007, 73(3/4), 269—281 |
| [13] | Li Z., Fu T.J., Zheng H. Y., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2011, 27(8), 1483—1490 |
| (李忠, 付廷俊, 郑华艳. 无机化学学报, 2011, 27(8), 1483—1490) | |
| [14] | Wang Y. C., Zheng H. Y.,Li Z., Xie K. C., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(124), 102323—102331 |
| [15] | Wang Y. C., Zheng H. Y., Li Z., Chin. J. Catal., 2016, 37(8), 1403—1412 |
| [16] | Wang Y. C., Zheng H. Y., Liu B., Zhang G. Q., Li Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12), 491—499 |
| (王玉春, 郑华艳, 刘斌, 张国强, 李忠. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(12), 491—499) | |
| [17] | Eriksson G., Siegbahn H., Andersson S., Turkki T., Muhammed M., Mater. Res. Bull., 1997, 32(5), 491—499 |
| [18] | Li Z., Xie K. C., Slade R. C. T., Appl. Catal. A: Gen, 2001, 205(1/2), 85—92 |
| [19] | Yaripour F., Shariatinia Z., Sahebdelfar S., Irandoukht A., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2015, 203, 41—53 |
| [20] | Bortolatto L. B., Boca Santa R. A. A., Moreira J. C., Machado D. B.,Martins M. A. P. M., Fiori M. A., Kuhnen N. C., Riella H. G., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2017, 248, 214—221 |
| [21] | Li G., Chen L. J. Bao J., Li T., Mei F. M., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2008, 346(1/2), 134—139 |
| [22] | Zhang G. Q., Zheng H. Y., Hao Z. Q., Li Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7), 1380—1389 |
| (张国强, 郑华艳, 郝志强, 李忠. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(7), 1380—1389) | |
| [23] | Fernandes R., Patel N., Miotello A., Jaiswal R., Kothari D.C., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(21), 13379—13391 |
| [24] | Alonso F., Melkonian T., Moglie Y., Yus M., Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2011, 2011(13), 2524—2530 |
| [25] | Xie H., Yi D.Z., Shi L., Meng X., Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 313, 663—670 |
| [26] | Lázaro Martínez J. M. Rodríguez-Castellón E., Sánchez R. M. T., Denaday L. R., Buldain G. Y., Campo Dall’ Orto V., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2011, 339(1/2), 43—51 |
| [27] | Singh L., Rekha P., Chand S., J. Environ. Manage., 2018, 215, 1—12 |
| [28] | Fu T.J., Wang X., Zheng H. Y., Li Z., Carbon, 2017, 115, 363—374 |
| [29] | Jin D.F., Hou Z. Y., Zhang L. W., Zheng X. M., Catal. Today, 2008, 131(1—4), 378—384 |
| [30] | Fei J. H. Hou Z. Y., Zhu B., Lou H., Zheng X. M., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2006, 304, 49—54 |
| [31] | Lin J. H., Guliants V. V., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2012, 445-446, 187—194 |
| [32] | Drake I.J., Zhang Y. H., Briggs D., Lim B., Chau T., Bell A. T., J. Phy. Chem. B, 2006, 110(24), 11654—11664 |
| [33] | Zhang Y. H., Bell A. T., J. Catal., 2008, 255(2), 153—161 |
| [34] | Zheng X. B., Bell A. T., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(13), 5043—5047 |
| [35] | Fu T.J., Zheng H. Y., Niu Y. Y., Wang R. Y., Li Z., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(15), 1765—1772 |
| (付廷俊, 郑华艳, 牛燕燕, 王瑞玉, 李忠. 化学学报, 2011, 69(15), 1765—1772) | |
| [36] | Engeldinger J., Domke C., Richter M., Bentrup U., Appl. Catal.A: Gen., 2010, 382(2), 303—311 |
| [37] | Kang L., Zhang J., Zhang R.G., Ling L. X., Wang B. J., Mol. Catal., 2018, 449, 38—48 |
| [38] | Engeldinger J., Richter M., Bentrup U., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(7), 2183—2191 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||