

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 140.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130278
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HASIMU Yushanjiang, LIU Ruiquan*( ), MI Hongyu
), MI Hongyu
Received:2013-03-26
Online:2014-01-10
Published:2013-11-25
Contact:
LIU Ruiquan
E-mail:liu.rq@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HASIMU Yushanjiang, LIU Ruiquan, MI Hongyu. Electrodeposition Behavior of Chromium in Ionic Liquid [BMIM]P
| ν/(mV?s-1) | Ipc/μA | Epc/V | Epc/2/V | ∣Epc-Epc/2∣/V | ν1/2/(mV?s-1)1/2 | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | -1.52 | -1.50 | -0.765 | 0.735 | 7.071 | 0.026 |
| 80 | -3.04 | -1.61 | -0.771 | 0.839 | 8.944 | 0.023 |
| 100 | -3.74 | -1.65 | -0.775 | 0.875 | 10.000 | 0.022 |
| 120 | -4.51 | -1.69 | -0.800 | 0.890 | 10.954 | 0.022 |
| 180 | -6.26 | -1.77 | 0.875 | 0.895 | 13.416 | 0.022 |
| Average | 0.023 |
Table 1 Data of cathodic polarization of [BMIM]PF6-Cr(Ⅲ)(0.1 mol/L) with various scan rates at 85 ℃
| ν/(mV?s-1) | Ipc/μA | Epc/V | Epc/2/V | ∣Epc-Epc/2∣/V | ν1/2/(mV?s-1)1/2 | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | -1.52 | -1.50 | -0.765 | 0.735 | 7.071 | 0.026 |
| 80 | -3.04 | -1.61 | -0.771 | 0.839 | 8.944 | 0.023 |
| 100 | -3.74 | -1.65 | -0.775 | 0.875 | 10.000 | 0.022 |
| 120 | -4.51 | -1.69 | -0.800 | 0.890 | 10.954 | 0.022 |
| 180 | -6.26 | -1.77 | 0.875 | 0.895 | 13.416 | 0.022 |
| Average | 0.023 |
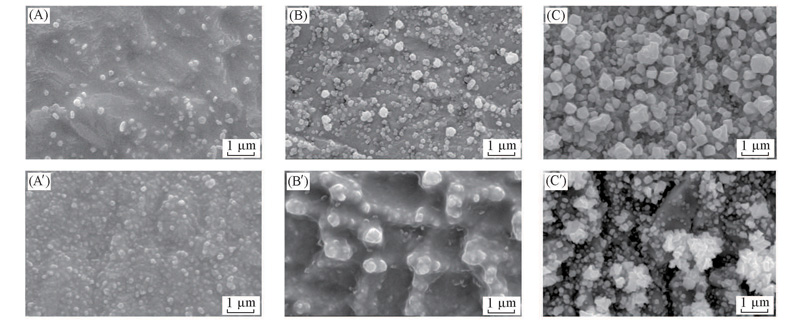
Fig.8 SEM images of Cr deposits from [BMIM]PF6-Cr(Ⅲ) electrolyte at 85 ℃, -1.50 V on Cu substrate (A—C) 0.1 mol/L Cr(Ⅲ); (A'—C') 0.4 mol/L Cr(Ⅲ). Deposition time/min: (A), ( A') 30; (B), (B') 60; (C), (C') 120.
| [1] | Heym F., Etzold B. J. M., Kern C., Jess A., Green Chemistry, 2011, 13, 1453—1466 |
| [2] | Sato T., Masuda G., Takagi K., Electrochim. Acta, 2004, 49(21), 3603—3611 |
| [3] | Hayyan M., Mjalli F. S., Hashim M. A., AlNashef I. M., Tan X. M., Ind. Eng. Chem., 2013, 19(1), 106—112 |
| [4] | Hu X. Y., Liu Q. G., Zhuo K. L., Wang J. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2), 324—330 |
| (胡晓宇, 刘千阁, 卓克垒, 王键吉.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(2), 324—330) | |
| [5] | Huang B. C., Huang Z. T., Industrial Catalysis, 2003, 11(2), 1—6 |
| (黄碧纯, 黄仲涛.工业催化, 2003,11(2), 1—6) | |
| [6] | Andrew P. A., Katy J. M., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2006, 8, 4265—4279 |
| [7] | Jiang G. F., Xie Z. B., Liu Y. H., Le Z. G., Speciality Petrochemicals, 2010, 27(2), 28—32 |
| (姜国芳, 谢宗波, 刘云海, 乐长高.精细石油化工, 2010,27(2), 28—32) | |
| [8] | Cai M. L., Pan X., Liu W. Q., Huo Z. P., Chen H. W., Zhang C. N., Dai S. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7), 1697—1702 |
| (蔡墨朗, 潘旭, 刘伟庆, 霍志鹏, 陈海伟, 张昌能, 戴松元.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(7), 1697—1702) | |
| [9] | Bayati M. R., Shariat M. H., Janghorban K., Renewable Energy, 2005, 30(14), 2163—2178 |
| [10] | Bi Z. N., Dong J. X., Materials Review, 2007, 2(1), 6—9 |
| (毕中南, 董建新.材料导报, 2007,2(1), 6—9) | |
| [11] | Surviliene S., Euge'nio S., Vilar R., J. Appl. Electrochem., 2011, 41(1), 107—114 |
| [12] | Eugénio S., Rangel C. M., Vilar R., Quaresma S., Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(28), 10347—10352 |
| [13] | Eugénio S., Rangel C. M., Vilar R., Rego A. M. B. D., Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(6), 1845—1850 |
| [14] | Behar D., Gonzalez C., Neta P., Phys. Chem. A, 2001, 105(32), 7607—7614 |
| [15] | Zhang D. C., Zhang L. P., Yu X. J., Chen E. Z., Chemical Industry Times, 2012, 26(2), 5—9 |
| (张德超, 张丽鹏, 于先进, 陈恩泽.化工时刊, 2012,26(2), 5—9) | |
| [16] | Jayakumar M., Venkatesan K. A., Srinivasan T. G., Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52(24), 7121—7127 |
| [17] | Jeng E. G. S., Sun I. W., Electrochem. Soc., 1998, 145(4), 1196—1201 |
| [18] | Teng D.Z., Xiang Z. Y. N., Jing S. C., Measures of Electrochemistry, Translated by Chen Z., Yao J. N., Peking University Press, Beijing, 1995, 154—160 |
| (陈震, 姚建年[译], 电化学测定方法, 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1995, 154—160) |
| [1] | CUI Wei, ZHAO Deyin, BAI Wenxuan, ZHANG Xiaodong, YU Jiang. CO2 Absorption in Composite of Aprotic Solvent and Iron-based Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220120. |
| [2] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [3] | JI Shuangqi, JIN Zhao, GUAN Wenna, PAN Xiangyu, GUAN Tong. Preparation and Chromatographic Performance of Mixed-mode Silica Stationary Phase Modified by Double Cationic Ionic Liquid and Octadecyl Group [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220008. |
| [4] | FAN Xiaoyong, ZHU Yongqiang, WU Yan, ZHANG Shuai, XU Lei, GOU Lei, LI Donglin. Three-dimensional Porous Sn-Zn Alloy Towards Uniform Zn Plating/stripping [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210861. |
| [5] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [6] | CHEN Feng, CHENG Na, ZHAO Jianwei, SONG Yitian, SUN Yanyan, LOU Xinli, TONG Xiayan. Electrodeposition Mechanism and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopic Effect of Nano-sized Silver Layer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1891. |
| [7] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [8] | WU Shuaini, ZHU Pengfei, SHI Huaiqi, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation of CoCrx/SAPO-34 Catalyst and Its Catalytic Combustion Performance for 1,2-Dichloroethane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3731. |
| [9] | WANG Man, WANG Xin, ZHOU Jing, GAO Guohua. Efficient Synthesis of Dimethyl Carbonate via Transesterification of Methanol and Ethylene Carbonate Catalyzed by Poly(ionic liquid)s [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3701. |
| [10] | CUI Jinping, CHEN Wenxian, YU Feifan, CAO Shiyu, LYU Weiyang, YAO Yuyuan. Adsorption Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium and co-Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants by Carbon Doped Hexagonal Boron Nitride Supported MoS2 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3125. |
| [11] | ZHOU Molin, JIANG Xin, YI Ting, YANG Xiangguang, ZHANG Yibo. Improvement of Interface Stability Between Sulfide Solid Electrolyte Li10GeP2S12 and Lithium Metal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1810. |
| [12] | SUN Qiangqiang, CAO Baoyue, ZHOU Chunsheng, ZHANG Guochun, WANG Zenglin. Enhancing Hydrogen Evolution Performance of a Regular Cube NiCu Nanocrystalline Electrocatalyst Fabricated by Normal Pluse Electrodeposition † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1287. |
| [13] | CHENG Shifu,HU Hao,CHEN Bihua,WU Haihong,GAO Guohua,HE Mingyuan. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Porous Carbons Prepared from Binary Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1048. |
| [14] | GAO Chong,YU Fengli,XIE Congxia,YU Shitao. Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Cyclic Ketones Catalyzed by Amino Alcohol Heteropoly Acid Ionic Liquid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1101. |
| [15] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||