

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 1260.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170648
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
DONG Shigang1, GAO Yingbo2, GUAN Zichao2, WANG Haipeng2, WANG Xia2, DU Ronggui2,*( ), SONG Guangling3
), SONG Guangling3
Received:2017-09-26
Online:2018-06-10
Published:2018-05-24
Contact:
DU Ronggui
E-mail:rgdu@xmu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
DONG Shigang, GAO Yingbo, GUAN Zichao, WANG Haipeng, WANG Xia, DU Ronggui, SONG Guangling. Inhibition Effect of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on Corrosion of Reinforcing Steel in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1260.
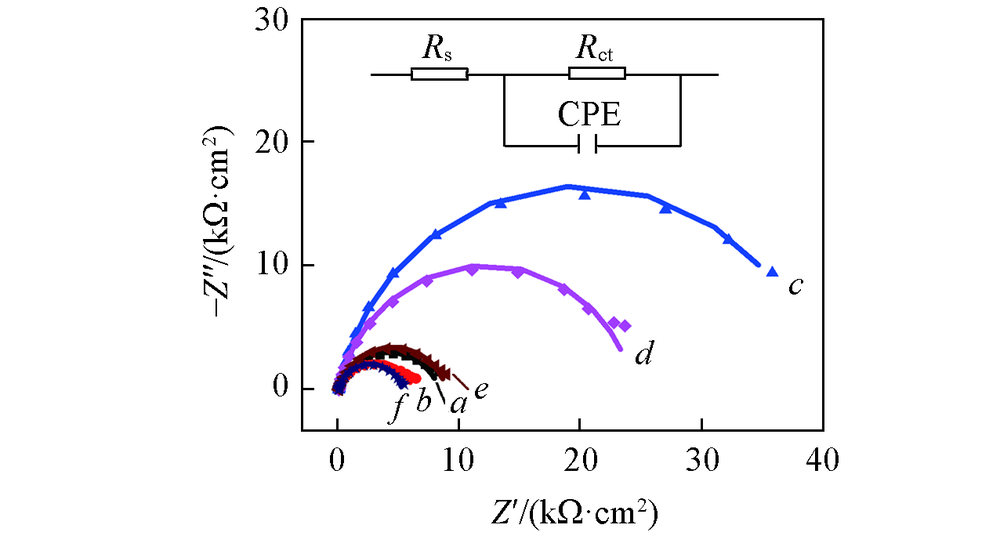
Fig.1 Nyquist plots of reinforcing steel in the simulated polluted concrete pore solution with different PVP concentrationsc(PVP)/(mg·L-1): a. 0; b. 10; c. 25; d. 50; e. 100; f. 300. Inset: equivalent circuit.
| c(PVP)/(mg·L-1) | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rct/(kΩ·cm2) | 105Y0/(Ω-1·cm-2·sn) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 45.4 | 8.28 | 14.70 | 0.81 |
| 10 | 22.8 | 6.13 | 17.00 | 0.82 |
| 25 | 31.6 | 39.70 | 9.07 | 0.88 |
| 50 | 17.4 | 24.40 | 9.47 | 0.88 |
| 100 | 36.3 | 8.89 | 13.00 | 0.84 |
| 300 | 26.1 | 5.23 | 10.90 | 0.86 |
Table 1 Fitting results for impedance spectra of reinforcing steel corresponding to Fig.1
| c(PVP)/(mg·L-1) | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rct/(kΩ·cm2) | 105Y0/(Ω-1·cm-2·sn) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 45.4 | 8.28 | 14.70 | 0.81 |
| 10 | 22.8 | 6.13 | 17.00 | 0.82 |
| 25 | 31.6 | 39.70 | 9.07 | 0.88 |
| 50 | 17.4 | 24.40 | 9.47 | 0.88 |
| 100 | 36.3 | 8.89 | 13.00 | 0.84 |
| 300 | 26.1 | 5.23 | 10.90 | 0.86 |
| c(PVP)/(mg·L-1) | icorr/(μA·cm-2) | Ecorr/V(vs. SCE) | Rp/(kΩ·cm2) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.490 | -0.507 | 9.48 | — |
| 10 | 0.469 | -0.470 | 7.19 | 4.31 |
| 25 | 0.053 | -0.387 | 38.80 | 89.1 |
| 50 | 0.145 | -0.414 | 20.20 | 70.4 |
| 100 | 0.477 | -0.452 | 10.10 | 2.65 |
| 300 | 0.602 | -0.455 | 5.91 | — |
Table 2 Fitting results for linear polarization curves of reinforcing steel in the simulated polluted concrete pore solution and inhibition efficiency of PVP
| c(PVP)/(mg·L-1) | icorr/(μA·cm-2) | Ecorr/V(vs. SCE) | Rp/(kΩ·cm2) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.490 | -0.507 | 9.48 | — |
| 10 | 0.469 | -0.470 | 7.19 | 4.31 |
| 25 | 0.053 | -0.387 | 38.80 | 89.1 |
| 50 | 0.145 | -0.414 | 20.20 | 70.4 |
| 100 | 0.477 | -0.452 | 10.10 | 2.65 |
| 300 | 0.602 | -0.455 | 5.91 | — |
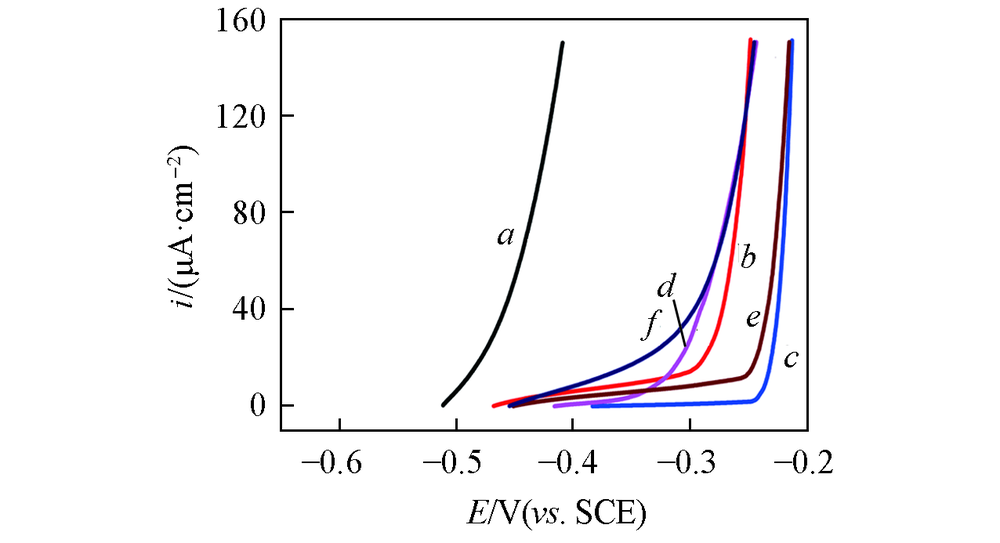
Fig.2 Potentiodynamic anodic polarization curves of reinforcing steel in the simulated polluted concrete pore solution with different PVP concentrationsc(PVP)/(mg·L-1): a. 0; b. 10; c. 25; d. 50; e. 100; f. 300.
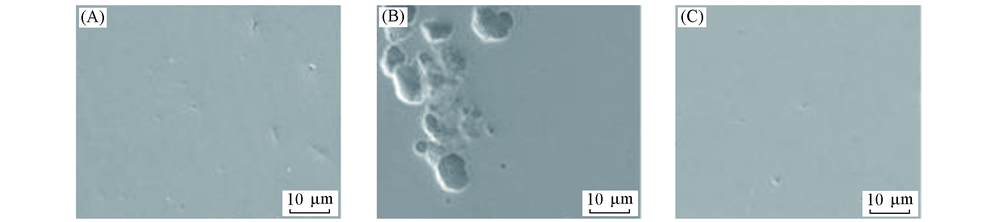
Fig.3 SEM images of reinforcing steel before and after immersion in the simulated polluted concrete pore solution(A) Before test; (B) the solution without PVP; (C) the solution with 25 mg/L PVP.
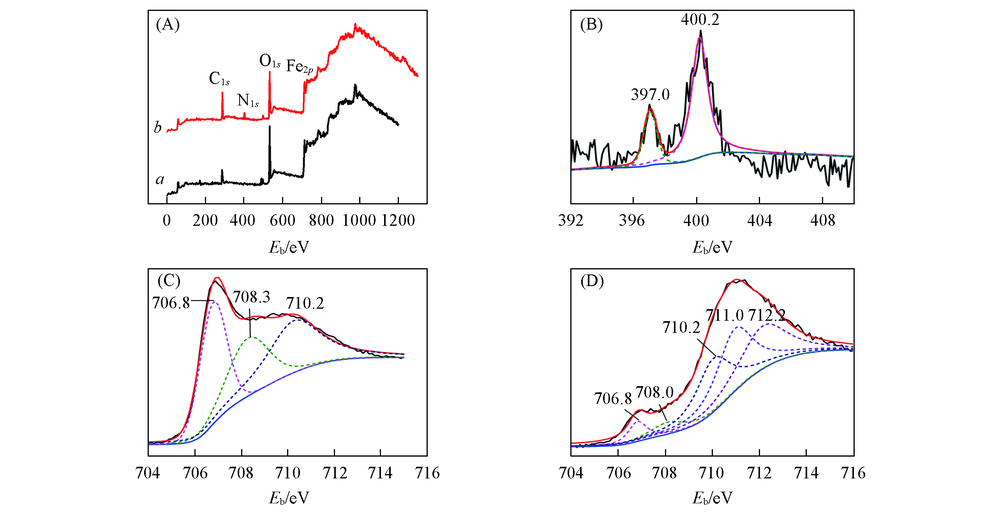
Fig.4 XPS spectra of reinforcing steel after immersion in the simulated polluted concrete pore solution without(a) and with(b) PVP(A), N1s with PVP(B), Fe2p3/2 without PVP(C) and with PVP(D)
| [1] | Mather B., Cem. Concr. Compos., 2004, 26(1), 3—4 |
| [2] | Rendon Diaz Miron L. E., Koleva D. A., Concrete Durability: Cementitious Materials and Reinforced Concrete Properties, Behavior and Corrosion Resistance, Springer International Publishing, Basel, 2017, 23—56 |
| [3] | Kumar V., Corros. Rev., 1998, 16(4), 317—358 |
| [4] | Kitowski C. J., Wheat H. G., Corrosion, 1997, 53(3), 216—226 |
| [5] | Hussain S. E., Rasheeduzzafar, Al-Musallam A., Al-Gahtani A. S., Cem. Concr. Res., 1995, 25(7), 1543—1555 |
| [6] | Yang R. J., Guo Y., Tang F. M., Wang X. P., Du R. G., Lin C. J., Acta Phys-Chim. Sin., 2012, 28(8), 1923—1928 |
| (杨榕杰, 郭亚, 唐方苗, 王小平, 杜荣归, 林昌健. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(8), 1923—1928) | |
| [7] | Gu R. A., Bao F., Shen X. Y., Cui Y., Yao J. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(5), 948—951 |
| (顾仁敖, 鲍芳, 沈晓英, 崔颜, 姚建林. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(5), 948—951) | |
| [8] | Zhao J. M., Li J., Acta Phys-Chim. Sin., 2012, 28(3), 623—629 |
| (赵景茂, 李俊. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(3), 623—629) | |
| [9] | Hu S. Q., Mi S. Q., Jia X. L., Guo A. L., Chen S. H., Zhang J., Liu X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(10), 2402—2409 |
| (胡松青, 米思奇, 贾晓林, 郭爱玲, 陈生辉, 张军, 刘新泳. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(10), 2402—2409) | |
| [10] | Chebabe D., Chikh Z. A., Hajjaji N., Srhiri A., Zucchi F., Corros. Sci., 2003, 45, 309—320 |
| [11] | Bi G., Gu Y .H., Mater. Protec., 1997, 30(2), 4—7 |
| (毕刚, 谷荧红. 材料保护, 1997, 30(2), 4—7) | |
| [12] | Hajjaji N., Rico I., Srhiri A., Lattes A., Soufiaoui M., Ben B.A., Corrosion, 1993, 49(4), 326—334 |
| [13] | Morsi M., Barakat Y., El-Sheikh R., Hassan A., Baraka A., Mater. Corros., 1993, 44(7), 304—308 |
| [14] | Umoren S., Ebenso E., Indian J. Chem. Techn., 2008, 15(4), 355—363 |
| [15] | John S., Kuruvilla M., Joseph A., Res. Chem. Intermediat., 2013, 39(3), 1169—1182 |
| [16] | Cho J. Y., Cui H., Park J. H., Park H. S., Park J. G., Electrochem. Solid ST., 2011, 14(11), H450—H452 |
| [17] | Al Juhaiman L. A., Abu Mustafa A., Mekhamer W. K., Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2012, 7(9), 8578—8596 |
| [18] | Al Juhaiman L. A., Abu Mustafa A., Mekhamer W. K., Anti-Corros. Method. Mater., 2013, 60(1), 28—36 |
| [19] | Frignani A., Grassi V., Zanotto F., Zucchi F., Corros. Sci., 2012, 63(5), 29—39 |
| [20] | Heakal E. T., Elkholy A. E., J. Mol. Liq., 2017, 230, 395—407 |
| [21] | Xu H., Liu Y., Chen W., Du R. G., Lin C. J., Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54(16), 4067—4072 |
| [22] | Sahoo G., Balasubramaniam R., Corros. Sci., 2008, 50(1), 131—143 |
| [23] | Zhou X., Yang H. Y., Wang F. H., Acta Phys-Chim. Sin., 2011, 27(3), 647—654 |
| (周欣, 杨怀玉, 王福会. 物理化学学报, 2011, 27(3), 647—654) | |
| [24] | Hamadou L., Kadri A., Benbrahim N., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 252(5), 1510—1519 |
| [25] | Sagüés A. A., Kranc S., Moreno E. I., Electrochim. Acta, 1996, 41(7), 1239—1243 |
| [26] | Sagüés A. A., Kranc S., Moreno E. I., Corros. Sci., 1995, 37(7), 1097—1113 |
| [27] | Neves R. S., De Robertis E., Motheo A. J., Electrochim. Acta, 2006, 51(7), 1215—1224 |
| [28] | Ye C. Q., Hu R. G., Dong S. G., Zhang X. J., Hou R. Q., Du R. G., Lin C. J., Pan J. S., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2013, 688(1), 275—281 |
| [29] | Leibig M., Halsey T. C., Electrochim. Acta, 1993, 38(14), 1985—1988 |
| [30] | Rao B. A., Rao M. V., Rao S. S., Sreedhar B., J. Chem. Sci., 2010, 122(4), 639—649 |
| [31] | Bayol E., Kayakırılmaz K., Erbil M., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2007, 104(1), 74—82 |
| [32] | Gao Y. B., Hu J., Zuo J., Liu Q., Zhang H., Dong S. G., Du R. G., Lin C. J., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2015, 162(10), C555—C562 |
| [33] | Morris W., Vico A., Vazquez M., De Sánchez S., Corros. Sci., 2002, 44(1), 81—99 |
| [34] | El Azhar M., Traisnel M., Mernari B., Gengembre L., Bentiss F., Lagrenee M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2002, 185(3), 197—205 |
| [35] | Luo H., Dong C. F., Li X. G., Xiao K., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 64(1), 211—220 |
| [36] | Guo Y., Wang X. P., Zhu Y. F., Zhang J., Gao Y. B., Yang Z. Y., Du R. G., Lin C. J., Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013, 8(12), 12769—12779 |
| [37] | Bouanis M., Tourabi M., Nyassi A., Zarrouk A., Jama C., Bentiss F., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 389, 952—966 |
| [38] | Baena L., Gomez M., Calderón J., Fuel, 2012, 95, 320—328 |
| [39] | Singh J., Singh D., Corros. Sci., 2012, 56, 129—142 |
| [40] | Nieuwoudt M., Comins J., Cukrowski I., J. Raman Spectrosc., 2011, 42(6), 1335—1339 |
| [41] | Neff D., Bellot-Gurlet L., Dillmann P., Reguer S., Legrand L., J. Raman Spectrosc., 2006, 37(10), 1228—1237 |
| [42] | Zhu J. C., Zhang X. A., Bai Y., Mo Y. J., J. Henan Univ.: Nat. Sci. Ed., 2004, 34(2), 20—23 |
| (朱纪春, 张新安, 白莹, 莫育俊. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 34(2), 20—23) | |
| [43] | Chen F., Zhou D. B., Qi W., Lv D., Chen Y. Y., Wen M. S., J. Mol. Catal., 2010, 24(5), 463—468 |
| (陈芳, 周德璧, 齐巍, 吕董, 陈云扬, 温美盛. 分子催化, 2010, 24(5), 463—468) | |
| [44] | Zhu H. M., Zhou D. B., Yu H. Y., Tang C., Xiong F. J., Appl. Chem. Ind., 2012 , 41(10), 1756—1759 |
| (朱红梅, 周德璧, 于红英, 唐超, 熊凤姣. 应用化工, 2012 , 41(10), 1756—1759) | |
| [45] | Ma H., Chen S., Liu G., Xu J., Zhou M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 252(12), 4327—4334 |
| [46] | Shi J. J., Sun W., Jiang J. Y., Zhang Y. M., Constr. Build. Mater., 2016, 111, 805—813 |
| [47] | Abd El Wanees S., Radwan A. B., Alsharif M. A., Abd El Haleem S. M., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2017, 190, 79—95 |
| [48] | Jiang S. B., Jiang L. H., Wang Z. Y., Jin M., Bai S. Y., Song S. Q., Yan X. C., Constr. Build. Mater., 2017, 150, 238—247 |
| [1] | QIAO Zhenghua, FAN Qi, HAO Jingcheng. Silicone Surfactant-enhanced Dual Networks and High Temperature Resistance Porous Silicone Elastomers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220384. |
| [2] | HAN Yixiu, WU Dianguo, LI Hongpu, YIN Hongyao, MEI Yongjun, FENG Yujun, ZHONG Zuqin. Interactions Between Hydrophobic Associating Poly(sodium acrylate) and a Zwitterionic Surfactant in Non-aqueous Media and Low Temperature Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2056. |
| [3] | HU Xueyi, HAN Lulu, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei. Admicelles and Adsolubilization of Extended Surfactants on Alumina [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 843. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xuan,ZHANG Tianci,JIANG Ping,GE Jijiang,ZHANG Guicai. Enhancement of CO2 Foam Stability with Modified Silica Nanoparticles in High Salinity Brine † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1076. |
| [5] | JI Lei,GUO Fanzuo,WANG Kehan,WANG Lei. Surfactant-assisted Formation of Nanoporous Pt Particles as Co-catalyst Loaded on P25 and Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1501. |
| [6] | Qiuchen DONG,Guanghua ZHANG,Wanbin ZHANG,Xue ZHANG,Jing LIU. Corrosion Inhibition of Q235 Steel by Ionic Liquid Based on the 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2556. |
| [7] | DONG Qiuchen,ZHANG Guanghua,ZHANG Wanbin,LIU Jing. Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Quinoline Diquaternary Ammonium Salt as Corrosion Inhibitor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2195. |
| [8] | ZHANG Guanghua,DONG Qiuchen,ZHANG Wanbin,WANG Shuang. Corrosion Inhibition of Q235 Steel by Octyl Dimethyl Benzyl Quaternary Ammonium Salt Ionic Liquid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 130. |
| [9] | YANG Yihan,WANG Dong,ZHANG Zhang,XU Yan. Activation of Esterification Activity of Rhizopus Chinensis Lipase in Organic Media by Surfactant† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1948. |
| [10] | YANG Jiarui, WANG Yifu, WANG Jilin, WANG Lulu, FENG Ruijiang. In situ Initiation, Polymerization and Construction of Cationic Active Sites of Gemini Molecules in Polysulfone Substrates† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1829. |
| [11] | LONG Shijun,CHEN Mingmin,ZHAO Youjiao,WANG Xiaotao,LI Xuefeng,LIAO Yonggui. Regulation of Gemini Surfactant on Photochromic Behavior of PVA Dispersed Spiropyran Organogel Thin Film† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 1078. |
| [12] | ZHAO Caixiu, YANG Yi, LIU Yiting, JIANG Ying, YUAN Fang, WANG Rui, CHEN Dongju. High Flux Polybenzimidazole Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration Membranes: Morphology Control and Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 785. |
| [13] | YIN Jinchao, CHEN Yukai, JIANG Jianzhong, CUI Zhenggang. Synthesis and Properties of pH and Redox Dual-switchable Surfactant† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1645. |
| [14] | XU Hongmei, LI Jie, QIAO Yunfan, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Hongyang, WANG Yuerong, HU Ping. Dispersion of Single-wall Carbon Nanotubes in Bile Salt Surfactants and Separation of SWCNTs(6,5) by Aqueous Two-phase Extraction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1148. |
| [15] | LI Dan, WU Qian, LIU Li, SUN Xiaori, GUO Meng, FENG Yimin. Preparation and Stability of Gemini Surfactant Modified Gold Nanofluids† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1829. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||