

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 1611.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170588
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles
YANG Zhaojie, LEI Bei, DU Wenhao, ZHANG Xi*( )
)
Received:2017-08-31
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-06-05
Contact:
ZHANG Xi
E-mail:zhangxi6352@163.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Zhaojie, LEI Bei, DU Wenhao, ZHANG Xi. Structure and Properties of Starch/Polybutylene Succinate Blends Modified by Magnesium Chloride/1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1611.
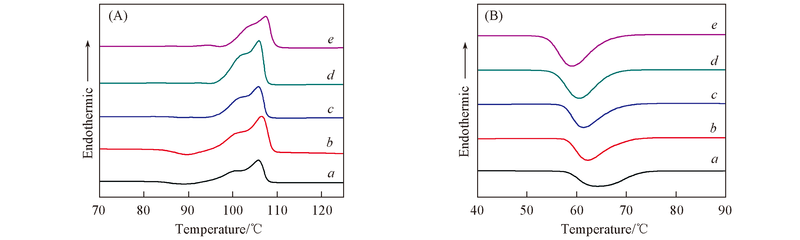
Fig.3 DSC curves of [BMIM]Cl modified starch/PBS blends with various magnesium chloride content^ (A) Melting process; (B) curve of crystallization. a. TPS; b. TPSM1; c. TPSM2; d. TPSM3; e. TPSM4.
| Sample | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | Tc /℃ | Tcc/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP | 28.63 | 47.59 | 64.22 | 88.33 |
| TSPM1 | 25.07 | 42.05 | 62.18 | 89.01 |
| TSPM2 | 24.43 | 41.34 | 61.40 | 89.68 |
| TSPM3 | 23.03 | 39.32 | 60.36 | 90.13 |
| TSPM4 | 21.97 | 37.84 | 59.19 | 91.71 |
Table 1 DSC data of [BMIM]Cl modified starch/PBS blends with various magnesium chloride content
| Sample | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | Tc /℃ | Tcc/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP | 28.63 | 47.59 | 64.22 | 88.33 |
| TSPM1 | 25.07 | 42.05 | 62.18 | 89.01 |
| TSPM2 | 24.43 | 41.34 | 61.40 | 89.68 |
| TSPM3 | 23.03 | 39.32 | 60.36 | 90.13 |
| TSPM4 | 21.97 | 37.84 | 59.19 | 91.71 |
| Sample | Tensile strength/MPa | Elongation at break(%) |
|---|---|---|
| TSP | 10.79 | 14.06 |
| TSPM1 | 13.34 | 15.90 |
| TSPM2 | 14.05 | 17.70 |
| TSPM3 | 15.17 | 18.36 |
| TSPM4 | 15.80 | 19.47 |
Table 2 Mechanical properties of [BMIM]Cl modified starch/PBS blends with various magnesium chloride content
| Sample | Tensile strength/MPa | Elongation at break(%) |
|---|---|---|
| TSP | 10.79 | 14.06 |
| TSPM1 | 13.34 | 15.90 |
| TSPM2 | 14.05 | 17.70 |
| TSPM3 | 15.17 | 18.36 |
| TSPM4 | 15.80 | 19.47 |
| [1] | Zhang C. H., Zhao X., Huang J. T., Plastics, 2008, 37(3), 8—10 |
| (张昌辉, 赵霞, 黄继涛. 塑料, 2008, 37(3), 8—10) | |
| [2] | Wang G.L., Xu J., Guo B. H.,Polymer Bulletin, 2011, (4), 99—109 |
| (王国利, 徐军, 郭宝华. 高分子通报, 2011, (4), 99—109) | |
| [3] | Liu X. Y., Tu Z. G.,Zhao S. F. Plastics Science and Technology,2014, 42(4), 92—13 |
| (刘晓燕, 涂志刚, 赵素芳.塑料科技, 2014, 42(4), 92—13) | |
| [4] | Liu J., Ji J. H., Zhang W., Wang X. W., Zhao J. New Chemical Materials,2013, 41(8), 1—3 |
| (刘军, 季君晖, 张维, 王小威, 赵剑.化工新型材料,2013, 41(8), 1—3) | |
| [5] | Zhang W., Ji J.H., Zhao J., Wang X. W., Xu Y., Yang B., Wang L. P.,New Chemical Materials, 2010, (7), 1—5 |
| (张维, 季君晖, 赵剑, 王小威, 许颖, 杨冰, 王萍丽. 化工新型材料, 2010, (7), 1—5) | |
| [6] | Averous L., Journal of Macromolecular Science,Part C: Polymer Reviews, 2004, 44(3), 231—274 |
| [7] | Li J. W, Luo X. G., Lin X . Y.Starch, 2013, 65, 831—839 |
| [8] | Wang X.L., Zhang Y. R., Wang Y. Z.Macromolecule Materials, 2011, (1), 24—37 |
| (汪秀丽, 张玉荣, 王玉忠. 高分子学报, 2011, (1), 24—37) | |
| [9] | Shi Y. F., Chen L. S., Jeng R. J., Polymer, 2008, 49, 4602—4611 |
| [10] | Zeng J. B., Jiao L., Li Y. D., Srinivasan M., Carbohydrate Polymer, 2011, 83, 762—768 |
| [11] | Dean K., Yu L., Bateman S., Wu D. Y., Polymer, 2007, 103, 802—811 |
| [12] | Boonprasith P., Wootthikanokkhan J., Nimitsiriwat N., Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 130(2), 1114—1123 |
| [13] | Cui Y. S., Wang X. Q., Ning Z. Y. Chinese Plastics,2014, 28(8), 1—6 |
| (崔永生,王训遒,宁卓远. 中国塑料, 2014, 28(8), 1—6) | |
| [14] | Lai S. M., Huang C. K., Shen H. F., Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2005, 97(1), 257—264 |
| [15] | Smits A. L. M., Kruiskamp P. H.,Van Soet J. J. G., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2003, 53(4), 409—416 |
| [16] | Liu B., Lv Q., Fang R., Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 306/307, 1717—1721 |
| [17] | Huang M., Yu J., Ma X., Polymer Degradation and Stability,2005, 90(3), 501—507 |
| [18] | Xing X. ,Zhang X . Z., Zhang Y., Chinese Plastics, 2013, 27(7), 1—7 |
| (邢潇, 张须臻, 张勇. 中国塑料, 2013, 27(7), 1—7) | |
| [19] | Xie F., Halley P. J., Avérous L., Progress in Polymer Science, 2012, 37(4), 595—623 |
| [20] | Xie F., Pollet E., Halley P. J., Progress in Polymer Science, 2013, 38, 1590—1628 |
| [21] | Lei B., Luo H., Shi M. K., Zhang X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9), 1722—1727 |
| (雷蓓, 罗辉, 石孟可, 张熙.高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(9), 1722—1727) | |
| [22] | Jiang X. C., Li H. M., Luo Y., International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 82, 223—230 |
| [23] | Liu G. M., Zheng L. C., Zhang X. Q., Li C. C., Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 5487—5493 |
| [24] | Zeng J. B., Li Y. D., Zhu Q. Y., Yang K. K., Wang X. L., Wang Y. Z., Polymer, 2009, 50, 1178—1186 |
| [1] | CUI Wei, ZHAO Deyin, BAI Wenxuan, ZHANG Xiaodong, YU Jiang. CO2 Absorption in Composite of Aprotic Solvent and Iron-based Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220120. |
| [2] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [3] | JI Shuangqi, JIN Zhao, GUAN Wenna, PAN Xiangyu, GUAN Tong. Preparation and Chromatographic Performance of Mixed-mode Silica Stationary Phase Modified by Double Cationic Ionic Liquid and Octadecyl Group [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220008. |
| [4] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [5] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [6] | WANG Man, WANG Xin, ZHOU Jing, GAO Guohua. Efficient Synthesis of Dimethyl Carbonate via Transesterification of Methanol and Ethylene Carbonate Catalyzed by Poly(ionic liquid)s [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3701. |
| [7] | ZHOU Molin, JIANG Xin, YI Ting, YANG Xiangguang, ZHANG Yibo. Improvement of Interface Stability Between Sulfide Solid Electrolyte Li10GeP2S12 and Lithium Metal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1810. |
| [8] | GAO Chong,YU Fengli,XIE Congxia,YU Shitao. Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Cyclic Ketones Catalyzed by Amino Alcohol Heteropoly Acid Ionic Liquid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1101. |
| [9] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| [10] | CHENG Shifu,HU Hao,CHEN Bihua,WU Haihong,GAO Guohua,HE Mingyuan. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Porous Carbons Prepared from Binary Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1048. |
| [11] | PIAO Huilan,MA Pinyi,QIN Zucheng,JIANG Yanxiao,SUN Ying,WANG Xinghua,SONG Daqian. Determination of Triazine Herbicides from Fruit Juice Samples Using Effervescence Assisted Microextraction Method Based on Acidic Ionic Liquid Packed Syringe [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 228. |
| [12] | ZHANG Li,QIAN Mingchao,LIU Xueke,Gao Shuaitao,YU Jiang,XIE Haishen,WANG Hongbin,SUN Fengjiang,SU Xianghong. Dynamic Study of Oxidative Desulfurization by Iron-based Ionic Liquids/NHD † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 317. |
| [13] | WANG Nan,YAO Kaisheng,ZHAO Chenchen,LI Tianjin,LU Weiwei. Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of AuPd Nanosponges and Their Catalytic Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 62. |
| [14] | LIU Xiaozhou, GUAN Xinyu, FANG Qianrong, JIN Yongri. Three-dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks Synthesized by Room Temperature Ionic Liquid Method† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1341. |
| [15] | LI Chenguang, HUA Er, LIU Tianxia. Tribological Behaviour of Protic Ionic Liquid Composed of 2-Ethylhexylethylenediaminium Cation and Trifluoromethanesulfonate Anion as Liquid Paraffin Additive† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1411. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||