

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 1687.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170037
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Haihong*( ), ZHANG Baoyu, ZHAO Zhipei
), ZHANG Baoyu, ZHAO Zhipei
Received:2017-01-16
Online:2017-09-10
Published:2017-08-25
Contact:
HUANG Haihong
E-mail:huanghaihong@hfut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Haihong, ZHANG Baoyu, ZHAO Zhipei. Degradation and Characterization of Recycling Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composites in Supercritical n-Butanol†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1687.

Fig.1 CF/EP before degradation and products after degradation(A) CF/EP before degradation; (B) solid residue of CF/EP after degradation; (C) liquid residue of CF/EP after degradation.
| Code | Process parameter | Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
| A | Reaction temperature/℃ | 290 | 300 | 310 | 320 | 330 |
| B | Holding time/min | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| C | cKOH/(mol·L-1) | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| D | V(n-Butanol)/mL | 400 | 425 | 450 | 475 | 500 |
Table 1 Process parameters and levels
| Code | Process parameter | Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
| A | Reaction temperature/℃ | 290 | 300 | 310 | 320 | 330 |
| B | Holding time/min | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| C | cKOH/(mol·L-1) | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| D | V(n-Butanol)/mL | 400 | 425 | 450 | 475 | 500 |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | F-value | P-value>F-value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relation | 0.066 | 12 | 19.53 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| A | 4.773×10-3 | 1 | 16.87 | 0.0007 | Significant |
| B | 0.011 | 1 | 38.60 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| C | 5.367×10-3 | 1 | 18.97 | 0.0004 | Significant |
| D | 6.055×10-4 | 1 | 2.14 | 0.1608 | Significant |
| AC | 1.830×10-3 | 1 | 6.47 | 0.0204 | Significant |
| CD | 4.442×10-4 | 1 | 1.57 | 0.2263 | Not significant |
| B2 | 3.353×10-3 | 1 | 11.85 | 0.0029 | Significant |
| C2 | 1.273×10-3 | 1 | 4.50 | 0.0480 | Significant |
| BCD | 1.051×10-3 | 1 | 3.72 | 0.0698 | Not significant |
| A2B | 4.726×10-3 | 1 | 16.70 | 0.0007 | Significant |
| A2D | 1.287×10-3 | 1 | 4.55 | 0.0470 | Significant |
| AB2 | 2.735×10-3 | 1 | 9.66 | 0.0061 | Significant |
| Residual | 5.093×10-3 | 18 | |||
| Lack of fit | 4.109×10-3 | 12 | 2.09 | 0.1884 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 9.843 | 6 |
Table 2 Analysis of variance for established mathematical model
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | F-value | P-value>F-value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relation | 0.066 | 12 | 19.53 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| A | 4.773×10-3 | 1 | 16.87 | 0.0007 | Significant |
| B | 0.011 | 1 | 38.60 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| C | 5.367×10-3 | 1 | 18.97 | 0.0004 | Significant |
| D | 6.055×10-4 | 1 | 2.14 | 0.1608 | Significant |
| AC | 1.830×10-3 | 1 | 6.47 | 0.0204 | Significant |
| CD | 4.442×10-4 | 1 | 1.57 | 0.2263 | Not significant |
| B2 | 3.353×10-3 | 1 | 11.85 | 0.0029 | Significant |
| C2 | 1.273×10-3 | 1 | 4.50 | 0.0480 | Significant |
| BCD | 1.051×10-3 | 1 | 3.72 | 0.0698 | Not significant |
| A2B | 4.726×10-3 | 1 | 16.70 | 0.0007 | Significant |
| A2D | 1.287×10-3 | 1 | 4.55 | 0.0470 | Significant |
| AB2 | 2.735×10-3 | 1 | 9.66 | 0.0061 | Significant |
| Residual | 5.093×10-3 | 18 | |||
| Lack of fit | 4.109×10-3 | 12 | 2.09 | 0.1884 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 9.843 | 6 |
| No. | Reactor temperature/℃ | Holding time/min | Additive concentration/ (mol·L-1) | V(n-Butanol)/ mL | Actual degradation rate(%) | Theoretical degradation rate(%) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 330 | 40 | 0.04 | 443 | 98.82 | 99.20 | -0.38 |
| 2 | 300 | 50 | 0.04 | 450 | 91.19 | 88.90 | 2.58 |
| 3 | 320 | 20 | 0.04 | 500 | 92.98 | 98.34 | -5.45 |
| 4 | 330 | 60 | 0.03 | 430 | 99.59 | 101.50 | -1.91 |
| 5 | 310 | 50 | 0.05 | 430 | 97.23 | 96.98 | 0.25 |
| 6 | 300 | 60 | 0.04 | 500 | 80.12 | 77.94 | -2.18 |
Table 3 Experiments of process parameters to verify the mathematical model
| No. | Reactor temperature/℃ | Holding time/min | Additive concentration/ (mol·L-1) | V(n-Butanol)/ mL | Actual degradation rate(%) | Theoretical degradation rate(%) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 330 | 40 | 0.04 | 443 | 98.82 | 99.20 | -0.38 |
| 2 | 300 | 50 | 0.04 | 450 | 91.19 | 88.90 | 2.58 |
| 3 | 320 | 20 | 0.04 | 500 | 92.98 | 98.34 | -5.45 |
| 4 | 330 | 60 | 0.03 | 430 | 99.59 | 101.50 | -1.91 |
| 5 | 310 | 50 | 0.05 | 430 | 97.23 | 96.98 | 0.25 |
| 6 | 300 | 60 | 0.04 | 500 | 80.12 | 77.94 | -2.18 |
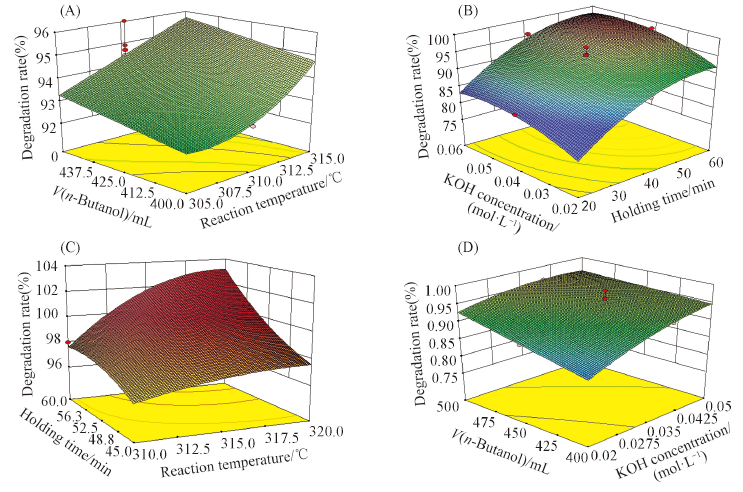
Fig.2 Effect of different process parameters on degradation rate(A) t=40 min, c=0.04 mol/L; (B) temperature=310 ℃, L= 450 mL; (C) c=0.04 mol/L, L= 450 mL;(D) t=40 min, temperature=310 ℃.
| No. | Reaction temperature/℃ | Holding time/ min | c(Additive)/ (mol·L-1) | V(n-Butanol)/ mL | Actual degradation rate(%) | Theoretical degradation rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 100.69 | 100.00 |
| 2 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 98.17 | |
| 3 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 99.50 | |
| 4 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 98.71 | |
| 5 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 100.40 | |
| 6 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 99.87 |
Table 4 Experiments under the optimal process parameters
| No. | Reaction temperature/℃ | Holding time/ min | c(Additive)/ (mol·L-1) | V(n-Butanol)/ mL | Actual degradation rate(%) | Theoretical degradation rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 100.69 | 100.00 |
| 2 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 98.17 | |
| 3 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 99.50 | |
| 4 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 98.71 | |
| 5 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 100.40 | |
| 6 | 330 | 60 | 0.0538 | 413 | 99.87 |
| Species | C(%) | O(%) | N(%) | Si(%) | K(%) | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original carbon fiber | 77.96 | 20.29 | 1.09 | 0.66 | 0 | 0.260 |
| Recycled carbon fiber | 78.46 | 16.70 | 1.86 | 1.71 | 1.27 | 0.213 |
Table 5 Elemental composition of carbon fibers from XPS spectra
| Species | C(%) | O(%) | N(%) | Si(%) | K(%) | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original carbon fiber | 77.96 | 20.29 | 1.09 | 0.66 | 0 | 0.260 |
| Recycled carbon fiber | 78.46 | 16.70 | 1.86 | 1.71 | 1.27 | 0.213 |
| Species | Comporition(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C—C | C—OH | C | COOH | C | |
| Original carbon fiber | 67.93 | 29.13 | 1.45 | 0.48 | 0.99 |
| Recycled carbon fiber | 33.76 | 44.74 | 18.74 | 1.23 | 1.53 |
Table 6 Oxygen functional groups of carbon fibers from XPS spectra
| Species | Comporition(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C—C | C—OH | C | COOH | C | |
| Original carbon fiber | 67.93 | 29.13 | 1.45 | 0.48 | 0.99 |
| Recycled carbon fiber | 33.76 | 44.74 | 18.74 | 1.23 | 1.53 |
| [1] | Zhang X. H., Meng Y., Zhang W., Fiber Compos., 2004, 21(1), 50—53 |
| (张晓虎, 孟宇, 张炜.纤维复合材料,2004, 21(1), 50—53) | |
| [2] | Su X. P., Hi-Tech. Fiber Appl., 2004, 29(5), 34—36 |
| (苏小萍.高科技纤维与应用,2004, 29(5), 34—36) | |
| [3] | Zhao J. X., Hi-Tech. Fiber Appl., 2003, 28(3), 1—4 |
| (赵稼祥.高科技纤维与应用,2003, 28(3), 1—4) | |
| [4] | Li W., Guo Q. F., Chin. J. Opt. Lett., 2011, 4(3), 201—212 |
| (李威, 郭权锋.中国光学,2011, 4(3), 201—212) | |
| [5] | Piñero-Hernanz R., Dodds C., Hyde J., García-Serna J., Composites Part A, 2008, 39(3), 454—461 |
| [6] | Bai Y. P., Wang Z., Feng L. Q., Mater. Des., 2010, 31(2), 999—1002 |
| [7] | Okajima I., Yamada K., Sugeta T., Kagaku Kogaku Ronbun, 2002, 28(5), 553—558 |
| [8] | Liu Y. Y., Meng L. L., Huang Y. D., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 91(5), 1912—1916 |
| [9] | Jiang G., Pickering S. J., Lester E., Compos. Sci. Technol., 2009, 69(2), 192—198 |
| [10] | Hyde J. R., Lester E., Kingman S., Composites Part A, 2006, 37(11), 2171—2175 |
| [11] | Piñero-Hernanz R., García-Serna J., Dodds C., J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2008, 46(1), 83—92 |
| [12] | Okajima I., Watanabe K., Haramiishi S., J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2017, 119, 44—51 |
| [13] | Liu Y. Y., Shan G. H., Meng L. H., Mater. Sci.Eng., A,2009, 520(1/2), 179—183 |
| [14] | Yan H., Lv C. X., Jing D. Q., New Carbon Mater., 2016, 31(1), 46—54 |
| (严华, 吕春祥, 经德齐.新型炭材料,2016, 31(1), 46—54) | |
| [15] | Huang H. H., Zhao Z. P., Cheng H. B., Yin Y. Z., Jing D. Q., Acta. Mater. Compos. Sin., 2016, 33(8), 1621—1629 |
| (黄海鸿, 赵志培, 成焕波, 殷晏珍, 经德齐.复合材料学报,2016, 33(8), 1621—1629) | |
| [16] | Huang H.H., Yin Y. Z., Cheng H. B., Zhao Z. P., Zhang B. Y.,J. Polym. Environ., 2016, 1—11 |
| [17] | GB/T31290-2014, Carbon Fibre. Determination of the Tensile Properties of Single-filament Specimens, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2014 |
| (GB/T31290-2014, 碳纤维-单丝拉伸性能的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014) | |
| [18] | GB/T3855-2005, Test Method for Resin Content of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics, Standards Press of China,Beijing, 2008 |
| (GB/T3855-2005, 碳纤维增强塑料树脂含量实验方法, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [19] | Bezerra M. A., Santelli R. E., Oliveira E. P., Talanta,2008, 76(5), 965—977 |
| [20] | Montgomery D.C., Disign and Analysis of Experiments, Translated by Fu Y. S., Zhang J., Wang Z. Y., The People s Posts and Telecommunications Press, Beijing, 2009, 366—379 |
| (傅钰生, 张健, 王振羽[译]. 实验设计与分析 , 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2009, 366—379) | |
| [21] | Qu L. L., Li Y. Q., Zheng B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(6), 1121—1127 |
| (渠凌丽, 黎源倩, 郑波.高等学校化学学报,2009, 30(6), 1121—1127) | |
| [22] | Xu X.H., He M. Z., Experimental design and Design-Expert, SPSS application, Science Press, Beijing, 2010, 109—124 |
| (徐向宏, 何明珠.试验设计与Design-Expert、 SPSS应用, 北京: 科学出版社, 2010, 109—124) |
| [1] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [2] | CHANG Shuqing, XIN Xu, HUANG Yaqi, ZHANG Xincong, FU Yanghe, ZHU Weidong, ZHANG Fumin, LI Xiaona. Pyroelectrically-induced Catalytic Performance of Zr-based MOF Under Cold-hot Alternation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2558. |
| [3] | PENG Xiaoming, WU Jianqun, DAI Hongling, YANG Zhanhong, XU Li, XU Gaoping, HU Fengping. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Single Atom Catalysts Ni⁃N⁃C for High Efficiency Degradation of Phenol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2581. |
| [4] | LI Dongping, LI Bin, LI Changheng, YU Xuegang, SHAN Yan, CHEN Kezheng. Synthesis and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Ni5P4/g-C3N4 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1292. |
| [5] | YAO Mingcai, YANG Qiang, MENG Jian, LIU Xiaojuan. Effect of Zn2+ Substituting Ga3+ on Structure and Photocatalytic Properties of Wurtzite β-CuGa1-xZnxO2 with Unequal Doping [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3561. |
| [6] | LI Li, LI Pengfei, WANG Bo. Photocatalytic Application of Covalent Organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1917. |
| [7] | LI Xiaoqian, ZHANG Hua, LU Haijian, LIU Chang, LIU Qinglong, MA Xiayu, FANG Yuanping, LIANG Dapeng. Mechanism of Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B by TiO2 Nanowire Array with Internal Extraction Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2003. |
| [8] | GAO Xia,PAN Huibin,QIAO Chengfang,CHEN Fengying,ZHOU Yuan,YANG Wenhua. Construction of HRP Immobilized Enzyme Reactor Based on Hierarchically Porous Metal-organic Framework and Its Dye Degradation Application† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1591. |
| [9] | WANG Rui,XU Mei,XIE Jiawen,YE Shengying,SONG Xianliang. Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Conditions on the Structure and Properties of Porous Spherical Bi2WO6 Photocatalyst † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1320. |
| [10] | LIU Dongxu, CHEN Xuebing, YANG Xia, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Changdong. Controllable Fabrication of Photogenerated Charges Gradient Continuous Transfer Chain to Enhance Photocatalytic Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 742. |
| [11] | LIU Congyuan, LIU Jia, DU Peiyao, ZHANG Zhen, LU Xiaoquan. Preparation of Hydrophilic FePt Nanoparticles and co-Catalyze Degrade Organic Pollutants † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 697. |
| [12] | LIU Yigang,ZHAO Peng,HAN Yugui,SONG Xin,HAN Zhipeng,XIE Liangbo,LI Zhuang,JIA Xiaoqing,LI Yi. W Element Doped CeO2 as Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Catalyst for Efficient Treatment of Oily Wastewater † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 498. |
| [13] | HUA Tao, LI Shengnan, LI Fengxiang, WANG Haonan. Treatment of Naphthalene by Microbial Electrochemical System and the Analysis of Microbial Communities † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1964. |
| [14] | ZHANG Kejie,LI Yu,XIA Yuan,HAN Shuo,CAO Jing,WANG Hanyang,LUO Wentao,ZHOU Zhiping. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of CdS/CuS Core-shell Nanocomposites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 489. |
| [15] | GAN Lu,DONG Yongchun. Photocatalytic Performance of Fe-complexes Prepared Using Cotton Fiber Modified with Different Dicarboxylic Acids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2205. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||