

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 1148.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160180
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Juan1, ZHOU Bing2, WANG Xinxin3, WU Xiujuan1, LI Ting1, ZHANG Wenke3, LIU Kangding1,*( )
)
Received:2016-03-25
Online:2016-06-10
Published:2016-05-10
Contact:
LIU Kangding
E-mail:kangdingliu@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Juan, ZHOU Bing, WANG Xinxin, WU Xiujuan, LI Ting, ZHANG Wenke, LIU Kangding. Preparation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Lentiviral Vector Infected EPCs for the Improvement of Angiogenesis and MRI Tracing†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1148.
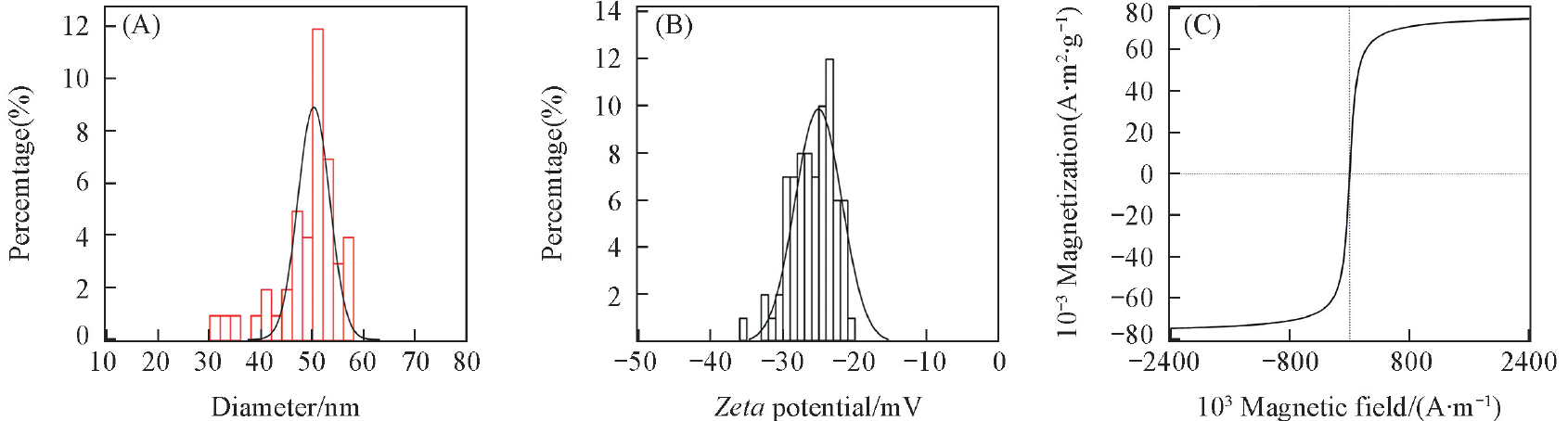
Fig.4 Particle size distribution of Fe3O4 NPs from dynamic light scattering analysis(A), zeta potential distribution of Fe3O4 NPs coated with sodium citrate in FBS solution at pH=7.0(B) and magnetic hysteresis curve of Fe3O4 NPs measured at 300 K(C)
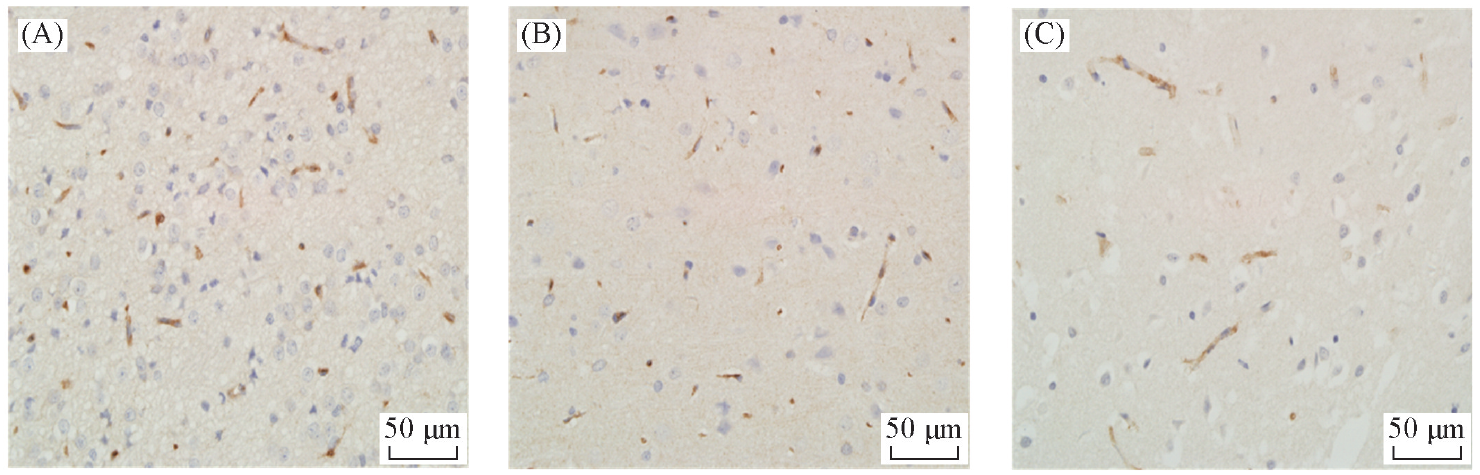
Fig.9 Immunohistochemistry of CD34 in the brain of MCAO rats in EPCs-VEGF-Fe3O4 NPs treatment group(A), EPCs-VEGF treatment group(B) and normal saline treatment group(C)
| [1] | Bao F., Yao R. A., Gu R. A., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(8), 1552—1554 |
| (鲍芳, 姚建林, 顾仁敖. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(8), 1552—1554) | |
| [2] | Qiao R. R., Yang C. H., Gao M. Y., J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19(35), 6274—6293 |
| [3] | Weinstein J. S., Varallyay C. G., Dosa E., Gahramanov S., Hamilton B., Rooney W. D., Muldoon L. L., Neuwelt E. A., J. Cerebr. Blood F Me., 2010, 30(1), 15—35 |
| [4] | Sun L., Liu G. F., Zhuang J. Q., Zhang H. M., Yang W. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(12), 2313—2315 |
| (孙琳, 刘桂峰, 庄家骐, 张惠茅, 杨文胜. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(12), 2313—2315) | |
| [5] | Thu M. S., Bryant L. H., Coppola T., Jordan E. K., Budde M. D., Lewis B. K., Chaudhry A., Ren J. Q., Varma N. R. S., Arbab A. S., Frank J. A., Nat. Med., 2012, 18(3), 463—467 |
| [6] | Kumar A., Jena P. K., Behera S., Lockey R. F., Mohapatra S., Mohapatra S., Nanomed-Nanotechnol, 2010, 6(1), 64—69 |
| [7] | Gaihre B., Khil M. S., Kim H. Y., J. Microencapsul., 2011, 28(4), 286—293 |
| [8] | Fan Y. F., Shen F. X., Frenzel T., Zhu W., Ye J. Q., Liu J. R., Chen Y. M., Su H., Young W. L., Yang G. Y., Ann. Neurol., 2010, 67(4), 488—497 |
| [9] | Fu S. S., Li F. J., Wang Y. Y., You A. B., Qie Y. L., Meng X., Li J. R., Li B. C., Zhang Y., Li Q. D., PLoS One, 2013, 8(9), e73035 |
| [10] | Wang J., Ren L. L., Li J. G., Huang J. S., Cheng D., Shuai X. T., RSC Adv., 2015, 27(5), 21103—21111 |
| [11] | Crafts T. D., Jensen A. R., Smith E. C., Markel T. A., Cytokine, 2015, 71(2), 385—393 |
| [12] | Birk D. M., Barbato J., Mureebe L., Chaer R. A., Vasc. Endovasc Surg., 2008, 42(6), 517—530 |
| [13] | Ma Y., Qu Y., Fei Z., J. Neurosci. Res., 2011, 89(7), 969—978 |
| [14] | Lever A. M. L., Strappe P. M., Zhao J. J., Biomed. Sci., 2004, 11(4), 439—449 |
| [15] | Nowak D. G., Woolard J., Amin E. M., Konopatskaya O., Saleem M. A., Churchill A. J., Ladomery M. R., Harper S. J., Bates D. O., J. Cell Sci., 2008, 121(20), 3487—3495 |
| [16] | Zhao L.J., Construction and Expression of Optimized Novel Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Lentiviral Vector Containing Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 164 and Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein, Changchun, Jilin University, 2011 |
| (赵丽静. VEGF164与EGFP双基因共表达的优化新型HIV-1慢病毒载体的构建及表达 , 长春:吉林大学, 2011) | |
| [17] | Wang H. J., Wang J., Li N., Gao H., Liu K. D., Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(6), 1056—1063 |
| [18] | Liu K. D., Sun Z. Q., Li Y. P., Rao M. L., J. Apoplexy Nerv. Dis., 1997, 2(14), 86—89 |
| (刘亢丁, 苏志强, 李毅平, 饶明俐. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 1997, 2(14), 86—89 | |
| [19] | Yang T. Z., Shen C. M., Li Z., Zhang H. R., Xiao C. W., Chen S. T., Xu Z. C., Shi D. X., Li J. Q., Gao H. J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 23233—23236 |
| [20] | Zhou H., Lee J., Park T. J., Lee S. J., Park J. Y., Lee J., Sensor Actuat. B: Chem., 2012, 163(1), 224—232 |
| [21] | Nightingale E. R. Jr., J. Phys. Chem., 1959, 63(9), 1381—1387 |
| [22] | Tansel B., Sager J., Rector T., Garland J., Strayer R. F., Levine L. F., Roberts M., Hummerick M., Bauer J., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2006, 51(1), 40—47 |
| [23] | Zha X.L., Zhou C. Y., Biochemistry, Peoples Medical Publishing House, Beijing, 2008, 30 |
| (查锡良, 周春燕. 生物化学, 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008, 30) | |
| [24] | Daldrup-Link H. E., Rudelius M., Piontek G., Metz S., Brauer R., Debus G., Corot C., Schlegel J., Link T. M., Peschel C., Rummeny E. J., Oostendorp R. A. J., Radiology, 2005, 234(1), 197—205 |
| [25] | Mornet S., Vasseur S., Grasset F., Veverka P., Goglio G., Demourgues A., Portier J., Pollert E., Duguet E., Prog. Solid State Chem., 2006, 34(2), 237—247 |
| [26] | Thorek D. L. J., Chen A., Czupryna J., Tsourkas A., Annal Biomed. Eng., 2006, 34(1), 23—38 |
| [27] | Shinto H., Hirata T., Fukasawa T., Fujii S., Maeda H., Okada M., Nakamura Y., Furuzono T., Colloid Surface B, 2013, 108, 8—15 |
| [28] | Duan H. W., Kuang M., Wang X. X., Wang Y. A., Mao H., Nie S. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(22), 8127—8131 |
| [29] | Weidner N., Breast Cancer Res. Treat, 1995, 36(2), 169—180 |
| [1] | LIU Ye, YAO Shunyu, FANG Chao, ZHAO Waiou, WANG Jingyuan, LI Yapeng. Synthesis and Characteristic of Double Model Molecule Probe Targeting Myeloperoxidase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1573. |
| [2] | ZHANG Long, WAN Xiaona, DUAN Wenjing, QIU Hu, HOU Jieqiong, WANG Xiaorui, LI Hui, DU Xueyan. Synthesis and Microwave Absorption Performance of Fe3O4@PPy@PANI Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 185. |
| [3] | LIU Ruiqing, LIANG Shuang, JIANG Cun, XU Zushun, XU Haibo. Synthesis and Proporties of Temperature and pH-sensitive and Gadolinium Contained Polymeric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 155. |
| [4] | WANG Xiaohui, , LI Xiaotian. TiO2 Nanofibers Embedded with Au and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Visible-light Photocatalysis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 976. |
| [5] | HU Qi, FANG Chao, ZHAO Wai’ou, LI Yapeng, CHEN Xia, WANG Jingyuan. Synthetic of PGMA-EDA-g-PEG-g-DS@IO as a Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agent for Atherosclerosis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2061. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhuoqi, GENG Haoran, XUAN Ruifei, CHEN Minmin, CHEN Hui, LIU Aihui, CAO Xichuan. Fabrication and TXL Anti-cancer Drug Delivery of Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1509. |
| [7] | KANG Congmin, ZHAO Xuhao, YU Yuqi, LÜ Yingtao. De novo Design of Indole Derivatives as VEGFR-2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 550. |
| [8] | , WANG Xiaohui, LI Xiaotian. Preparation and Photocatalytic Efficiency of Fe3O4/TiO2 Nanocomposite Fibers Modified with Ag Nanoparticles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 357. |
| [9] | ZHANG Zhijie, TANG Tao. Structure and Properties of Fe3O4/Polystyrene Nanocomposites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11): 2472. |
| [10] | CHEN Zhuo-Yue, LI Quan-Li, ZHAO Yuan-Cong, CHEN Jia-Long, YOU Tian-Xue, XIONG Kai-Qin, HUANG Nan*. Immobilization of Peptide Aptamer of Specific Indentification of Endothelial Progenitor Cell on Titanium Surface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(1): 100. |
| [11] | SUN Lin LIU GuiFeng ZHUANG JiaQi ZHANG HuiMao YANG WenSheng. Effect of Polyaspartic Acid Modification on Stability and MRI Enhancement of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(12): 2313. |
| [12] | LI Zhong-Feng1,2, LI Wei-Sheng1,2, LIAO Pei-Qiu1,2, WEI Lai1,2, LI Xiao-Jing1*, JING Feng-Ying1, PEI Feng-Kui1*, WANG Xu-Xia2,3, LEI Hao3. Study of Two Sandwich-type Manganese Polyoxometalates as Potential MRI Contrast Agents [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(11): 2021. |
| [13] | ZHENG Shu-Zhan, JIAN Ya-Jun, BAI Yin-Juan, XIE Zhan-Feng, CHANG Jian-Hua. Synthesis, Relaxivity of Gd(Ⅲ), Fe(Ⅲ) and Mn(Ⅱ) Complexes with Dihydropyridine Derivatives of Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(9): 1652. |
| [14] | SUN Guo-Ying, FENG Jiang-Hua, JING Feng-Ying, PEI Feng-Kui . Arabinogalactan as a Carrier for Contrast Agent in Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(10): 1837. |
| [15] | WEI Jun-Fa, ZHUO Ren-Xi. Paramagnetic Metal Chelates of DTPA-and EDTA-dipyridoxolester Derivatives and Their NMR T1Relaxivities in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1998, 19(8): 1242. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||