

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 114.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150450
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Jia1,3, YAN Li1, JIANG Miao1,3, DING Yunjie1,2,*( )
)
Received:2015-06-09
Online:2016-01-10
Published:2015-12-20
Contact:
DING Yunjie
E-mail:dyj@dicp.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Jia, YAN Li, JIANG Miao, DING Yunjie. Effect of Metal Particle Size on the Performance of Tethered-phosphine Modified Rh/SiO2 in Hydroformylation†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 114.
| Catalyst | H2 uptake /(μmol·g-1) | Dispersion(%) | Diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh/SiO2-0.2 | 10.71 | 44.07 | 2.45 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.4 | 12.44 | 51.22 | 2.11 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.6 | 14.12 | 58.11 | 1.85 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.8 | 14.37 | 59.16 | 1.82 |
Table 1 H2 chemical adsorption of samples
| Catalyst | H2 uptake /(μmol·g-1) | Dispersion(%) | Diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh/SiO2-0.2 | 10.71 | 44.07 | 2.45 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.4 | 12.44 | 51.22 | 2.11 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.6 | 14.12 | 58.11 | 1.85 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.8 | 14.37 | 59.16 | 1.82 |
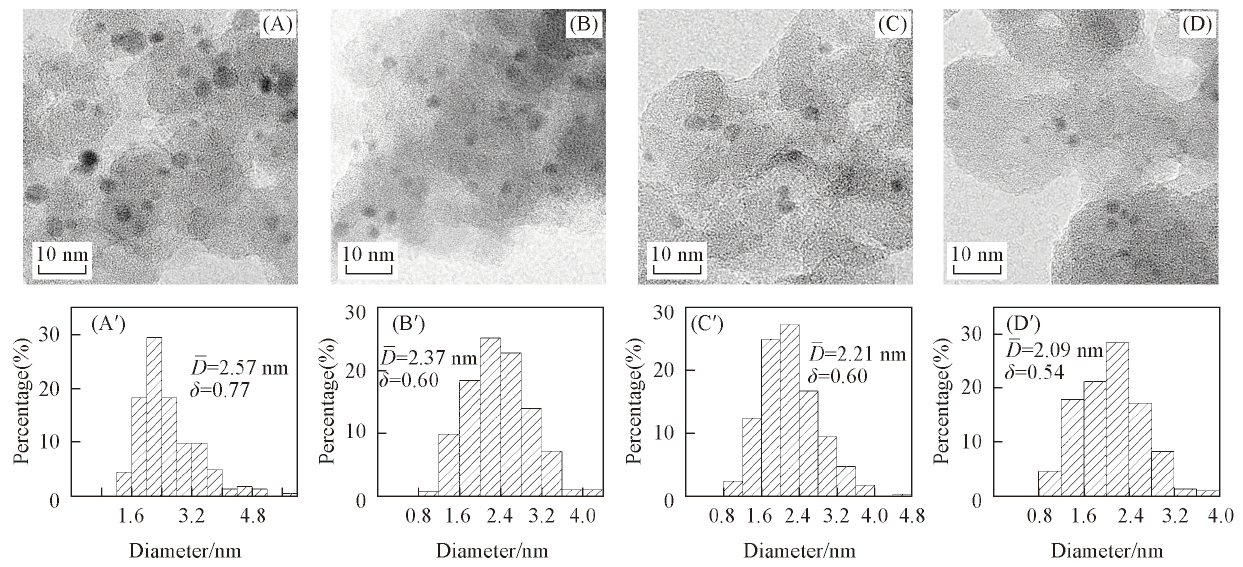
Fig.2 TEM images(A—D) and corresponding Rh particle size distributions(A'—D') of Rh/SiO2-n^ (A, A') Rh/SiO2-0.2; (B, B') Rh/SiO2-0.4; (C, C') Rh/SiO2-0.6; (D, D') Rh/SiO2-0.8.
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Total pore volume, Vp/(cm3·g-1) | Average pore radius, Dp/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 256.3 | 0.95 | 7.4 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.2 | 229.7 | 0.79 | 6.9 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.4 | 235.2 | 0.79 | 6.7 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.6 | 229.3 | 0.73 | 6.4 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.8 | 230.4 | 0.81 | 7.0 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.2 | 221.0 | 0.77 | 7.0 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.4 | 224.1 | 0.75 | 6.7 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.6 | 221.5 | 0.75 | 6.7 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.8 | 220.2 | 0.71 | 6.4 |
Table 2 Texture properties of samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Total pore volume, Vp/(cm3·g-1) | Average pore radius, Dp/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 256.3 | 0.95 | 7.4 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.2 | 229.7 | 0.79 | 6.9 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.4 | 235.2 | 0.79 | 6.7 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.6 | 229.3 | 0.73 | 6.4 |
| Rh/SiO2-0.8 | 230.4 | 0.81 | 7.0 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.2 | 221.0 | 0.77 | 7.0 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.4 | 224.1 | 0.75 | 6.7 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.6 | 221.5 | 0.75 | 6.7 |
| D-Rh/SiO2-0.8 | 220.2 | 0.71 | 6.4 |
| [1] | Ma X. F., Zhao Y. H., Su H. Y., Li W. X., Chin. J. Catal., 2012, 33(10), 1706—1711 |
| (马秀芳, 赵永慧, 苏海燕, 李微雪. 催化学报, 2012, 33(10), 1706—1711) | |
| [2] | Franke R., Selent D., Börner A., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(11), 5675—5732 |
| [3] | Hashemihezaveh M., Mahanpoor K., Soudbar D., Petrol. Sci. Technol., 2015, 33(4), 473—480 |
| [4] | Oliveira K. C. B., Carvalho S. N., Duarte M. F., Gusevskaya E. V., dos Santos E. N., Karroumi J. E., Gouygou M., Urrutigoïty M., Appl. Catal. A, 2015, 497(1), 10—16 |
| [5] | Gil W., Trzeciak A. M., Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2011, 255(3/4), 473—483 |
| [6] | Agabekov V., Seiche W., Breit B., Chem. Sci., 2013, 4(6), 2418—2422 |
| [7] | Jones C., McKittrick M., Nguyen J., Yu K., Top. Catal., 2005, 34(1), 67—76 |
| [8] | Li P., Kawi S., J. Catal., 2008, 257(1), 23—31 |
| [9] | Such-Basanez I., Salinas-Martinez de Lecea C., C. Roman-Martinez M., Curr. Catal., 2012, 1(2), 100—106 |
| [10] | Li X. M., Ding Y. J., Jiao G. P., Li J. W., Lin R. H., Gong L. F., Yan L., Zhu H. J., Appl. Catal. A, 2009, 353(2), 266—270 |
| [11] | Arakawa H., Takahashi N., Hanaoka T., Takeuchi K., Matsuzaki T., Sugi Y., Chem. Lett., 1988, 17(11), 1917—1918 |
| [12] | Hanaoka T., Arakawa H., Matsuzaki T., Sugi Y., Kanno K., Abe Y., Catal. Today, 2000, 58(4), 271—280 |
| [13] | Lu J. Q., Hu Q. Q., Ding R., Zhang X., Zhou X. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(11), 2478—2482 |
| (吕鉴泉, 胡芹芹, 丁然, 张霞, 周兴旺. 高等学学化学学报, 2013, 34(11), 2478—2482) | |
| [14] | Luo C. X., Cui Y., Yu H. M., Kong G. Z., Hu J. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9), 1948—1953 |
| (罗春香, 崔莺, 喻慧敏, 孔格致, 胡家文. 高等学学化学学报, 2014, 35(9), 1948—1953>) | |
| [15] | Ren Y. L., Li X. Y., Zhao Q. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11), 2435—2441 |
| (任延琳, 李新勇, 肇启东. 高等学学化学学报, 2014, 35(11), 2435—2441) | |
| [16] | Zhuang Y. Q., Claeys M., van Steen E., Appl. Catal. A, 2006, 301(1), 138—142 |
| [17] | Capka M., Syn. React. Inorg. Metal-Org. Chem., 1977, 7(4), 347—354 |
| [18] | Zhu H. J., Ding Y. J., Yan L., He D. P., Wang T., Chen W. M., Lu Y., Lin L. W., Chin. J. Catal., 2004, 25(8), 653—658 |
| (朱何俊, 丁云杰, 严丽, 何代平, 王涛, 陈维苗, 吕元, 林励吾. 催化学报,2004, 25(8), 653—658) | |
| [19] | Zhang D. L., Fu H. Y., Zhao X. Y., Zhao H. W., Chen H., Liu Y. M., Li X. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(8), 1835—1841 |
| (张定林, 付海燕, 赵先英, 赵华文, 陈华, 刘毅敏, 李贤均. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(8), 1835—1841) | |
| [20] | Zhang X. Y., Zheng C.Y., Zheng X. L., Fu H. Y., Yuan M. L., Li R. X., Chen H., Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2015, 31(4), 738—742 |
| (张晓亚, 郑从野, 郑学丽, 付海燕, 袁茂林, 李瑞祥, 陈华. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(4), 738—742 | |
| [21] | Gerritsen L., Van Meerkerk A., Vreugdenhil M. H., Scholten J. J. F., J. Mol. Catal., 1980, 9(2), 139—155 |
| [22] | Chuang S. S. C., Stevens R. W. Jr., Khatri R., Top. Catal., 2005, 32(3), 225—232 |
| [23] | Chen M. Y., Wong W. Z., Hua W. Q., Yi X. D., Wan H. L., Chin. J. Catal., 2011, 32(4), 672—681 |
| (陈明英, 翁维正, 华卫琦, 伊晓东, 万惠霖. 催化学报,2011, 32(4), 672—681) | |
| [24] | Yin H. M., Ding Y. J., Luo H. Y., He D. P., Xiong J. M., Chen W. M., Pan Z. D., Lin L. W., Chin. J. Catal., 2004, 25(7), 547—550 |
| (尹红梅, 丁云杰, 罗洪原, 何代平, 熊建民, 陈维苗, 潘振栋, 林励吾. 催化学报,2004, 25(7), 547—550>) | |
| [25] | Yan L., Ding Y. J., Zhu H. J., Xiong J. M., Wang T., Pan Z. D., Lin L. W., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2005, 234(1/2), 1—7 |
| [26] | Chen Y. Q., Zhang Y. L., Chen Y., Xin Q., Ying P. L., Guo X. X., Chin. J. Catal., 1991, 12(1), 1—6 |
| (陈耀强, 张堰黎, 陈豫, 辛勤, 应品良, 郭燮贤. 催化学报, 1991, 12(1), 1—6) | |
| [27] | Bluemel J., Inorg. Chem., 1994, 33(22), 5050—5056 |
| [28] | Chang J. R., Lin H. M., Cheng S. W., Tseng C. K., Tzou D. L., Shyu S. G., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2010, 329(1/2), 27—35 |
| [29] | Bogár K., Krumlinde P., Bacsik Z., Hedin N., Bäckvall J. E., Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2011, 2011(23), 4409—4414 |
| [30] | Zhang Y., Yuan Y. Z., Chen Z., Lin G. D., Zhang H. B.,J. Xianmen Univ. ( Nature Science), 1998, 37(2), 228—232 |
| (张宇, 袁友珠, 陈忠, 林国栋, 张鸿斌. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 37(2), 228—232) |
| [1] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [2] | ZHAO Sheng, HUO Zhipeng, ZHONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Hong, HU Liqun. Preparation of Modified Gadolinium/Boron/Polyethylene Nanocomposite and Its Radiation Shielding Performance for Neutron and Gamma-ray [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [3] | LIU Jiaxin, MIN Jie, XU Huajie, REN Haisheng, TAN Ningxin. Interaction Between Produced Radicals During Ethylene Combustion and Nitrogen Molecules Based on Reaxff Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210834. |
| [4] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [6] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [7] | HUANG Huilong, HUANG Hanxiong. Low-temperature Impact Behavior of Droplet on Injection-compression Molded Nanostructured PP/POE Blend Surfaces [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3195. |
| [8] | WANG Rui,XU Mei,XIE Jiawen,YE Shengying,SONG Xianliang. Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Conditions on the Structure and Properties of Porous Spherical Bi2WO6 Photocatalyst † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1320. |
| [9] | REN Wen, ZHANG Guoli, YAN Han, HU Xinghua, LI Kun, WANG Jingfeng, LI Ruiqi. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Polyaniline/Polytetrafluoroethylenethylene Composite Membrane and Its Separation Ability for Oil-Water Emulsion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 846. |
| [10] | ZHANG Li,QIAN Mingchao,LIU Xueke,Gao Shuaitao,YU Jiang,XIE Haishen,WANG Hongbin,SUN Fengjiang,SU Xianghong. Dynamic Study of Oxidative Desulfurization by Iron-based Ionic Liquids/NHD † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 317. |
| [11] | GUO Zhaopei,LIN Lin,CHEN Jie,TIAN Huayu,CHEN Xuesi. Polyglutamic Acid Grafted Polyethylene Glycol@Calcium Carbonate Based Shielding System for Improving Polyethyleneimine Gene Transfection Efficiency † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 235. |
| [12] | XU Jianling,ZHANG Di,NIE Miaoqing,WANG Hanxi,LI Longwei. Adsorption of Cr 6+ on Polyethyleneimine-functionalized Straw Biochar from Aqueous Solution † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 155. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ling,DUAN Hongchang,TAN Zhengguo,WU Qinming,MENG Xiangju,XIAO Fengshou. Recent Advances in the Preparation of 8MR Zeolites for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx(NH3-SCR) in Diesel Engines † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 19. |
| [14] | LI Lin, XU Xinru, LI Yingqi, ZHANG Caifeng. Preparation of Targeting Nanodiamond-metaminopterone Drug System and Its Interaction with MCF-7 Cells † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1998. |
| [15] | LIU Fen, ZHOU Min, WANG Suxia, WANG Rong, YANG Ning, MA Yongjun. Study on Photoelectrocatalytic Decolorization Mechanism of Methylene Blue Under the Visible-light Irradiation by Measuring Chemical Oxygen Demand Index† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1988. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||