

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 1542.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150296
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Zhihui1, XUE Xin1, XING Yue1, LI Shumei1,*( ), LIU Bin1, HAN Dongxue2,*(
), LIU Bin1, HAN Dongxue2,*( ), NIU Li2
), NIU Li2
Received:2015-04-15
Online:2015-08-10
Published:2015-07-17
Contact:
LI Shumei,HAN Dongxue
E-mail:lishumei_2010@126.com;dxhan@ciac.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Zhihui, XUE Xin, XING Yue, LI Shumei, LIU Bin, HAN Dongxue, NIU Li. Preparation and Biocompatibility of Ag Nanoparticles Modified Stainless Steel†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8): 1542.
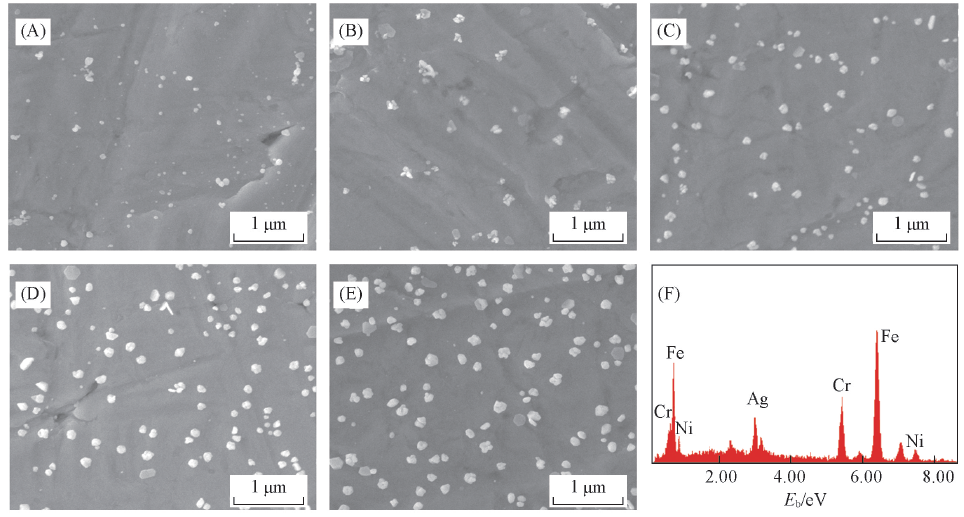
Fig.1 SEM images of 316L stainless steels with various time of electrochemically deposited Ag coats(A)100 s; (B) 500 s; (C) 800 s; (D) 1000 s; (E) 1500 s; (F) EDX pattern of sample (E).
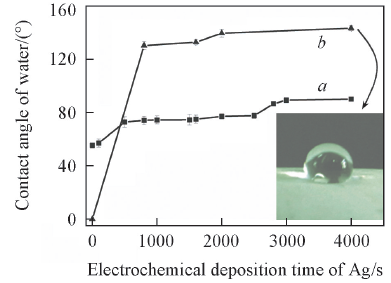
Fig.2 Contact angles of water at electrochemical deposited Ag(a) and electrochemically deposited Ag/PFOTES modified 316L stainless steels(b) with various timeInset is photograph of water drop at electrochemically deposited Ag(4000 s)/PFOTES modified 316L stainless steels.
| Experiment material | 24 h | 72 h | 120 h | 168 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 0.173±0.0239 | 0.413±0.0265 | 0.767±0.0519 | 0.834±0.0467 |
| Bare stainless steel | 0.168±0.0203 | 0.376±0.0323 | 0.757±0.0535 | 0.809±0.0578 |
| 800 s group | 0.179±0.0285 | 0.430±0.0266 | 0.734±0.0587 | 0.817±0.0532 |
| 1600 s group | 0.189±0.0246 | 0.387±0.0286 | 0.729±0.0423 | 0.868±0.0534 |
| 2000 s group | 0.175±0.0308 | 0.381±0.0405 | 0.721±0.0525 | 0.780±0.0480 |
| 4000 s group | 0.180±0.0269 | 0.398±0.0298 | 0.720±0.0632 | 0.785±0.0626 |
Table 1 OD values of different group at different time
| Experiment material | 24 h | 72 h | 120 h | 168 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 0.173±0.0239 | 0.413±0.0265 | 0.767±0.0519 | 0.834±0.0467 |
| Bare stainless steel | 0.168±0.0203 | 0.376±0.0323 | 0.757±0.0535 | 0.809±0.0578 |
| 800 s group | 0.179±0.0285 | 0.430±0.0266 | 0.734±0.0587 | 0.817±0.0532 |
| 1600 s group | 0.189±0.0246 | 0.387±0.0286 | 0.729±0.0423 | 0.868±0.0534 |
| 2000 s group | 0.175±0.0308 | 0.381±0.0405 | 0.721±0.0525 | 0.780±0.0480 |
| 4000 s group | 0.180±0.0269 | 0.398±0.0298 | 0.720±0.0632 | 0.785±0.0626 |
| Experiment material | G0/G1 stage(%) | S stage(%) | M stage(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 65.3±4.07 | 20.3±3.05 | 13.5±1.64 |
| Bare stainless steel | 66.8±3.71 | 17.6±2.62 | 12.6±1.63 |
| 800 s group | 67.2±3.39 | 17.1±3.08 | 13.5±2.07 |
| 1600 s group | 65.6±3.51 | 17.5±1.68 | 13.4+1.58 |
| 2000 s group | 68.7±3.60 | 17.1±3.74 | 13.0±2.75 |
| 4000 s group | 68.6±4.56 | 16.8±2.63 | 13.5±2.34 |
Table 2 Ratio of stage in cell cycle of different groups by FCM
| Experiment material | G0/G1 stage(%) | S stage(%) | M stage(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 65.3±4.07 | 20.3±3.05 | 13.5±1.64 |
| Bare stainless steel | 66.8±3.71 | 17.6±2.62 | 12.6±1.63 |
| 800 s group | 67.2±3.39 | 17.1±3.08 | 13.5±2.07 |
| 1600 s group | 65.6±3.51 | 17.5±1.68 | 13.4+1.58 |
| 2000 s group | 68.7±3.60 | 17.1±3.74 | 13.0±2.75 |
| 4000 s group | 68.6±4.56 | 16.8±2.63 | 13.5±2.34 |
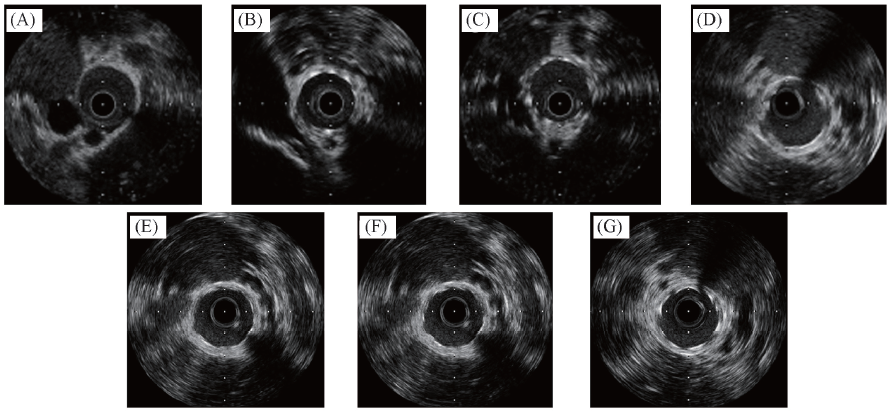
Fig.3 IVUS images of pre and after stent implantation(A)Pre-stent implantation of bare stainless steel group; (B) after stent implantation of bare metal group; (C) 30 d after stent implantation of bare stainless steel group; (D) 30 d after stent implantation of 800 s group; (E) 30 d after stent implantation of 1600 s group; (F) 30 d after stent implantation of 2000 s group; (G) 30 d after stent implantation of 4000 s group.
| [1] | Hu D. Y., Chinese Journal of Cardiology, 2005, 33(6), 582—584 |
| (胡大一. 中华心血管病杂志, 2005, 33(6), 582—584) | |
| [2] | Hu D. Y., Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Review, 2006, 4(10), 721—723 |
| (胡大一. 中国心血管病研究杂志, 2006, 4(10), 721—723) | |
| [3] | Dong S., Sapieha S., Schreiber H. P., Poly. Eng. Sci., 1993, 33, 343—346 |
| [4] | He M. X., He S. L., Bulletin of Biology, 2000, 35, 4—6 |
| (何美霞, 贺石林. 生物学通报, 2000, 35, 4—6) | |
| [5] | Zhang J.R., New Chitosan Derivative Anticoagulant Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 2004 |
| (张建荣. 新型壳聚糖衍生物抗凝血材料, 天津: 天津大学, 2004) | |
| [6] | Chen B. L., Wang D. A., Feng L. X., Zhang X., Suihua University Journal, 2007, 21, 186—188 |
| (陈宝林, 王东安, 封麟先, 张欣. 绥化大学学报, 2007, 21, 186—188) | |
| [7] | Liu J. X., Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2001, 18, 169—172 |
| (刘敬肖. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2001, 18, 169—172) | |
| [8] | Wu B., Function Materials, 2013, 22, 3291—3295 |
| (吴勃. 功能材料, 2013, 22, 3291—3295) | |
| [9] | Liu Q., Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2009, 23, 323—326 |
| (刘强. 材料研究学报, 2009, 23, 323—326) | |
| [10] | Xue X., Fan L. S., Niu L., Liu B., Chang J., Zhang J., Zhang J. C., Zhao L., Zhao Z., Li S. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10), 2289—2294 |
| (薛歆, 范立双, 牛利, 刘斌, 常静, 张晶, 张基昌, 赵雷, 赵卓, 李淑梅. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(10), 2289—2294) | |
| [11] | Cheng Z. J., Du M., Lai H., Zhang N. Q., Sun K. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(3), 606—609 |
| (成中军, 杜明, 来华, 张乃庆, 孙克宁. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(3), 606—609) | |
| [12] | Du Y., Chen H. J., Cheng Z. J., Lai H., Zhang N. Q., Sun K. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1), 105—109 |
| (都颖, 陈海杰, 成中军, 来华, 张乃庆, 孙克宁. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(1), 105—109) | |
| [13] | Pang Y. C., Zhao Y., Feng J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(4), 919—924 |
| (庞艺川, 赵颖, 冯杰. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(4), 919—924) | |
| [14] | Chen Y., Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24, 697—706 |
| (陈钰. 化学进展, 2012, 24, 697—706) | |
| [15] | Guo C. F., Materials Research and Applications, 2010, 4, 161—163 |
| (郭春芳, 材料研究进展, 2010, 4, 161—163) | |
| [16] | Uyanik M., Arpac E., Schmidt H., Akarsu M., Sayilkan F., Sayilkan H., J. Appl.Polym. Sci., 2006, 100, 2386—2392 |
| [17] | Kessman A. J., Huckaby D. K. P., Snyder C. R., Kukureka S. N., Cairns D. R., Wear, 2009, 267, 614—618 |
| [18] | Yang J., Zhang Z. Z., Men X. H., Xu X. H., Zhu X. T., Zhou X. Y., Xue Q. J., J. Colloid Inter. Sci., 2012, 366, 191—195 |
| [19] | Zhu X. T., Zhang Z. Z., Men X. H., Yang J., Wang K., Xu X. H., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 15793—15797 |
| [20] | Wang D. A., Wang X. L., Liu X. J., Zhou F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 9938—9944 |
| [21] | Curtis A. S., Gadegaard N., Dalby M. J., IEEE Trans Nanobioscience, 2004, 3(1), 61—65 |
| [22] | Gallagher J. O., Mcghee K. F., Wilkinson C. D. W., IEEE Trans Nanobioscience, 2002, 1(1), 24—28 |
| [23] | Poon V. K., Burd A., Burns, 2004, 30, 140—147 |
| [24] | Bosetti M., Cannas M., Biomaterials, 2002, 23, 887—892 |
| [25] | Gutensohn K., Beythien C., Bau J., Thrombosis Research, 2000, 99, 577—586 |
| [26] | Child T., Vanooji W. J., Trans IMF, 1999, 77, 64—70 |
| [27] | Godin B., Sakamoto J. H., Serda R. E., Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2010, 31, 199—205 |
| [28] | Price R. L., Waid M. C., Haberstroh K. M., Biomaterials, 2003, 24, 1877—1886 |
| [1] | FAN Wenqian, ZHONG Zhengxiang, TIAN Gongwei, WANG Yu, GONG Guifen, QI Dianpeng. Application of Conductive Polymer in Nerve Interface Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1146. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ruiyang,YU Chunyan,HAN Jishu,FU Yunlei,LI Ming,HU Dehua,LIU Fusheng. Preparation of Photo-responsive Film by Electrochemical Deposition Method and the Application in Optical Information Storage† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 358. |
| [3] | YANG Qinghua, WANG Longgang, LIU Jie, LU Yong, CHEN Tianyun. Preparation and Characterization of Star-shaped β-Cyclodextrin Based Polymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 793. |
| [4] | FENG Dongyang,GUO Di,LIU Xiaoxia. Functionalization of Carbon Electrode and Subsequent Electrochemical Deposition of Nanostructured Manganese Oxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2280. |
| [5] | PAN Shuai, LI Zhanhong, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Xueling, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Zhigang. Glucose Biosensor Based on Rebuilding the Surface of the Spiral-type Pt-Ir Electrode† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1163. |
| [6] | LI Yingying, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Yiheng, WANG Lei. Preparation of NF/rGO/Co3O4/NiO Electrode and Its Application in Supercapacitor† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2031. |
| [7] | LI Ruiyan, WANG Shuang, LI Dongdong, QIN Yanguo, YU Jihong. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of VPI-7 Zeolite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1935. |
| [8] | LI Ning, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Qing-Qing, SONG Qin, QI Lin, WANG Long, TANG Ming-Liang, JIN Gang, CHENG Guo-Sheng. Synthesis and Biocompatibility of Amphiphilic Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(1): 50. |
| [9] | WU Jian, ZHENG Yu-Dong, GAO Shuang, GUO Jia, CUI Qiu-Yan, DING Xun, CHEN Xiao-Hua. Synthesis, Structural Characteristics and Properties of Silver Nanoparticles in situ Bacterial Cellulose Gelatinous Membrane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(1): 210. |
| [10] | MAO Jun, BO Shu-Qin, JI Xiang-Ling. Enzymatic Degradation of Biocompatible Block Polyelectrolyte Micelles in Aqueous Solutions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(09): 2099. |
| [11] | YANG Shan, WANG Yan-Bing, ZONG Ming-Ming, GONG Ming, MA Jia-Ni, GONG Yong-Kuan. Synthesis and Coating Properties of Biomembrane Mimetic Copolymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(07): 1579. |
| [12] | GAO Xia, ZHANG Fu, CHEN Zhi-Chun, LIN Xian-Fu. Hepatic-targeting Microcapsules Construction by Layer-by-layer Self-assembly of Lactose-branched Polyelectrolyte [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(4): 957. |
| [13] | WANG Ying-Bo, LU Xiong*, FENG Bo, QU Shu-Xin, WENG Jie. Investigation of the Stability and Biocompatibility of HA/ZrO2 Nanocomposite Coatings Prepared by Pulsed Electrochemical Deposition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(2): 253. |
| [14] | CHEN PeiRong WANG Bin YAO HongZhang LIN HuaFeng HUANG Bo LI ZengZhi. Protection of ZnO Nanoparticles to Beauveria bassiana Conidia from Ultraviolet Radiation and Their Biocompatibility [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(12): 2322. |
| [15] | ZHANG Jing-Jing, LI Wen-Di, RONG Jian-Hua*. Preparation and Characterization of PVP/Clay Nanocomposite Hydrogels [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(10): 2081. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||