

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (10): 1969.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150288
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Haijie1,2,*( ), CHEN Lingxia2, HUANG Zhenxu2, LIU Shouchang1, LIU Zhongyi1,*(
), CHEN Lingxia2, HUANG Zhenxu2, LIU Shouchang1, LIU Zhongyi1,*( )
)
Received:2015-04-13
Online:2015-10-10
Published:2015-09-14
Contact:
SUN Haijie,LIU Zhongyi
E-mail:sunhaijie406@163.com;Liuzhongyi@zzu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SUN Haijie, CHEN Lingxia, HUANG Zhenxu, LIU Shouchang, LIU Zhongyi. Particle Size Effect of Ru-Zn Catalysts on Selective Hydrogenation of Benzene to Cyclohexene†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1969.
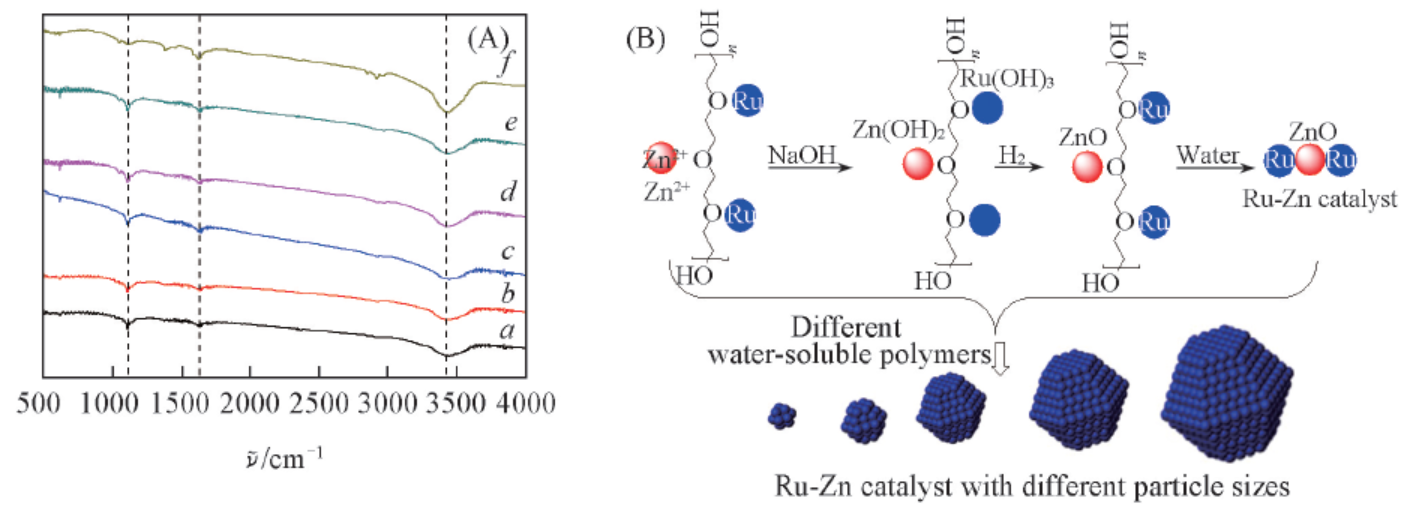
Fig.2 FTIR spectra of Ru-Zn catalysts modified by different water-soluble polymers after hydrogenation(A) and the mechanism of the water-soluble polymers in preparing Ru-Zn catalysts with different particle sizes(B)a. Blank; b. 0.4 g PVA-1750; c. 0.4 g PEG-20000; d. 0.4 g PEG-10000; e. 0.8 g PEG-20000; f. 1.2 g PEG-20000.
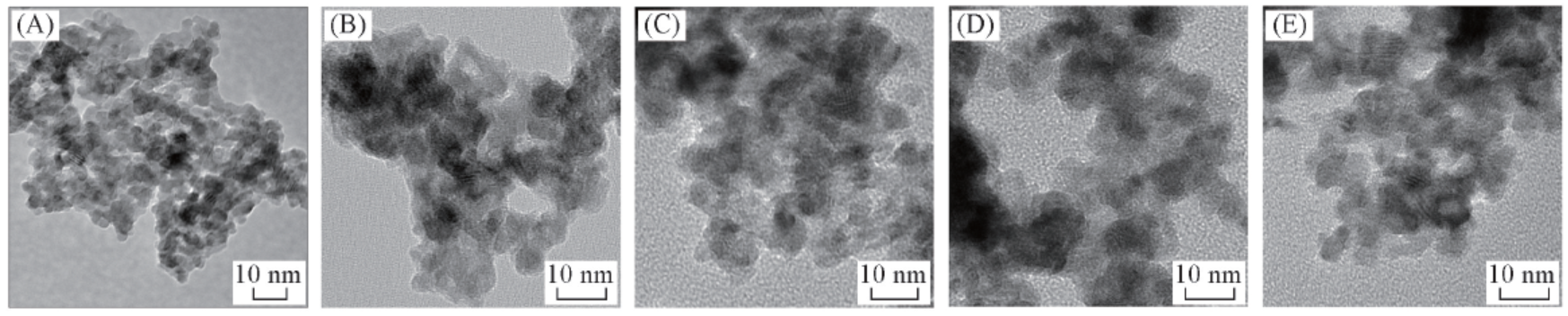
Fig.3 TEM images of the Ru-Zn catalysts modified by different dosages of PEG-20000(A) 1.2 g PEG-20000; (B) 0.4 g PEG-10000; (C) 0.4 g PEG-20000; (D) 0.4 g PVA-1750; (E) blank.
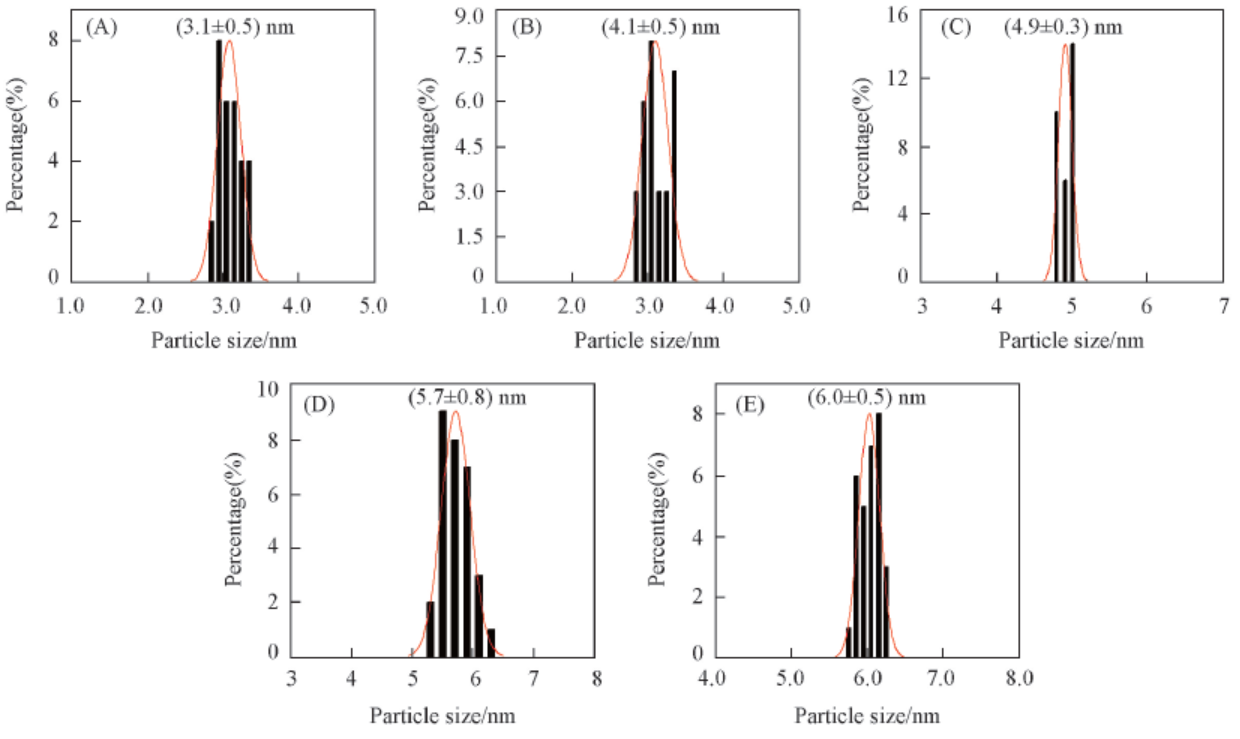
Fig.4 Particle size distribution of the Ru-Zn catalysts modified by different dosages of PEG-20000 (A) 1.2 g PEG-20000; (B) 0.4 g PEG-10000; (C) 0.4 g PEG-20000; (D) 0.4 g PVA-1750; (E) blank.
| Modifier | Particle size/nm | Zn/Ru(atomic ratio) | SBET/(m2·g-1) | dpore/nm | Vpore/(cm3·g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulka | Surfaceb | |||||
| Blank | 5.9 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 65 | 0.12 | 7.54 |
| 0.4 g PVA-1750 | 5.6 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 66 | 0.11 | 7.69 |
| 0.4 g PEG-20000 | 4.8 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 67 | 0.12 | 7.87 |
| 0.4 g PEG-10000 | 4.2 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 68 | 0.11 | 7.89 |
| 0.8 g PEG-20000 | 3.7 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 70 | 0.09 | 7.99 |
| 1.2 g PEG-20000 | 3.0 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 72 | 0.10 | 7.95 |
Table 1 Particle size, compositions and texture properties of Ru-Zn catalysts modified by different water-soluble polymers after hydrogenation
| Modifier | Particle size/nm | Zn/Ru(atomic ratio) | SBET/(m2·g-1) | dpore/nm | Vpore/(cm3·g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulka | Surfaceb | |||||
| Blank | 5.9 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 65 | 0.12 | 7.54 |
| 0.4 g PVA-1750 | 5.6 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 66 | 0.11 | 7.69 |
| 0.4 g PEG-20000 | 4.8 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 67 | 0.12 | 7.87 |
| 0.4 g PEG-10000 | 4.2 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 68 | 0.11 | 7.89 |
| 0.8 g PEG-20000 | 3.7 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 70 | 0.09 | 7.99 |
| 1.2 g PEG-20000 | 3.0 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 72 | 0.10 | 7.95 |
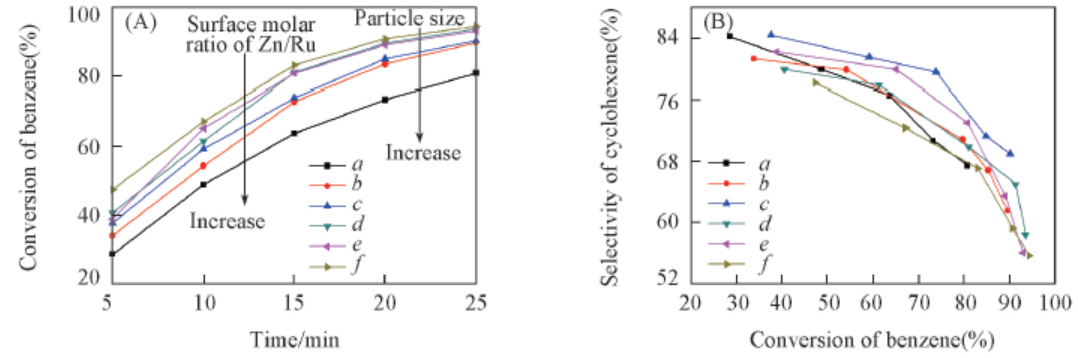
Fig.6 Performance of Ru-Zn catalysts modified by different water-soluble polymers for selective hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexenea. Blank; b. 0.4 g PVA-1750; c. 0.4 g PEG-20000; d. 0.4 g PEG-10000; e. 0.8 g PEG-20000; f. 1.2 g PEG-20000.
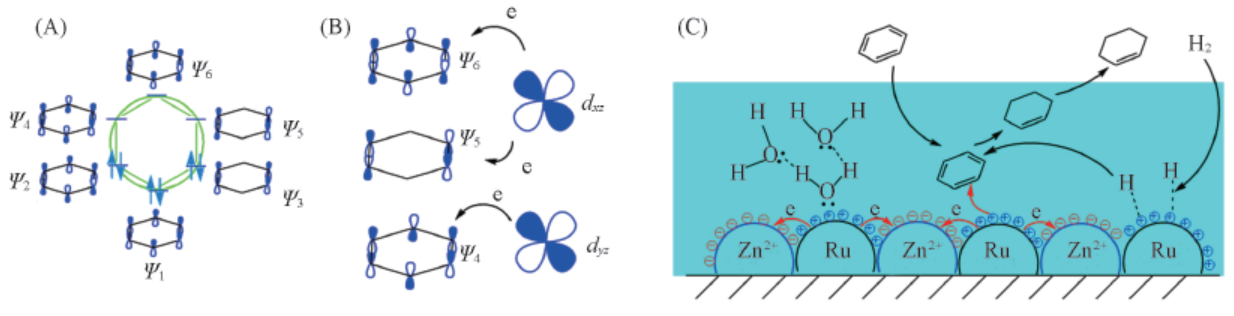
Fig.8 Hückel molecular orbitals of benzene(A), the interaction between the d orbital of Ru and Hückel antibonding orbital(Ψ4 and Ψ5) of benzene(B) and the selective hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexene over Ru-Zn catalyst surface(C)
| [1] | Wang Z. B., Zhang Q., Lu X. F., Chen S. J., Liu C. J., Chin. J. Catal., 2015, 36(3), 400—407 |
| (王正宝, 张琪, 路晓飞, 陈双佳, 刘春杰. 催化学报,2015, 36(3), 400—407) | |
| [2] | Sun H. J., Li Y. Y., Li S. H., Zhang Y. X., Liu S. C., Liu Z. Y., Ren B. Z., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30(7), 1332—1340 |
| (孙海杰, 李永宇, 李帅辉, 张元馨, 刘寿长, 刘仲毅, 任保增. 物理化学学报,2014, 30(7), 1332—1340) | |
| [3] | Zhang Y., Fu H. Y., Li R. X., Chen H., Li X. J., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(3), 577—582 |
| (张晔, 付海燕, 李瑞祥, 陈华, 李贤均. 无机化学学报,2013, 29(3), 577—582) | |
| [4] | Sun H. J., Jiang H. B., Li S. H., Wang H. X., Pan Y. J., Dong Y. Y., Liu S. C., Liu Z. Y., Chin. J. Catal., 2013, 34(4), 684—694 |
| (孙海杰, 江厚兵, 李帅辉, 王红霞, 潘雅洁, 董莹莹, 刘寿长, 刘仲毅. 催化学报,2013, 34(4), 684—694) | |
| [5] | Bu J., Liu J. L., Chen X. Y., Zhuang J. H., Yan S. R., Qiao M. H., He H. Y., Fan K. N., Catal. Commun., 2008, 9, 2612—2615 |
| [6] | Zhou G. B., Tan X. H., Dou R. M., Pei Y., Fan K. N., Qiao M. H., Sun B., Zong B. N., Sci. Sin. Chim., 2014, 44(1), 121—130 |
| (周功兵, 谭晓荷, 窦镕飞, 裴燕, 范康年, 乔明华, 孙斌, 宗保守. 中国科学: 化学,2014, 44(1), 121—130) | |
| [7] | Milone C., Neri G., Donato A., Musolino M. G., Mercadante L., J. Catal., 1996, 159, 253—258 |
| [8] | Singh U. K., Vannice M. A., Appl. Catal. A, 2001, 213, 1—24 |
| [9] | Sun H. J., Jiang H. B., Li S. H., Dong Y. Y., Wang H. X., Pan Y. J., Liu S. C., Tang M. S., Liu Z. Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 218, 415—424 |
| [10] | Wu J. M., Yang Y. F., Chen J. L., Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2003, 22(3), 295—297 |
| (吴济民, 杨炎锋, 陈聚良. 化工进展,2003, 22(3), 295—297) | |
| [11] | Hu S. C., Chen Y. W., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2001, 40(26), 6099—6104 |
| [12] | Wang J. Q., Wang Y. Z., Xie S. H., Qiao M. H., Li H. X., Fan K. N., Appl. Catal. A, 2004, 272, 29—36 |
| [13] | Zhang P., Wu T. B., Jiang T., Wang W. T., Liu H. Z., Fan H. L., Zhang Z. F., Han B. X., Green Chem., 2013, 15, 152—159 |
| [14] | Sun H. J., Wang H. X., Jiang H. B., Li S. H., Liu S. C., Liu Z. Y., Yuan X. M., Yang K. J., Appl. Catal. A, 2013, 450, 160—168 |
| [15] | Huang X., Zhang H., Liang L. Y., Tan B. E., Preg. Chem., 2010, 22(5), 953—961 |
| [16] | Kötz R., Lewerenz H. J., Stucki S., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1983, 130(4), 825—829 |
| [17] | Peplinski B., Unger W. E. S., Grohmann I., Appl. Surf. Sci., 1992, 62(3), 115—129 |
| [18] | Ramos-Fernándze E. V., Ferreira A. E. P., Sepúlveda-Escribano A., Kapteijn F., Rodríguez-Reinoso F., J. Catal., 2008, 258, 52—60 |
| [19] | Nefedov V. I., J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 1982, 25(1), 29—47 |
| [20] | Sun H. J., Zhang X. D., Chen Z. H., Zhou X. L., Guo W., Liu Z. Y., Liu S. C., Chin. J. Catal., 2011, 32(2), 224—230 |
| (孙海杰, 张旭东, 陈志浩, 周小莉, 郭伟, 刘仲毅, 刘寿长. 催化学报,2011, 32(2), 224—230) | |
| [21] | Zhao S. L., Chen J. R., Zhou Y. F., Xie Y. M., Li X. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(8), 1552—1554 |
| (赵松林, 陈俊如, 周娅芬, 谢永美, 李贤均. 高等学校化学学报,2004, 25(8), 1552—1554) | |
| [22] | Fan G. Y., Jiang W. D., Wang J. B., Li R. X., Chen H., Li X. J., Catal. Commun., 2008, 10, 98—102 |
| [23] | Mazzieri V. A., L’Argentière P. C., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2003, 42, 2269—2272 |
| [24] | Struijk J., d’Angremond M., Lucas-De Regt W. J. M., Scholten J. J. F., Appl. Catal. A, 1992, 83, 263—295 |
| [25] | Liu J. L., Zhu Y., Liu J., Pei Y., Li Z. H., Li H., Li H. X., Qiao M. H., Fan K. N., Appl. Catal. A, 2009, 268, 100—105 |
| [26] | Sun H. J., Chen L. X., Li S. H., Jiang H. B., Zhang Y. X., Ren B. Z., Liu Z. Y., Liu S. C., J. Rare Earths, 2013, 31(10), 1023—1028 |
| [1] | LIU Suyu, DING Fei, LI Qian, FAN Chunhai, FENG Jing. Azobenzene-integrated DNA Nanomachine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220122. |
| [2] | GAO Jian, FENG Yiyu, FANG Wenyu, WANG Hui, GE Jing, FENG Wei. Alkane Grafted Phase Change Azobenzene Materials Based on Low Temperature Heat Release [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220146. |
| [3] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [4] | SUN Xingyu, LUO Jing, WANG Xiadi, ZHU Qing, ZHOU Hui, LYU Xiaobing. Synthesis and Characterization of Stereoregular and Discrete Oligo(cyclohexene carbonate)s [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220204. |
| [5] | LI Xueyu, WANG Zhao, CHEN Ya, LI Keke, LI Jianquan, JIN Shunjing, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Enhanced Catalytic Performance of Supported Nano-gold by the Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance for Selective Hydrogenation of Butadiene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220174. |
| [6] | WANG Gaobo, MA Jing. Binding Selectivity Between Diazobenzene and Different Nucleophilic Reagents: Covalent and Noncovalent Interactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2238. |
| [7] | LI Xinyu, LI Zhiwei, ZHANG Xingyuan. Construction of Room Temperature Phosphorescence System of Thioflavin-based Polylactide/Benzenesulfonic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1987. |
| [8] | ZHU Min, ZHANG Xiao, YOU Shuli. Visible-light-promoted Dearomatization of Benzene and Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1407. |
| [9] | LI Shanshan, ZHAO Wenjuan, LI Hui, FANG Qianrong. A Photoresponsive Azobenzene-functionalized Covalent Organic Framework † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1384. |
| [10] | BAI Ruonan, LI Qing, QIAO Shanlin, ZHANG Chunhuan, ZHAO Yongsheng. Controlled Preparation and Optical Waveguide Property of 1,4-Dicarbazolidinylbenzene Microwires † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 967. |
| [11] | HE Xiaoke, LI Xiaoyun, WANG Zhao, HU Nian, DENG Zhao, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Self-reduction for the Synthesis of Co Supported on Hierarchically Porous Carbon for Selective Hydrogenation Reaction † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 639. |
| [12] | DONG Xinrui, XIA Zhe, WANG Zhenxue, BIAN Qiang, LI Huabin. Design, Synthesis and Biological Activity of Pyrazole-4-carboxamides Compounds Containing 1,2,4,5-Tetrasubstituted Phenyl [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2759. |
| [13] | ZHANG Hui, ZHANG Chenjie, XU Minmin, YUAN Yaxian, YAO Jianlin. Investigation on the Reaction of o-Aminothiophenol and 2-Iodobenzoyl Chloride Monitored by SERS-HPLC Technique [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2496. |
| [14] | WANG Yue, GUO Xiaohong, ZHOU Guangdong, CHENG Tiexin. Effect of Alkyl Benzene Sulfonate Surfactant on Morphology and Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1795. |
| [15] | HU Xueyi, CHEN Miaomiao, FANG Yun, FENG Ruiqin, HAN Huihui. Investigation on Pseudo-polyanions of Cationic Cellulose-Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1464. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||