

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 1737.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150232
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Shang*( ), LI Pei, ZHAO Wei, KANG Huan, PAN Mu
), LI Pei, ZHAO Wei, KANG Huan, PAN Mu
Received:2015-03-25
Online:2015-09-10
Published:2015-08-17
Contact:
LI Shang
E-mail:lishang@whut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Shang, LI Pei, ZHAO Wei, KANG Huan, PAN Mu. Graphene-supported Fe-N/C Composite Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1737.
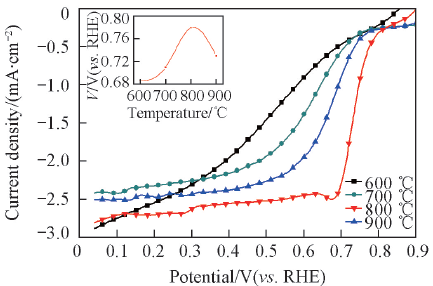
Fig.4 Effect of heat treatment temperature on ORR curves on a glassy carbon electrode coated with NG/Fe-N/C-25 catalystsElectrode: O2-saturated 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution; electrode rotating rate: 400 r/min; potential scan rate: 5 mV/s; NG/Fe-N/C-25 catalysts loading: 0.40 mg/cm2. The inset shows the ORR kinetic activity potential at 0.5 mA/cm2 vs. heat treatment temperature.
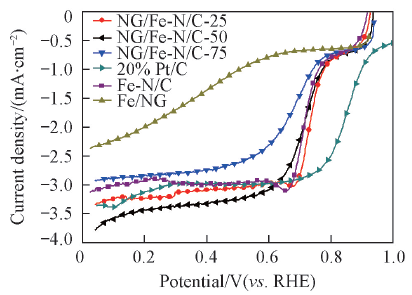
Fig.5 Effect of doping content of N-doped graphene on ORR curves on a glassy carbon electrode coated with the NG/Fe-N/C catalysts at 800 ℃ with different doping ratiosElectrode: O2-saturated 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution; electrode rotating rate: 400 r/min; potential scan rate: 5 mV/s; NG/Fe-N/C-25 catalysts loading: 0.40 mg/cm2.
| Element | C1s | O1s | N1s | Fe2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic fraction(%) | 85.62 | 8.1 | 5.17 | 1.12 |
Table 1 Percentage of C, O, N and Fe elements on the surface of NG/Fe-N/C-25 catalyst
| Element | C1s | O1s | N1s | Fe2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic fraction(%) | 85.62 | 8.1 | 5.17 | 1.12 |
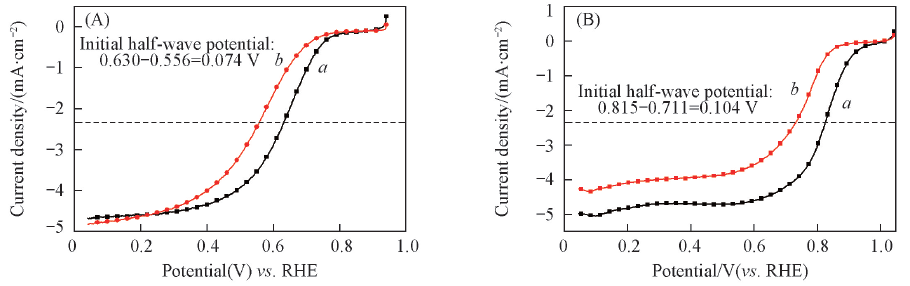
Fig.7 ORR polarization curves for NG/Fe-N/C-25 catalyst(A) and 20%Pt/C catalyst(B) before(a) and after AAT(b)The ORR tests were performed in O2 saturated 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 at room temperature with a rotation speed of 1600 r/min and a sweep rate of 5 mV/s.
| [1] | Wu G., More K. L., Johnston C. M., Zelenay P., Science, 2011, 332(6028), 443—447 |
| [2] | Hirano S., Kim J., Srinivasan S., Electrochimica Acta, 1997, 42(10), 1587—1593 |
| [3] | Antoine O., Bultel Y., Ozil P., Durand R., Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(27), 4493—4500 |
| [4] | Tian Z. Q., Jiang S. P., Liang Y. M., Shen P. K., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(11), 5343—5350 |
| [5] | Becerik I., Süzer S., Kadirgan F., Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1999, 476(2), 171—176 |
| [6] | Lopes T., Antolini E., Colmati F., Gonzalez E. R., Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 164(1), 111—114 |
| [7] | Yu P., Pemberton M., Plasse P., Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 144(1), 11—20 |
| [8] | Arbizzani C., Beninati S., Manferrari E., Soavi F., Mastragostino M., Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 161(2), 826—830 |
| [9] | Zha Q.X., Introduction to the Kinetics of Electrode Process, 3rd Ed., Science Press, Beijing, 2002, 137—258 |
| (査全性. 电极过程动力学导论, 第3版, 北京: 科学出版社, 2002, 137—258) | |
| [10] | Liu Y., Ishihara A., Mitsushima S., Kamiya N., Ota K. I., Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2005, 8(8), A400—A402 |
| [11] | Ishihara A., Lee K., Doi S., Mitsushima S., Kamiya N., Hara M., Domen K., Fukuda K., Ota K. I., Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2005, 8(4), A201—A203 |
| [12] | Vante N. A., Tributsch H., Nature, 1986, 323(6087), 431—432 |
| [13] | Wiesener K., Ohms D., Neumann V., Franke R., Mater. Chem. Phys., 1989, 22, 457 |
| [14] | Millán W. M., Thompson T. T., Arriaga L. G., Smit M. A., International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(2), 694—702 |
| [15] | Zhong H., Zhang H., Liu G., Liang Y., Hu J., Yi B., Electrochemistry Communications, 2006, 8(5), 707—712 |
| [16] | Liu G., Zhang H. M., Wang M. R., Zhong H. X., Chen J., Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 172(2), 503—510 |
| [17] | Bashyam R., Zelenay P., Nature, 2006, 443(7107), 63—66 |
| [18] | Zhang L., Xia Z., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(22), 11170—11176 |
| [19] | Geng D. S., Chen Y., Chen Y. G., Li Y. L., Li R. Y., Sun X. L., Ye S. Y., Knights S., Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(3), 760—764 |
| [20] | Liang Y. Y., Li Y. G., Wang H. L., Zhou J. G., Wang J., Regier T., Dai H. J., Nature Materials, 2011, 10(10), 780—786 |
| [21] | Wu Z. S., Yang S., Sun Y., Parvez K., Feng X. L., Mullen K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(22), 9082—9085 |
| [22] | Liu Q., Zhang H., Zhong H., Zhang S. M., Chen S. L., Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 81, 313—320 |
| [23] | Li S., Zhao W., Wang J. T., Qian L., Wang K., Pan M., Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2013, 35(1), 1—6 |
| (李赏, 赵伟, 王家堂, 钱柳, 王坤, 潘牧. 武汉理工大学学报, 2013, 35(1), 1—6) | |
| [24] | Jahnke H., Schonborn M., Zimmermann G., Organic Dyestuffs as Catalysts for Fuel Cells, Physical and Chemical Applications of Dyestuffs, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 1976, 133—181 |
| [25] | Lefèvre M., Dodelet J. P., Bertrand P., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104(47), 11238—11247 |
| [26] | Lefèvre M., Dodelet J. P., Bertrand P., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(34), 8705—8713 |
| [27] | Lefèvre M., Dodelet J. P., Electrochimica Acta, 2003, 48(19), 2749—2760 |
| [1] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [2] | ZHENG Anni, JIN Lei, YANG Jiaqiang, WANG Zhaoyun, LI Weiqing, YANG Fangzu, ZHAN Dongping, TIAN Zhongqun. Effects of 5,5-Dimethylhydantoin on Electroless Copper Plating [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220191. |
| [3] | LIU Shuwei, JIN Hao, YIN Wanzhong, ZHANG Hao. Gemcitabine/polypyrrole Composite Nanoparticles for Chemo-photothermal Combination Ovarian Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220345. |
| [4] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, JIANG Wei, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Activation of Biochar from Cattail and the VOCs Adsorption Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [5] | LI Weihui, LI Haobo, ZENG Cheng, LIANG Haoyue, CHEN Jiajun, LI Junyong, LI Huiqiao. Hot-pressed PVDF-based Difunctional Protective Layer for Lithium Metal Anodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210629. |
| [6] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [7] | YUE Shengli, WU Guangbao, LI Xing, LI Kang, HUANG Gaosheng, TANG Yi, ZHOU Huiqiong. Research Progress of Quasi-two-dimensional Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1648. |
| [8] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, SONG Fujiao, ZHU Ting, HUANG Weiqiu, ZHONG Jing, CHEN Ruoyu. Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption Properties of Hollow Carbon Nanospheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1704. |
| [9] | WANG Kunhua, YAO Jisong, YANG Junnan, SONG Yonghui, LIU Yuying, YAO Hongbin. Synthesis and Device Optimization of Highly Efficient Metal Halide Perovskite Light-emitting Diodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1464. |
| [10] | WANG Jie, LI Ying, SHAO Liang, BAI Yang, MA Zhonglei, MA Jianzhong. Preparation and Properties of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/polypyrrole Composite Conductive Hydrogel Strain Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 929. |
| [11] | LIU Yao, DENG Zhengtao. Fast Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Two-dimensional Tin-halide Perovskites by Anti-solvent Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3774. |
| [12] | ZHANG Ruqiang, ZHANG Guoliang, LONG Zhu, ZHANG Dan, LI Zhiqiang, WANG Shihua, HU Ailin. Preparation and Properties of Light-weight Flexible Polyimide Paper-based Electromagnetic Shielding Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3211. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jun, WANG Bin, PAN Li, MA Zhe, LI Yuesheng. Synthesis and Properties of Imidazolium-based Polyethylene Ionomer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2070. |
| [14] | WANG Tingting, LEI Yuhan, LIN Yujuan, HUANG Jialing, LIU Cuie, ZHENG Fengying, LI Shunxing. Preparation of Liposome-terminated CsPbX3(X=Cl,Br,I) Nanocrystals and Applications in Light-emitting Diode Devices [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1896. |
| [15] | WU Chunxiao, AI Xin, CHEN Yingxin, CUI Zhiyuan, LI Feng. Effects of Introducing Halogen Atoms to Biphenylmethyl Radical on Photostability, Photophysical and Electroluminescent Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 972. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||