

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 821.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150015
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Meiling1,2, QIN Dongdong1, SONG Yumin1,*( )
)
Received:2015-01-07
Online:2015-05-10
Published:2015-04-20
Contact:
SONG Yumin
E-mail:songym@nwnu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Meiling, QIN Dongdong, SONG Yumin. Syntheses and Anticoagulant Action of Rare Earth Ternary omplexes with Warfarin and Ferulic Acid†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 821.
| Complex | Found(Calcd.)(%) | Λ/(S·cm2·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | RE | ||
| FA-W-La | 49.96(49.66) | 5.30(5.10) | 14.93(14.15) | 29.3 |
| FA-W-Ce | 46.88(46.43) | 5.53(5.02) | 15.68(14.23) | 27.4 |
| FA-W-Nd | 46.01(46.44) | 5.75(5.03) | 16.04(14.58) | 19.6 |
| FA-W-Eu | 49.20(49.43) | 4.11(4.53) | 17.36(15.27) | 18.4 |
Table 1 Elemental analysis and molar conductivity of the complexes
| Complex | Found(Calcd.)(%) | Λ/(S·cm2·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | RE | ||
| FA-W-La | 49.96(49.66) | 5.30(5.10) | 14.93(14.15) | 29.3 |
| FA-W-Ce | 46.88(46.43) | 5.53(5.02) | 15.68(14.23) | 27.4 |
| FA-W-Nd | 46.01(46.44) | 5.75(5.03) | 16.04(14.58) | 19.6 |
| FA-W-Eu | 49.20(49.43) | 4.11(4.53) | 17.36(15.27) | 18.4 |
| Parameter | W-FA-La | W-FA-Nd | W-FA-Ce | W-FA-Eu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | 0.9624 | 0.9790 | 0.9644 | 0.9819 |
| b1/2 | 0.1371 | 0.1025 | 0.1334 | 0.0951 |
| δ | 3.9 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 1.8 |
Table 2 Caculated values of various covalency parameters of the complexes
| Parameter | W-FA-La | W-FA-Nd | W-FA-Ce | W-FA-Eu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | 0.9624 | 0.9790 | 0.9644 | 0.9819 |
| b1/2 | 0.1371 | 0.1025 | 0.1334 | 0.0951 |
| δ | 3.9 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 1.8 |
| Compound | Concentration/(mol·L-1) | CT/min | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 4 | <0.05 |
| FA | 2.0×10-4 | 6 | <0.05 |
| W | 2.0×10-4 | 7 | <0.05 |
| W-Laa | 2.5×10-4 | 11.0 | <0.05 |
| W-Nda | 2.5×10-4 | 13.0 | <0.05 |
| W-Eua | 2.5×10-4 | 9.5 | <0.05 |
| W-Ya | 2.5×10-4 | 8.8 | <0.05 |
| FA-Ndb | 2.5×10-4 | 13.4 | <0.05 |
| FA-Ceb | 2.5×10-4 | 11.3 | <0.05 |
| FA-Eub | 2.5×10-4 | 11.9 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-La | 2.0×10-4 | 25 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-4 | 44 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-4 | 40 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-4 | 42 | <0.05 |
Table 3 Coagulation time of the ligands and complexes
| Compound | Concentration/(mol·L-1) | CT/min | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 4 | <0.05 |
| FA | 2.0×10-4 | 6 | <0.05 |
| W | 2.0×10-4 | 7 | <0.05 |
| W-Laa | 2.5×10-4 | 11.0 | <0.05 |
| W-Nda | 2.5×10-4 | 13.0 | <0.05 |
| W-Eua | 2.5×10-4 | 9.5 | <0.05 |
| W-Ya | 2.5×10-4 | 8.8 | <0.05 |
| FA-Ndb | 2.5×10-4 | 13.4 | <0.05 |
| FA-Ceb | 2.5×10-4 | 11.3 | <0.05 |
| FA-Eub | 2.5×10-4 | 11.9 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-La | 2.0×10-4 | 25 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-4 | 44 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-4 | 40 | <0.05 |
| W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-4 | 42 | <0.05 |
| Compound | Concentration/(mol·L-1) | CT/min | P | Compound | Concentration/(mol·L-1) | CT/min | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 2.0×10-5 | 4 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-5 | 31 | <0.05 |
| 2.0×10-4 | 6 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 40 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-3 | 7 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-3 | 45 | <0.05 | ||
| W | 2.0×10-5 | 6 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-5 | 42 | <0.05 |
| 2.0×10-4 | 7 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 44 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-3 | 10 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-3 | 50 | <0.05 | ||
| W-FA-La | 2.0×10-5 | 20 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-5 | 26 | <0.05 |
| 2.0×10-4 | 25 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 42 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-3 | 29 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-3 | 50 | <0.05 |
Table 4 Coagulation time of the ligands and complexes
| Compound | Concentration/(mol·L-1) | CT/min | P | Compound | Concentration/(mol·L-1) | CT/min | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 2.0×10-5 | 4 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-5 | 31 | <0.05 |
| 2.0×10-4 | 6 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 40 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-3 | 7 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-3 | 45 | <0.05 | ||
| W | 2.0×10-5 | 6 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-5 | 42 | <0.05 |
| 2.0×10-4 | 7 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 44 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-3 | 10 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-3 | 50 | <0.05 | ||
| W-FA-La | 2.0×10-5 | 20 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-5 | 26 | <0.05 |
| 2.0×10-4 | 25 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 42 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-3 | 29 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-3 | 50 | <0.05 |
| Compound | RT/min | P | Compound | RT/min | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 2 | <0.05 | FA-Ndb | 11 | <0.05 |
| FA | 4 | <0.05 | FA-Ceb | 10 | <0.05 |
| W | 5 | <0.05 | FA-Eub | 9 | <0.05 |
| W-Laa | 7 | <0.05 | W-FA-La | 10 | <0.05 |
| W-Nda | 10 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 19 | <0.05 |
| W-Eua | 9 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 18 | <0.05 |
| W-Ya | 6 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 15 | <0.05 |
Table 5 Recalcification time of the ligands and complexes
| Compound | RT/min | P | Compound | RT/min | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 2 | <0.05 | FA-Ndb | 11 | <0.05 |
| FA | 4 | <0.05 | FA-Ceb | 10 | <0.05 |
| W | 5 | <0.05 | FA-Eub | 9 | <0.05 |
| W-Laa | 7 | <0.05 | W-FA-La | 10 | <0.05 |
| W-Nda | 10 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 19 | <0.05 |
| W-Eua | 9 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 18 | <0.05 |
| W-Ya | 6 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 15 | <0.05 |
| Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P | Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 27.50 | 12.40 | <0.05 | W-Eub | 2.0×10-4 | 38.20 | 13.10 | <0.05 |
| FA | 2.0×10-4 | 34.00 | 13.00 | <0.05 | W-Yb | 2.0×10-4 | 37.30 | 13.10 | <0.05 |
| W | 2.0×10-4 | 32.70 | 12.30 | <0.05 | W-FA-La | 2.0×10-4 | 45.50 | 13.60 | <0.05 |
| FA-Nda | 2.0×10-4 | 44.20 | 13.40 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-4 | 48.50 | 14.00 | <0.05 |
| FA-Cea | 2.0×10-4 | 42.20 | 13.10 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-4 | 43.60 | 12.70 | <0.05 |
| FA-Eua | 2.0×10-4 | 43.30 | 13.40 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-4 | 48.20 | 13.90 | <0.05 |
| W-Lab | 2.0×10-4 | 36.70 | 12.50 | <0.05 | Reference | 25—37 | 10—13 | <0.05 | |
| W-Ndb | 2.0×10-4 | 39.50 | 13.30 | <0.05 | valuec |
Table 6 Coagulant activity of the ligands and complexes
| Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P | Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 27.50 | 12.40 | <0.05 | W-Eub | 2.0×10-4 | 38.20 | 13.10 | <0.05 |
| FA | 2.0×10-4 | 34.00 | 13.00 | <0.05 | W-Yb | 2.0×10-4 | 37.30 | 13.10 | <0.05 |
| W | 2.0×10-4 | 32.70 | 12.30 | <0.05 | W-FA-La | 2.0×10-4 | 45.50 | 13.60 | <0.05 |
| FA-Nda | 2.0×10-4 | 44.20 | 13.40 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-4 | 48.50 | 14.00 | <0.05 |
| FA-Cea | 2.0×10-4 | 42.20 | 13.10 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-4 | 43.60 | 12.70 | <0.05 |
| FA-Eua | 2.0×10-4 | 43.30 | 13.40 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-4 | 48.20 | 13.90 | <0.05 |
| W-Lab | 2.0×10-4 | 36.70 | 12.50 | <0.05 | Reference | 25—37 | 10—13 | <0.05 | |
| W-Ndb | 2.0×10-4 | 39.50 | 13.30 | <0.05 | valuec |
| Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P | Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 27.50 | 12.40 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-3 | 48.90 | 14.10 | <0.05 |
| FA | 2.0×10-3 | 34.20 | 13.10 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 48.50 | 14.00 | <0.05 | |
| 2.0×10-4 | 34.00 | 13.00 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-5 | 39.90 | 13.20 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-5 | 33.60 | 12.70 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-3 | 43.80 | 12.80 | <0.05 | |
| W | 2.0×10-3 | 32.80 | 12.50 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 43.60 | 12.70 | <0.05 | |
| 2.0×10-4 | 32.70 | 12.30 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-5 | 40.00 | 12.00 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-5 | 32.10 | 11.90 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-3 | 48.50 | 13.90 | <0.05 | |
| W-FA-La | 2.0×10-3 | 45.80 | 13.70 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 48.20 | 13.80 | <0.05 | |
| 2.0×10-4 | 45.50 | 13.60 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-5 | 47.80 | 13.10 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-5 | 0.25 | 45.00 | 13.10 | <0.05 |
Table 7 Coagulant activity of the ligands and complexes with different concentrations
| Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P | Compound | c/(mol·L-1) | APTT/s | PT/s | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 27.50 | 12.40 | <0.05 | W-FA-Nd | 2.0×10-3 | 48.90 | 14.10 | <0.05 |
| FA | 2.0×10-3 | 34.20 | 13.10 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 48.50 | 14.00 | <0.05 | |
| 2.0×10-4 | 34.00 | 13.00 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-5 | 39.90 | 13.20 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-5 | 33.60 | 12.70 | <0.05 | W-FA-Ce | 2.0×10-3 | 43.80 | 12.80 | <0.05 | |
| W | 2.0×10-3 | 32.80 | 12.50 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 43.60 | 12.70 | <0.05 | |
| 2.0×10-4 | 32.70 | 12.30 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-5 | 40.00 | 12.00 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-5 | 32.10 | 11.90 | <0.05 | W-FA-Eu | 2.0×10-3 | 48.50 | 13.90 | <0.05 | |
| W-FA-La | 2.0×10-3 | 45.80 | 13.70 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-4 | 48.20 | 13.80 | <0.05 | |
| 2.0×10-4 | 45.50 | 13.60 | <0.05 | 2.0×10-5 | 47.80 | 13.10 | <0.05 | ||
| 2.0×10-5 | 0.25 | 45.00 | 13.10 | <0.05 |
| Compound | IC50/(mol·L-1) | Compound | IC50/(mol·L-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | A549 | HeLa | HepG2 | A549 | HeLa | ||
| W | La(NO3)3 | ||||||
| FA | W-FA-La | 10-5 | ≥10-5 | ≥10-5 | |||
| Nd(NO3)3 | 10-3 | Ce(NO3)3 | |||||
| W-FA-Nd | ≥10-4 | 10-4 | ≥10-4 | W-FA-Ce | 10-4 | 10-5 | 10-5 |
| Eu(NO3)3 | cis-PtCl2(NH3)2 | ||||||
| W-FA-Eu | ≥10-4 | ≥10-5 | ≥10-5 | ||||
Table 8 IC50 values of the ligands and complexes on different tumor cells
| Compound | IC50/(mol·L-1) | Compound | IC50/(mol·L-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | A549 | HeLa | HepG2 | A549 | HeLa | ||
| W | La(NO3)3 | ||||||
| FA | W-FA-La | 10-5 | ≥10-5 | ≥10-5 | |||
| Nd(NO3)3 | 10-3 | Ce(NO3)3 | |||||
| W-FA-Nd | ≥10-4 | 10-4 | ≥10-4 | W-FA-Ce | 10-4 | 10-5 | 10-5 |
| Eu(NO3)3 | cis-PtCl2(NH3)2 | ||||||
| W-FA-Eu | ≥10-4 | ≥10-5 | ≥10-5 | ||||
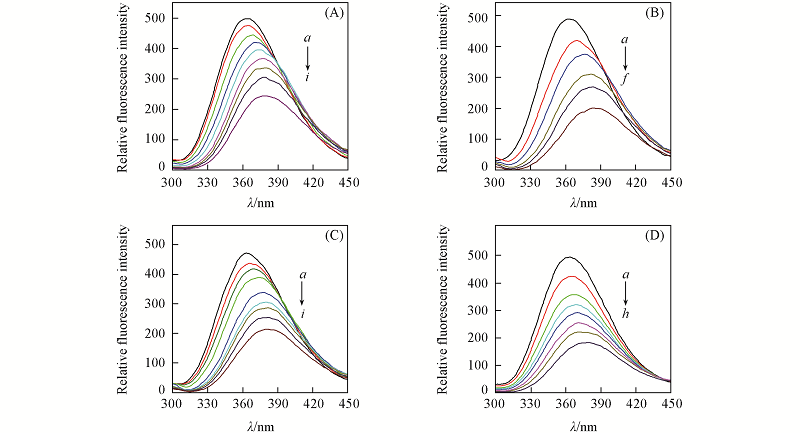
Fig.6 Fluorescence spectra of HSA with W-FA-La(A), W-FA-Ce(B), W-FA-Nd(C) and -FA-Eu(D) cHSA=1.0×10-5 mol/L, ccomplex/(μmol·L-1) from a to i: 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160.
| [1] | Guo H. X., Liang C. H., Progress in Biomedical Engineering,2011, 22(3), 44—47 |
| (郭海霞, 梁成浩. 上海生物医学工程, 2011, 22(3), 44—47) | |
| [2] | Xiang Z. B., Huo D. Q., Hou C. J., J. Mol.Diagn. Therapy,2002, 14(4), 25—29 |
| (项昭保, 霍丹群, 侯长军. 现代医学仪器与应用, 2002, 14(4), 25—29) | |
| [3] | Zhu Y. C., Yao K. L., Li Y., Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 2005, 41(6), 61—65 |
| (朱元成, 姚卡玲, 李英. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 41(6), 61—65) | |
| [4] | Song Y. M., Dong Y. L., Fu Y. L., Acta Chim. Sinica,2007, 65(8), 678—682 |
| (宋玉民, 董银龙, 付云龙, 化学学报, 2007, 65(8), 678—682) | |
| [5] | Wang K. J., Luan N. N., SongY. M., Acta Chim. Sinica,2009, 67(10), 1042—1046 |
| (王坤杰, 栾尼娜, 宋玉民. 化学学报, 2009, 67(10), 1042—1046) | |
| [6] | Wang K. J., Song Y. M., Biopolymers,2010, 93(10), 887—892 |
| [7] | Gao Q. K., Wang K. J., Wang C. X., Acta Chim. Sinica,2012, 70(2), 207—211 |
| (高琦宽, 王坤杰, 王喜存. 化学学报, 2012, 70(2), 207—211) | |
| [8] | Eitsuka T., Tatewaki N., Nishida H., Kurata T., Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun., 2014, 453(3), 606—611 |
| [9] | Woranuch S., Yoksan R., Carbohyd. Poly., 2013, 96(2), 495—502 |
| [10] | Dong Q. R., Bian R. Y., Qu Y., Fang Y. S., J. Tianjin Med., 2011, 39(10), 965—96 |
| (董巧荣, 边如玉, 曲媛, 冯云生. 天津医药, 2011, 39(10), 965—966) | |
| [11] | Wang H. J., Li W. J., Da F. L., Wang J. Y., J. Phys. Chem. B,2008, 112, 2671—2677 |
| [12] | Wang X. D., Jin L. M., Sun Z., Li D. N., Liu T. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2013, 29(4), 721—723 |
| [13] | Wang P. Y., Bian C. X., Song Y. M., J. Chin. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28(8), 1609—1616 |
| (王璞玉, 卞常鑫, 宋玉民. 无机化学学报, 2012, 28(8), 1609—1616) | |
| [14] | Sindhu M., Emilia A. T., Food Hydrocolloids,2008, 22, 826—835 |
| [15] | Zhou C. R., An N., Shi X. H., Wang H. F., J. Zhengzhou University,2007, 28(2), 47—48 |
| (周彩荣, 安娜, 石晓华, 王海峰. 郑州大学学报, 2007, 28(2), 47—48) | |
| [16] | Yu X. J., Wu R. H., Song H. Y., Su Q. D., J. Analy. Sci., 2003, 19(2), 101—104 |
| (于锡娟, 伍荣护, 宋慧宇, 苏庆德. 分析科学学报, 2003, 19(2), 101—104) | |
| [17] | Mogren M., Al-Farhan K., Hasanein A. A., J. Saudi.Chem. Soc., 2013, 17(1), 87—95 |
| [18] | Song Y. M., Bian C. X., Wang P. Y., Chem. & Bioeng., 2011, 28(12), 32—34 |
| (宋玉民, 卞常鑫, 王璞玉. 化学与生物工程, 2011, 28(12), 32—34) | |
| [19] | Fan X.L., Physiology, People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, 2002, 54—60 |
| (樊小力. 生理学, 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2002, 54—60) | |
| [20] | Zhou H.H., Pharmacology, Science Press, Beijing, 2007, 37, 318—320 |
| (周宏灏. 药理学, 北京:科学出版社, 2007, 37, 318—320) | |
| [21] | Inorganic Chemisty Teaching Group of Beijing Normal University, Huazhong Normal University and Nanjing Normal University, Inorganic Chemistry, Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2003, 648, 816 |
| (北京师范大学、 华中师范大学、 南京师范大学无机化学教研室. 无机化学, 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003, 648; 816) | |
| [22] | Chen Y., Xu C., Su J. C., J. Chin. Inorg. Chem., 2011, 27(4), 625—630 |
| (陈于, 徐灿, 苏佳灿. 无机化学学报, 2011, 27(4), 625—630) | |
| [23] | Song Y. M., Liu Z., Wang K. J., Acta Chim. Sinica,2010, 68(21), 2191—2198 |
| (宋玉民, 刘哲, 王坤杰. 化学学报, 2010, 68(21), 2191—2198) | |
| [24] | Zhao F., Huang C. F., Liang H., J.Chin. Anal. Chem., 2006, 39(3), 401—404 |
| (赵芳, 黄超峰, 梁慧. 分析化学, 2006, 39(3), 401—404) | |
| [25] | Kong D. L., Wei B., Zhou S. Y., Yang H. S., Jiang Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2013, 29(6), 1055—1058 |
| [26] | Yang S. P., Han L. J., Pang Y., Wang D. Q., Wang N. N., Wang T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(2), 364—374 |
| (杨树平, 韩立军, 潘燕, 王大奇, 王南南, 王婷. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(2), 364—374) | |
| [27] | Huang Y., Wang J., Guo G. Y., Tao Z., Xue S. F., Zhu Q. J., Zhou Q. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(2), 375—380 |
| (黄英, 王娟, 郭改英, 陶朱, 薛赛凤, 祝黔江, 周清娣. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(2), 375—380) | |
| [28] | Zhang G. W., Wang L., Pan J. H., J.Agri.Food Chem., 2012, 60, 2721—2729 |
| [1] | LU Cong, LI Zhenhua, LIU Jinlu, HUA Jia, LI Guanghua, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescence Detection Properties of a New Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220037. |
| [2] | ZHOU Yonghui, LI Yao, WU Yuxuan, TIAN Jing, XU Longquan, FEI Xu. Synthesis of A Novel Photoluminescence Self-healing Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210606. |
| [3] | HAN Zongsu, YU Xiaoyong, MIN Hui, SHI Wei, CHENG Peng. A Rare Earth Metal-Organic Framework with H6TTAB Ligand [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210342. |
| [4] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| [5] | ZHANG Aiqin, WANG Man, SHEN Gangyi, JIN Jun. Interactions Between Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Using SPR and Molecular Docking [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2054. |
| [6] | LIANG Longqi, CHEN Cailing, YU Ying, LI Yuxin, LI Chunguang, SHI Zhan. Synthesis, Luminescence and Cell Imaging Properties of Amino Acid Capped YVO4∶Eu Nanoparticles † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 425. |
| [7] | RAN Shiya,SHEN Haifeng,LI Xiaonan,WANG Zilu,GUO Zhenghong,FANG Zhengping. Effect and Mechanism of Rare Earth Trifluoromethanesulfonate on the Thermal Stability of Polypropylene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1333. |
| [8] | LI Bing,WANG Xuemin,BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing. Synthesises, Structures and Antibacterial Activities of a Series of Rare Earth Nitrogen Heterocyclic Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 632. |
| [9] | LIANG Donglei, SONG Qiusheng, YAO Yutian, LIU Ben. Preparation of Complex Nanogel with Up-conversion Fluorescence-responsive Performance and Its Fluorescence Energy Transfer Behavior† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 583. |
| [10] |
ZHANG Yan, ZHANG Shengming, FANG Guizhen.
Antioxidant Property of Catalyzed Lignosulfonate Using S2 |
| [11] | TANG Keyun,LI Luoyuan,FU Limin,AI Xicheng,ZHANG Jianping. Effect of Crystal Matrix on Energy Transfer Mechanism in Rare-earth Upconversion Nanomaterials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2136. |
| [12] | CHEN Chen, LI Li, CHEN Jinhua, ZHANG Xiaohua, XU Jie, LI Yibo, WEI Jie. Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance for Methanol Oxidation of Pt-CeO2/Sodium-4-styrenesulfonate Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 157. |
| [13] | GUO Zhenghong, FANG Zhengping, CHEN Chao. Synergistic Flame Retardant and Suppression Smoke Mechanism of Cerium Phenylphosphonate and Decabromodiphenyl Oxide in Glass-fiber Reinforced Poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate) Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 284. |
| [14] | TANG Qian, SU Jinhong, CAO Hongyu, WANG Lihao, SHI Fei, WANG Ailing, GONG Tingting, JIN Xiaojun, ZHENG Xuefang. Interaction of Pyrimidine Derivatives with Human Serum Albumin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1982. |
| [15] | WANG Xiaoqing, LING Jun, SHEN Zhiquan. Synthesis and Self-assembly of Thermoplastic Elastomer Poly(ε-decalactone)-Poly(L-lactide)-PEG with Rare Earth Catalyst† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1182. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||