

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 838.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20141097
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Guangyao1, ZHANG Jiawei1, LI Aiwu1,*( ), LIU Lianqing2, YANG Hai3, WANG Jiping4,*(
), LIU Lianqing2, YANG Hai3, WANG Jiping4,*( )
)
Received:2014-12-15
Online:2015-05-10
Published:2015-04-17
Contact:
LI Aiwu,WANG Jiping
E-mail:liaiwud115@163.com;wangjiping2014@21cn.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WEI Guangyao, ZHANG Jiawei, LI Aiwu, LIU Lianqing, YANG Hai, WANG Jiping. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Ferroferric Oxide-Mesoporous Silica Janus Nanoparticles†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 838.
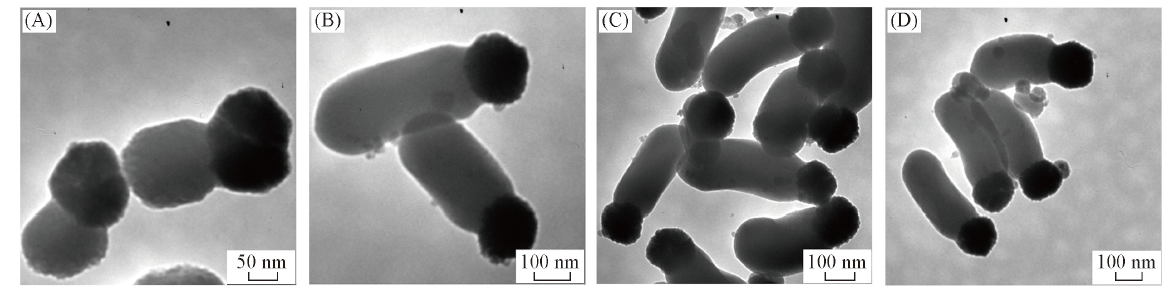
Fig.4 TEM images of Fe3O4-SiO2 Janus particles in particular lengths of 200 nm(A), 300 nm(B),400 nm(C) and 400 nm(D) V(TEOS)/μL: (A) 10; (B) 20; (C) 30; (D) 40.
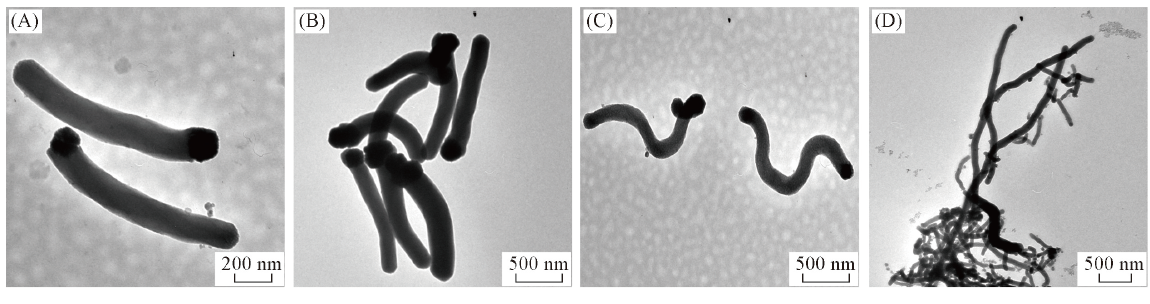
Fig.5 TEM images of Fe3O4-SiO2 Janus particles in particular length of 1 μm(A), 1.5 μm(B) and 2 μm(C) via a secondary growth method and of 4 μm(D) via a muti-growth methodV(TEOS)/μL: (A) 10; (B) 20; (C) 30.
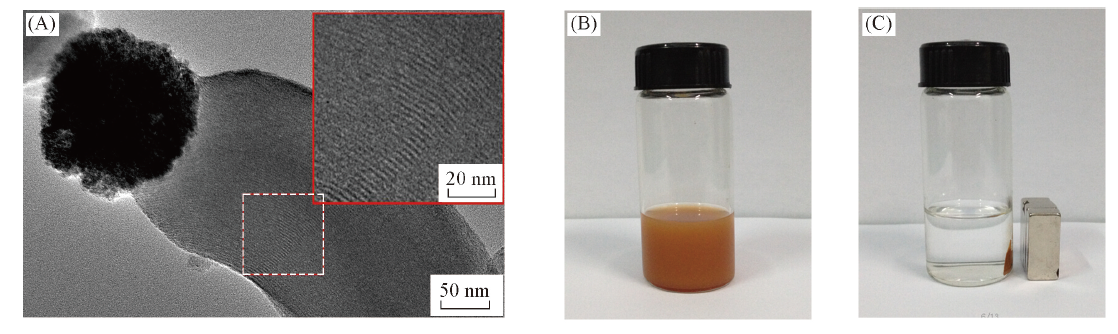
Fig.6 HRTEM images of Fe3O4-SiO2 mesoporous Janus nanoparticles with enlarged view of selected area(A and the inset) and pictures of Fe3O4-SiO2 mesoporous Janus nanoparticles without(B) and with(C) magnetic field for 2 min
| [1] | 苏鹏飞, 赵珺, 陈国. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32( 7), 1472- 1477 |
| Su P., F. , Zhao, J. , Chen, G. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32( 7), 1472- 1477 | |
| [2] | 王岩, 王笑英, 吕言云, 许文斌, 郭轶, 徐立. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34( 12), 2866- 2870 |
| Wang, Y. , Wang X., Y. , Lü, Y. Y. , Xu W., B. , Guo, Y. , Xu, L. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34( 12), 2866- 2870 | |
| [3] | 陈明洁, 熊小敏, 沈辉, 刘海峰. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34( 8), 1801- 1805 |
| Chen M., J. , Xiong X., M. , Shen, H. , Liu H., F. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34( 8), 1801- 1805 | |
| [4] | Mura, S. , Nicolas, J. , Couvreur, P. , Nat. Mater., 2013, 12( 11), 991- 1003 |
| [5] | Zhang, L. , Dong W., F. , Tang Z., Y. , Song J., F. , Xia, H. , Sun H., B. , Opt. Lett., 2010, 35( 19), 3297- 3299 |
| [6] | Chen., W. , Pan X., L. , Bao X., H. , J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129( 23), 7421- 7426 |
| [7] | Wang, J. , Black K. C., L. , Luehmann, H. , Li, W. , Zhang, Y. , Cai, X. , Wan, D. , Liu S., Y. , Li, M. , Kim, P. , Li Z., Y. , Wang L., V. , Liu, Y. , Xia, Y. , ACS Nano, 2013, 7( 3), 2068- 2077 |
| [8] | 洪友良, 商铁存, 靳玉伟, 杨帆, 王策. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26( 5), 985- 987 |
| Hong Y., L. , Shang T., C. , Jin Y., W. , Yang, F. , Wang, C. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26( 5), 985- 987 | |
| [9] | Zhang L., Y. , Wang T., T. , Yang, L. , Liu, C. , Wang C., G. , Liu H., Y. , Wang Y., A. , Su Z., M. , Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18( 39), 12512- 12521 |
| [10] | Chen, Y. , Chen H., R. , Zhang S., J. , Chen, F. , Zhang L., X. , Zhang J., M. , Zhu, M. , Wu H., X. , Guo L., M. , Feng J., W. , Shi J., L. , Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, 21( 2), 270- 278 |
| [11] | Zhang, E. , Kircher M., F. , Koch, M. , Eliasson, L. , Goldberg S., N. , ACS Nano, 2014, 8( 4), 3192- 3201 |
| [12] | Wang, C. , Xu C., J. , Zeng, H. , Sun S., H. , Adv. Mater., 2009, 21( 30), 3045- 3052 |
| [13] | Jiang, S. , Chen, Q. , Tripathy, M. , Luijten, E. , Schweizer K., S. , Adv. Mater., 2010, 22( 10), 1060- 1071 |
| [14] | Lattuada, M. , Hatton T., A. , Nano Today, 2011, 6( 3), 286- 308 |
| [15] | Zhang Y., L. , Chen Q., D. , Xia, H. , Sun H., B. , Nano Today, 2010, 5( 5), 435- 448 |
| [16] | Girshovitz, P. , Shaked N., T. , Light-Science & Applications, 2014, 3, e151 |
| [17] | Gao B., R. , Wang H., Y. , Hao Y., W. , Fu L., M. , Fang H., H. , Jiang, Y. , Wang, L. , Chen Q., D. , Xia, H. , Pan L., Y. , Ma Y., G. , Sun H., B. , J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114( 1), 128- 134 |
| [18] | Feng, J. , Li, F. , Gao W., B. , Liu S., Y. , Liu, Y. , Wang, Y. , Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 78( 25), 3947- 3949 |
| [19] | Su Y., H. , Ke Y., F. , Cai S., L. , Yao Q., Y. , Light-Science & Applications, 2012, 1, e14 |
| [20] | Zhang Y., L. , Guo, L. , Wei, S. , He Y., Y. , Xia, H. , Chen Q., D. , Sun H., B. , Nano Today, 2010, 5( 1), 15- 20 |
| [21] | Xia, H. , Wang, J. , Tian, Y. , Chen Q., D. , Du X., B. , Zhang Y., L. , He, Y. , Sun H., B. , Adv. Mater., 2010, 22( 29), 3204- 3207 |
| [22] | Guo, L. , Jiang H., B. , Shao R., Q. , Zhang Y., L. , Xie S., Y. , Wang J., N. , Li X., B. , Jiang, F. , Chen Q., D. , Zhang, T. , Sun H., B. , Carbon, 2012, 50( 4), 1667- 1673 |
| [23] | Yang, R. , Yu Y., S. , Xue, Y. , Chen, C. , Chen Q., D. , Sun H., B. , Opt. Lett., 2011, 36( 23), 4482- 4484 |
| [24] | Wu, D. , Wu S., Z. , Chen Q., D. , Zhang Y., L. , Yao, J. , Yao, X. , Niu L., G. , Wang J., N. , Jiang, L. , Sun H., B. , Adv. Mater., 2011, 23( 4), 545- 549 |
| [25] | Zhang, L. , Wang Y., S. , Yang, Y. , Zhang, F. , Dong W., F. , Zhou S., Y. , Pei W., H. , Chen H., D. , Sun H., B. , Chem. Commun., 2012, 48( 91), 11238- 11240 |
| [26] | Huang X., L. , Teng, X. , Chen, D. , Tang F., Q. , He J., Q. , Biomaterials, 2010, 31( 3), 438- 448 |
| [27] | Deng Y., H. , Qi D., W. , Deng C., H. , Zhang X., M. , Zhao D., Y. , J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130( 1), 28- 29 |
| [1] | HE Beibei, YANG Kuihua, LYU Rui. Construction of Mn-Cu Bimetal Containing Phyllosilicate Nanozyme and Evaluation of the Enzyme-like Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220150. |
| [2] | YAN Zhixuan, MA Ji, QU Jinlei, LIU Li, SUN Chong, LIU Jiwen, LIU Guangye, SUN Lishui, HE Lixia. Synthesis and Application of Modified Low Molecular Weight Polyisoprene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220066. |
| [3] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jie, YIN Bo, LIU Weixin, LIU Xingping, LIAN Wenxian, TANG Shaokun. Fabrication of Boehmite Fiber-reinforced Silica Aerogels and Their Performances [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220483. |
| [5] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [6] | WANG Yuxiang, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LYU Jiamin, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. One-step Synthesis of Amorphous Silica Aluminum Support Materials with Controllable Acidity and Porosity and Catalytic Performance of Their Pd-based Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1826. |
| [7] | HAN Yandong, HAN Mingyong, YANG Wensheng. Sol-gel Construction of Mesoporous Silica Nanomicrostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 965. |
| [8] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [9] | SONG Wenyao, ZHOU Zhanglang, YANG Xinli, CHEN Lan, GE Guanglu. Tunable Enantioselective Adsorption of the As⁃synthesized Mesoporous Silica Through Chiral Imprinting [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3144. |
| [10] | WANG Mingxia, LIU Zhihui, ZHU Zhen, LI Lingfeng, WANG Bowei. Preparation and Properties of Nano Lithium Magnesium Silicate-chitosan-sodium Alginate Composite Scaffold Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3240. |
| [11] | WANG Juan, WANG Linying, ZHU Dali, CUI Wenhao, WANG Yifeng, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongmin. Progress in Direct Synthesis of High Silica Zeolite Y [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 1. |
| [12] | WANG Jianyu, ZHANG Qiang, YAN Wenfu, YU Jihong. Roles of Hydroxyl Radicals in Zeolite Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 11. |
| [13] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [14] | JIAO Meichen, JIANG Jingang, XU Hao, WU Peng. Structural Stabilization, Modification and Catalytic Applications of Germanosilicates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 29. |
| [15] | WANG Huan, SUO Jinquan, WANG Chunyan, WANG Runwei. Glucose Oxidase Immobilization with Amino Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Its Application in Glucose Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1731. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||