

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (12): 2706.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140722
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Min1,*( ), JING Jingjing1, LI Chengtao1, WANG Hui1, MA Xiaoyan2
), JING Jingjing1, LI Chengtao1, WANG Hui1, MA Xiaoyan2
Received:2014-08-01
Online:2014-12-10
Published:2014-10-14
Contact:
ZHANG Min
E-mail:yanjiushi206@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Min, JING Jingjing, LI Chengtao, WANG Hui, MA Xiaoyan. Performance of PBS-based Copolymer Containing Different Ether Bond and Its Enzymatic Degradation by Molecular Simulation†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(12): 2706.
| Polymer | n(BS):n(TDGS) | PDIb | Polymer | n(BS):n(DEGS) | PDIb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 100:0 | 0 | 71200 | 2.05 | PBS-DEGS5 | 95:5 | 4.64 | 64800 | 1.71 |
| PBS-TDGS5 | 95:5 | 5.70 | 69300 | 1.98 | PBS-DEGS10 | 90:10 | 11.55 | 68700 | 1.82 |
| PBS-TDGS10 | 90:10 | 10.50 | 65200 | 1.93 | PBS-DEGS15 | 85:15 | 14.32 | 70400 | 1.67 |
| PBS-TDGS15 | 85:15 | 15.45 | 69200 | 1.78 | PBS-DEGS20 | 80:20 | 19.34 | 73200 | 1.85 |
| PBS-TDGS20 | 80:20 | 21.32 | 64300 | 2.09 |
Table 1 Composition and relative molecular weight of copolymers
| Polymer | n(BS):n(TDGS) | PDIb | Polymer | n(BS):n(DEGS) | PDIb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 100:0 | 0 | 71200 | 2.05 | PBS-DEGS5 | 95:5 | 4.64 | 64800 | 1.71 |
| PBS-TDGS5 | 95:5 | 5.70 | 69300 | 1.98 | PBS-DEGS10 | 90:10 | 11.55 | 68700 | 1.82 |
| PBS-TDGS10 | 90:10 | 10.50 | 65200 | 1.93 | PBS-DEGS15 | 85:15 | 14.32 | 70400 | 1.67 |
| PBS-TDGS15 | 85:15 | 15.45 | 69200 | 1.78 | PBS-DEGS20 | 80:20 | 19.34 | 73200 | 1.85 |
| PBS-TDGS20 | 80:20 | 21.32 | 64300 | 2.09 |
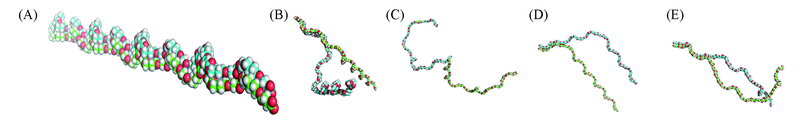
Fig.4 Molecular structures of copolymers(carbon atoms of two chains in blue and green) (A) PBS; (B) PBS-TDGS10; (C) PBS-TDGS20; (D) PBS-DEGS10; (E) PBS-DEGS20.
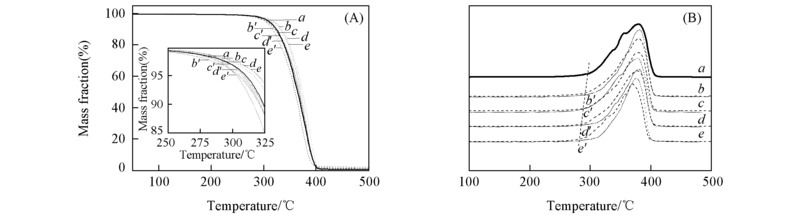
Fig.5 TGA(A) and DTG(B) curves of copolymers a. PBS; b. PBS-DEGS5; c. PBS-DEGS10; d. PBS-DEGS15; e. PBS-DEGS20;b'. PBS-TDGS5; c'. PBS-TDGS10; d'. PBS-TDGS15; e'. PBS-TDGS20.
| Sample | Td,5%/℃ | Tmax/℃ | Tm/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | Tc/℃ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | WXRD | ||||||
| PBS | 310.41 | 310.41 | 112.00 | 70.20 | 62.68 | 59.34 | 77.90 |
| PBS-TDGS5 | 304.62 | 380.32 | 110.77 | 79.86 | 58.30 | 54.29 | 73.90 |
| PBS-TDGS10 | 309.08 | 378.89 | 105.96 | 67.23 | 51.03 | 48.25 | 66.98 |
| PBS-TDGS15 | 307.85 | 376.98 | 100.48 | 45.45 | 40.58 | 43.34 | 62.17 |
| PBS-TDGS20 | 303.17 | 369.80 | 98.57 | 37.70 | 33.66 | 38.14 | 58.88 |
| PBS-DEGS5 | 316.11 | 381.28 | 111.05 | 58.09 | 51.87 | 54.39 | 75.35 |
| PBS-DEGS10 | 305.97 | 378.41 | 104.33 | 47.61 | 42.51 | 43.54 | 67.85 |
| PBS-DEGS15 | 320.16 | 380.32 | 103.33 | 50.32 | 44.90 | 46.72 | 64.53 |
| PBS-DEGS20 | 319.64 | 376.88 | 96.69 | 40.54 | 36.60 | 45.12 | 56.34 |
Table 2 Thermal properties of the synthesized copolymers
| Sample | Td,5%/℃ | Tmax/℃ | Tm/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | Tc/℃ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | WXRD | ||||||
| PBS | 310.41 | 310.41 | 112.00 | 70.20 | 62.68 | 59.34 | 77.90 |
| PBS-TDGS5 | 304.62 | 380.32 | 110.77 | 79.86 | 58.30 | 54.29 | 73.90 |
| PBS-TDGS10 | 309.08 | 378.89 | 105.96 | 67.23 | 51.03 | 48.25 | 66.98 |
| PBS-TDGS15 | 307.85 | 376.98 | 100.48 | 45.45 | 40.58 | 43.34 | 62.17 |
| PBS-TDGS20 | 303.17 | 369.80 | 98.57 | 37.70 | 33.66 | 38.14 | 58.88 |
| PBS-DEGS5 | 316.11 | 381.28 | 111.05 | 58.09 | 51.87 | 54.39 | 75.35 |
| PBS-DEGS10 | 305.97 | 378.41 | 104.33 | 47.61 | 42.51 | 43.54 | 67.85 |
| PBS-DEGS15 | 320.16 | 380.32 | 103.33 | 50.32 | 44.90 | 46.72 | 64.53 |
| PBS-DEGS20 | 319.64 | 376.88 | 96.69 | 40.54 | 36.60 | 45.12 | 56.34 |
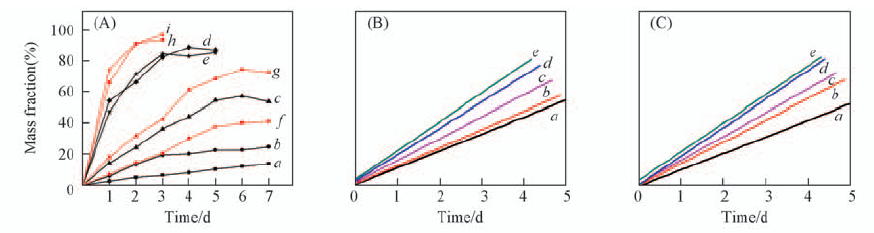
Fig.6 Enzymatic degradation(A) and kinetics curves(B, C) of copolymers (A) a. PBS; b. PBS-TDGS5; c. PBS-TDGS10; d. PBS-TDGS15; e. PBS-TDGS20; f. PBS-DEGS5; g. PBS-DEGS10; h PBS-DEGS15; i. PBS-DEGS20. (B) a. PBS, k=0.345; b. PBS-TDGS5, k=0.370; c. PBS-TDGS10, k=0.446; d. PBS-TDGS15, k=0.940; e. PBS-TDGS20, k=1.373. (C) a. PBS, k=0.345; b. PBS-DEGS5, k=0.454; c. PBS-DEGS10, k=0.581; d. PBS-DEGS15, k=1.394; e. PBS-DEGS20, k=1.395.
| Ligand | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDGS-TDG | -13.77 | -34.98 | -33.97 | -1.51 | -9.50 | 21.21 |
| DEGS-DEG | -18.66 | -39.83 | -39.08 | -1.26 | -13.85 | 21.21 |
Table 3 Docking results of TDGS-TDG and DEGS-DEG with the Auto Dock program
| Ligand | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDGS-TDG | -13.77 | -34.98 | -33.97 | -1.51 | -9.50 | 21.21 |
| DEGS-DEG | -18.66 | -39.83 | -39.08 | -1.26 | -13.85 | 21.21 |
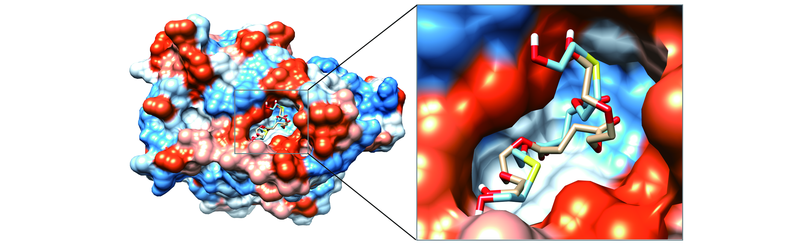
Fig.9 Surface of the top-ranking docked conformation of compounds TDGS(carbon atoms in light blue) and DEGS(light brown) combined with active site of N435 lipase
| [1] | Gigli M., Negroni A., Zanaroli G., Lotti N., Fava F., Munari A., React. Funct. Polym., 2013, 73(5), 764—771 |
| [2] | Jiang T., He F., Zhuo R. X., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2013, 98(1), 325—330 |
| [3] | Hwang S. Y., Yoo E. S., Im S. S., Polym. J., 2012, 44(12), 1179—1190 |
| [4] | Liu Y. J., Mao L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(12), 2903—2910 |
| (刘跃军, 毛龙. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(12), 2903—2910) | |
| [5] | Zhu Q. Y., He Y. S., Zeng J. B., Huang Q., Wang Y. Z., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 130(3), 943—949 |
| [6] | Zhang S. P., Wang D., Dang Y., Shi S. Q., Gong Y. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(2), 416—420 |
| (张世平, 王丹,党媛, 史肃青, 宫永宽. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(2), 416—420) | |
| [7] | Frohberga P., Pietzschb M., Ulricha J., Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2010, 88(9), 1148—1152 |
| [8] | Díaz-Celorio E., Franco L., Rodríguez-Galán A., Eur. Polym. J., 2012, 48(1), 60—73 |
| [9] | Ding M. L., Zhang M., Yang J.M., Qiu J. H., Biodegradation,2012, 23(1), 127—132 |
| [10] | Hwang S. Y., Jin X. Y., Yoo E. S., Im S. S., Polymer,2011, 52(13), 2784—2791 |
| [11] | Zhou X. M., Mater. Sci. Eng, C, 2012, 32(8), 2459—2463 |
| [12] | Soulis S., Triantou D., Weidner S., Falkenhagen J., Simitzis J., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2012, 97(11), 2091—2103 |
| [13] | Gigli M., Lotti N., Gazzano M., Finelli L., Munari A., React. Funct. Polym., 2012, 72(5), 303—310 |
| [14] | Zhang M., Ding M. L., Zhang T., Yang J. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(3), 612—615 |
| (张敏, 丁明亮, 张婷, 杨金明. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(3), 612—615) | |
| [15] | Luic M., Sytefanic Z., Ceilinger I., Hodoscek M., Janezic D., Lenac T., Asler L. I., Syepac D., Tomic S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112(16), 4876—4883 |
| [16] | Krieger E., Koraimann G., Vriend G., Proteins,2002, 47(3), 393—402 |
| [17] | Krieger E., Darden T., Nabuurs S., Finkelstein A., Proteins,2004, 57(4), 678—683 |
| [18] | Morris G. M., Goodsell D. S., Halliday R. S., Huey R., Hart W. E., Belew R. K., Olson A. J., Autodock, Version 4.0.1, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA, USA, 2007 |
| [19] | DeLano W. L., The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Revision 0.99, DeLano Scientific, San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002 |
| [20] | Gigli M., Lotti N., Gazzano M., Finelli L. Munari A., Applied Polymer, 2012, 126(2), 686—696 |
| [21] | Lotti N., Siracusa V., Finelli L., Marchese P., Munari A., Eur. Polym. J., 2006, 42(12), 3374—3382 |
| [22] | Díaz A., Franco L., Estrany F., del Valle L. J., Puiggalí J., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2014, 99, 80—91 |
| [1] | LI Haibo, XIAO Changfa, JIANG Long, HUANG Yun, DAN Yi. Copolymerization of Methyl Acrylate and 1-Octene Catalyzed by the Loaded Aluminum Chloride on MCM-41 Molecular Sieve [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2974. |
| [2] | XU Xiaozhou, LIU Yi, HE Minhui, MO Song, LAN Bangwei, ZHAI Lei, FAN Lin. Effect of Copolymerization Structure and Molecular Weight on Melt Fluidity and Thermal Properties of Thermoplastic Polyimide Resins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 919. |
| [3] | DU Xinyao, WANG Wei, LIN Yu, WU Guozhang. Synthesis and Optical Properties of Polycarbonates Copolymerized with Bisphenol Fluorene Moiety [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3765. |
| [4] | YE Chenghao, LIANG Heng, LI Enmin, XU Liyan, LI Peng, CHEN Guanghui. High-throughput Virtual Screening of CDK2/Cyclin A2 Target Inhibitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3135. |
| [5] | ZHANG Junying, PENG Wei, CHEN Ziwei, HE Aihua. Effect of the Polymerization Temperature on the Copolymerization of Butadiene and Isoprene Catalyzed by Supported Ziegler-Natta Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1873. |
| [6] | CHEN Xiaofeng,NING Hejia,YANG Li,PENG Changjun,SUN Wei. Molecular Simulation Study on Influence and Screening of Micro-porous Materials for Phosgene Adsorption and Diffusion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 317. |
| [7] | WANG Jianwei, REN Yingchun, MI Puke, XU Sheng. Synthesis of TiCl3 Complexes Containing Aryloxy Groups and Application for Ethylene Polymerization and Copolymerization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1806. |
| [8] | YANG Zhaojie, LEI Bei, DU Wenhao, ZHANG Xi. Structure and Properties of Starch/Polybutylene Succinate Blends Modified by Magnesium Chloride/1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1611. |
| [9] | ZHANG Cui,WANG Lijuan,LÜ Zhongwen,XU Sheng,MI Puke. Synthesis of Binuclear Complexes Containing Phenoxyimine Ligands and Application for Ethylene Polymerization and Copolymerization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2811. |
| [10] | LU Zhiwei, CHEN Shun, JU Yanyun, ZHANG Yang, XIONG Chuanxi, DONG Lijie. Synthesis and Properties of PS-b-P(DMS-stat-VMS) Block Copolymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1484. |
| [11] | LI Yingtu, LI Libo, ZHOU Jian. Molecular Dynamics Simulations on the Adhesion of DOPA to Self-assembled Monolayers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 798. |
| [12] | ZHANG Danfeng, ZHANG Yujun, YU Guocong, GAO Wenhao. Copolymerization of Ethylene and Methyl Methacrylate with Salicylaldiminate Nickel(Ⅱ) Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2082. |
| [13] | LEI Bei, LUO Hui, SHI Mengke, ZHANG Xi. Structure and Properties of Starch/Poly(butylene succinate) Blends Plasticized by [BMIM]Cl† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1722. |
| [14] | WU Xiaomeng, CHEN Xiaoyu, Shi LI, FAN Zhongyong. Preparation, Structure and Properties of PLLA-TMC/PDLA-TMC Stereocomplexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2101. |
| [15] | LÜ Haoting, MIAO Qun, SUN Huailin. Alternating Copolymerization of Aryl Aldehyde Imines and Carbon Monoxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||