

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (10): 2258.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140406
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qiuxiang1,2, CHEN Jianhua2,3, LU Hongbin1,*( ), TANG Wei1, LU Yu1, GAO Yangzhi1
), TANG Wei1, LU Yu1, GAO Yangzhi1
Received:2014-04-28
Online:2014-10-10
Published:2014-09-11
Contact:
LU Hongbin
E-mail:luhb@nju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Qiuxiang, CHEN Jianhua, LU Hongbin, TANG Wei, LU Yu, GAO Yangzhi. Preparation and Properties of Paraffin Microencapsulated Phase-change Materials with Fine Particle Size†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10): 2258.
| Sample | m(Paraffin)/g | m(Tween-80)/g | m(Span-80)/g | m(SDS)/g | m(CTAB)/g | m(MMA)/g | m(AA)/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 8 | 2 | |
| 3 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 8 | 2 | |
| 4 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 5 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 10 | ||
| 6 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 9 | 1 | |
| 7 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 7 | 3 | |
| 8 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 6 | 4 | |
| 9 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 5 | 5 |
Table 1 Formulations of MicroPCMs*
| Sample | m(Paraffin)/g | m(Tween-80)/g | m(Span-80)/g | m(SDS)/g | m(CTAB)/g | m(MMA)/g | m(AA)/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 8 | 2 | |
| 3 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 8 | 2 | |
| 4 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 5 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 10 | ||
| 6 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 9 | 1 | |
| 7 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 7 | 3 | |
| 8 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 6 | 4 | |
| 9 | 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 5 | 5 |
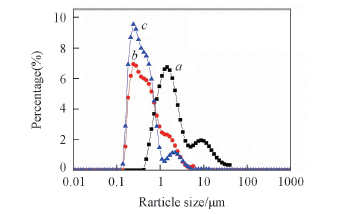
Fig.1 Particle size distribution of paraffin emulsions a. Non-ionic emulsifiers(Tween-80+span-80); b. anionic and non-ionic composite emulsifiers(SDS+Tween-80+span-80); c. cationic and non-ionic composite emulsifiers(CTAB+Tween-80+span-80).
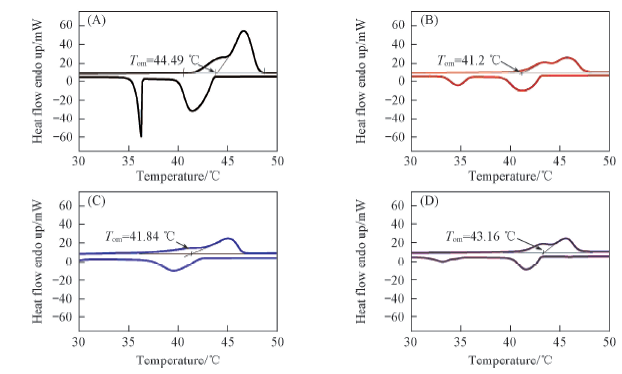
Fig.4 DSC curves of MicroPCMs prepared with pure paraffin(A), cationic and non-ionic emulsifiers(B), non-ionic emulsifier(C) and anionic and non-ionic emulsifiers(D)
| Emulsifier | Tom/℃ | Tpm/℃ | Toc/℃ | Tpc/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | Paraffin content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure paraffin | 44.49 | 46.69 | 43.64 | 41.50 | 249.20 | 216.10 | 100 |
| Cationic and non-ionic composite emulsifiers | 41.20 | 45.74 | 43.10 | 41.26 | 127.96 | 126.23 | 54.63 |
| Non-ionic emulsifier | 41.84 | 44.98 | 42.17 | 39.51 | 94.42 | 76.75 | 36.79 |
| Anionic and non-ionic composite emulsifiers | 43.16 | 45.59 | 43.14 | 41.62 | 71.04 | 58.63 | 27.87 |
Table 2 Thermal properties of MicroPCMs prepared with different emulsifiers*
| Emulsifier | Tom/℃ | Tpm/℃ | Toc/℃ | Tpc/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | Paraffin content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure paraffin | 44.49 | 46.69 | 43.64 | 41.50 | 249.20 | 216.10 | 100 |
| Cationic and non-ionic composite emulsifiers | 41.20 | 45.74 | 43.10 | 41.26 | 127.96 | 126.23 | 54.63 |
| Non-ionic emulsifier | 41.84 | 44.98 | 42.17 | 39.51 | 94.42 | 76.75 | 36.79 |
| Anionic and non-ionic composite emulsifiers | 43.16 | 45.59 | 43.14 | 41.62 | 71.04 | 58.63 | 27.87 |
| m(MMA)∶m(AA) | Tom/℃ | Tpm/℃ | Toc/℃ | Tpc/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | Paraffin content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure MMA | 41.22 | 43.73 | 41.65 | 39.53 | 16.53 | 12.67 | 6.28 |
| 9∶1 | 42.05 | 46.53 | 43.12 | 41.09 | 168.57 | 164.76 | 71.64 |
| 8∶2 | 41.20 | 45.74 | 43.10 | 41.26 | 127.96 | 126.23 | 54.63 |
| 7∶3 | 43.26 | 45.59 | 43.11 | 42.12 | 105.86 | 94.91 | 43.15 |
| 6∶4 | 41.75 | 45.86 | 43.30 | 42.05 | 125.79 | 121.03 | 53.05 |
| 5∶5 | 42.89 | 45.55 | 43.04 | 41.35 | 48.92 | 44.94 | 20.17 |
Table 3 Thermal properties of MicroPCMs at different monomer compositions
| m(MMA)∶m(AA) | Tom/℃ | Tpm/℃ | Toc/℃ | Tpc/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | Paraffin content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure MMA | 41.22 | 43.73 | 41.65 | 39.53 | 16.53 | 12.67 | 6.28 |
| 9∶1 | 42.05 | 46.53 | 43.12 | 41.09 | 168.57 | 164.76 | 71.64 |
| 8∶2 | 41.20 | 45.74 | 43.10 | 41.26 | 127.96 | 126.23 | 54.63 |
| 7∶3 | 43.26 | 45.59 | 43.11 | 42.12 | 105.86 | 94.91 | 43.15 |
| 6∶4 | 41.75 | 45.86 | 43.30 | 42.05 | 125.79 | 121.03 | 53.05 |
| 5∶5 | 42.89 | 45.55 | 43.04 | 41.35 | 48.92 | 44.94 | 20.17 |
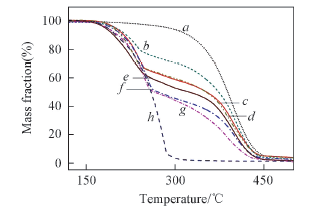
Fig.7 TG curves of polymer shell(a), MMA(b) and MicroPCMs at different monomer compositions(c—g) m(MMA)∶m(AA): a. 8∶2; b. MMA; c. 5∶5; d. 6∶4; e. 7∶3; f. 9∶1; g. 8∶2. h. paraffin.
| m(MMA)∶m(AA) | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | Penetration rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure MMA | 14.81 | 9.52 | 16.68 |
| 9∶1 | 152.66 | 150.33 | 9.10 |
| 8∶2 | 120.43 | 119.57 | 5.58 |
| 7∶3 | 62.42 | 53.77 | 42.13 |
| 6∶4 | 95.35 | 90.01 | 24.90 |
| 5∶5 | 42.18 | 39.14 | 13.36 |
Table 4 Penetration rate of MicroPCMs at different monomer compositions
| m(MMA)∶m(AA) | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | Penetration rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure MMA | 14.81 | 9.52 | 16.68 |
| 9∶1 | 152.66 | 150.33 | 9.10 |
| 8∶2 | 120.43 | 119.57 | 5.58 |
| 7∶3 | 62.42 | 53.77 | 42.13 |
| 6∶4 | 95.35 | 90.01 | 24.90 |
| 5∶5 | 42.18 | 39.14 | 13.36 |
| [1] | Sharma A., Tyagi V. V., Chen C. R., Buddhi D., Renew. Sust. Energ Rev., 2009, 13(2), 318—345 |
| [2] | Zhou D., Zhao C. Y., Tian Y., Appl. Energ., 2012, 92, 593—605 |
| [3] | Hawlader M. N. A., Uddin M. S., Khin M. M., Appl. Energ., 2003, 74(1/2), 195—202 |
| [4] | Pomianowski M., Heiselberg P., Zhang Y. P., Energ. Buildings,2013, 67, 56—69 |
| [5] | Ma L., Yin D. Z., Du X., Jia J., New Chem. Mater., 2014, 3, 1—3 |
| (马荔, 尹德忠, 杜筱, 贾佳. 化工新型材料, 2014,3,1—3) | |
| [6] | Sánchez L., Sánchez P., Lucas A., Carmona M., Rodríguez J. F., Colloid. Polym. Sci., 2007, 285(12), 1377—1385 |
| [7] | Shi H. F., Li J. H., Yin Y. P., Zhang X. X., Wang D. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(7), 1613—1618 |
| (石海峰, 李剑华, 尹义平, 张兴祥, 王笃金. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(7), 1613—1618) | |
| [8] | Ni H., Kawaguchi H., Endo T., Colloid. Polym. Sci., 2007, 285(7), 819—826 |
| [9] | Luo Y. W., Liu B., Wang Z. H., Gao J., Li B., J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem., 2007, 45(11), 2304—2315 |
| [10] | Li M. G., Zhang Y., Xu Y. H., Zhang D., Polym. Bull., 2011, 67(3), 541—552 |
| [11] | Konuklu Y., Unal M., Paksoy H. O., Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C,2014, 120, 536—542 |
| [12] | Zhang Y. L., Rao Z. H., Wang S. F., Zhang Z., Li X. P., Energ. Convers. Manage., 2012, 59, 33—39 |
| [13] | Wang X., Zhu J. H., Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2014, 1, 131—135 |
| (王轩, 朱金华. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2014, 1, 131—135) | |
| [14] | Wang L. X., Ren X. L., Ren L., Su J. F., Acta Mater. Compositae Sinica,2006, 2, 53—58 |
| (王立新, 任晓亮, 任丽, 苏峻峰. 复合材料学报, 2006, 2, 53—58) | |
| [15] | Meng X., Zhang H. Z., Zhao Z. M., Sun L. X., Xu F., Zhang J., Jiao Q. Z., Bao Y., Ma J. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(3), 526—530 |
| (孟新, 张焕芝, 赵梓名, 孙立贤, 徐芬, 张箭, 焦庆祝, 鲍艳, 马建中. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(3), 526—530) | |
| [16] | Cao F. Y., Bao Y., Appl. Energ,2014, 113, 1512—1518 |
| [17] | Zhang Z. L., Tang X. F., Meng J. Y., Zhang X. X., Shi H. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(1), 175—179 |
| (张智力, 唐孝芬, 孟洁云, 张兴祥, 石海峰. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(1), 175—179) | |
| [18] | Huang Q. G., Zhang K., Yang W. B., Wang X. J., Fang J. H., Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2014, 3, 34—38 |
| (黄全国, 张凯, 杨文彬, 王小静, 范敬辉. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2014, 3, 34—38) | |
| [19] | Zhu K. Y., Wang S., Qi H. Z., Li H., Zhao Y. H., Yuan X. Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2012, 28(3), 539—541 |
| [20] | Alkan C., Sarı A., Karaipekli A., Uzun O., Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C,2009, 93(1), 143—147 |
| [21] | Zhang M., Tong X. M., Zhang H., Qiu J. H., Energ. Source. Part. A,2012, 34(5—8), 396—403 |
| [22] | Ma S. D., Song G. L., Li W., Fan P. F., Tang G. Y., Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C,2010, 94(10), 1643—1647 |
| [23] | Tang X. F., Li W., Shi H. F., Wang J. P., Han N., Zhang X. X., Sci. Adv. Mater., 2014, 6(1), 120—127 |
| [24] | Tang X. F., Li W., Zhang X. X., Shi H. F., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(4), 1678—1687 |
| [25] | Qiu X. L., Song G. L., Chu X. D., Li X. Z., Tang G. Y., Thermochim. Acta,2013, 551, 136—144 |
| [26] | Su J., Wang L. X., Ren L., Huang Z., Meng X., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2006, 102, 4996—5006 |
| [27] | Yin J.H., Mo Z. S., Modern Polymer Physics, Science Press, Beijing, 2001 |
| (殷敬华, 莫志深. 现代高分子物理学, 北京: 科学出版社, 2001) |
| [1] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [2] | LI Bowen,WANG Ruoheng,LI Li,XIAO Yang. Adsorption of Toluene by Alkali Activated Porous Carbons and Activation/Adsorption Mechanism † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 284. |
| [3] | LI Chenguang, HUA Er, LIU Tianxia. Tribological Behaviour of Protic Ionic Liquid Composed of 2-Ethylhexylethylenediaminium Cation and Trifluoromethanesulfonate Anion as Liquid Paraffin Additive† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1411. |
| [4] | LI Wa, LI Fengyun, SHI Zhisheng, HUANG Jue, CAI Qiang, ZHANG Wei. Preparation and Characterization of Strong-lightweight Porous Silica Spheres in Millimeter Scale† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1655. |
| [5] | ZHANG Ruizhen, WANG Cui, XING Pu, WEN Shaobo, WANG Jian, ZHAO Liangfu, LI Yuping. Preparation of Hierarchical Porous HZSM-5 and Its Application in Light Paraffin Aromatization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 725. |
| [6] | ZHANG De-Long, LI Wan-Wan, WANG Xie-Bing, SUN Kang. Preparation and Properties of High-quality CdSeS Alloyed Quantum Dots in Liquid Paraffin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(07): 1383. |
| [7] | MA Li*, JIA Chun-Yue, GAN Meng-Yu, HAO Shao-Na, LIU Xing-Min, LI Zhi-Chun. Synthesis and Electrochemical Behavior of Polyainiline by Composite Emulsifier Microemulision Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(7): 1656. |
| [8] | XING Bin, LI Wan-Wan, DOU Hong-Jing, SUN Kang*. High-quality CdTe Quantum Dots Synthesized in Liquid Paraffin Wax [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(2): 230. |
| [9] | WANG Hai-Bo, LIU De-Shan . Investigation of the Factors Influencing the Process of Emulsification United Effect of cmc_O and cmc_W [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(9): 1743. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||