

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (10): 2182.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140331
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIN Jiaolong, PANG Wenwen, YANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Teng, REN Tianrui*( )
)
Received:2014-04-09
Online:2014-10-10
Published:2014-09-18
Contact:
REN Tianrui
E-mail:trren@shnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
QIN Jiaolong, PANG Wenwen, YANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Teng, REN Tianrui. Studies on the Surface Properties of Alcohol Ethoxylate and the Application in Suspension Concentrate†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10): 2182.
| No. | γcmc/(mN·m-1) | 105cmc/(mol·L-1) | Acmc/(nm2·molecule-1) | ΔGm/(kJ·mol-1) | HLB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEO-4 | 25.80 | 3.79 | 0.601 | -25.14 | 9.96 |
| AEO-7 | 26.80 | 4.63 | 0.941 | -24.74 | 12.55 |
| AEO-9 | 29.10 | 6.52 | 0.956 | -23.89 | 13.49 |
| AEO-15 | 37.50 | 7.86 | 0.960 | -23.43 | 15.16 |
| AEO-20 | 41.90 | 8.44 | 1.266 | -23.25 | 15.69 |
Table 1 Surface and micellar properties of AEO surfactants obtained in aqueous solution*
| No. | γcmc/(mN·m-1) | 105cmc/(mol·L-1) | Acmc/(nm2·molecule-1) | ΔGm/(kJ·mol-1) | HLB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEO-4 | 25.80 | 3.79 | 0.601 | -25.14 | 9.96 |
| AEO-7 | 26.80 | 4.63 | 0.941 | -24.74 | 12.55 |
| AEO-9 | 29.10 | 6.52 | 0.956 | -23.89 | 13.49 |
| AEO-15 | 37.50 | 7.86 | 0.960 | -23.43 | 15.16 |
| AEO-20 | 41.90 | 8.44 | 1.266 | -23.25 | 15.69 |
| Sample | Bingham model | Herschel-Bulkley model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ0/Pa | ηP/(Pa·s) | R2 | n | K/(Pa·sn) | τ0/Pa | R2 | ||
| SC | 18.22 | 0.0227 | 0.9458 | 1.1489 | 0.009358 | 18.47 | 0.9468 | |
| SC-AEO-4 | 8.967 | 0.01184 | 0.9945 | 0.8802 | 0.02433 | 8.828 | 0.9970 | |
| SC-AEO-7 | 1.2806 | 0.0302 | 0.9458 | 0.6507 | 0.2238 | 0.3696 | 0.9999 | |
| SC-AEO-9 | 0.8827 | 0.02191 | 0.9487 | 0.6551 | 0.1575 | 0.2436 | 0.9999 | |
| SC-AEO-15 | 2.8473 | 0.02439 | 0.9692 | 0.7128 | 0.1317 | 2.176 | 0.9982 | |
| SC-AEO-20 | 1.3026 | 0.02536 | 0.9498 | 0.6385 | 0.2040 | 0.4668 | 0.9999 | |
Table 2 Rheological parameters of SC-AEOs
| Sample | Bingham model | Herschel-Bulkley model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ0/Pa | ηP/(Pa·s) | R2 | n | K/(Pa·sn) | τ0/Pa | R2 | ||
| SC | 18.22 | 0.0227 | 0.9458 | 1.1489 | 0.009358 | 18.47 | 0.9468 | |
| SC-AEO-4 | 8.967 | 0.01184 | 0.9945 | 0.8802 | 0.02433 | 8.828 | 0.9970 | |
| SC-AEO-7 | 1.2806 | 0.0302 | 0.9458 | 0.6507 | 0.2238 | 0.3696 | 0.9999 | |
| SC-AEO-9 | 0.8827 | 0.02191 | 0.9487 | 0.6551 | 0.1575 | 0.2436 | 0.9999 | |
| SC-AEO-15 | 2.8473 | 0.02439 | 0.9692 | 0.7128 | 0.1317 | 2.176 | 0.9982 | |
| SC-AEO-20 | 1.3026 | 0.02536 | 0.9498 | 0.6385 | 0.2040 | 0.4668 | 0.9999 | |
| Ssmple | W1(%) | W2(%) | St | τ0/Pa | τflow/Pa | γflow(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 30.00 | 25.00 | 813.5 | 18.47 | 18.47 | 2.492 |
| SC-AEO-4 | 94.55 | 91.05 | 745.6 | 8.828 | 2.228 | 29.09 |
| SC-AEO-7 | 95.92 | 94.57 | 12.24 | 0.3696 | 0.2967 | 10.59 |
| SC-AEO-9 | 94.42 | 96.12 | 11.12 | 0.2436 | 0.2286 | 13.46 |
| SC-AEO-15 | 94.89 | 94.47 | 89.23 | 2.176 | 0.7787 | 27.70 |
| SC-AEO-20 | 95.01 | 95.81 | 18.41 | 0.4668 | 0.6075 | 23.31 |
Table 3 Stability analysis of SC-AEOs
| Ssmple | W1(%) | W2(%) | St | τ0/Pa | τflow/Pa | γflow(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 30.00 | 25.00 | 813.5 | 18.47 | 18.47 | 2.492 |
| SC-AEO-4 | 94.55 | 91.05 | 745.6 | 8.828 | 2.228 | 29.09 |
| SC-AEO-7 | 95.92 | 94.57 | 12.24 | 0.3696 | 0.2967 | 10.59 |
| SC-AEO-9 | 94.42 | 96.12 | 11.12 | 0.2436 | 0.2286 | 13.46 |
| SC-AEO-15 | 94.89 | 94.47 | 89.23 | 2.176 | 0.7787 | 27.70 |
| SC-AEO-20 | 95.01 | 95.81 | 18.41 | 0.4668 | 0.6075 | 23.31 |
| Sample | Structure recovery ratio(%) | R(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 s | 7 s | 10 s | 15 s | ||
| SC | 113.9 | 111.4 | 112.2 | 111.7 | ≥20 |
| SC-AEO-4 | 76.69 | 83.84 | 91.68 | 99.07 | 10 |
| SC-AEO-7 | 54.92 | 60.06 | 64.37 | 68.78 | 7 |
| SC-AEO-9 | 44.26 | 49.70 | 54.05 | 58.41 | ≤5 |
| SC-AEO-15 | 27.91 | 31.41 | 35.06 | 38.75 | ≤3 |
| SC-AEO-20 | 40.63 | 45.17 | 48.97 | 52.93 | ≤3 |
Table 4 Rheological data of three interval thixotropy and residual pourability test
| Sample | Structure recovery ratio(%) | R(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 s | 7 s | 10 s | 15 s | ||
| SC | 113.9 | 111.4 | 112.2 | 111.7 | ≥20 |
| SC-AEO-4 | 76.69 | 83.84 | 91.68 | 99.07 | 10 |
| SC-AEO-7 | 54.92 | 60.06 | 64.37 | 68.78 | 7 |
| SC-AEO-9 | 44.26 | 49.70 | 54.05 | 58.41 | ≤5 |
| SC-AEO-15 | 27.91 | 31.41 | 35.06 | 38.75 | ≤3 |
| SC-AEO-20 | 40.63 | 45.17 | 48.97 | 52.93 | ≤3 |
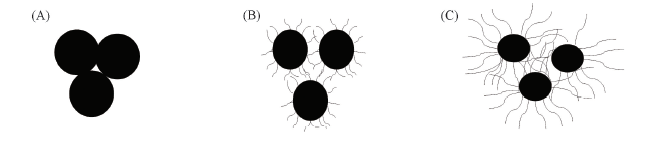
Fig.12 Effect of AEOs with different EO chains on dispersion ability of particles (A) Short or no AEO: flocculation; (B) proper EO chains: dispersion; (C) too long EO chains: bridging.
| [1] | Luckham P. F., Powder Technology, 1989, 58(2), 75—91 |
| [2] | Luckham P. F., Pesticide Science, 1989, 25(1), 25—34 |
| [3] | GuoW. L., Liquid Pharmaco Kinetical Preparations, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2004, 196—224 |
| (郭武棣. 液体制剂, 北京:化学工业出版社, 2004, 196—224) | |
| [4] | Faers M. A., Kneebone G. R., Pesticide Science,1999, 55(3), 312—325 |
| [5] | Winzeler H. B., Vogel R., Dudler A., Advances in Pesticide Science,1979, 3, 798—809 |
| [6] | Xu Y. K., World Pesticides, 1980, 6, 1—6 |
| (徐义宽. 世界农药, 1980, 6, 1—6) | |
| [7] | Zhou Y., Tang A. S., Agrochemicals,1995, 34(5), 6—9 |
| (周瑛, 唐霭淑. 农药, 1995, 34(5), 6—9) | |
| [8] | Shen D. L., Tan C. X., Agrochemicals,1998, 37(11), 11—13 |
| (沈德隆, 谭成侠. 农药, 1998, 37(11), 11—13) | |
| [9] | Shen J., The Research of Rheology and Physical Storage Stability in Pesticide Suspension Concentrate , the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, 2008 |
| (沈娟. 农药悬浮剂流变学特性及贮存物理稳定性研究, 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2008) | |
| [10] | Wu Q. M., Ruan J. M., Huang B. Y., Acta Chimica Sinica,2006, 64(15), 1543—1547 |
| (伍秋美, 阮建明, 黄伯云. 化学学报, 2006, 64(15), 1543—1547) | |
| [11] | Maranzano B. J., Wagner N. J., Journal of Rheology,2001, 45(5), 1205—1222 |
| [12] | Duro R., Alvarez C., Martínez-Pacheco R., European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics,1998, 45(2), 181—188 |
| [13] | Nasu A., Otsubo Y., Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2008, 326(1), 92—97 |
| [14] | Lv Y., Liu H., Sang Y., Journal of Materials Science,2010, 45(3), 706—712 |
| [15] | Feng J. Y., Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 27(3), 289—291 |
| (冯建跃. 分析化学, 1999, 27(3), 289—291) | |
| [16] | Ma C., Liu F., Mu W.,Modern Agrochemicals, 2006, 4, 15—17 |
| (马超, 刘峰, 慕卫. 现代农药, 2006, 4, 15—17) | |
| [17] | Liu Y., Study on the Environmental Friendly Pesticide Formulation Based on the Green Surfactants, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 2012 |
| (刘迎. 基于绿色表面活性剂的农药环境友好型制剂的研究, 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012) | |
| [18] | Wang Z.D., Hu L. M.,Speciality Petrochemicals, 1996, (6), 58—62 |
| (王正东, 胡黎明. 精细石油化工, 1996, (6), 58—62) | |
| [19] | Li Z. X., Chen W. H., China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics,1990, 6, 25—29 |
| (李智新, 陈文海. 日用化学工业, 1990, 6, 25—29) | |
| [20] | Martin J.S., Nonionic Surfactants: Physical Chemistry, CRC Press, New York, 1987, 500 |
| [21] | Wei Y. C., Zhang H. Y., Wu W. K., Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2011, 2, 53—56 |
| (韦迎春, 张海燕, 邬伟魁. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2011, 2, 53—56) | |
| [22] | Zhang D. X., Zhang G. S., Chen B., Agrochemicals Research & Application,2010, 1, 18—20 |
| (张大侠, 张贵森, 陈波. 农药研究与应用, 2010, 1, 18—20) | |
| [23] | Xian Y., Wang L. P., Pesticide Science and Administration,2003, 24(7), 20—21 |
| (鲜艳, 王列平. 农药科学与管理, 2003, 24(7), 20—21) | |
| [24] | Dai Y. J., Zhang Z. D., Pesticide Science and Administration,2006, 3, 12—14 |
| (戴永军, 张兆栋. 农药科学与管理, 2006, 3, 12—14 | |
| [25] | Rosen M. J., CohenA. W., Dahanayake M., J. Phys. Chem., 1982, 86(4), 541—545 |
| [26] | Adkins S., Chen X., Nguyen Q. P., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2010, 346(2), 455—463 |
| [27] | Carey M. C., Small D. M., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 1969, 31(3), 382—396 |
| [28] | Yang Y. W., Deng N. J., Yu G., Zhou Z. K., Attwood D., Booth C., Langmuir,1995, 11(12), 4703—4711 |
| [29] | Gao C. Y., Feng Y. P., Lin L., Fine Chemical Intermediates,2009, 39(4), 11—13 |
| (高长义, 冯银鹏, 林丽. 精细化工中间体, 2009, 39(4), 11—13) | |
| [30] | Zhang G. S., Li L. G., World Pesticides,2010, 32(4), 40—47 |
| (张国生, 李琳光. 世界农药, 2010, 32(4), 40—47) | |
| [31] | Kausalya R. N., Foster A., Styring M. G., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 1990, 136(2), 588—592 |
| [32] | Corkill J. M., Goodman J. F., Ottewill R. H., Transactions of the Faraday Society,1961, 57, 1627—1636 |
| [33] | Kratzat K., Finkelmann H., Langmuir,1996, 12(7), 1765—1770 |
| [34] | Schick M. J., Beyer E. A., Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society,1963, 40(2), 66—68 |
| [35] | Geng L., Study on the Correlations Between Critical Micelle Concentration and Molecular Energies, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, 2012 |
| (耿林. 表面活性剂的临界胶束浓度与分子能量项和分子结构的关系研究, 无锡: 江南大学, 2012) | |
| [36] | Raghavan S. R., Khan S. A., Journal of Rheology,1995, 39(6), 1311—1325 |
| [37] | Ran Q., Somasundaran P., Miao C., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2009, 336(2), 624—633 |
| [38] | Lü S. Y., Shao Z. Q., Zhang Z. L., Wang F. J., Wang W. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(2), 409—415 |
| (吕少一, 邵自强, 张振玲, 王飞俊, 王文俊. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(2), 409—415) | |
| [39] | Xie Y., Lü Z. Y., Sun Z. Y., An L. J., Li X. H., Wu Z. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(6), 1521—1526 |
| (谢宇, 吕中元, 孙昭艳, 安立佳, 李秀宏, 吴忠华. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(6), 1521—1526) | |
| [40] | Bo X.L., Huang Q. L., Wang G. P.,Agrochemicals, 2006, 4, 231—236 |
| (卜小莉, 黄啟良, 王国平. 农药, 2006, 4, 231—236) | |
| [41] | Hu S. H., Li H., Hu W., Journal of Hubei University of Technology,2012, 27(2), 57—60 |
| (胡圣飞, 李慧, 胡伟. 湖北工业大学学报, 2012, 27(2), 57—60) | |
| [42] | BoX. L., Huang Q. L., Wang G. P., Pesticide Science and Administration,2006, 27(4), 24—28 |
| (卜小莉, 黄啟良, 王国平. 农药科学与管理, 2006, 27(4), 24—28) | |
| [43] | Mezger T.G., The Rheology Handbook: for Users of Rotational and Oscillatory Rheometers, Vincentz Network GmbH & Co. KG, 2006 |
| [44] | Hao R. G., Hu Z. L., Liu S. J., China Writing Instruments,2009, 4, 9—13 |
| (郝瑞光, 胡卓林, 刘守君. 中国制笔, 2009, 4, 9—13) |
| [1] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [2] | DU Bin, CHEN Shangtao, ZHANG Fengbo, SHI Xingbo, LI Rongbo. Nonlinear Rheological Behavior of Long Chain Branching Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2034. |
| [3] | WANG Longjie, FAN Hongchuan, QIN Yu, CAO Qiue, ZHENG Liyan. Research Progress of Metal-organic Frameworks in the Field of Chemical Separation and Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [4] | FAN Ye, LI Qian, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei. Fabrication of Lamellar Liquid Crystals of Conjugated Linoleic Acid as Drug Delivery Systems † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 750. |
| [5] | GUO Lanlei, ZHU Yangwen, XU Zhicheng, GONG Qingtao, JIN Zhiqiang, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lu. Effect of Branched Hydrophobic Group on the Surface Dilational Rheology of Betaine Surfactants [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1399. |
| [6] | GUO Zhenhao, GUI Qifeng, ZHANG Bo, REN Shuaizhen, ZHANG Shupeng, LI Xinzhong, REN Tianrui. Application of Polycarboxylate and Naphthalenesulfonate Dispersants in High Concentration Suspension Concentrate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1278. |
| [7] | SHI Suqing, ZHAO Yang, ZHANG Qin, GAO Na, YANG Yang, GONG Yongkuan. Fabrication and Surface Properties of Hydrolyticly Function-switchable Polymer Brush† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 1093. |
| [8] | LI Jing, YANG Yong, CAO Xulong, ZHANG Jichao, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lu, ZHAO Sui. Interfacial Shear Rheological Properties of Enhanced Oil Recovery Polymers with Different Structures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 791. |
| [9] | YUAN Jing, ZHAI Xueru, XU Guiying, TAN Yebang, ZHANG Jian. Influence of Inorganic Salts on the Demulsification of Block Polyether with Seven Branches for Crude Oil Emulsion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 325. |
| [10] | CHEN Meng-Ting, TAN Ye-Qiang, SONG Yi-Hu. Rheological Behavior of Carbon Black Filled Polystyrene Melts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(9): 2228. |
| [11] | XIE Yu, LV Zhong-Yuan, SUN Zhao-Yan, AN Li-Jia, LI Xiu-Hong, WU Zhong-Hua. Gel Structure of the 17R4/F127 Mixed Solutions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(6): 1521. |
| [12] | TANG Li, LUO Lan, FANG Hong-Bo, ZONG Hua, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lu, ZHAO Sui. Dilational Rheology Properties of Branch-performed Particle Gel by Relaxation Measurements [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(6): 1434. |
| [13] | GUAN Qing-Xiang, LU Jing-Wen, GUO Jie, NING Zhao-Lun, CHEN Chen, YIN Jian-Yuan. Investigation on in situ Gel Based on Liposomal Vesicle [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5): 1174. |
| [14] | LI Hai-Ping, LIU Sheng-Bo, HOU Wan-Guo. Flow Behavior of Aqueous Solution of Exopolysaccharide Secreted by a Deep-sea Mesophilic Bacterium [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(05): 1025. |
| [15] | JIANG Yue, QIN Yuan-Hang, NIU Dong-Fang, ZHANG Xin-Sheng, ZHOU Xing-Gui, SUN Shi-Gang, YUAN Wei-Kang. Effects of Surface Properties and Microstructures of Carbon Nanofibers on Their Electrocatalytic Activity for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(05): 1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||