

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 325.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130915
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Jing1, ZHAI Xueru1, XU Guiying1,*( ), TAN Yebang1, ZHANG Jian2
), TAN Yebang1, ZHANG Jian2
Received:2013-09-17
Online:2014-02-10
Published:2014-01-02
Contact:
XU Guiying
E-mail:xuguiying@sdu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YUAN Jing, ZHAI Xueru, XU Guiying, TAN Yebang, ZHANG Jian. Influence of Inorganic Salts on the Demulsification of Block Polyether with Seven Branches for Crude Oil Emulsion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 325.
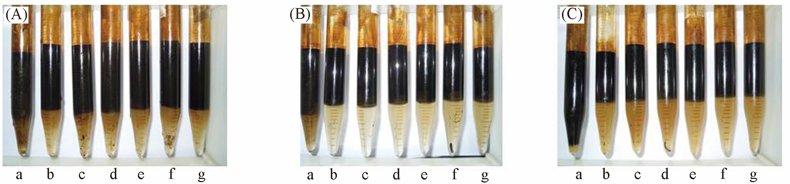
Fig.3 Effect of inorganic salts on water quality at 60 min at different temperaturesa.Blank; b.AE73; c.AE73/NaCl; d.AE73/MgCl2; e.AE73/CaCl2; f.AE73/NaI; g.AE73/NaSCN. Temperature/℃: (A) 25; (B) 45; (C) 65.
| Sample | 65 ℃ | 45 ℃ | 25 ℃ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil-water interface | Dehydration water | Hang wall | Oil-water interface | Dehydration water | Hang wall | Oil-water interface | Dehydration wall | Hang wall | |
| Blank | Indistinct | Slightly turbid | Hang | Indistinct | Turbid | Hang | Indistinct | Turbid | Hang |
| Without Salt | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Slightly hang | Neat | Turbid | Slightly hang |
| 1 mol/L NaCl | Neat | Slightly turbid | Slightly hang | Neat | Clearly | Not hang | Slightly neat | Turbid | Hang |
| 0.5 mol/L MgCl2 | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Not hang | Neat | Turbid | Hang |
| 0.5 mol/L CaCl2 | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Not hang | Slightly neat | Turbid | Hang |
| 1 mol/L NaI | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Slightly hang | Neat | Turbid | Slightly hang |
| 1 mol/L NaSCN | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not Hang | Indistinct | Clearly | Slightly hang | Neat | Turbid | Slightly hang |
Table 1 Effect of inorganic salt on water quality at 180 min and different temperatures
| Sample | 65 ℃ | 45 ℃ | 25 ℃ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil-water interface | Dehydration water | Hang wall | Oil-water interface | Dehydration water | Hang wall | Oil-water interface | Dehydration wall | Hang wall | |
| Blank | Indistinct | Slightly turbid | Hang | Indistinct | Turbid | Hang | Indistinct | Turbid | Hang |
| Without Salt | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Slightly hang | Neat | Turbid | Slightly hang |
| 1 mol/L NaCl | Neat | Slightly turbid | Slightly hang | Neat | Clearly | Not hang | Slightly neat | Turbid | Hang |
| 0.5 mol/L MgCl2 | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Not hang | Neat | Turbid | Hang |
| 0.5 mol/L CaCl2 | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Not hang | Slightly neat | Turbid | Hang |
| 1 mol/L NaI | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not hang | Neat | Clearly | Slightly hang | Neat | Turbid | Slightly hang |
| 1 mol/L NaSCN | Neat | Slightly turbid | Not Hang | Indistinct | Clearly | Slightly hang | Neat | Turbid | Slightly hang |
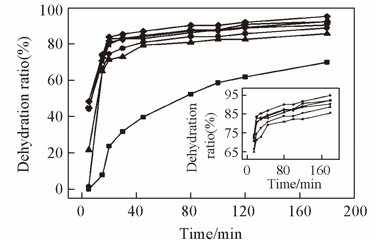
Fig.4 Effect of inorganic salts on the demulsification of AE73 at 45 ℃—■ — Blank; —●— without salt; —▲— 0.5 mol/L CaCl2; —▼— 0.5 mol/L MgCl2; —?— 1 mol/L NaCl; —?— 1 mol/L NaI; —◆— 1 mol/L NaSCN.Inset shows the curve of the turning points enlarge.
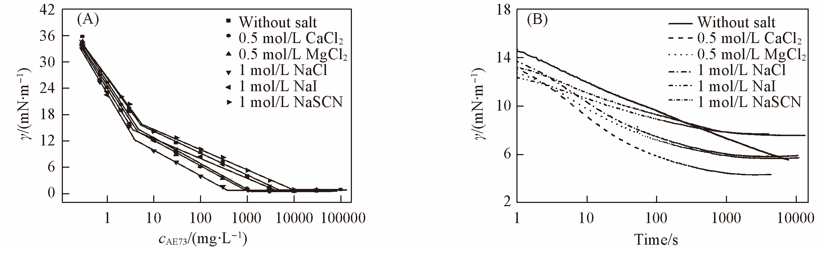
Fig.6 Interfacial tension curves of 100 mg/L AE73 in the absence and presence of inorganic salts at 25 ℃ (A) Equilibrium interfacial tension at n-heptane/water interface; (B) dynamic interfacial tension at n-heptane/water interface.
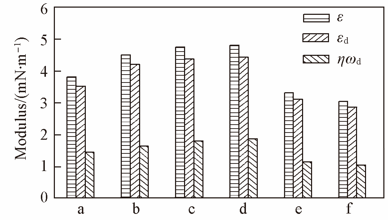
Fig.7 Dilational rheological property of AE73 at n-heptane/water interface in the absence and presence of inorganic saltsa. Without salt; b. 0.5 mol/L CaCl2; c. 0.5 mol/L MgCl2; d. 1 mol/L NaCl; e. 1 mol/L NaSCN; f. 1 mol/L NaI. ε: Dilational modulus; εd: dilational elastic modulus; ηωd: dilational viscous modulus. Dilational frequency: 0.01 Hz, cAE73=100 mg/L.
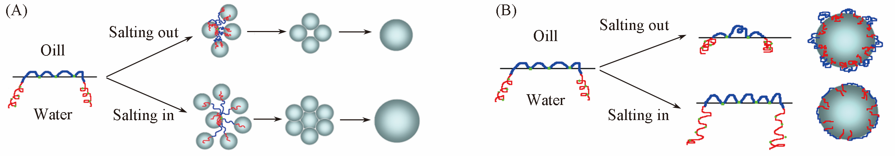
Fig.8 Schematic diagram of demulsification of branched polyether(A) and contact point and distribution of block polyether(B)Effect of salts with salting out and salting in type. Blue: PO group; Red: EO group; Green: Ether oxygen atoms; Gray balls: water-drop.
| [1] | Xia L. X., Lu S. W., Cao G. Y., Chem. Eng. Commun., 2004, 191(8), 1053—1063 |
| [2] | Wu X., Energy Fuels, 2002, 17(1), 179—190 |
| [3] | Xia L. X., Lu S. W., Cao G. Y., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2004, 271(2), 504—506 |
| [4] | Li M. Y., Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing Section), 1995, 11(3), 1—6 |
| (李明远.石油学报(石油加工), 1995, 11(3), 1—6) | |
| [5] | Wu J., Xu Y., Dabros T., Hamza H., Energy Fuels, 2003, 17(6), 1554—1559 |
| [6] | Kang W. L., Liu S. R., Xu B., Wang X. Z., Zhang B. T., Bai B. J., Pet. Sci. Technol., 2013, 31(6), 572—579 |
| [7] | Kang W. L., Jing G. L., Zhang H. Y., Li M. Y., Wu Z. Y., Colloids Surf. A, 2006, 272, 27—31 |
| [8] | Tong K., Zhang Y., Chu P. K., Colloids Surf. A, 2013, 419, 46—52 |
| [9] | Al-Sabagh A. M., Kandile N. G., Noor El-Din M. R., Sep. Sci. Technol., 2011, 46(7), 1144—1163 |
| [10] | Mokhtari B., Pourabdollah K., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2012, 28(5), 807—813 |
| [11] | Wang J., Li C. Q., An N., Yang Y., Sep. Sci. Technol., 2012, 47(10), 1583—1589 |
| [12] | El-Ghazawy R. A., Al-Sabagh A. M., Kandile N. G., El-Din M. R. N., J. Dispersion Sci. Technol., 2010, 31(10), 1423—1431 |
| [13] | Qiu J., Pet. Sci. Technol., 2013, 31(2), 142—147 |
| [14] | Cendejas G., Arreguin F., Castro L. V., Flores E. A., Vazquez F., Fuel, 2013, 103, 356—363 |
| [15] | Xie Y. J., Yan F., Yan Z. J., Zhang J. M., Li J. X., J. Dispersion Sci. Technol., 2012, 33(12), 1674—1681 |
| [16] | Zhai X. R., Liu T., Xu G. Y., Tan G. R., Lv X., Zhang J., Acta Phys-Chim Sin., 2013, 29(6), 1253—1259 |
| (翟雪如, 刘腾, 徐桂英, 檀国荣, 吕鑫, 张健.物理化学学报,2013, 29(6), 1253—1259) | |
| [17] | Zhang Z. Q., Xu G. Y., Wang F., Dong S. L., Li Y., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2004, 277(2), 464—470 |
| [18] | Qin S. F., Li W. L., Oilfield Chemistry, 1988, 5(1), 6—10 |
| (覃守凤, 李外郎.油田化学,1988, 5(1), 6—10) | |
| [19] | Fang X. L., Qin S. F., Li W. L., Oilfield Chemistry, 1989, 6(3), 221—225 |
| (方晓烈, 覃守凤, 李外郎.油田化学,1989, 6(3), 221—225) | |
| [20] | Mei Z., Xu J., Sun D. J., Colloids Surf. A, 2011, 375, 102—108 |
| [21] | Xia L. X., Cao G. Y., Lu S. W., Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing Section), 2003, 19(4), 94—97 |
| (夏立新, 曹国英, 陆世伟.石油学报(石油加工), 2003, 19(4), 94—97) | |
| [22] | Zhai X. R., Xu G. Y., Chen Y. J., Liu T., Zhang J., Yuan J., Tan Y. B., Zhang J., Colloid. Polym. Sci., 2013, 291 (12), 2825—2836 |
| [23] | Gong H. J., Xu G. Y., Ding H., Shi X. F., Tan Y. B., Eur. Polym. J., 2009, 45(9), 2540—2548 |
| [24] | Li G.Z., Zheng L. Q., Xu G. Y., Colloid Chemistry in Petroleum Exploration and Development, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2007, 47—97 |
| (李干佐, 郑利强, 徐桂英. 石油开采中的胶体化学, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007, 47—97) | |
| [25] | Kumar S., Patel H., Patil S., Colloid. Polym. Sci., 2013, 291(9), 2069—2077 |
| [26] | Zhao G.X., Zhu B. Y., Principles of Surfactant Action, China Light Industry Press, Beijing, 2003, 269—270 |
| (赵国玺, 朱王步瑶. 表面活性剂作用原理, 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2003, 269—270) | |
| [27] | Wang Y.J., Aggregation Behavior of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-ethoxylate/propoxylate at Interface, Shandong University,Jinan, 2009 |
| (王雅静. 聚氧乙烯聚氧丙烯二甲基硅氧烷的界面聚集行为, 济南: 山东大学, 2009) | |
| 28 | [28] Zhang Z. Q., Xu G. Y., Wang F., Dong S. L., Chen Y. J., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2005, 282(1), 1—4 |
| [29] | Wang Z. L., Li Z. Q., Zhang L., Huang H. Y., Zhang L., Zhao S., Yu J. Y., J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2011, 56(5), 2393—2398 |
| [30] | Ramírez P., Stocco A., Muñoz J., Miller R., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 378(1), 135—143 |
| [31] | Zhang H. X., Xu G. Y., Wu D., Wang S. W., Colloids Surf., A, 2008, 317(1—3), 289—296 |
| [32] | Ji G. D., Zhou G. H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2012, 28(3), 419—423 |
| [1] | XU Haiyan,REN Sili,JIA Weihong,WANG Jinqing. Preparation of Magnetically Recyclable Fluorinated Graphene and Its Demulsification Performance for Emulsified Oily Wastewater† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 508. |
| [2] | WANG Gang,WANG Keliang,LU Chunjing,WANG Ying. Preparation and Foam Properties of Janus Particles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 990. |
| [3] | KANG Wan-Li, SHAN Xi-Lin, LONG An-Hou, LI Jun-Gang . Studies on Demulsification Mechanism of Demulsifier for the Three compound Combination Flooding Effluent Emulsions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1999, 20(5): 759. |
| [4] | LIU Chang-Xin, CUI Yu, YANG Yong-Hui, SUN Si-Xiu, SUN Guo-Xin. Interfacial Activity of HDEHP and Its Kinetics Mechanism of Nickel Extraction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(3): 460. |
| [5] | CHU Ying, LIU Pei-Yan, MA Zhan-Fang, WU Zi-Sheng, YAN Zhong, SONG You. The Law and Mechanism of Grinding Demulsion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1996, 17(8): 1285. |
| [6] | YU Jing-fen, JI Chen . Interfacial Chemistry and Kinetics-Controlled Reaction Mechanism of Organo-Phosphoric Acid Mixed Extraction Systems [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1992, 13(2): 224. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||