

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 85.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130905
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
TAN Weiqiang1, ZANG Duyang1,*( ), LI Yunfei1, ZHANG Yongjian2, LU Chenjun1, LI Zhiguang1
), LI Yunfei1, ZHANG Yongjian2, LU Chenjun1, LI Zhiguang1
Received:2013-09-16
Online:2014-01-10
Published:2013-12-09
Contact:
ZANG Duyang
E-mail:dyzang@nwpu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
TAN Weiqiang, ZANG Duyang, LI Yunfei, ZHANG Yongjian, LU Chenjun, LI Zhiguang. Stability Mechanisms of Pickering Emulsion Co-stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles and PEO†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1): 85.

Fig.1 Appearance of the systems containing 65% water, 35% xylene and 0.5% silica nanoparticles(A) Before shearing; (B) and (C) sheared at rotation speeds of 5000 and 9000 r/min, respectively, shearing time: 3 min;(D) Pickering emulsion obtained at 24000 r/min is solid-like.
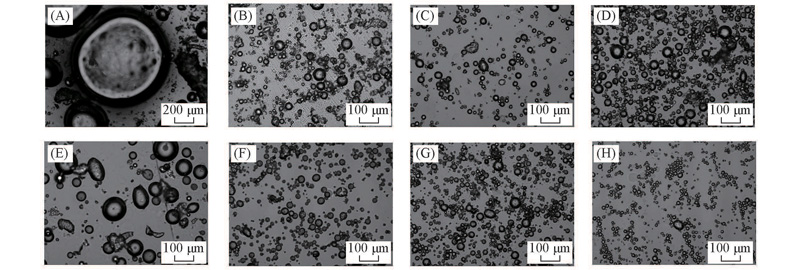
Fig.3 Optical microscope images of Pickering emulsion droplets of type A(A—D) and type B(E—H) obtained at different rotation speeds Rotation speed/(r·min-1): (A, E) 5000; (B, F) 12000; (C, G) 20000; (D, H) 24000.
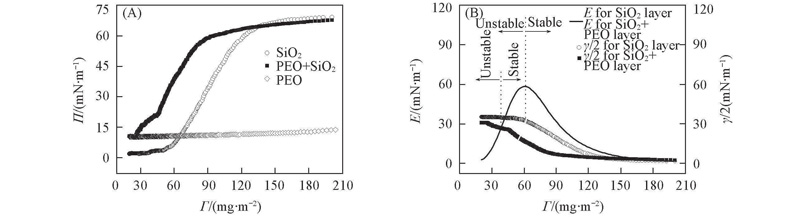
Fig.9 Rheological properties of silica nanoparticle layer at the air/water interface(A) Π-Γ isotherms; (b) comparison between compression modulus E and γ/2.
| [1] | Ramsden C. W., Proc. Roy. Soc. A., 1903, 72, 156—164 |
| [2] | Pickering S.U., J. Chem. Soc., 1907, 91,2001—2021 |
| [3] | Kalashnikova I., Bizot H., Cathala B., Capron I., Langmuir, 2011, 27, 7471—7479 |
| [4] | Clegg P. S., Herzig E. M., Schofield A. B., Horozov T. S., Binks B. P., Cates M. E., Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2005, 17, S3433—S3438 |
| [5] | Li T., Liu H., Zeng L., Yang S., Li Z., Zhang J., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 12865—12872 |
| [6] | Lee M. N., Mohraz A., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4836—4841 |
| [7] | He Y., Li K., J. Colloids and Surfaces, 2007, 306, 296—299 |
| [8] | Lin Y., Skaff H., Emrick T., Dinsmore A. D., Russell T. P., Science, 2003, 299, 226—229 |
| [9] | Yang F., Liu S., Xu J., Lan Q., Wei F., Sun D., J. Colloids and Surfaces, 2006, 302, 159—169 |
| [10] | Yang F.,Wang J., Lan Q., Sun D. J., Li C. X., Pro. in Chem., 2009, 21, 1418—1426 |
| (杨飞, 王君, 蓝强, 孙德军, 李传宪.化学进展, 2009, 21, 1418—1426) | |
| [11] | Gibbs J.W., The Scientific Papers of J. Willard Gibbs: Thermodynamics, Ox Bow Press, Woodbridge, 1993 |
| [12] | Lucassen-Reynders E. H., Cagna A., Lucassen J., J. Colloids Surf. A, 2001, 186, 63—72 |
| [13] | Zang D. Y., Rio E., Langevin D., Wei B., Binks B. P., European Physical Journal E, 2010, 31, 125—134 |
| [14] | Zang D. Y., Zhang Y. J., Langevin D., Acta. Physica. Sinica, 2011, 60(7), 076801-1—076801-7 |
| (臧渡洋, 张永建, Langevin D., 物理学报, 2011, 60(7), 076801-1—076801-7) | |
| [15] | Cervantes Martinez A., Rio E., Delon G., Saint-Jalmes A., Langevin D., Binks B. P., Soft Matter, 2008, 4, 1531—1535 |
| [16] | Stocco A., Drenckhan W., Rio E., Langevin D., Binks B. P., Soft Matter, 2009, 5, 2215—2222 |
| [17] | Binks B. P., Clint J. H., Langmuir, 2002, 18, 1270—1273 |
| [18] | Binks B. P., Rodrigues J. A., Angewandte Chemie, 2005, 44, 441—444 |
| [19] | Zou S. W., Wang C. Y., Wei Z. J., Liu H., Tong Z., Acta. Chimica. Sinica, 2012, 70, 133—136 |
| (邹声文, 王朝阳, 魏增江, 刘浩, 童真.化学学报, 2012, 70, 133—136) | |
| [20] | Zang D. Y., Clegg P. S., Soft Matter, 2013, 9, 7042—7048 |
| [21] | Binks B.P., Modern Aspects of Emulsion Science, The Royal Society of Chemistry,Cambridge, 1998 |
| [22] | Zebrowski J., Prasad V., Zhang W., Walker L. M., Weitz D. A., Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical Engineering Aspects, 2003, 213, 189—197 |
| [23] | Wang D. P., Yang M. Q., Dong Z. X., Bo S. Q., Ji X. L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(4), 820—824 |
| [24] | Zang D. Y., Wang X. L., Geng X. G., Zhang Y. J., Chen Y. M., Soft Matter, 2013, 9, 394—400 |
| [25] | Saito Y., Hirose Y., Otsubo Y., Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2011, 384, 40—46 |
| [26] | Zhang Y. J., Liu Z. T., Zang D. Y., Qian Y. M., Lin K. J., Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron., 2013, 56, 1712—1718 |
| [27] | Madivala B., Fransaer J., Vermant J., Langmuir, 2009, 25, 2718—2728 |
| [28] | Langevin D., Adv. Colloid. Intersurface, 2000, 88, 209—222 |
| [1] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [2] | LIANG Pingping, LIU Shuai, LI Hongyi, DING Yadan, WEN Xiaokun, LIU Junping, HONG Xia. Self-floating Porous PVDF-CNT Microbeads for Highly Efficient Solar-driven Interfacial Water Evaporation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2689. |
| [3] | ZHENG Zirui, LI Zilu, ZHAO Kefei, WU Tianyue, ZHANG Chenhui, GAO Yuxia, DU Fengpei. Interfacial Behaviors of Bio-based Surfactant Escin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3107. |
| [4] | LI Boxin, YANG Junge, YIN Dezhong, GAO Chengqian, ZHANG Qiuyu. Preparation of Large-sized Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials Through Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Monodisperse Polymer Microspheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2085. |
| [5] | JIA Xuemei, CHENG Tiexin, ZHOU Guangdong. Synergism Between Asphaltene and Its Subfractions and Alkylbenzene Sulfonate Solutions in Lowering Dynamic Interfacial Tensions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1631. |
| [6] | LI Ming,CUI Xiaoqian,WANG Xuan,LI Zaijun. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Sustained Release Effect on L-Menthol † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 324. |
| [7] | CHEN Jing,CHEN Jinhua,YIN Dezhong,ZHANG Wei. Phase Inversion of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Adipate-functionalized SiO2 Particles † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 140. |
| [8] | XIAO Zuoxu, CAO Hongyan, JIANG Xubao, KONG Xiangzheng. Preparation of Pickering Emulsion of Paraffin Wax and Microspheres Using Polymer Particles as Pickering Stabilizer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1797. |
| [9] | TONG Yongchun, WANG Qingyun, BAI Qingling, LI Zhen, JIA Chuanming. Preparation of Inorganic-organic Composite Hollow Microspheres by Double Pickering Emulsion Template† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1462. |
| [10] | WANG Gang,WANG Keliang,LU Chunjing,WANG Ying. Preparation and Foam Properties of Janus Particles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 990. |
| [11] | LUO Jianhui,YANG Jie,LI Yuanyang,HE Lipeng,JIANG Bo. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Silica Nanoparticles with Double-sphere Morphology† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2170. |
| [12] | JIANG Rongjun, LUO Jianhui, BAI Ruibing, JIANG Bo, ZHOU Ge. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Behavior of Common Surfactants at the Oil/Water Interface in Complex Systems† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1804. |
| [13] | LIU Kaihong, LIN Qi, CUI Zhenggang, PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong. pH-Responsive Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles in Combination with N-Dodecyl-β-aminopropionate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 85. |
| [14] | LIU Xuewu,CHEN Shuhua,ZHAN Shiping. Experimental Study and Theoretical Phase Diagram Calculation for Polystyrene Membranes Prepared by Supercritical CO2-induced Phase Inversion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1573. |
| [15] | YAN Huiqiong, CHEN Xiuqiong, LI Jiacheng, FENG Yuhong, WU Jianbo, LIN Qiang, SHI Zaifeng, WANG Xianghui. Synthesis of Amidic Alginate Derivatives Modified Silica Nanoparticles via Ugi Multicomponent Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 1018. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||