

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 250.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130801
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUE Weichao, CAI Zhuo*( ), JIANG Cuiwen, YE Danni
), JIANG Cuiwen, YE Danni
Received:2013-08-19
Online:2014-02-10
Published:2013-12-05
Contact:
CAI Zhuo
E-mail:zhuocai@gxu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YUE Weichao, CAI Zhuo, JIANG Cuiwen, YE Danni. Determination of Levodopa Using Biosynthesed Gold Nanoparticles/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/L-Cysteine Composite Film Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 250.
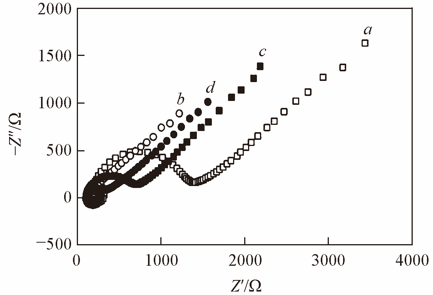
Fig.4 Alterating current impedance spectra of GCE(a), MWCNTs/GCE(b) MWCNTs/L-Cys/GCE(c) and Au/MWCNTs/L-Cys/GCE(d) in 0.10 mol/L KCl containing 5.0×10-3 mol/L Fe(CN)63-/4-(volume ratio 1∶1)Frequency range: 0.001—105 Hz.
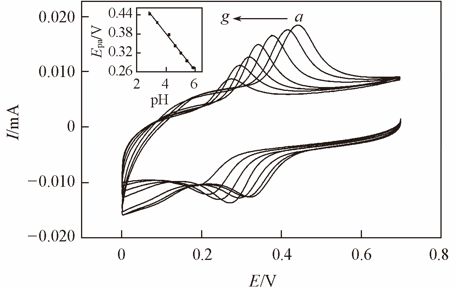
Fig.6 CV curves of 1.0×10-4 mol/L levodopa in buffers with different pH valuespH values from a to g: 2.6, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0. Inset shows the effect of pH on peak potential.
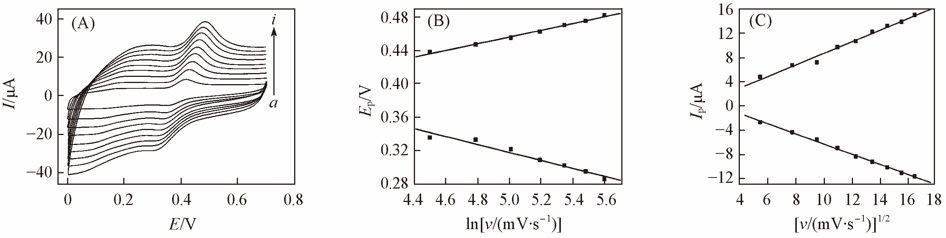
Fig.7 Cyclic voltammograms of 1.0×10-4 mol/L levodopa with different scan rates(A), effects of the natural logarithm of scan rate on peak potential(B) and the square root of scan rate on peak current(C)Scan rate(mV·s-1) from a to i: 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, 240, 270.
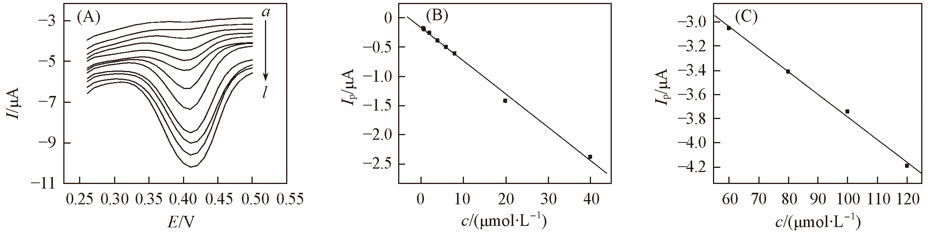
Fig.8 Differential pulse voltammograms of levodopa with different concentrations(A) and calibration curves of levodopa in the range of 0.6—40 μmol/L(B) and 60—120 μmol/L(C)(A) c(Levodopa)/(μmol·L-1): 0.6, 0.8, 2, 4, 6, 8, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120.
| Labelled amount/(mg·table-1) | Found/(mg·table-1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical method | UV-Vis method | |
| 250.0 | 252.3 | 256.3 |
| 250.0 | 249.4 | 254.5 |
| 250.0 | 251.6 | 253.2 |
| 250.0 | 248.5 | 255.6 |
| 250.0 | 250.5 | 253.2 |
| Average value±SD | 250.5±1.4 | 254.9±2.1 |
Table 1 Determination of levodopa in tablet
| Labelled amount/(mg·table-1) | Found/(mg·table-1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical method | UV-Vis method | |
| 250.0 | 252.3 | 256.3 |
| 250.0 | 249.4 | 254.5 |
| 250.0 | 251.6 | 253.2 |
| 250.0 | 248.5 | 255.6 |
| 250.0 | 250.5 | 253.2 |
| Average value±SD | 250.5±1.4 | 254.9±2.1 |
| Labelled amount/(μmol·L-1) | Added/(μmol·L-1) | Found/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.02 | 2.00 | 3.99 | 99.2 | 4.04 |
| 2.02 | 4.00 | 6.10 | 101.3 | |
| 2.02 | 6.00 | 8.22 | 91.2 | |
| 2.02 | 8.00 | 10.05 | 102.5 | |
| 2.02 | 10.00 | 12.06 | 100.3 |
Table 2 Recovery of the method
| Labelled amount/(μmol·L-1) | Added/(μmol·L-1) | Found/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.02 | 2.00 | 3.99 | 99.2 | 4.04 |
| 2.02 | 4.00 | 6.10 | 101.3 | |
| 2.02 | 6.00 | 8.22 | 91.2 | |
| 2.02 | 8.00 | 10.05 | 102.5 | |
| 2.02 | 10.00 | 12.06 | 100.3 |
| [1] | Xing X., Zhao C. Y., J. Heze Med. College, 2001, 13(3), 10—12 |
| (邢霞, 赵存英.荷泽医专学报,2001, 13(3), 10—12) | |
| [2] | Wang C., Wang Z., Han D. D., Hu Y. X., Zhao J., Yang X. M., Song S. J., Chin. J. Chrom., 2006, 24(4), 389—341 |
| (王春, 王志, 韩丹丹, 胡彦学, 赵锦, 杨秀敏, 宋双居.色谱,2006, 24(4), 389—341) | |
| [3] | Li S. Y., Yang Y. P., Chen Y. F., Chin. J. Pharm. Anal., 2006, 26(10), 1506—1507 |
| (李省云, 杨毅萍, 陈艳芳.药物分析杂志,2006, 26(10), 1506—1507) | |
| [4] | Zhu A. Z., Liu J., Fu C. G., J. Instrum. Anal., 1997, 16(6), 47—50 |
| (朱爱芝, 刘军, 傅承光.分析测试学报,1997, 16(6), 47—50) | |
| [5] | Ma H. Y., Zheng X. W., Zhang Z. J., J. Instrum. Anal., 2005, 24(4), 58—60 |
| (马红燕, 郑行望, 章竹君.分析测试学报,2005, 24(4), 58—60) | |
| [6] | Xiang C.L., Studies on the Characterization of Nafion Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode and Its Analytical Applications, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 2006 |
| (向翠丽. Nafion膜修饰电极的研究与应用, 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2006) | |
| [7] | Geng G. G., Northern Horticulture, 2012, 26(2), 26—27 |
| (耿贵工.北方园艺,2012, 26(2), 26—27) | |
| [8] | Shen H., Xiao H., Li R., Practical Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies, 2010, 13(1), 32—36 |
| (沈鸿, 肖红, 李瑞.实用药物与临床,2010, 13(1), 32—36) | |
| [9] | Zhao Y. Y., Liu L. Y., Han Y. Y., Bai J., Du G. L., Gao Q., Chin. J. Chrom., 2011, 29(2), 48—50 |
| (赵燕燕, 刘丽艳, 韩媛媛, 白洁, 杜光玲, 高茜.色谱,2011, 29(2), 48—50) | |
| [10] | Voorhees P. W., J. Statist. Phys., 1985, 38(1/2), 231—252 |
| [11] | Wang G. F., Zhu Y. H., Chen L., Wang L., Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 2013, 41(4), 608—615 |
| (王广凤, 朱艳红, 陈玲, 王伦.分析化学,2013, 41(4), 608—615) | |
| [12] | Castro L. E., Vilchis N. A., Avalos B. M., Colloid Surf. B: Biointerfaces, 2011, 83(1), 42—48 |
| [13] | Shankar S. S., Rai A., Anlkamwar B., Singh A., Ahmad A., Sastry M., Nat. Mater., 2004, 3(7), 482—488 |
| [14] | Chandran S. P., Chaudhary M., Pasricha R., Ahmad A., Sastry M., Biotechnol. Prog., 2006, 22(2), 577—583 |
| [15] | Gardea T. J., Parsons J. G., Gomez E., Peralta V. J., Troiani H. E., Santiago P., Yacaman M. J., Nano Lett., 2002, 2(4), 397—401 |
| [16] | Shankar S. S., Rai A., Ahmad A., Sastry M., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2004, 275(2), 496—502 |
| [17] | Anlkamwar B., Chaudhary M., Sastry M., Synth. React. Inorg. Met.: Org. Nanometal Chem., 2005, 35(1), 19—26 |
| [18] | Huang J. L., Li Q. B., Sun D. H., Lu Y. H., Su Y. B., Yang X., Wang H. X., Wang Y. P., Shao W. Y., He N., Hong J. Q., Nanotechnology, 2007, 18(10), 105104-1—105104-11 |
| [19] | Philip D., Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 2010, 77A(4), 807—810 |
| [20] | Kong W. Q., Li Y. W., Research and Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2005, 7(6), 22—24 |
| (孔文琦, 李严巍.中药研究与信息,2005, 7(6), 22—24) | |
| [21] | Chen T. R., Zhang W., Meng X. Y., Sun J., Applied Chemical Industry, 2009, 38(9), 1273—1275 |
| (陈亭汝, 张玮, 孟祥英, 孙瑾. 应用化工. 2009, 38(9), 1273—1275 | |
| [22] | Laviron E., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1979, 101(1), 19—28 |
| [1] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [2] | GUAN Fanglan,LI Xin,ZHANG Qun,GONG Yan,LIN Ziyu,CHEN Yao,WANG Lejun. Fabrication and Capacitance Performance of Laser-machined RGO/MWCNT/CF In-plane Flexible Micro-supercapacitor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 300. |
| [3] | SUN Mengmeng,CHANG Chunrui,ZHANG Zhiming,AN Libao. Preparation and Electrical Contact Properties of Palladium-doped Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 11. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yanan, YANG Lingling, TU Jiawei, CUI Ran, PANG Daiwen. Live-cell Synthesis of ZnSe Quantum Dots in Staphylococcus aureus† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1158. |
| [5] | MIAO Rui,WU Dongxue,WANG Qiuying,ZHAO Huanxi,LI Xue,XIU Yang,LIU Shuying. Rapid Separation of Ginsenosides Based on Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2178. |
| [6] | XU Kaige, ZHANG Di, LEI Jie, PENG Yage, PENG Juan, JIN Xiaoyong. Au Nanowires-MWCNTs Modified Electrode for Catalyzing the Oxidization of Glucose† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1864. |
| [7] | LI Yan-Yan, RAO Lu, JIANG Yan-Xia, LIU Zi-Li, HE Chun-Lan, ZHANG Bin-Wei, SUN Shi-Gang. Electrooxidation of Ethanol on Platinum Nanocubes Supported on Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2): 408. |
| [8] | XUE Shan-Shan, SUI Gang, YANG Xiao-Ping. Preparation and Characterization of the Precursor Nanofiber of Nano-Carbon Fibers with Carboxylated Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2): 288. |
| [9] | ZHAO Hong-Bin*, XU Lan-Lan, WANG Hong-Ke, ZHANG Hui, WANG Wu-Lin, .... Covalently and Non-covalently Modification of Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes with Tetra-(4-hydrazidephenyl)porphyrin and Metalloporphyrin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(4): 696. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xue-Yu, LIU Xing-Mei, LIU Wei-Lu, YANG Ming*, ZHANG Zhi-Quan*. Electrochemical Behavior and Determination of Indole-3-acetic Acid at NanoAu/MWNTs/chitosant Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(1): 33. |
| [11] | XIA Xiao-Dong*, SHEN Guo-Li, YU Ru-Qin. Silver Colloid Induced Noncovalent Surface Modification of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(8): 1477. |
| [12] |
YE She-Fang1*, ZHONG Li-Ming1, WU Yi-Hui1, ZHANG Qi-Qing1,2* . Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes Exposure Induces Oxidative Stress and Depolarizes Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Cultured A549 Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(3): 497. |
| [13] | WANG Xiao1, ZHANG Chen1, LIU Yan-Xin1, LI Cong-Ju2, DU Zhong-Jie1, LI Hang-Quan1. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyurethane-grafted Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(2): 366. |
| [14] | ZHANG Xiong-Wei, CHU Wei, ZHUANG Hui-Xiang, XU Shi-Wei . Modification of Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes and Its Performance for Hydrogen Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(3): 493. |
| [15] | LIU Jing, MAO Zong-Qiang, HAO Dong-Hui, ZHANG Xian-Feng, XU Cai-Lu, WU De-Hai . Electrochemical Storage Hydrogen of the Aligned Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(2): 334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||