

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1864.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160907
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Kaige, ZHANG Di, LEI Jie, PENG Yage, PENG Juan, JIN Xiaoyong*( )
)
Received:2016-12-16
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-09-22
Contact:
JIN Xiaoyong
E-mail:jinxy588@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XU Kaige, ZHANG Di, LEI Jie, PENG Yage, PENG Juan, JIN Xiaoyong. Au Nanowires-MWCNTs Modified Electrode for Catalyzing the Oxidization of Glucose†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1864.
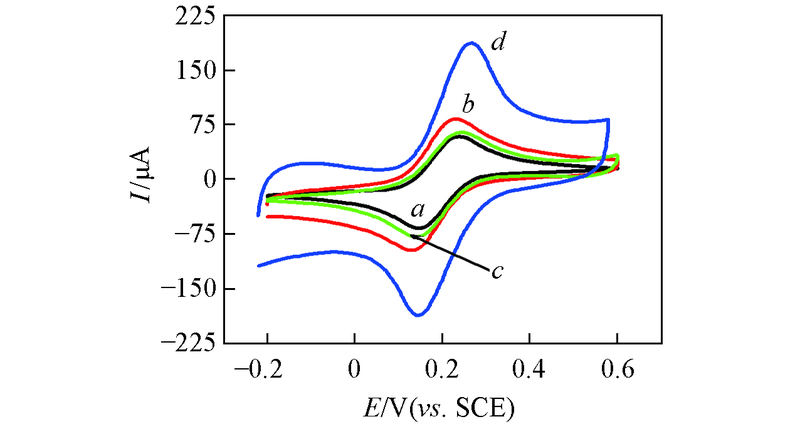
Fig.3 CV curves of bare GCE(a), MWCNTs/GCE(b), Au nanowires/GCE(c), Au nanowires-MWCNTs/GCE(d) in 10.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6] solution containing 0.1 mol/L KCl at the scan rate of 100 mV/s
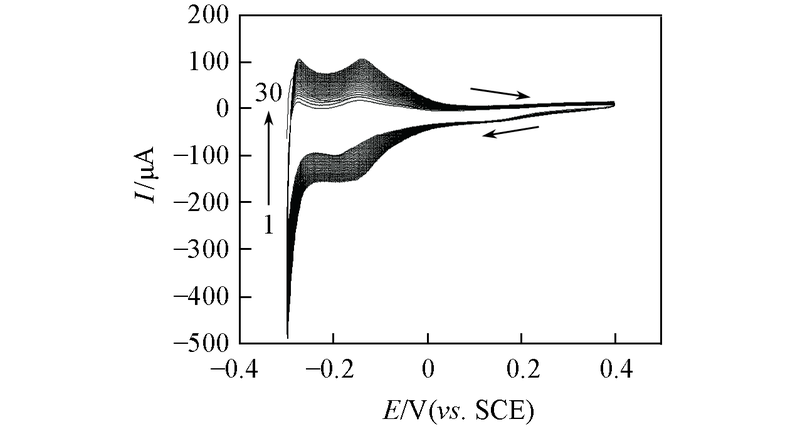
Fig.4 CV curves for electrodeposition process of the Pt film obtained from a solution mixture containing 1.8 × 10-3 mol/L H2PtCl6 and 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 between 0.4 and -0.3 V(vs. SCE) at 100 mV/s
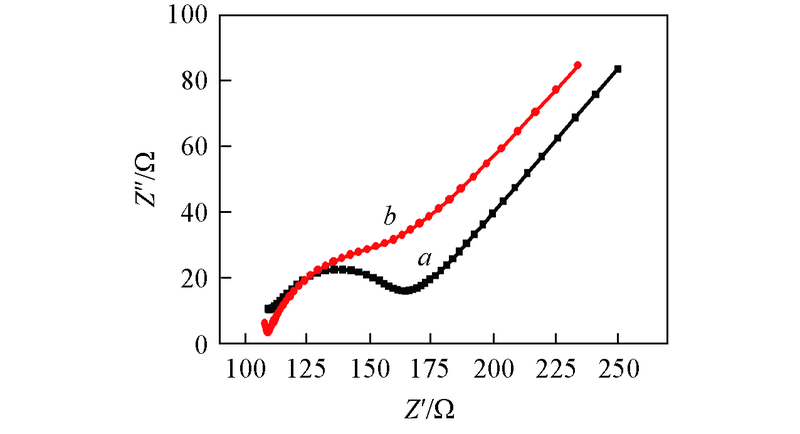
Fig.5 Electrochemical impedance spectra(EIS) in a mixture containing 5.0 mmol/L [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- and 0.1 mol/L KCl at bare GCE(a) and Pt/GCE(b), respectively
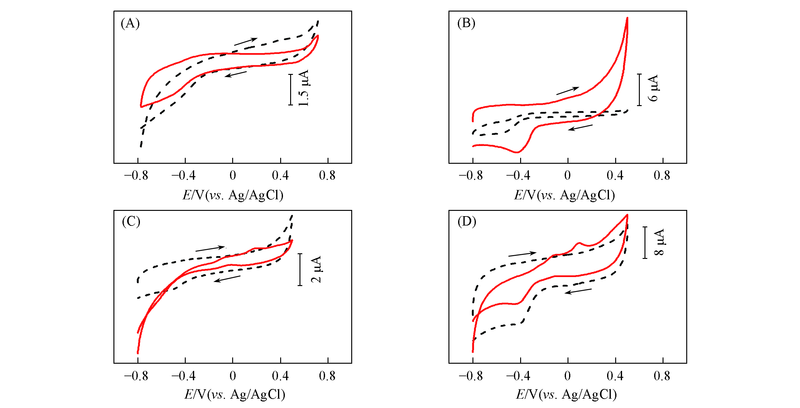
Fig.6 CV curves of bare GCE(A), MWCNTs/GCE(B), Au nanowires/GCE(C), Au nanowires-MWCNTs/GCE(LBL2)(D) in 0.5 mol/L NaOH in the absence(dash line) and presence(solid line) of 5 mmol/L glucose at the scan rate of 60 mV/s
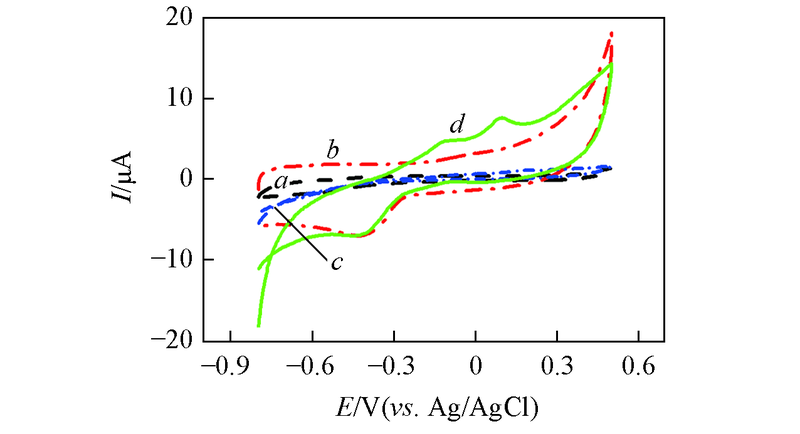
Fig.7 CV curves of bare GCE(a), MWCNTs/GCE(b), Au nanowires/GCE(c) and Au nanowires-MWCNTs/GCE(LBL2)(d) in 0.5 mol/L NaOH in the presence 5 mmol/L glucose at the scan rate of 60 mV/s
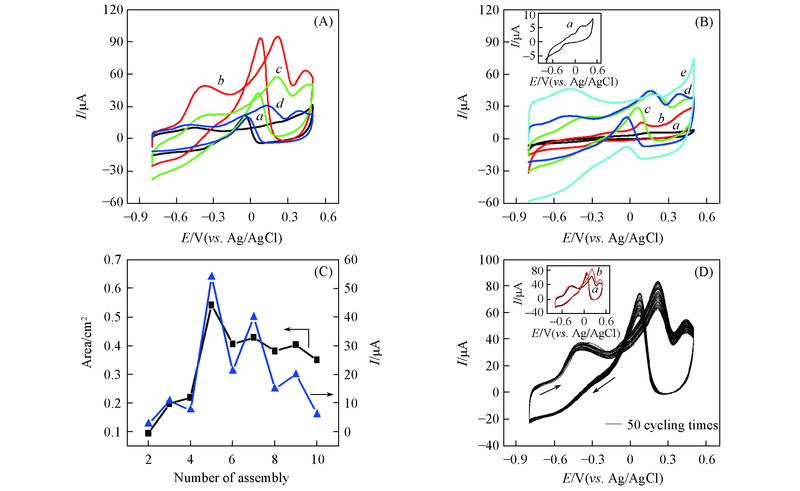
Fig.8 CV curves of network film electrodes with odd numbers of layers(A) and even numbers of layers(B) in 0.5 mol/L NaOH+20.0 mmol/L glucose at the scan rate of 60 mV/s, the line graphs of the response current(▲) and effective electrode area(■) to the number of assembly layers(C) and the cycling CV curves of Au nanowires-MWCNTs/GCE(LBL5) for 50 cycling times in 0.5 mol/L NaOH+20.0 mmol/L glucose at the scan rate of 60 mV/s(D)(A) a. LBL3; b. LBL5; c. LBL7; d. LBL9. (B) a. LBL2; b. LBL4; c. LBL6; d. LBL8; e. LBL10. Inset of (D) shows the CV curves of the first cycling times(a) and the last cycling times(b).
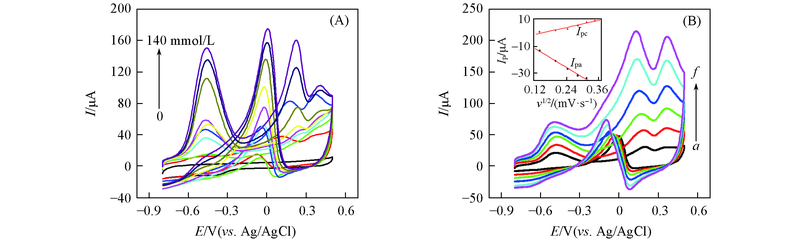
Fig.9 CV curves of Au nanowires-MWCNTs/GCE(LBL5) in 0.5 mol/L NaOH containing 0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 40.0, 60.0, 80.0, 100.0, 120.0, 140.0 mmol/L glucose at the scan rate of 60 mV/s(A) and CV curves of Au nanowires-MWCNTs/GCE(LBL5) in 0.5 mol/L NaOH solution containing 20.0 mmol/L glucose at scan rates of 20(a), 40(b), 60(c), 80(d), 100(e), 120 mV/s(f)(B), respectivelyInset of (B) shows the plots of anodic and cathodic peak currents vs. v1/2.
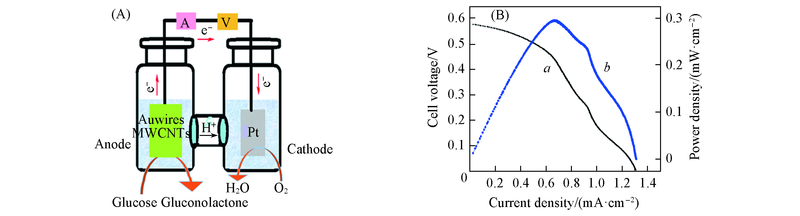
Fig.11 Schematic illustration for the principle of glucose/O2 fuel cell(A) and polarization curve(a) and power density curve(b) at room temperature for a glucose/O2 fuel cell(B)Anode: LBL5 in 0.5 mol/L NaOH cotaining 100.0 mmol/L glucose. Cathode: Pt/GCE in 0.1 mol/L PBS filled with O2.
| Mimic enzyme | Open circuit-potential/V | Maximum power density/(μW·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co/NG | 0.79 | 150 | [ |
| Auglu/GCE | 0.916 | 307 | [ |
| 3D porous Pd | 0.650±0.005 | 5.7±0.4 | [ |
| Au nanowires | 0.425 | 126 | [ |
| MWCNT/(DPDE)Ⅲ | 0.64 | 182 | [ |
| Au nanowires-MWCNTs | 0.57 | 280 | This work |
Table 1 Performance comparison for glucose fuel cell among nanoparticles film electrodes
| Mimic enzyme | Open circuit-potential/V | Maximum power density/(μW·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co/NG | 0.79 | 150 | [ |
| Auglu/GCE | 0.916 | 307 | [ |
| 3D porous Pd | 0.650±0.005 | 5.7±0.4 | [ |
| Au nanowires | 0.425 | 126 | [ |
| MWCNT/(DPDE)Ⅲ | 0.64 | 182 | [ |
| Au nanowires-MWCNTs | 0.57 | 280 | This work |
| [1] | Zebda A., Cosnier S., Alcaraz J. P., Holzinger M., Le G. A., Gondran C., Boucher F., Giroud F., Gorgy K., Lamraoui H., Cinquin P., Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 1516—1520 |
| [2] | Tayhas R. P. G., Trends Biotechnol., 2004, 22(3), 99—100 |
| [3] | Zou Q., Liu J., Zhu G. B., Zhang X. H., Chen J. H., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71, 1154—1160 |
| (邹琼, 刘娟, 朱刚兵, 张小华, 陈金华. 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1154—1160) | |
| [4] | Devaraj M., Deivasigamani R. K., Jeyadevan S., Colloids Surf. B, 2013, 102, 554—561 |
| [5] | Lee Y. J., Park J. Y., Sensors, IEEE, 2010, 1875—1878 |
| [6] | Fujiwara N., Yamazaki S., Siroma Z., Ioroi T., Senoh H., Yasuda K., Electrochem. Commun., 2009, 11(2), 390—392 |
| [7] | Zhang W., Wang Z., Shen Y., Xi M., Chu X., Xi C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2015, 31(6), 1007—1011 |
| [8] | Xiong T., Lin J. Y., Shang Z. J., Zhang X. T., Lin X., Tian W., Zhong Q. L., Ren B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(11), 2460—2465 |
| (熊婷, 林剑云, 商中瑾, 张贤土, 林旋, 田伟, 钟起玲, 任斌. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(11), 2460—2465) | |
| [9] | Ci S. Q., Wen Z. H., Mao S., Hou Y., Cui S. M., He Z., Chen J. H., Chem. Commun., 2015, 51(45), 9354—9357 |
| [10] | You X. X., Fan J. C., Huang W., Zhou Y. Z., Wei J. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(9), 1694—1700 |
| (游向轩, 樊金串, 黄伟, 周由之, 魏珺谊. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(9), 1694—1700) | |
| [11] | Navaeea A., Narimania M., Korania A., Ahmadib R., Salimia A., Soltanianc S., Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 208, 325—333 |
| [12] | An L., Zhao T. S., Shen S. Y., Wu Q. X., Chen R., J. Power Sources,2011, 196(1), 186—190 |
| [13] | Xu K., Li Y., Zhao N., Du W. X., Zeng W. W., Gao S., Cheng X. N., Yang J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(8), 1476—1484 |
| (徐凯, 李毅, 赵南, 杜文修, 曾炜炜, 高帅, 程晓农, 杨娟. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(8), 1476—1484) | |
| [14] | Kaura B., Srivastava R., Satpatib B., ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(4), 2654—2663 |
| [15] | Hu J., Shao D., Chen C., Sheng G., Ren X., Wang X., J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 185(1), 463—471 |
| [16] | Liu S. M., Zheng Y. D., Li W., Sun Y., Yue L. N., Zhao Z. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(2), 290—296 |
| (刘树敏, 郑裕东, 李伟, 孙乙, 岳丽娜, 赵振江. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2), 290—296) | |
| [17] | Elouarzaki K., Le Goff. A., Holzinger M., Thery J., Cosnier S., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 134(34), 14078—14085 |
| [18] | Zhu N. N., Lin Y. Q., Yu P., Su L., Mao L. Q., Anal. Chim. Acta,2009, 650(1), 44—48 |
| [19] | Yang L., Zhang Y., Chu M., Deng W., Tan Y., Ma M., Su X., Xie Q., Yao S., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 52, 105—110 |
| [20] | Wang P., Li F., Huang X., Li Y., Wang L., Electrochem. Commun., 2008, 10(2), 195—199 |
| [21] | Qin Q. X., Liu S. L., Plating and Finishing,2008, 30(7), 29—34 |
| (覃奇贤, 刘淑兰. 电镀与精饰, 2008, 30(7), 29—34) | |
| [22] | Huo Z. Y., Tsung C., Huang W. Y., Zhang X. F., Yang P. D., Nano Lett., 2008, 8(7), 2041—2044 |
| [23] | Yu A. M., Liang Z. J., Cho J. H., Caruso F., Nano Lett., 2003, 3(9), 1203—1207 |
| [24] | Kruusenberg I., Alexeyeva N., Tammeveski K., Carbon,2009, 47(3), 651—658 |
| [25] | Deo R. P., Wang J., Electrochem. Commun., 2004, 6(3), 284—287 |
| [26] | YeJ. S., Wen Y., Zhang W. D., Gan L. M., Xu G. Q., Sheu F. S., Electrochem. Commun., 2004, 6(1), 66—70 |
| [27] | Chen W., Chen S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(24), 4386—4389 |
| [28] | Cherevko S., Chung C., Sens. Actuators B, 2009, 142(1), 216—223 |
| [29] | Rong L., Yang C., Qian Q., Xia X., Talanta,2007, 72(2), 819—824 |
| [30] | Song Y., Zhang D., Gao W., Xia X., Chem. Eur. J., 2005, 11(7), 2177—2182 |
| [31] | Dong S. J.,Chemistry Online, 1981, (12), 713—721 |
| (董绍俊. 化学通报, 1981, (12), 713—721) | |
| [32] | Xie F. Y., Huang Z., Chen C., Xie Q. J., Huang Y., Qin C., Liu Y., Su Z. H., Yao S. Z., Electrochem. Commun., 2012, 18, 108—111 |
| [33] | Zhao Y., Fan L. Z., Hong B., Zhang Y., Zhang M. S., Que Q. M., Ji J. Y., Energy Technology, 2016, 4(2), 249—255 |
| [1] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [2] | LI Zhiguang, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Role of Catalyst Acidity in Glucose Conversion over Sn-Al-β Zeolite as Studied by Solid-state NMR [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220138. |
| [3] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [4] | LUO Bian, ZHOU Fen, PAN Mu. Study on Preparation and Accessibility of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Supported Platinum Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [5] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [6] | XIA Dacheng, ZHOU Rui, TU Bo, CAI Zhiwei, GAO Nan, JI Xiaoxu, CHANG Gang, REN Xiaoming, HE Yunbin. Fabrication of Ag/Au Nanowires Array as a SERS Substrate for High-sensitivity Malachite Green Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210731. |
| [7] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [8] | YUAN Chunling, YAO Xiaotiao, XU Yuanjin, QIN Xiu, SHI Rui, CHENG Shiqi, WANG Yilin. Colorimetry/Ratio Fluorimetry Determination of Glucose with Bifunctional Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2428. |
| [9] | CAO Kaiyue, PENG JinWu, LI Hongbin, SHI Chengying, WANG Peng, LIU Baijun. High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole/hyperbranched-polymer Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2049. |
| [10] | PU Yangyang, NING Cong, LU Yao, LIU Lili, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Characterizations of Cross-linked Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Partially Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Blend Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2002. |
| [11] | LI Liu, SUN Shiyong, LYU Rui, GOLUBEV Yevgeny Aleksandrovich, WANG Ke, DONG Faqin, DUAN Tao, KOTOVA Olga Borisovna, KOTOVA Elena Leonidovna. Construction of Fe-aminoclay-glucose Oxidase Nanocomposite Catalyst and Its Multi-enzyme Cascade Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 803. |
| [12] | WANG Baichun, YUAN Yuxin, YAN Yinghua, DING Chuanfan, TANG Keqi. Glucose-6-phosphate Functionalized Hydrophilic Magnetic Probe: a Dual-purpose Affinity Material for Effective Separation and Enrichment of Glycopeptides/Phosphopeptides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3062. |
| [13] | WANG Huan, SUO Jinquan, WANG Chunyan, WANG Runwei. Glucose Oxidase Immobilization with Amino Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Its Application in Glucose Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1731. |
| [14] | WANG Yuemin, MENG Qinglei, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Enhancement of Performance of Fe-N-C Catalysts by Copper and Sulfur Doping for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1843. |
| [15] | YE Xiaodong, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Glucose Oxidation on Au-supported SBA-15 Molecular Sieve † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 960. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||