

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 20240305.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240305
收稿日期:2024-06-24
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-08-15
通讯作者:
韩珍珍
E-mail:hanzhenzhen@ahmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIN Ying1, ZHANG Junjie1, ZHANG Yixin1, YUAN Yue2, HAN Zhenzhen1( )
)
Received:2024-06-24
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-08-15
Contact:
HAN Zhenzhen
E-mail:hanzhenzhen@ahmu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
外泌体是多泡体与细胞质膜融合时释放的细胞外囊泡, 含有蛋白质、 脂质和核酸等. 它以细胞外囊泡的形式运送货物, 参与多种癌症过程(如侵袭和转移), 被认为是液体活检的新兴靶标, 其在细胞通讯、 信号传导和免疫应答中发挥着重要的作用. 质谱法已成为蛋白质组学研究领域不可或缺的一部分, 外泌体的蛋白质组学分析是发现潜在癌症生物标志物的一种很有前途的方法. 高分辨率分离、 高效质谱分析和全蛋白质组数据库的最新进展都有助于患者样本中外泌体的成功分析. 本文综合评述了外泌体的分离方法、 蛋白质组学分析技术以及基于外泌体的蛋白质组学分析在临床疾病诊断的应用研究. 最后, 对外泌体分离和蛋白质组学面临的挑战及在临床应用中的前景进行了展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
靳莹, 张俊杰, 张毅欣, 袁悦, 韩珍珍. 外泌体分离和蛋白质组学分析的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240305.
JIN Ying, ZHANG Junjie, ZHANG Yixin, YUAN Yue, HAN Zhenzhen. Research Progress in Exosome Isolation and Proteomics Analysis. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(11): 20240305.
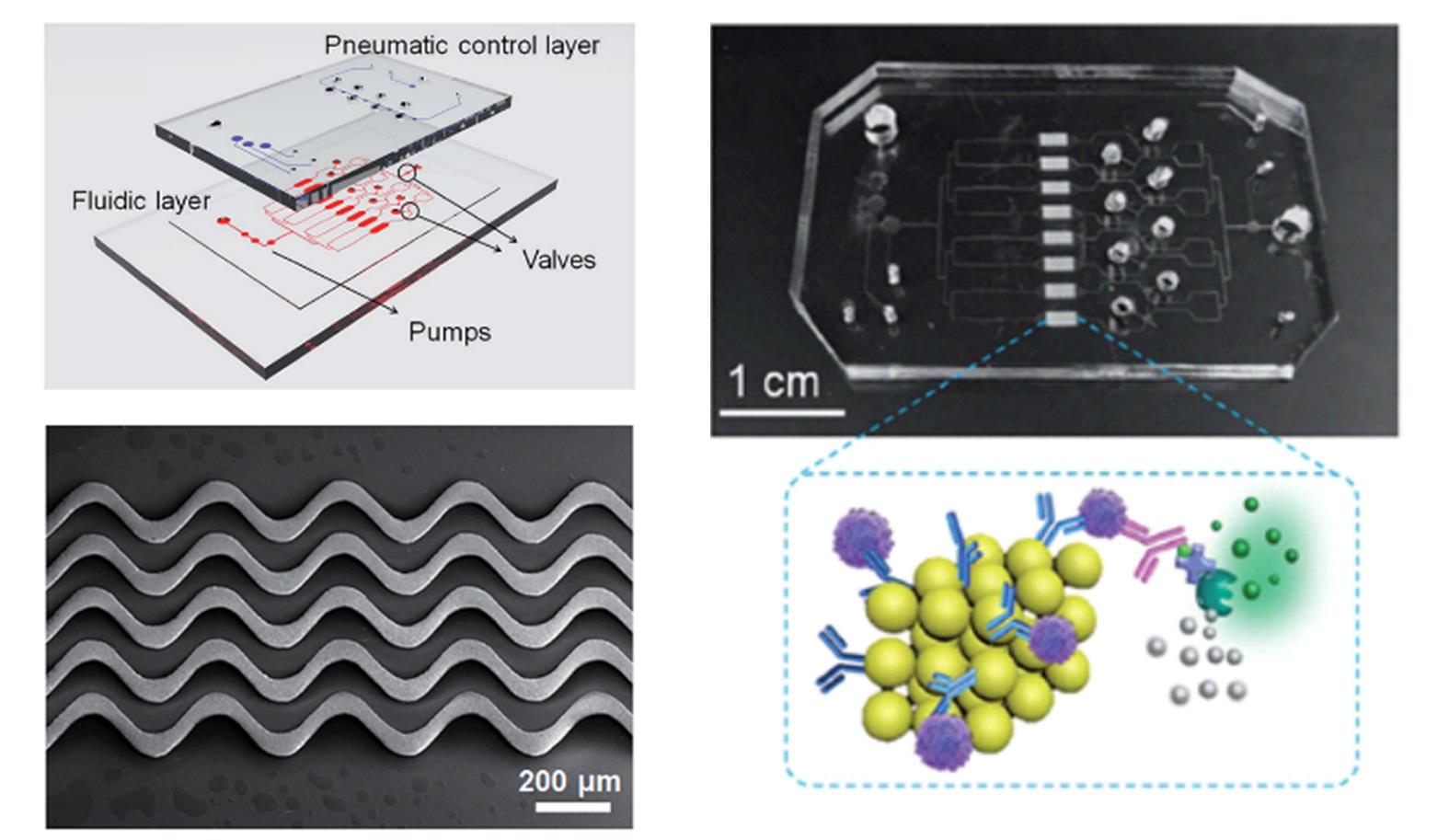
Fig.5 ExoProfile chip consists of pneumatic and fluidic layer and 3D serpentine nanostructures for in situ immunophenotyping of exosomes[44]Copyright 2019, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
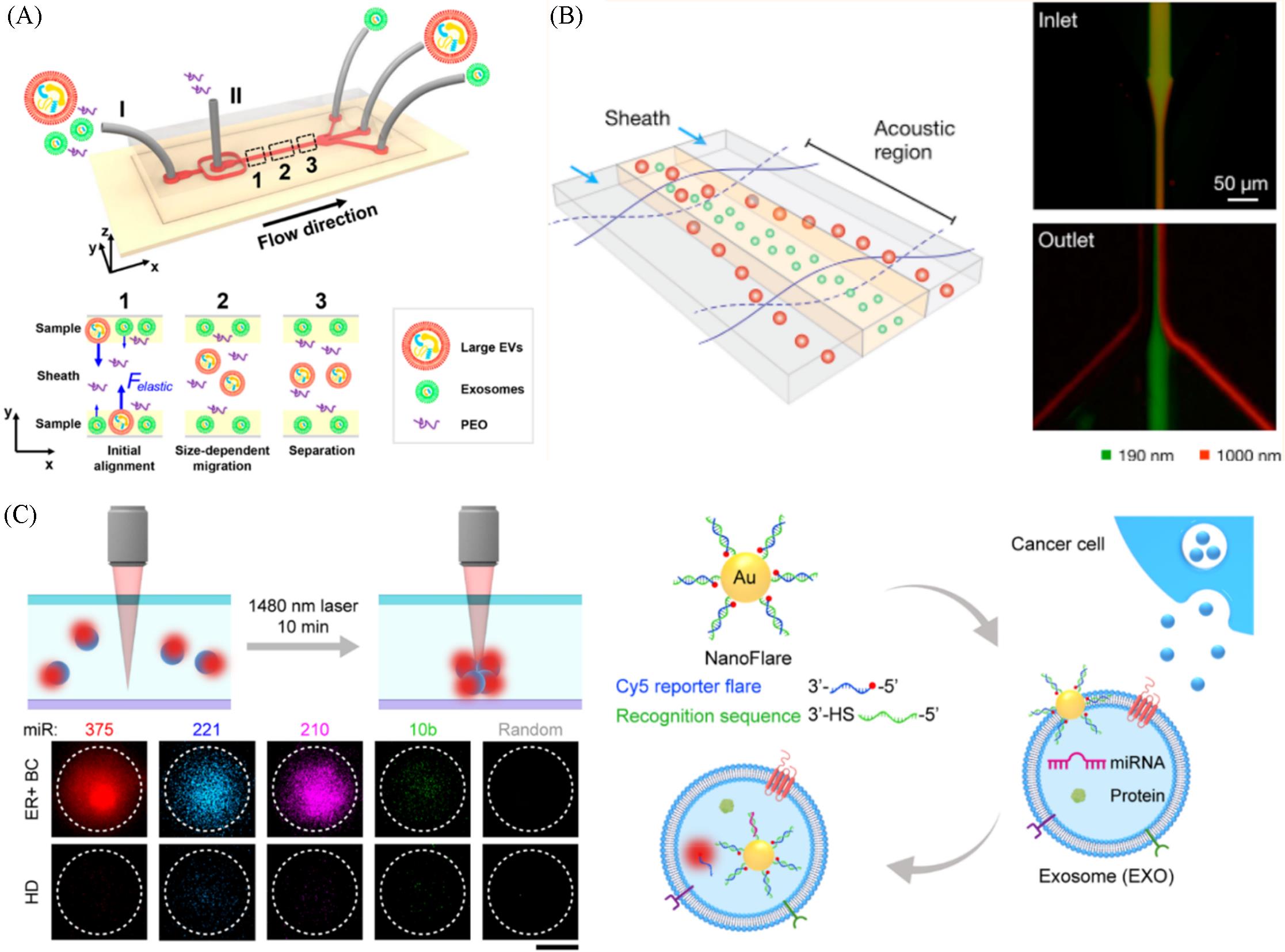
Fig.6 Viscoelastic microfluidic system consisted of a high⁃aspect⁃ratio straight microchannel for size⁃based exosome isolation(A)[45], the acoustic nanofilter system size⁃specifically separating microvesicles in a continuous and contact⁃free manner(B)[49], the thermophoretic aptasensor implemented with nanoflares for in situ detection of exosomal miRNAs(C)[53](A) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| Sample⁃handling approach | Beneficial feature | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| In⁃gel digestion | Enzymatic digestion of proteins within the gel environment, enhancing protein recovery rates Simplify operational steps Robustness and efficient impurity removal capability | Time⁃consuming Introduce contamination from the gel, enzymes, or other reagents |
In⁃solution processing methods, such as standard in⁃solution digestion | Applicable to virtually any sample Simple protocols that require minimal handling Generally, afford high recovery of protein input, making them adaptable to a wide range of sample quantities Easily adaptable to high⁃throughput regimes | Limited selection of reagents that can be used for protein extraction and solubilization In specific scenarios, processing volumes required for dilution can challenge downstream handling Diluted chaotropes in solution can hinder proteolysis Downstream removal of acid⁃labile detergents can result in material losses |
| FASP | Compatible with a wide range of lysis and protein solubilization components Effective processing of high input quantities of material Most protocols are simple and flexible for adaptation to different sample types | Processing can be time consuming and laborious When working with small input quantities, material losses can be substantial Reagent compatibility can be limited by consumables(e. g., filter compatibility) |
| SP3 | Applicable to virtually any sample Compatible with a wide range of lysis and protein solubilization components Simple protocol that requires minimal handling Provides high recovery of protein input, making it adaptable to a wide range of sample quantities Rapid processing of large numbers of samples in parallel | Recovery of intact proteins from the paramagnetic beads can be challenging High concentrations of intact chromatin can reduce performance Bead clumping and aggregation can hinder adaptation to high⁃throughput automation |
| SISPROT | The preparation steps of proteomics samples are fully integrated Simple protocol that requires minimal handling Easily multiplexed on standard centrifuges with good reproducibility | It is not compatible with the rare cell proteomic reactor cell lysis buffer which contains 1% Triton Xs100 Costly consumables, high expenses |
| SPA | Simple protocol that requires minimal handling Provides improved efficiency, anti⁃interference ability, and recovery of low⁃input samples | Covalent binding of proteins hinders release of cysteine⁃containing peptides Low sequence coverage of proteins |
Table 1 Comparison between the properties of different proteome sample-handling approaches
| Sample⁃handling approach | Beneficial feature | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| In⁃gel digestion | Enzymatic digestion of proteins within the gel environment, enhancing protein recovery rates Simplify operational steps Robustness and efficient impurity removal capability | Time⁃consuming Introduce contamination from the gel, enzymes, or other reagents |
In⁃solution processing methods, such as standard in⁃solution digestion | Applicable to virtually any sample Simple protocols that require minimal handling Generally, afford high recovery of protein input, making them adaptable to a wide range of sample quantities Easily adaptable to high⁃throughput regimes | Limited selection of reagents that can be used for protein extraction and solubilization In specific scenarios, processing volumes required for dilution can challenge downstream handling Diluted chaotropes in solution can hinder proteolysis Downstream removal of acid⁃labile detergents can result in material losses |
| FASP | Compatible with a wide range of lysis and protein solubilization components Effective processing of high input quantities of material Most protocols are simple and flexible for adaptation to different sample types | Processing can be time consuming and laborious When working with small input quantities, material losses can be substantial Reagent compatibility can be limited by consumables(e. g., filter compatibility) |
| SP3 | Applicable to virtually any sample Compatible with a wide range of lysis and protein solubilization components Simple protocol that requires minimal handling Provides high recovery of protein input, making it adaptable to a wide range of sample quantities Rapid processing of large numbers of samples in parallel | Recovery of intact proteins from the paramagnetic beads can be challenging High concentrations of intact chromatin can reduce performance Bead clumping and aggregation can hinder adaptation to high⁃throughput automation |
| SISPROT | The preparation steps of proteomics samples are fully integrated Simple protocol that requires minimal handling Easily multiplexed on standard centrifuges with good reproducibility | It is not compatible with the rare cell proteomic reactor cell lysis buffer which contains 1% Triton Xs100 Costly consumables, high expenses |
| SPA | Simple protocol that requires minimal handling Provides improved efficiency, anti⁃interference ability, and recovery of low⁃input samples | Covalent binding of proteins hinders release of cysteine⁃containing peptides Low sequence coverage of proteins |
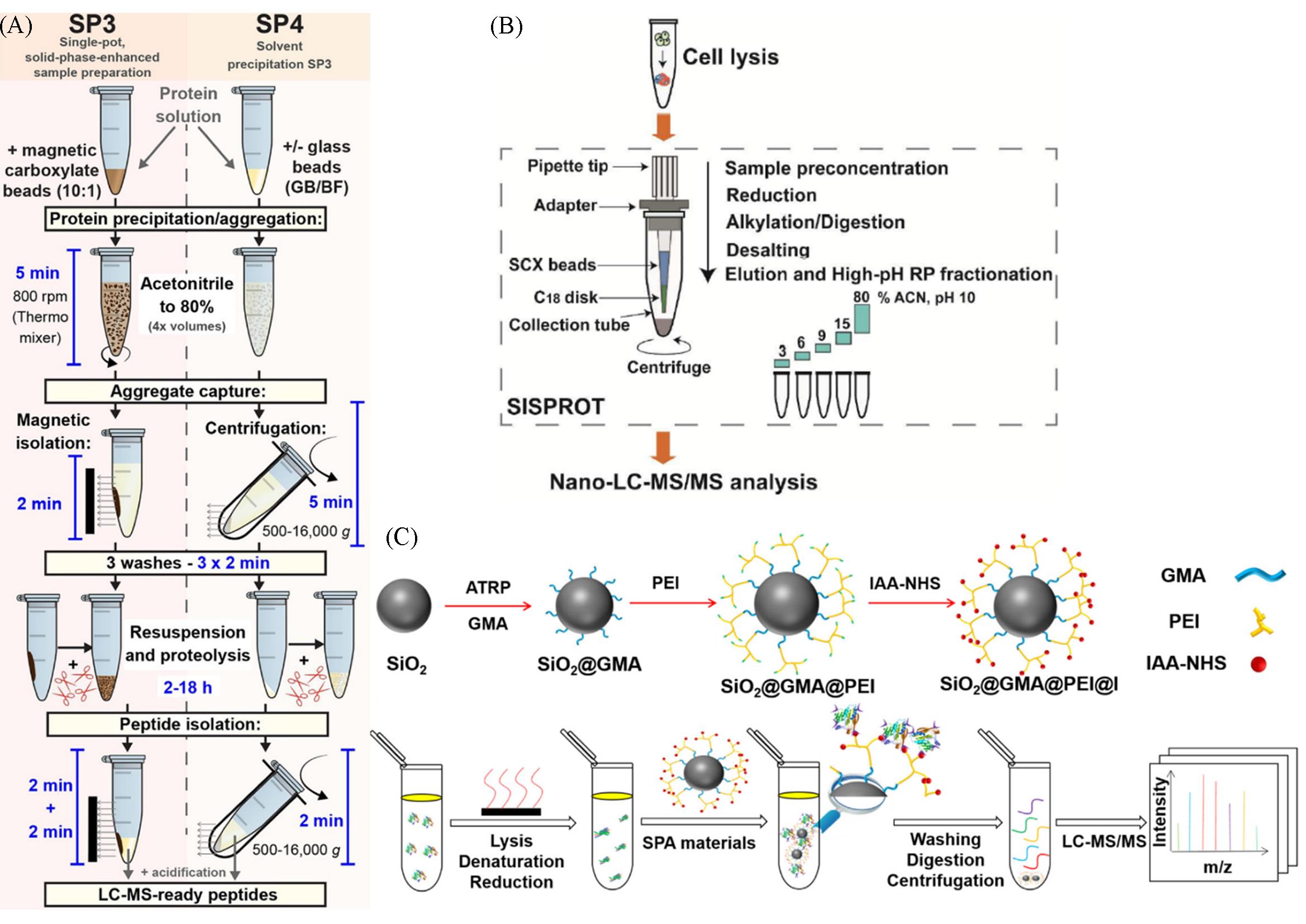
Fig.8 Summary of the SP3 and SP4 workflows(A)[61], schematic workflow of the simple and integrated SISPROT for deep proteome profiling(B)[62], the principle and procedure of the SPA⁃based sample preparation workflow(C)[66](A) Copyright 2022, Open Access; (B) Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
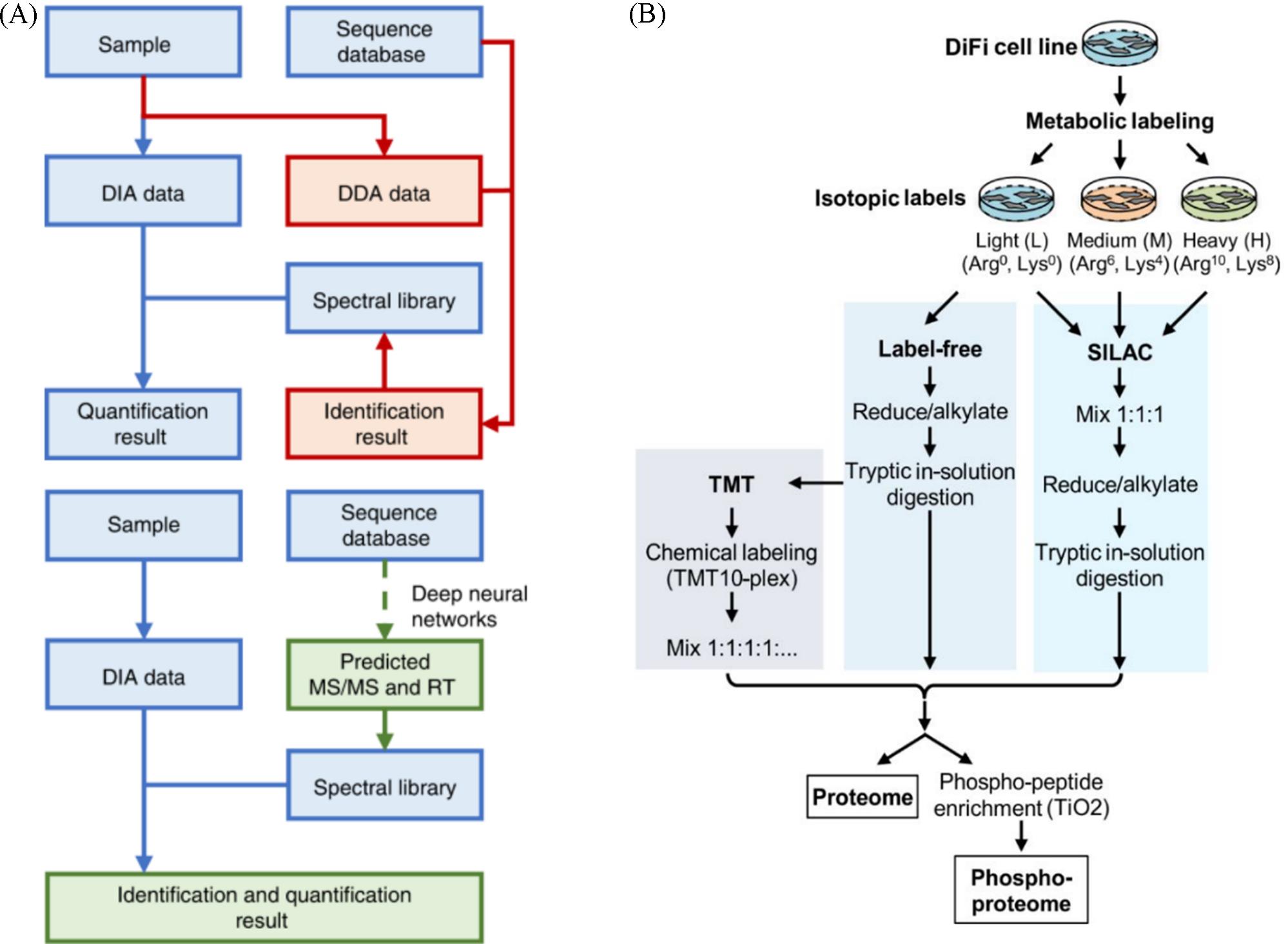
Fig.9 Workflow of conventional DIA analysis and DeepDIA(A)[82], cells were SILAC labeled with the light⁃labeled cells also analyzed by label⁃free and TMT approaches(B)[96](A) Copyright 2020, Nature; (B) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
| Type | Name | Labeling level | Beneficial feature | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic labeling | SILAC | Cells, organisms | Efficient labeling, one label for(tryptic) peptide, semiautomatic data analysis Applicable to cells but can be expanded to tissues or model organisms using internal standards (e.g., super⁃SILAC) | High costs, especially when applied to whole organisms Super⁃SILAC experiments have reduced quantitative proteome coverage Requires metabolically active cells to introduce labels |
| 15N labeling | Cells, organisms | Efficient labeling Applicable to cells and model organisms | Expensive Complex data analysis Limited multiplexing capability(up to 2⁃plex) Not suitable for clinical samples | |
Chemical labeling (in vitro) ⁃isobaric labeling | iTRAQ | Peptide | Efficient labeling enhanced signal intensity in MS and MS/MS, high multiplexing capability, simple data analysis Applicable to any sample(cells, animal or human tissue) Commercially available | Expensive Does not allow in vivo labeling Quantitative precision dependent on the reproducibility of sample preparation |
| TMT | Peptide | Efficient labeling enhanced signal intensity in MS and MS/MS, high multiplexing capability, simple data analysis Applicable to any sample(cells, animal or human tissue) | Expensive Requires fragmentation with HCD or ETD Does not allow in vivo labeling Quantitative precision dependent on the reproducibility of sample preparation | |
| Type | Name | Labeling level | Beneficial feature | Limitation |
| Enzymatic labeling (in vitro) | 18O labeling | Peptide | Low costs, simple in handling Applicable to any sample(cells, animal or human tissue) | Incomplete labeling complicates data analysis Limited multiplexing capability(up to 2⁃plex) Not suitable for in vivo labeling Overlapping isotopic peaks Varied labeling efficiencies |
| Label⁃free | Spectral counting | NA | Low costs, simple in handling Broad applicability | Less accurate than the labeling methods More time needed for MS analysis |
| Chromatographic peak area | NA | Low costs, simple in handling Broad applicability | Less accurate than the labeling methods More time needed for MS analysis |
Table 2 Comparison between the label-free and labeled quantitative proteomics techniques
| Type | Name | Labeling level | Beneficial feature | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic labeling | SILAC | Cells, organisms | Efficient labeling, one label for(tryptic) peptide, semiautomatic data analysis Applicable to cells but can be expanded to tissues or model organisms using internal standards (e.g., super⁃SILAC) | High costs, especially when applied to whole organisms Super⁃SILAC experiments have reduced quantitative proteome coverage Requires metabolically active cells to introduce labels |
| 15N labeling | Cells, organisms | Efficient labeling Applicable to cells and model organisms | Expensive Complex data analysis Limited multiplexing capability(up to 2⁃plex) Not suitable for clinical samples | |
Chemical labeling (in vitro) ⁃isobaric labeling | iTRAQ | Peptide | Efficient labeling enhanced signal intensity in MS and MS/MS, high multiplexing capability, simple data analysis Applicable to any sample(cells, animal or human tissue) Commercially available | Expensive Does not allow in vivo labeling Quantitative precision dependent on the reproducibility of sample preparation |
| TMT | Peptide | Efficient labeling enhanced signal intensity in MS and MS/MS, high multiplexing capability, simple data analysis Applicable to any sample(cells, animal or human tissue) | Expensive Requires fragmentation with HCD or ETD Does not allow in vivo labeling Quantitative precision dependent on the reproducibility of sample preparation | |
| Type | Name | Labeling level | Beneficial feature | Limitation |
| Enzymatic labeling (in vitro) | 18O labeling | Peptide | Low costs, simple in handling Applicable to any sample(cells, animal or human tissue) | Incomplete labeling complicates data analysis Limited multiplexing capability(up to 2⁃plex) Not suitable for in vivo labeling Overlapping isotopic peaks Varied labeling efficiencies |
| Label⁃free | Spectral counting | NA | Low costs, simple in handling Broad applicability | Less accurate than the labeling methods More time needed for MS analysis |
| Chromatographic peak area | NA | Low costs, simple in handling Broad applicability | Less accurate than the labeling methods More time needed for MS analysis |
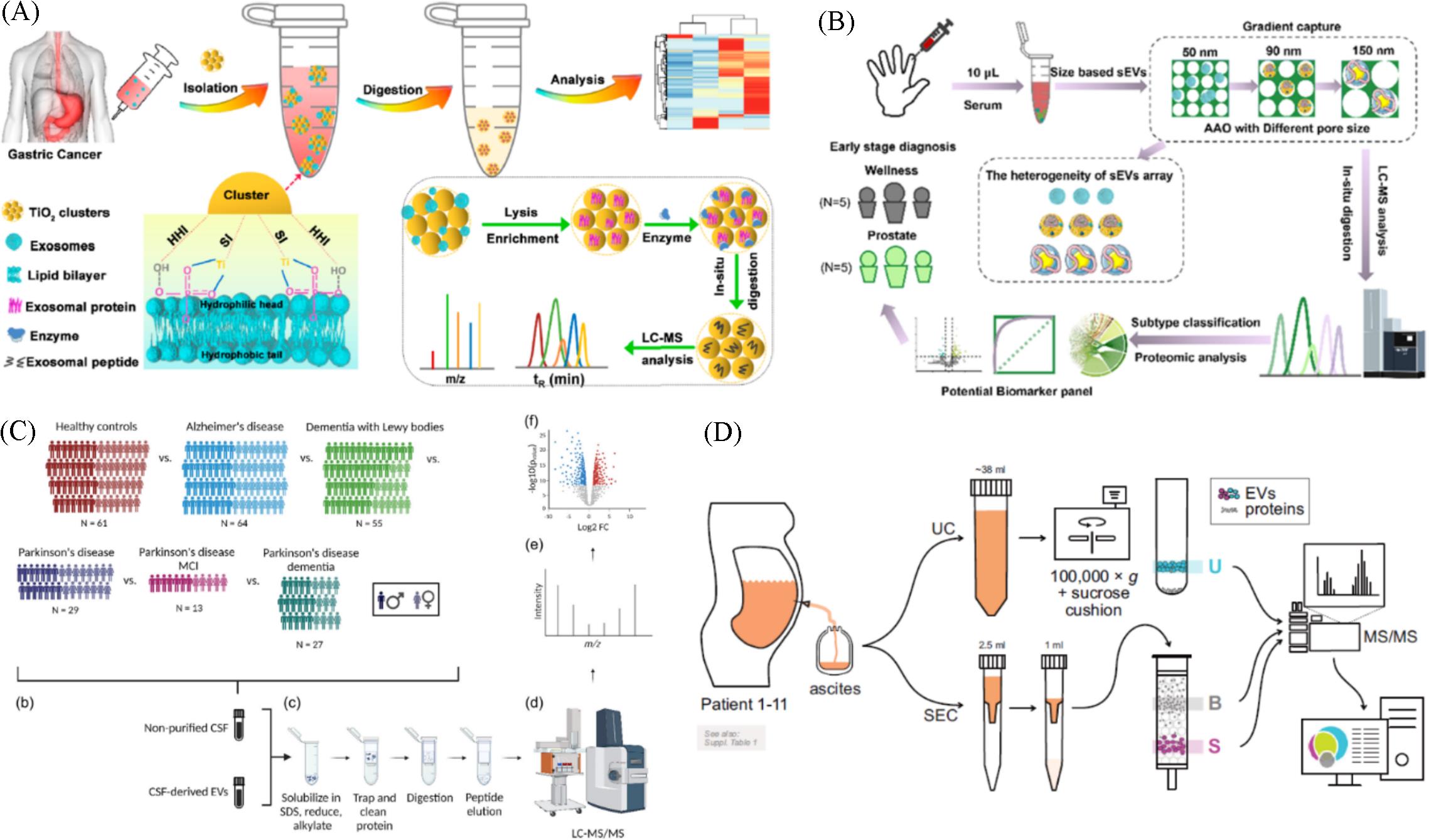
Fig.10 All⁃in⁃one strategy for downstream molecular profiling of tumor⁃derived exosomes(A)[109], nanoarray enabled size⁃dependent isolation and proteomics profiling of small EV subpopulations(B)[110], proteomic comparison between non⁃purified cerebrospinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid⁃derived EVs(C)[123], processing and isolation of samples from patient ascites and the MS analysis(D)[125](A) Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2023, Open Access; (D) Copyright 2024, Open Access.
| Disease | Sample | Type of MS | Potential finding | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Plasma | LC⁃MS/MS | CLDN4, EPCAM, CD151, LGALS3BP, HIST2H2BE and HIST2H2BF | [ |
| Multiple cancers | Tissue explants, plasma, and other bodily fluids | LC⁃MS/MS, DDA | ACTB, MSN and RAP1B | [ |
| Osteosarcoma | Plasma | LC⁃MS/MS, MALDI⁃TOF MS | IGLV2⁃23, IGLV4⁃3, IGLV1⁃51, IGKV3⁃15, IGHV4⁃4, IGLV4⁃60, HBA1 | [ |
| Prostate cancer | Serum | LC⁃MS/MS | Vinculin, ECM, Rac, VASP | [ |
| Alzheimer | Cerebrospinal fluid, plasma | Orbitrap, LC⁃MS | Cathepsin B | [ |
| Breast cancer | Plasma | LC⁃MS/MS, label⁃free | 144 Phosphoproteins | [ |
| Colorectal cancer | Serum | DIA, TMT | Fibrinogen α chain, phosphorylated fibronectin 1, haptoglobin | [ |
Hepatocellular carcinoma | Serum | DDA, DIA | Von Willebrand factor, LGALS3BP, TGFB1, SERPINC1, HPX, HP, HBA1, FGA, FGG, FGB | [ |
| Lung cancer | Serum | UPLC⁃MS/MS, Q⁃exactive | Lipopolysaccharide⁃binding proteins | [ |
| Liver cancer | Serum | LC‐MS, LTQ⁃orbitrap XL | Thrombospondin⁃1, fibulin⁃1, fibrinogen gamma chain | [ |
Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Serum | LC⁃MS, Q‐exactive, orbitrap | PF4V1, CXCL7, F13A1, ApoA1 | [ |
| Epithelial ovarian cancer | Plasma | LC‐MS/MS, TMT | Fibrinogen alpha chain, fibrinogen alpha chain | [ |
| Prostate cancer | Serum | LC‐MS/MS | Filamin A | [ |
Table 3 Proteomic analysis of tumor-derived exosomes for clinical disease diagnosis
| Disease | Sample | Type of MS | Potential finding | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Plasma | LC⁃MS/MS | CLDN4, EPCAM, CD151, LGALS3BP, HIST2H2BE and HIST2H2BF | [ |
| Multiple cancers | Tissue explants, plasma, and other bodily fluids | LC⁃MS/MS, DDA | ACTB, MSN and RAP1B | [ |
| Osteosarcoma | Plasma | LC⁃MS/MS, MALDI⁃TOF MS | IGLV2⁃23, IGLV4⁃3, IGLV1⁃51, IGKV3⁃15, IGHV4⁃4, IGLV4⁃60, HBA1 | [ |
| Prostate cancer | Serum | LC⁃MS/MS | Vinculin, ECM, Rac, VASP | [ |
| Alzheimer | Cerebrospinal fluid, plasma | Orbitrap, LC⁃MS | Cathepsin B | [ |
| Breast cancer | Plasma | LC⁃MS/MS, label⁃free | 144 Phosphoproteins | [ |
| Colorectal cancer | Serum | DIA, TMT | Fibrinogen α chain, phosphorylated fibronectin 1, haptoglobin | [ |
Hepatocellular carcinoma | Serum | DDA, DIA | Von Willebrand factor, LGALS3BP, TGFB1, SERPINC1, HPX, HP, HBA1, FGA, FGG, FGB | [ |
| Lung cancer | Serum | UPLC⁃MS/MS, Q⁃exactive | Lipopolysaccharide⁃binding proteins | [ |
| Liver cancer | Serum | LC‐MS, LTQ⁃orbitrap XL | Thrombospondin⁃1, fibulin⁃1, fibrinogen gamma chain | [ |
Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Serum | LC⁃MS, Q‐exactive, orbitrap | PF4V1, CXCL7, F13A1, ApoA1 | [ |
| Epithelial ovarian cancer | Plasma | LC‐MS/MS, TMT | Fibrinogen alpha chain, fibrinogen alpha chain | [ |
| Prostate cancer | Serum | LC‐MS/MS | Filamin A | [ |
| 1 | Li Q., Zhang Z., Wang F., Wang X., Zhan S., Yang X., Xu C., Liu D., Sci. Adv., 2023, 9(15), eadf4568 |
| 2 | Kalluri R., McAndrews K. M., Cell, 2023, 186(8), 1610—1626 |
| 3 | Li Z., Liu C., Cheng Y., Li Y., Deng J., Bai L., Qin L., Mei H., Zeng M., Tian F., Zhang S., Sun J., Sci. Adv., 2023, 9(16), eade2819 |
| 4 | Ding L., Liu X., Zhang Z., Liu L. E., He S., Wu Y., Effah C. Y., Yang R., Zhang A., Chen W., Yarmamat M., Qu L., Yang X., Wu Y., Lab Chip, 2023, 23(6), 1694—1702 |
| 5 | Zhang L., Yin W., Tong Y., Zhang Y., Xu Y., Liu S. Y., Dai Z., Zou X., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(31), 10991—10999 |
| 6 | Wang X., Xiang Z., Liu Y., Huang C., Pei Y., Wang X., Zhi H., Wong W. H. S., Wei H., Ng I. O. L., Lee P. P. W., Chan G. C. F., Lau Y. L., Tu W., Sci. Transl. Med., 2020, 12(563), eaaz3426 |
| 7 | Zhang K., Cheng K., Nat. Rev. Bioeng., 2023, 12, 1—2 |
| 8 | Zhang M., Hu S., Liu L., Dang P., Liu Y., Sun Z., Qiao B., Wang C., Signal Transduct. Target. Ther., 2023, 8(1), 124 |
| 9 | Das S., Lyon C. J., Hu T., ACS Nano, 2024, 18(14), 9784—9797 |
| 10 | Novikova S. E., Soloveva N. A., Farafonova T. E., Tikhonova O. V., Liao P. C., Zgoda V. G., Molecules, 2021, 26(20), 6145 |
| 11 | Lane R. E., Korbie D., Hill M. M., Trau M., Clin. Transl. Med., 2018, 7(1), 14 |
| 12 | Keerthikumar S., Chisanga D., Ariyaratne D., Al Saffar H., Anand S., Zhao K., Samuel M., Pathan M., Jois M., Chilamkurti N., Gangoda L., Mathivanan S., J. Mol. Biol., 2016, 428(4), 688—692 |
| 13 | Pathan M., Fonseka P., Chitti S. V., Kang T., Sanwlani R., Van Deun J., Hendrix A., Mathivanan S., Nucleic Acids Res., 2019, 47(D1), D516—D519 |
| 14 | Abramowicz A., Widlak P., Pietrowska M., Mol. Biosyst., 2016, 12(5), 1407—1419 |
| 15 | Johnstone R. M., Bianchini A., Teng K., Blood, 1989, 74(5), 1844—1851 |
| 16 | Théry C., Clayton A., Amigorena S., Raposo G., Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol., 2006, Chapter 3, Unit 3.22 |
| 17 | Yan H., Li Y., Cheng S., Zeng Y., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(11), 4739—4774 |
| 18 | Principe S., Jones E. E., Kim Y., Sinha A., Nyalwidhe J. O., Brooks J., Semmes O. J., Troyer D. A., Lance R. S., Kislinger T., Drake R. R., Proteomics, 2013, 13(10/11), 1667—1671 |
| 19 | Principe S., Kim Y., Fontana S., Ignatchenko V., Nyalwidhe J. O., Lance R. S., Troyer D. A., Alessandro R., Semmes O. J., Kislinger T., Drake R. R., Medin J. A., J. Proteome Res., 2012, 11(4), 2386—2396 |
| 20 | Chia B. S., Low Y. P., Wang Q., Li P., Gao Z., TrAC⁃Trend. Anal. Chem., 2017, 86, 93—106 |
| 21 | Li P., Kaslan M., Lee S. H., Yao J., Gao Z., Theranostics, 2017, 7(3), 789—804 |
| 22 | Crescitelli R., Lasser C., Jang S. C., Cvjetkovic A., Malmhall C., Karimi N., Hoog J. L., Johansson I., Fuchs J., Thorsell A., Gho Y. S., Olofsson Bagge R., Lotvall J., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2020, 9(1), 1722433 |
| 23 | Sódar B. W., Kittel Á., Pálóczi K., Vukman K. V., Osteikoetxea X., Szabó⁃Taylor K., Németh A., Sperlágh B., Baranyai T., Giricz Z., Wiener Z., Turiák L., Drahos L., Pállinger É., Vékey K., Ferdinandy P., Falus A., Buzás E. I., Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1), 24316 |
| 24 | Bard M. P., Hegmans J. P., Hemmes A., Luider T. M., Willemsen R., Severijnen L. A., van Meerbeeck J. P., Burgers S. A., Hoogsteden H. C., Lambrecht B. N., Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 2004, 31(1), 114—121 |
| 25 | Keller S., Ridinger J., Rupp A. K., Janssen J. W., Altevogt P., J. Transl. Med., 2011, 9, 86 |
| 26 | Tauro B. J., Greening D. W., Mathias R. A., Ji H., Mathivanan S., Scott A. M., Simpson R. J., Methods, 2012, 56(2), 293—304 |
| 27 | Patel G. K., Khan M. A., Zubair H., Srivastava S. K., Khushman M., Singh S., Singh A. P., Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 5335 |
| 28 | Welton J. L., Webber J. P., Botos L. A., Jones M., Clayton A., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2015, 4, 27269 |
| 29 | Taylor D. D., Shah S., Methods, 2015, 87, 3—10 |
| 30 | Stranska R., Gysbrechts L., Wouters J., Vermeersch P., Bloch K., Dierickx D., Andrei G., Snoeck R., J. Transl. Med., 2018, 16(1), 1 |
| 31 | Karimi N., Cvjetkovic A., Jang S. C., Crescitelli R., Hosseinpour Feizi M. A., Nieuwland R., Lotvall J., Lasser C., Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2018, 75(15), 2873—2886 |
| 32 | Yang D., Zhang W., Zhang H., Zhang F., Chen L., Ma L., Larcher L. M., Chen S., Liu N., Zhao Q., Tran P. H. L., Chen C., Veedu R. N., Wang T., Theranostics, 2020, 10(8), 3684—3707 |
| 33 | Lane R. E., Korbie D., Trau M., Hill M. M., Proteomics, 2019, 19(8), e1800156 |
| 34 | Takov K., Yellon D. M., Davidson S. M., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2019, 8(1), 1560809 |
| 35 | Nordin J. Z., Lee Y., Vader P., Mager I., Johansson H. J., Heusermann W., Wiklander O. P., Hallbrink M., Seow Y., Bultema J. J., Gilthorpe J., Davies T., Fairchild P. J., Gabrielsson S., Meisner⁃Kober N. C., Lehtio J., Smith C. I., Wood M. J., El Andaloussi S., Nanomedicine, 2015, 11(4), 879—883 |
| 36 | Lobb R. J., Becker M., Wen S. W., Wong C. S., Wiegmans A. P., Leimgruber A., Moller A., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2015, 4, 27031 |
| 37 | Thompson A. G., Gray E., Mager I., Fischer R., Thezenas M. L., Charles P. D., Talbot K., El Andaloussi S., Kessler B. M., Wood M., Turner M. R., Proteomics, 2018, 18(24), e1800257 |
| 38 | Busatto S., Vilanilam G., Ticer T., Lin W. L., Dickson D. W., Shapiro S., Bergese P., Wolfram J., Cells, 2018, 7(12), 273 |
| 39 | Han Z., Peng C., Yi J., Zhang D., Xiang X., Peng X., Su B., Liu B., Shen Y., Qiao L., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2021, 333, 129563 |
| 40 | Hua X., Zhu Q., Liu Y., Zhou S., Huang P., Li Q., Liu S., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2023, 1258, 341160 |
| 41 | Bu J., Nair A., Iida M., Jeong W. J., Poellmann M. J., Mudd K., Kubiatowicz L. J., Liu E. W., Wheeler D. L., Hong S., Nano Lett., 2020, 20(7), 4901—4909 |
| 42 | Contreras⁃Naranjo J. C., Wu H. J., Ugaz V. M., Lab Chip, 2017, 17(21), 3558—3577 |
| 43 | Zhang K., Yue Y., Wu S., Liu W., Shi J., Zhang Z., ACS Sens., 2019, 4(5), 1245—1251 |
| 44 | Zhang P., Zhou X., Zeng Y., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(21), 5495—5504 |
| 45 | Liu C., Guo J., Tian F., Yang N., Yan F., Ding Y., Wei J., Hu G., Nie G., Sun J., ACS Nano, 2017, 11(7), 6968—6976 |
| 46 | Kang K., Lee S. S., Hyun K., Lee S. J., Kim J. M., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 2567 |
| 47 | Liu C., Ding B., Xue C., Tian Y., Hu G., Sun J., Anal. Chem., 88(24), 12547—12553 |
| 48 | Liu C., Zhao J., Tian F., Chang J., Zhang W., Sun J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(9), 3817—3821 |
| 49 | Lee K., Shao H., Weissleder R., Lee H., ACS Nano, 2015, 9(3), 2321—2327 |
| 50 | Wu M., Ouyang Y., Wang Z., Zhang R., Huang P. H., Chen C., Li H., Li P., Quinn D., Dao M., Suresh S., Sadovsky Y., Huang T. J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2017, 114(40), 10584—10589 |
| 51 | Wang Z., Wang H., Becker R., Rufo J., Yang S., Mace B. E., Wu M., Zou J., Laskowitz D. T., Huang T. J., Microsyst. Nanoeng., 2021, 7, 20 |
| 52 | Liu C., Zhao J., Tian F., Cai L., Zhang W., Feng Q., Chang J., Wan F., Yang Y., Dai B., Cong Y., Ding B., Sun J., Tan W., Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2019, 3(3), 183—193 |
| 53 | Zhao J., Liu C., Li Y., Ma Y., Deng J., Li L., Sun J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(11), 4996—5001 |
| 54 | Mallia A., Gianazza E., Zoanni B., Brioschi M., Barbieri S. S., Banfi C., Diagnostics, 2020, 10(10), 843 |
| 55 | Kim H., Kim D. W., Cho J. Y., Proteome Sci., 2019, 17, 5 |
| 56 | Fontana S., Saieva L., Taverna S., Alessandro R., Proteomics, 2013, 13(10/11), 1581—1594 |
| 57 | Ludwig K. R., Schroll M. M., Hummon A. B., J. Proteome Res., 2018, 17(7), 2480—2490 |
| 58 | Manza L. L., Stamer S. L., Ham A. J., Codreanu S. G., Liebler D. C., Proteomics, 2005, 5(7), 1742—1745 |
| 59 | Wisniewski J. R., Zougman A., Nagaraj N., Mann M., Nat. Methods, 2009, 6(5), 359—362 |
| 60 | Hughes C. S., Moggridge S., Muller T., Sorensen P. H., Morin G. B., Krijgsveld J., Nat. Protoc., 2019, 14(1), 68—85 |
| 61 | Johnston H. E., Yadav K., Kirkpatrick J. M., Biggs G. S., Oxley D., Kramer H. B., Samant R. S., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(29), 10320—10328 |
| 62 | Chen W., Wang S., Adhikari S., Deng Z., Wang L., Chen L., Ke M., Yang P., Tian R., Anal. Chem., 2016, 88(9), 4864—4871 |
| 63 | Xu R., Tang J., Deng Q., He W., Sun X., Xia L., Cheng Z., He L., You S., Hu J., Fu Y., Zhu J., Chen Y., Gao W., He A., Guo Z., Lin L., Li H., Hu C., Tian R., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90(9), 5879—5886 |
| 64 | Huang P., Kong Q., Gao W., Chu B., Li H., Mao Y., Cai Z., Xu R., Tian R., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2020, 1127, 140—148 |
| 65 | Shah P., Zhang B., Choi C., Yang S., Zhou J., Harlan R., Tian Y., Zhang Z., Chan D. W., Zhang H., Anal. Biochem., 2015, 469, 27—33 |
| 66 | Li Y., Yuan H., Cheng M., Zhu X., Yang K., Zhang W., Sui Z., Zhang C., Zhang L., Zhang Y., Sci. Bull., 2022, 67(16), 1628—1631 |
| 67 | Mathew B., Mansuri M. S., Williams K. R., Nairn A. C., Brain Sci., 2021, 11(2), 258 |
| 68 | Wallen H., Nat. Rev. Methods Primers, 2024, 4(1), 39 |
| 69 | Doyle L., Wang M., Cells, 2019, 8(7), 727 |
| 70 | Jalaludin I., Lubman D. M., Kim J., Mass Spectrom. Rev., 2023, 42(2), 844—872 |
| 71 | Toby T. K., Fornelli L., Kelleher N. L., Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2016, 9(1), 499—519 |
| 72 | Aebersold R., Agar J. N., Amster I. J., Baker M. S., Bertozzi C. R., Boja E. S., Costello C. E., Cravatt B. F., Fenselau C., Garcia B. A., Ge Y., Gunawardena J., Hendrickson R. C., Hergenrother P. J., Huber C. G., Ivanov A. R., Jensen O. N., Jewett M. C., Kelleher N. L., Kiessling L. L., Krogan N. J., Larsen M. R., Loo J. A., Ogorzalek Loo R. R., Lundberg E., MacCoss M. J., Mallick P., Mootha V. K., Mrksich M., Muir T. W., Patrie S. M., Pesavento J. J., Pitteri S. J., Rodriguez H., Saghatelian A., Sandoval W., Schlüter H., Sechi S., Slavoff S. A., Smith L. M., Snyder M. P., Thomas P. M., Uhlén M., Van Eyk J. E., Vidal M., Walt D. R., White F. M., Williams E. R., Wohlschlager T., Wysocki V. H., Yates N. A., Young N. L., Zhang B., Nat. Chem. Biol., 2018, 14(3), 206—214 |
| 73 | Zhu Y., Pick H., Gasilova N., Li X., Lin T. E., Laeubli H. P., Zippelius A., Ho P. C., Girault H. H., Chem, 2019, 5(5), 1318—1336 |
| 74 | Buck K. M., Roberts D. S., Aballo T. J., Inman D. R., Jin S., Ponik S., Brown K. A., Ge Y., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(20), 7164—7168 |
| 75 | Brahmadhi A., Chuang Y. K., Wang S. Y., Kao C. C., Tsai I. L., J. Food Drug Anal., 2022, 30(2), 202—222 |
| 76 | Guan S., Taylor P. P., Han Z., Moran M. F., Ma B., J. Proteome Res., 2020, 19(8), 3230—3237 |
| 77 | Zhang Z., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2012, 23(8), 1400—1407 |
| 78 | Bian Y., Zheng R., Bayer F. P., Wong C., Chang Y. C., Meng C., Zolg D. P., Reinecke M., Zecha J., Wiechmann S., Heinzlmeir S., Scherr J., Hemmer B., Baynham M., Gingras A. C., Boychenko O., Kuster B., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 157 |
| 79 | Wu A. Y., Ueda K., Lai C. P., Proteomics, 2019, 19(1/2), e1800162 |
| 80 | Zhao L., Shi J., Chang L., Wang Y., Liu S., Li Y., Zhang T., Zuo T., Fu B., Wang G., Ruan Y., Zhang Y., Xu P., ACS Omega, 2021, 6(1), 827—835 |
| 81 | Zheng X., Xu K., Zhou B., Chen T., Huang Y., Li Q., Wen F., Ge W., Wang J., Yu S., Sun L., Zhu L., Liu W., Gao H., Yue L., Cai X., Zhang Q., Ruan G., Zhu T., Wu Z., Zhu Y., Shao Y., Guo T., Zheng S., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2020, 9(1), 1750202 |
| 82 | Yang Y., Liu X., Shen C., Lin Y., Yang P., Qiao L., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 146 |
| 83 | Yang Y., Yan G., Kong S., Wu M., Yang P., Cao W., Qiao L., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 6073 |
| 84 | Derks J., Leduc A., Wallmann G., Huffman R. G., Willetts M., Khan S., Specht H., Ralser M., Demichev V., Slavov N., Nat. Biotechnol., 2022, 41(1), 50—59 |
| 85 | Patel V. J., Thalassinos K., Slade S. E., Connolly J. B., Crombie A., Colin Murrell J., Scrivens J. H., J. Proteome Res., 2009, 8(7), 3752—3759 |
| 86 | Neilson K. A., Ali N. A., Muralidharan S., Mirzaei M., Mariani M., Assadourian G., Lee A., van Sluyter S. C., Haynes P. A., Proteomics, 2011, 11(4), 535—553 |
| 87 | Lobo M. D., Moreno F. B., Souza G. H., Verde S. M., Moreira R. A., Monteiro⁃Moreira A. C., Front. Oncol., 2017, 7, 14 |
| 88 | Lee J., McKinney K. Q., Pavlopoulos A. J., Niu M., Kang J. W., Oh J. W., Kim K. P., Hwang S., Mol. Cells, 2018, 41(3), 179—187 |
| 89 | Xu L., Gimple R. C., Lau W. B., Lau B., Fei F., Shen Q., Liao X., Li Y., Wang W., He Y., Feng M., Bu H., Wang W., Zhou S., Mass Spectrom. Rev., 2020, 39(5/6), 745—762 |
| 90 | Lindemann C., Thomanek N., Hundt F., Lerari T., Meyer H. E., Wolters D., Marcus K., Biol. Chem., 2017, 398(5/6), 687—699 |
| 91 | Wang S., Chen G., Lin X., Xing X., Cai Z., Liu X., Liu J., Oncol. Lett., 2017, 14(6), 8122—8131 |
| 92 | Sun H., Wang C., Hu B., Gao X., Zou T., Luo Q., Chen M., Fu Y., Sheng Y., Zhang K., Zheng Y., Ren X., Yan S., Geng Y., Yang L., Dong Q., Qin L., Signal Transduct. Target. Ther., 2021, 6(1), 187 |
| 93 | Clark D. J., Fondrie W. E., Liao Z., Hanson P. I., Fulton A., Mao L., Yang A. J., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(20), 10462—10469 |
| 94 | Huang Y., Liu Y., Huang Q., Sun S., Ji Z., Huang L., Li Z., Huang X., Deng W., Li T., Front. Immunol., 2022, 13, 800902 |
| 95 | Dephoure N., Gygi S. P., Sci. Signal., 2012, 5(217), rs2 |
| 96 | Stepath M., Zülch B., Maghnouj A., Schork K., Turewicz M., Eisenacher M., Hahn S., Sitek B., Bracht T., J. Proteome Res., 2019, 19(2), 926—937 |
| 97 | Simpson K. L., Whetton A. D., Dive C., J. Chromatogr. B, 2009, 877(13), 1240—1249 |
| 98 | Li H., Han J., Pan J., Liu T., Parker C. E., Borchers C. H., J. Mass Spectrom., 2017, 52(5), 319—341 |
| 99 | DeSouza L. V., Romaschin A. D., Colgan T. J., Michael Siu K. W., Anal. Chem., 2009, 81(9), 3462—3470 |
| 100 | Rauniyar N., Yates J. R., J. Proteome Res., 2014, 13(12), 5293—5309 |
| 101 | Clark D. J., Fondrie W. E., Yang A., Mao L., J. Proteomics, 2016, 133, 161—169 |
| 102 | Kugeratski F. G., Hodge K., Lilla S., McAndrews K. M., Zhou X., Hwang R. F., Zanivan S., Kalluri R., Nat. Cell Biol., 2021, 23(6), 631—641 |
| 103 | Chen X., Wei S., Ji Y., Guo X., Yang F., Proteomics, 2015, 15(18), 3175—3192 |
| 104 | Schey K. L., Luther J. M., Rose K. L., Methods, 2015, 87, 75—82 |
| 105 | Castillo J., Bernard V., San Lucas F. A., Allenson K., Capello M., Kim D. U., Gascoyne P., Mulu F. C., Stephens B. M., Huang J., Wang H., Momin A. A., Jacamo R. O., Katz M., Wolff R., Javle M., Varadhachary G., Wistuba II, Hanash S., Maitra A., Alvarez H., Ann. Oncol., 2018, 29(1), 223—229 |
| 106 | Melo S. A., Luecke L. B., Kahlert C., Fernandez A. F., Gammon S. T., Kaye J., LeBleu V. S., Mittendorf E. A., Weitz J., Rahbari N., Reissfelder C., Pilarsky C., Fraga M. F., Piwnica⁃Worms D., Kalluri R., Nature, 2015, 523(7559), 177—182 |
| 107 | Hoshino A., Kim H. S., Bojmar L., Gyan K. E., Cioffi M., Hernandez J., Zambirinis C. P., Rodrigues G., Molina H., Heissel S., Mark M. T., Steiner L., Benito⁃Martin A., Lucotti S., di Giannatale A., Offer K., Nakajima M., Williams C., Nogues L., Pelissier Vatter F. A., Hashimoto A., Davies A. E., Freitas D., Kenific C. M., Ararso Y., Buehring W., Lauritzen P., Ogitani Y., Sugiura K., Takahashi N., Aleckovic M., Bailey K. A., Jolissant J. S., Wang H., Harris A., Schaeffer L. M., Garcia⁃Santos G., Posner Z., Balachandran V. P., Khakoo Y., Raju G. P., Scherz A., Sagi I., Scherz⁃Shouval R., Yarden Y., Oren M., Malladi M., Petriccione M., de Braganca K. C., Donzelli M., Fischer C., Vitolano S., Wright G. P., Ganshaw L., Marrano M., Ahmed A., DeStefano J., Danzer E., Roehrl M. H. A., Lacayo N. J., Vincent T. C., Weiser M. R., Brady M. S., Meyers P. A., Wexler L. H., Ambati S. R., Chou A. J., Slotkin E. K., Modak S., Roberts S. S., Basu E. M., Diolaiti D., Krantz B. A., Cardoso F., Simpson A. L., Berger M., Rudin C. M., Simeone D. M., Jain M., Ghajar C. M., Batra S. K., Stanger B. Z., Bui J., Brown K. A., Rajasekhar V. K., Healey J. H., de Sousa M., Kramer K., Sheth S., Baisch J., Pascual V., Heaton T. E., La Quaglia M. P., Pisapia D. J., Schwartz R., Zhang H., Liu Y., Shukla A., Blavier L., DeClerck Y. A., LaBarge M., Bissell M. J., Caffrey T. C., Grandgenett P. M., Hollingsworth M. A., Bromberg J., Costa⁃Silva B., Peinado H., Kang Y., Garcia B. A., O'Reilly E. M., Kelsen D., Trippett T. M., Jones D. R., Matei I. R., Jarnagin W. R., Lyden D., Cell, 2020, 182(4), 1044—1061 |
| 108 | Han Z., Peng C., Yi J., Wang Y., Liu Q., Yang Y., Long S., Qiao L., Shen Y., iScience, 2021, 24(8), 102906 |
| 109 | Wang S., He Y., Lu J., Wang Y., Wu X., Yan G., Fang X., Liu B., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(32), 36341—36352 |
| 110 | Wang S., He Y., Tian T., Lu J., Lu Y., Huang X., Zou Y., Zhang L., Fang X., Liu B., Anal. Chem., 2023, 95(41), 15276—15285 |
| 111 | Yuyama K., Sun H., Fujii R., Hemmi I., Ueda K., Igeta Y., Brain, 2024, 147(2), 627—636 |
| 112 | Hunter T., Cell, 2000, 100, 113—127 |
| 113 | Chen I. H., Xue L., Hsu C. C., Paez J. S., Pan L., Andaluz H., Wendt M. K., Iliuk A. B., Zhu J. K., Tao W. A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2017, 114(12), 3175—3180 |
| 114 | Andaluz Aguilar H., Iliuk A. B., Chen I. H., Tao W. A., Nat. Protoc., 2020, 15(1), 161—180 |
| 115 | Wang N., Song X., Liu L., Niu L., Wang X., Song X., Xie L., Cancer Sci., 2018, 109(5), 1701—1709 |
| 116 | Uzzaman A., Zhang X., Qiao Z., Zhan H., Sohail A., Wahid A., Shang Z., Guan X., Cao C. X., Xiao H., Biochimie, 2020, 177, 132—141 |
| 117 | Li C., Zhou Y., Liu J., Su X., Qin H., Huang S., Huang X., Zhou N., Cancer Epidem. Biomar., 2019, 28(10), 1668—1681 |
| 118 | Zhang W., Ou X., Wu X., Int. J. Oncol., 2019, 54, 1719—1733 |
| 119 | Panigrahi G. K., Praharaj P. P., Kittaka H., Mridha A. R., Black O. M., Singh R., Mercer R., van Bokhoven A., Torkko K. C., Agarwal C., Agarwal R., Abd Elmageed Z. Y., Yadav H., Mishra S. K., Deep G., Cancer Med., 2019, 8(3), 1110—1123 |
| 120 | Wang X., Tian L., Lu J., Ng I. O. L., Oncogenesis, 2022, 11(1), 54 |
| 121 | Chen G., Huang A. C., Zhang W., Zhang G., Wu M., Xu W., Yu Z., Yang J., Wang B., Sun H., Xia H., Man Q., Zhong W., Antelo L. F., Wu B., Xiong X., Liu X., Guan L., Li T., Liu S., Yang R., Lu Y., Dong L., McGettigan S., Somasundaram R., Radhakrishnan R., Mills G., Lu Y., Kim J., Chen Y. H., Dong H., Zhao Y., Karakousis G. C., Mitchell T. C., Schuchter L. M., Herlyn M., Wherry E. J., Xu X., Guo W., Nature, 2018, 560(7718), 382—386 |
| 122 | Garcia⁃Silva S., Benito⁃Martin A., Sanchez⁃Redondo S., Hernandez⁃Barranco A., Ximenez⁃Embun P., Nogues L., Mazariegos M. S., Brinkmann K., Amor Lopez A., Meyer L., Rodriguez C., Garcia⁃Martin C., Boskovic J., Leton R., Montero C., Robledo M., Santambrogio L., Sue Brady M., Szumera⁃Cieckiewicz A., Kalinowska I., Skog J., Noerholm M., Munoz J., Ortiz⁃Romero P. L., Ruano Y., Rodriguez⁃Peralto J. L., Rutkowski P., Peinado H., J. Exp. Med., 2019, 216(5), 1061—1070 |
| 123 | Hirschberg Y., Valle⁃Tamayo N., Dols⁃Icardo O., Engelborghs S., Buelens B., Vandenbroucke R. E., Vermeiren Y., Boonen K., Mertens I., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2023, 12(12), e12383 |
| 124 | Zhang J., Guan M., Lv M., Liu Y., Zhang H., Zhang Z., Zhang K., ACS Nano, 2023, 17(20), 20120—20134 |
| 125 | Vyhlídalová Kotrbová A., Gömöryová K., Mikulová A., Plešingerová H., Sladeček S., Kravec M., Hrachovinová Š., Potěšil D., Dunsmore G., Blériot C., Bied M., Kotouček J., Bednaříková M., Hausnerová J., Minář L., Crha I., Felsinger M., Zdráhal Z., Ginhoux F., Weinberger V., Bryja V., Pospíchalová V., J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2024, 13(3), e12420 |
| [1] | 侯泽金, 李荣其, 李健, 冯怡宁, 靳茜茜, 孙俊红, 曹洁. 基于GC-MS和机器学习的深静脉血栓形成预测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(9): 20240199. |
| [2] | 石倩, 刘冬梅, 方小泥, 刘宝红. 基于基质辅助激光解析质谱的高通量酪氨酸酶活性及抑制剂分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240330. |
| [3] | 蒋龑, 陈妍琳, 宋高瑜, 陈炎炎, 白晶, 朱莹娣, 李娟. 细菌的蛋白质组成分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240345. |
| [4] | 闫勇杰, 高文博, 鲁晨辉, 杨成, 徐姝婷. 基于微萃取-纳喷雾质谱技术的纳升脑脊液中咖啡多酚的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240327. |
| [5] | 张磊, 申华莉. 标志物研究中常用蛋白组学质谱方法的定量准确性评估[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240311. |
| [6] | 胡宇虹, 俞相明, 宋丽丽, 邢清和, 周峰. DEEP SEQ方法检测新生儿毛干蛋白质组动态变化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240326. |
| [7] | 范智瑞, 方群, 杨奕. 基于质谱的单细胞蛋白质组学分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240294. |
| [8] | 曹宜青, 侯静欣, 刘建业, 李嫣. 体液外泌体代谢组学研究进展和挑战[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240324. |
| [9] | 许霞, 秦伟达, 李若萌, 王倩倩, 刘宁, 李功玉. 深度覆盖蛋白质组学质谱分析: 细胞蛋白提取方法的评估[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240344. |
| [10] | 续红妹, 王梁臣, 闵乾昊. 面向小分子检测的MALDI MS基质研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240285. |
| [11] | 黄玉滢, 于成鲲, 刘斯奇, 任艳. 利用无标记单细胞蛋白质组学方法构建小鼠外周血单个核细胞的细胞图谱[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240355. |
| [12] | 刘思盈, 粟雯, 周仲燕, 杨治渝, 裴华夫, 何芷茹, 王娜, 岳磊. 温度控制的泛素/三磷酸腺苷相互作用的电喷雾质谱研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240382. |
| [13] | 沈枫林, 冯兆莹, 方静, 张磊, 刘晓慧, 周新文. 基于质谱的单细胞分辨的空间蛋白质组学新技术研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240299. |
| [14] | 霍志远, 周金萍, 马秀敏, 周严, 黄琳. 基于质谱的单细胞多组学分析技术研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240389. |
| [15] | 董沛滢, 刘彤, 秦伟捷. RNA-蛋白质复合物规模化富集与鉴定新方法[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(11): 20240091. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||