

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 20230188.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230188
收稿日期:2023-04-14
出版日期:2023-10-10
发布日期:2023-05-23
通讯作者:
郑基深
E-mail:jszheng@ustc.edu.cn
基金资助:
HAN Dongyang1, REN Yuxiang1, YANG Ziyi1, HUANG He2, ZHENG Jishen2( )
)
Received:2023-04-14
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-05-23
Contact:
ZHENG Jishen
E-mail:jszheng@ustc.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
分裂内含肽通过剪接反应实现多肽片段的连接, 具有高效且无痕的特点, 受到了广泛关注. 本文基于分裂内含肽的结构特征与剪接反应过程, 结合近年来关于分裂内含肽性能优化和应用研究进展进行了综合评述, 揭示其作为一种日渐成熟的蛋白质工程化技术在蛋白质化学合成领域的前景, 并简要分析了目前分裂内含肽工具面临的问题与挑战, 并对可能的解决方案进行了展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
韩东阳, 任宇祥, 杨子毅, 黄赫, 郑基深. 分裂内含肽: 一种高效的无痕多肽片段连接工具. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230188.
HAN Dongyang, REN Yuxiang, YANG Ziyi, HUANG He, ZHENG Jishen. Split Intein: a Versatile Tool for Traceless Peptide Segment Ligation. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(10): 20230188.
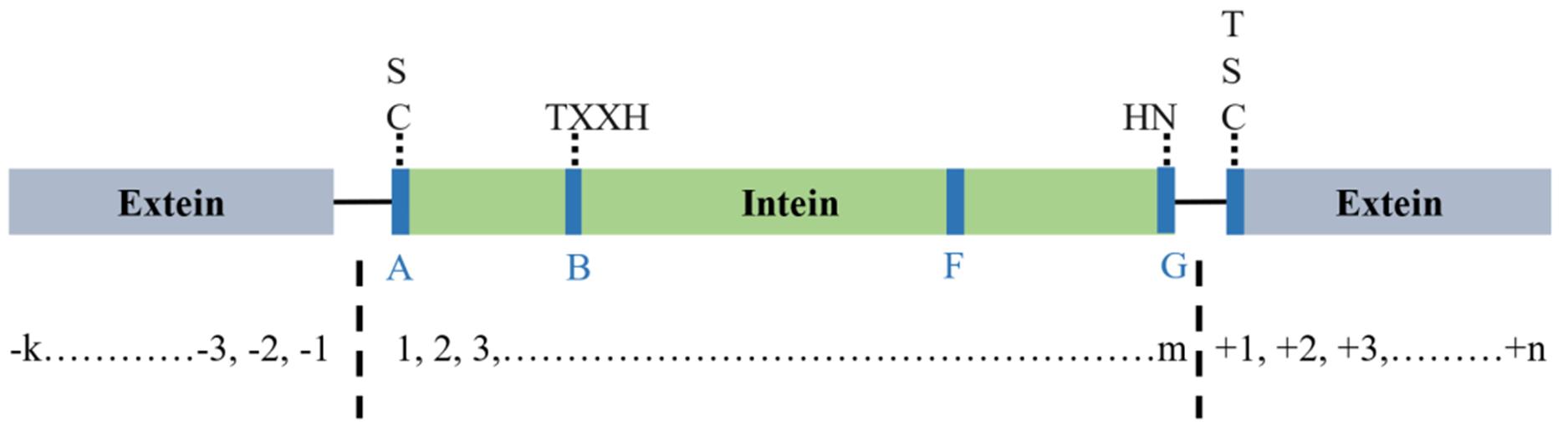
Fig.2 Sequence characteristics of InteinsThe Intein sequence is flanked by two exteins. The N-terminal peptide contains A and B structural motifs, and the C-terminal peptide contains F and G motifs. A-block usually has Cys or Ser as a conservative residue. Zone B usually contains His and Thr residues, while Zone F usually contains Asp and His. In addition, G-Block has two conservative residues; the penultimate His and the last Asn.
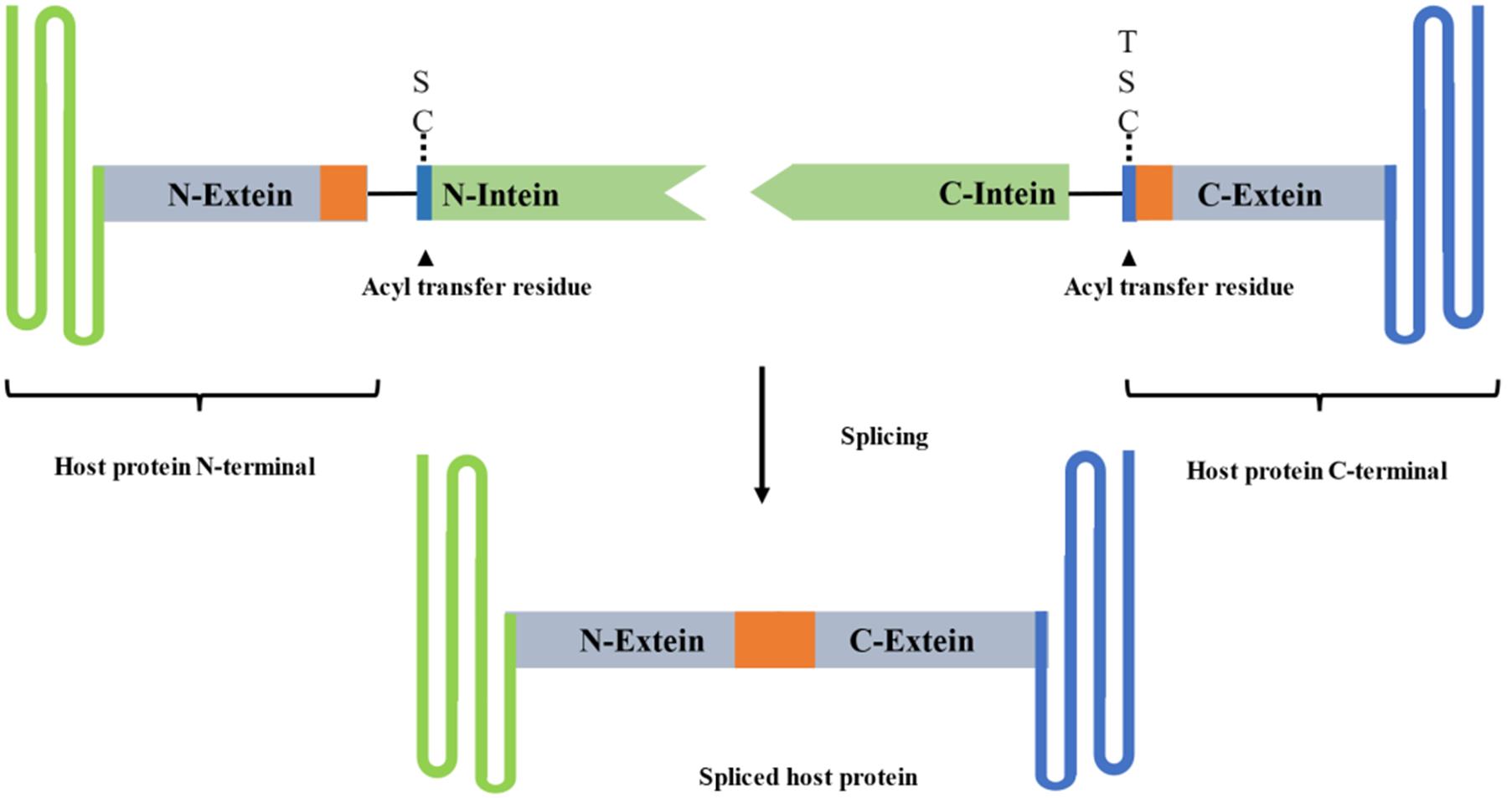
Fig.3 Principle of protein trans⁃splicing by split inteinThe N⁃terminal and C⁃terminal segments of the split intein were connected with the two segments of the host protein respectively, and the complete mature host protein was obtained by splicing reaction. The orange area in the figure is the connection position between the intein and the extein. The amino acid sequence at this position greatly impacts the splicing efficiency.
| Host protein | Species | N⁃flanking sequence | C⁃ flanking sequence | Acyl transfer residues | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DnaB | Rma | LRESG/C | AHN/SIEQDA | CS | [ |
| GyrB | Ssp | DSAGG/C | FVHN/SAKQG | CS | [ |
| DnaB | Ssp | LRESG/C | VHN/SIEQD | CS | [ |
| VMA | Sce | RGTLE/C | VVVHN/CG | CC | [ |
| RIR1 | Pfu⁃site1 | GGG/C | HN/TGL | CT | [ |
| RIR1 | Pfu⁃site2 | TNP/C | SHN/CGEE | CC | [ |
| GB⁃D pol1 | Psp | GTLEA/SILPEE | LYAHN/SGLNS | SS | [ |
| RecA | Mtu | VVVKNK/C | VVVHN/CSPPFK | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Ter(TerDnaE⁃3) | TYGVL/C | VVVHN/CYQEQY | CC | [ |
Table 1 Previously reported artificial split intein
| Host protein | Species | N⁃flanking sequence | C⁃ flanking sequence | Acyl transfer residues | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DnaB | Rma | LRESG/C | AHN/SIEQDA | CS | [ |
| GyrB | Ssp | DSAGG/C | FVHN/SAKQG | CS | [ |
| DnaB | Ssp | LRESG/C | VHN/SIEQD | CS | [ |
| VMA | Sce | RGTLE/C | VVVHN/CG | CC | [ |
| RIR1 | Pfu⁃site1 | GGG/C | HN/TGL | CT | [ |
| RIR1 | Pfu⁃site2 | TNP/C | SHN/CGEE | CC | [ |
| GB⁃D pol1 | Psp | GTLEA/SILPEE | LYAHN/SGLNS | SS | [ |
| RecA | Mtu | VVVKNK/C | VVVHN/CSPPFK | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Ter(TerDnaE⁃3) | TYGVL/C | VVVHN/CYQEQY | CC | [ |
| Host protein | Species | N⁃flanking sequence | C⁃flanking sequence | Acyl transfer residue | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DnaE | Ssp | FDQMVKFAEY/C | AN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Npu | FEQMLKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Nsp | FDDMLKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Asp | FDDMLKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Oli | FEQMVKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSMAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Tvu | DFAEY/C | AN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1 | KILAN/SIL | AHN/SYYGY | SS | [ |
| B⁃type DNA polymerase | Neq | EEGFKVIYGD/S | HN/TDSLFISGDK | ST | [ |
| NrdJ | (GOS)* | GTNPC/C | HN/SEIVL | CS | [ |
| gp41 | (GOS)* | TRSGY/C | HN/SSSDV | CS | [ |
| gp41 | (GOS)* | SQLNR/C | HN/SAVEE | CS | [ |
| IMPDH | (GOS)* | GIGGG/C | HN/SICST | CS | [ |
| Vidal T4Lh⁃1 | LAS/C | SHN/TNVG | CT | [ | |
| Vidal UvsX⁃2 | ESG/C | SHN/SGK | CS | [ | |
| NrdHF | (GOS∶AceL) a | SIRDE/A | TGN/SMHVE | Class3 b CS | [ |
| TerL | (GOS∶AceL) a | EFE/C | SHN/CEFL | CC | [ |
Table 2 General naturally split intein from different species
| Host protein | Species | N⁃flanking sequence | C⁃flanking sequence | Acyl transfer residue | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DnaE | Ssp | FDQMVKFAEY/C | AN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Npu | FEQMLKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Nsp | FDDMLKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Asp | FDDMLKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Oli | FEQMVKFAEY/C | SN/CFNKSHSMAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Tvu | DFAEY/C | AN/CFNKSHSTAY | CC | [ |
| DnaE | Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1 | KILAN/SIL | AHN/SYYGY | SS | [ |
| B⁃type DNA polymerase | Neq | EEGFKVIYGD/S | HN/TDSLFISGDK | ST | [ |
| NrdJ | (GOS)* | GTNPC/C | HN/SEIVL | CS | [ |
| gp41 | (GOS)* | TRSGY/C | HN/SSSDV | CS | [ |
| gp41 | (GOS)* | SQLNR/C | HN/SAVEE | CS | [ |
| IMPDH | (GOS)* | GIGGG/C | HN/SICST | CS | [ |
| Vidal T4Lh⁃1 | LAS/C | SHN/TNVG | CT | [ | |
| Vidal UvsX⁃2 | ESG/C | SHN/SGK | CS | [ | |
| NrdHF | (GOS∶AceL) a | SIRDE/A | TGN/SMHVE | Class3 b CS | [ |
| TerL | (GOS∶AceL) a | EFE/C | SHN/CEFL | CC | [ |
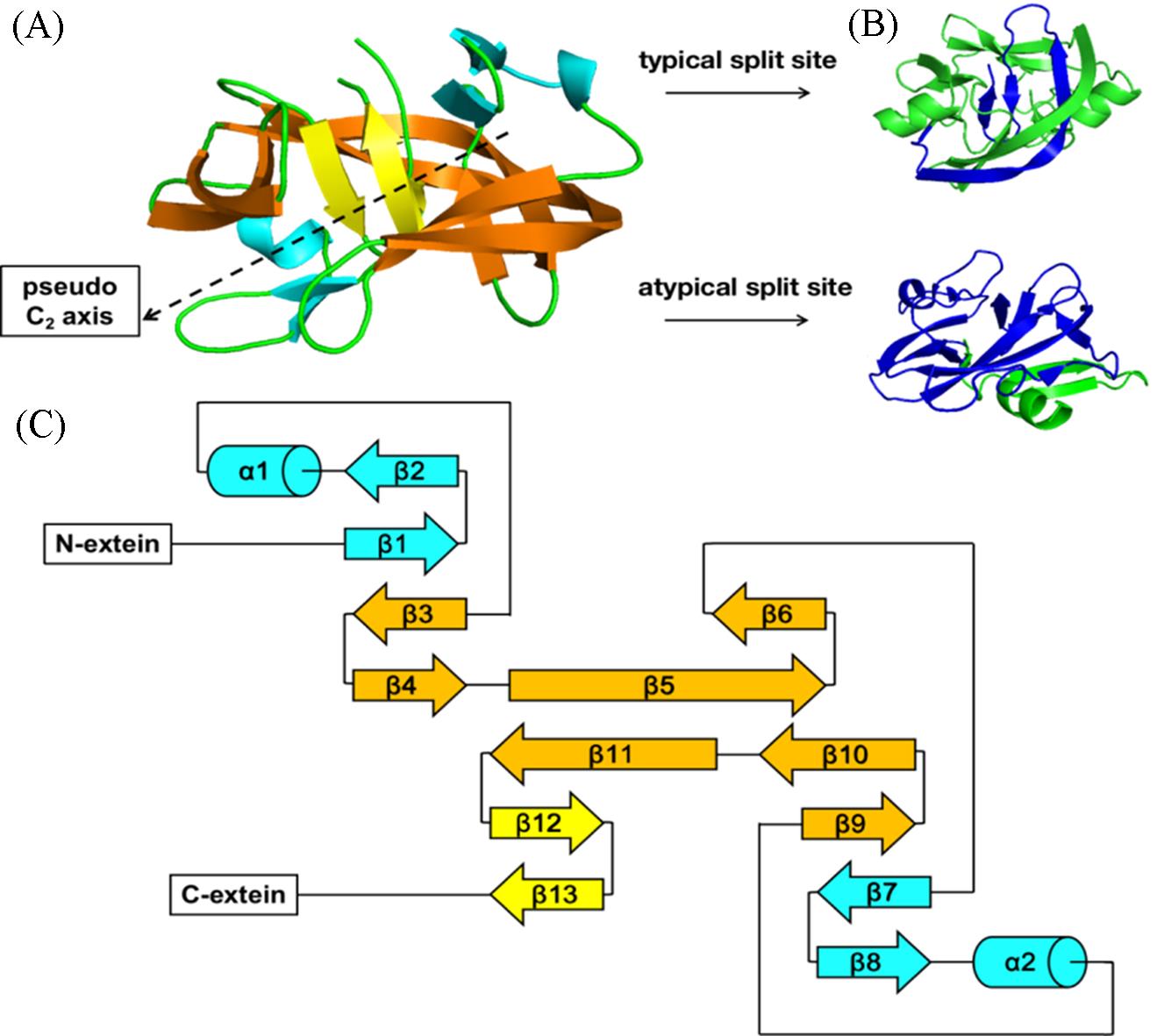
Fig.4 General structure and different split sites of split intein complex(A) Crystal structure of Npu DnaB(PDB code 4OIR); orange represents β-sheets that form the horseshoe-like plane; cyan represents the ββα motif, yellow represents vertical β-sheets connecting to the C-extein; (B) crystal structure of Ssp DnaE(PDB code 3NZM) and NMR solution structure of Cat(PDB code 6DSL); green represents N-intein and blue represents C-intein; (C) scheme of the general secondary structure of split intein complex, colored corresponding to structure in (A).
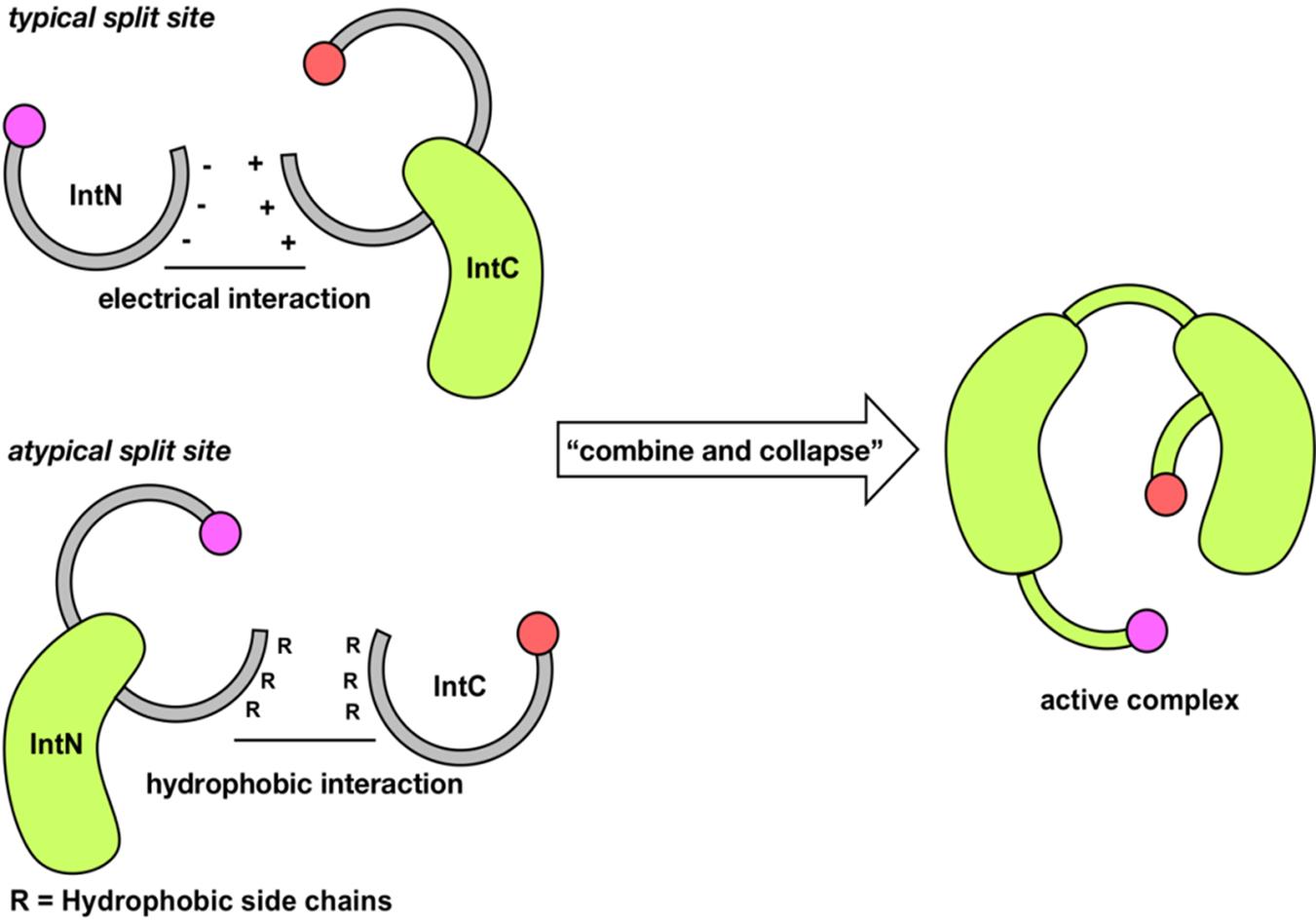
Fig.5 Combination of split inteinGray represents disordered or dynamic structure. Green represents stable folded structure. Purple and red represents N-extein and C-extein, respectively.
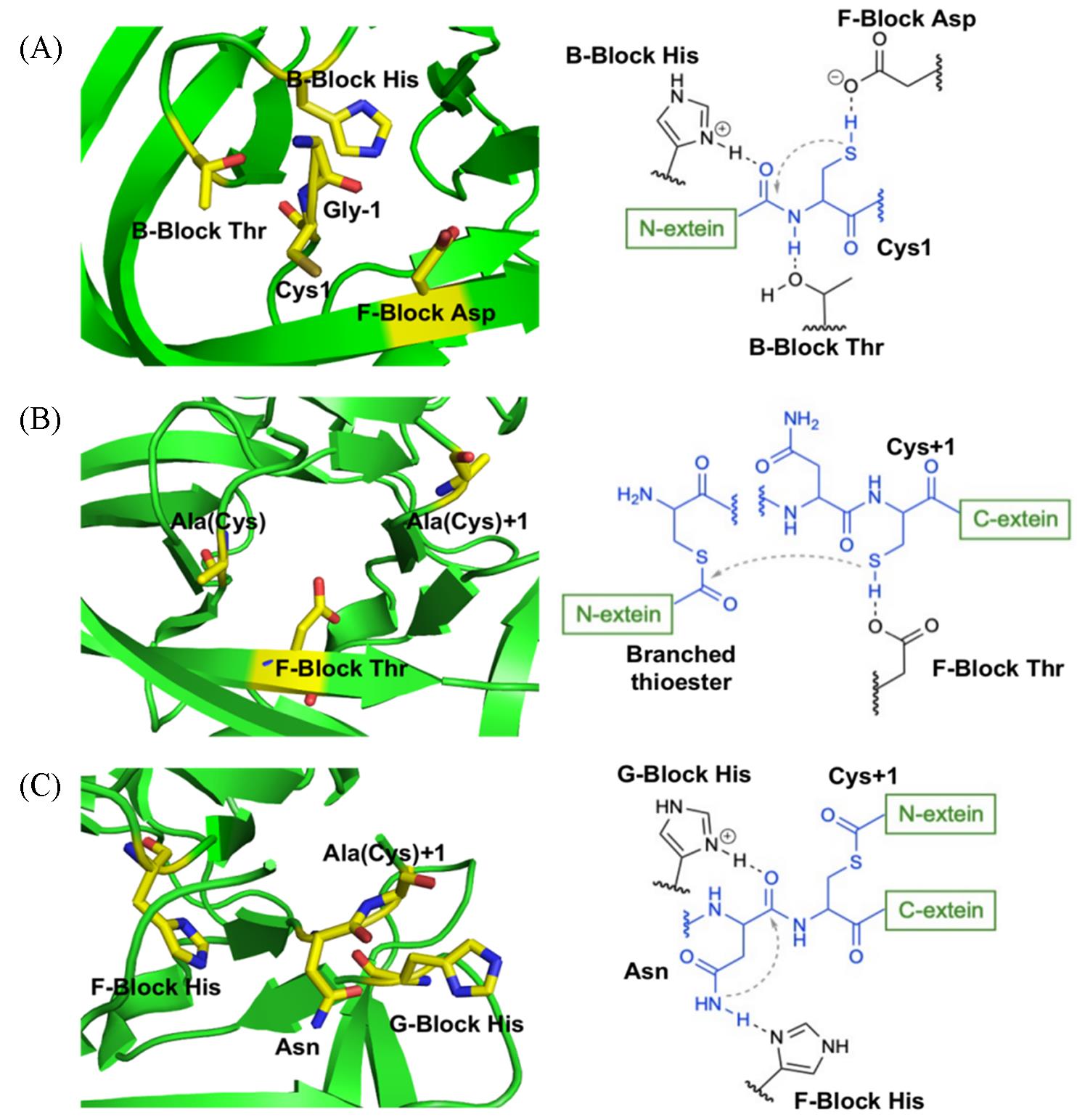
Fig.7 Catalytic environment of protein trans⁃splicing mediated by split inteinThe first step(A), the second step(B) and the third step(C) of protein trans⁃splicing are described by crystal structures on the left side and the mechanism schemes on the right side. (A) Uses the crystal structure of Ssp DnaE(PDB code 3NZM); (B) and (C) use the crystal structure of Npu DnaE(PDB code 4 KL5).
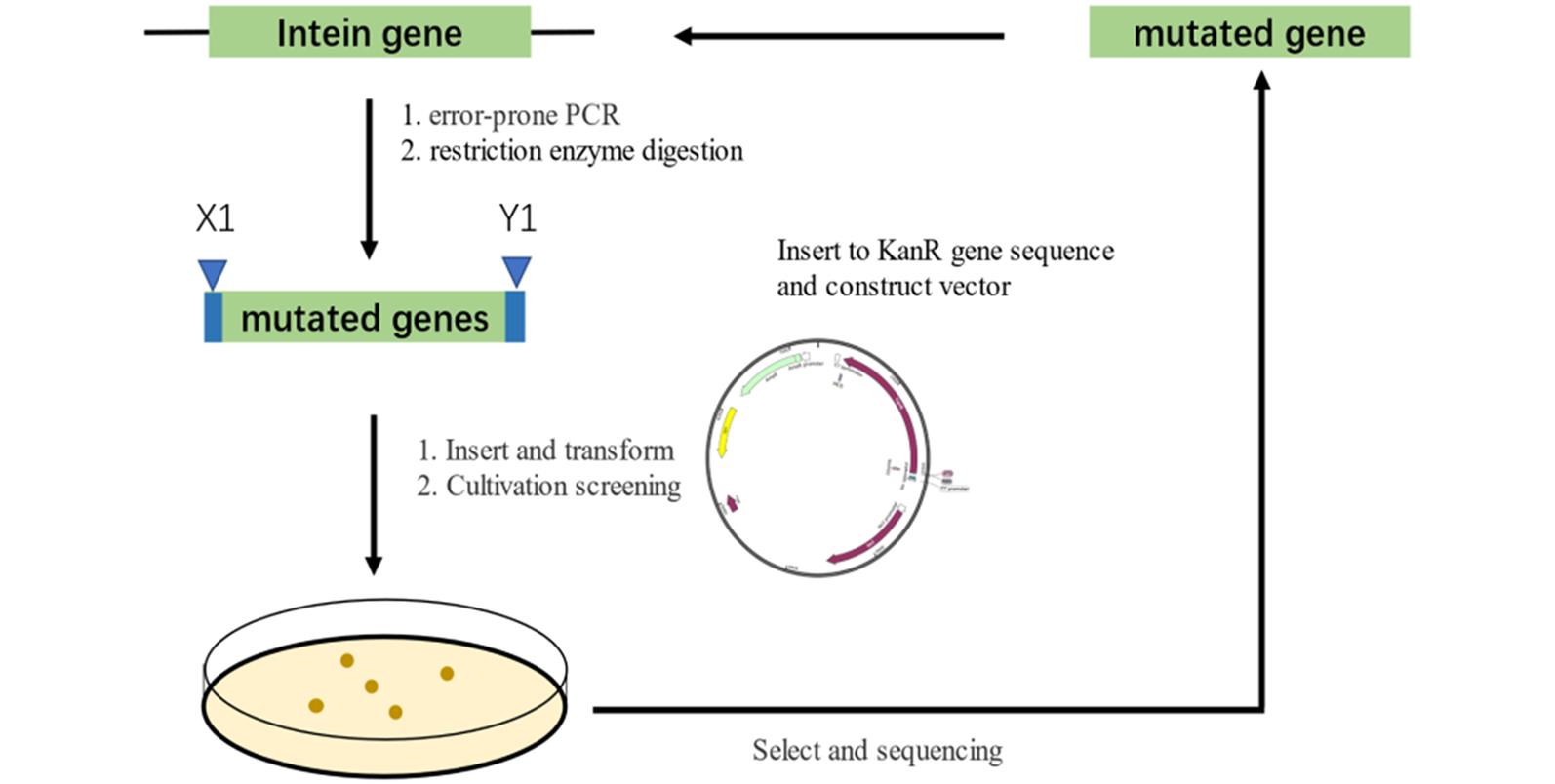
Fig.8 Sequence evolution processA large number of randomly mutated genes obtained from error-prone PCR were screened to obtain the mutated peptide sequence that can perform splicing reaction at the insertion site.
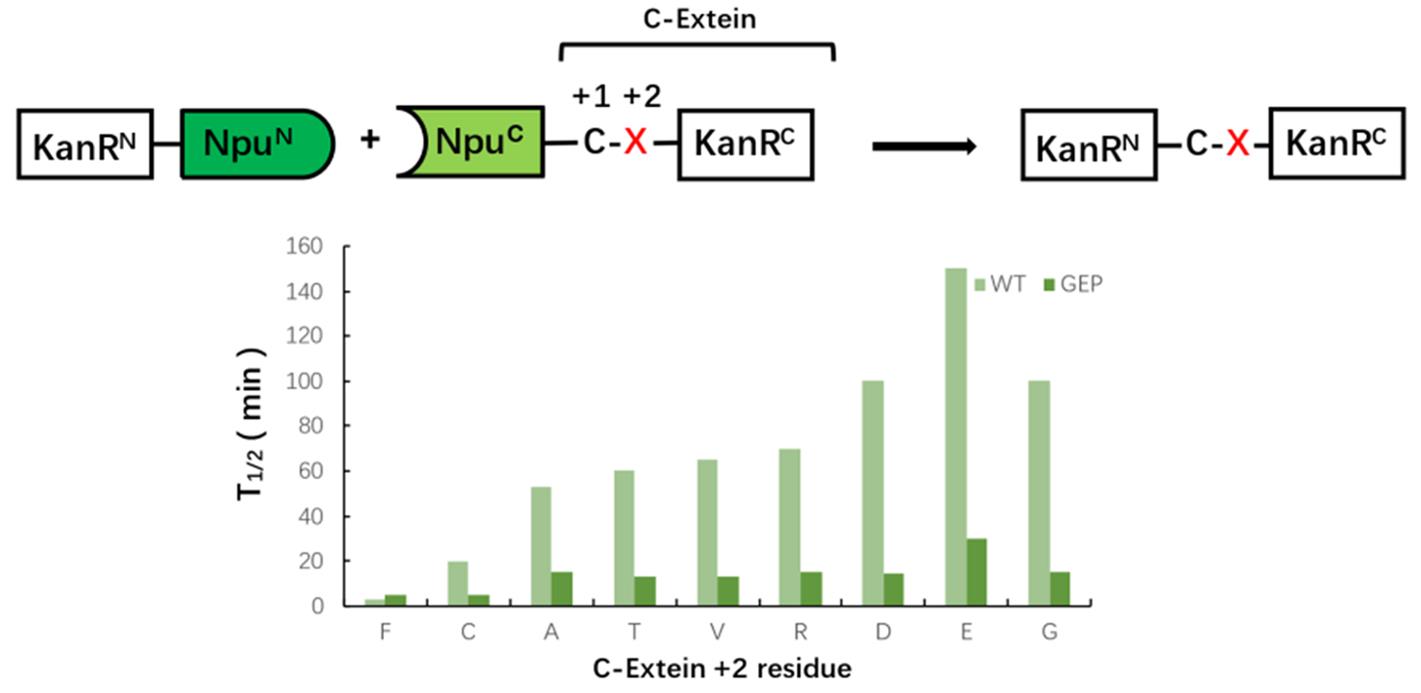
Fig.9 Compatibility of extein+2 positionCompared with WT, the split intein mutation in the ring(residue 122-124) where His125 is located led to a faster reaction rate to different extein +2 amino acid residue.
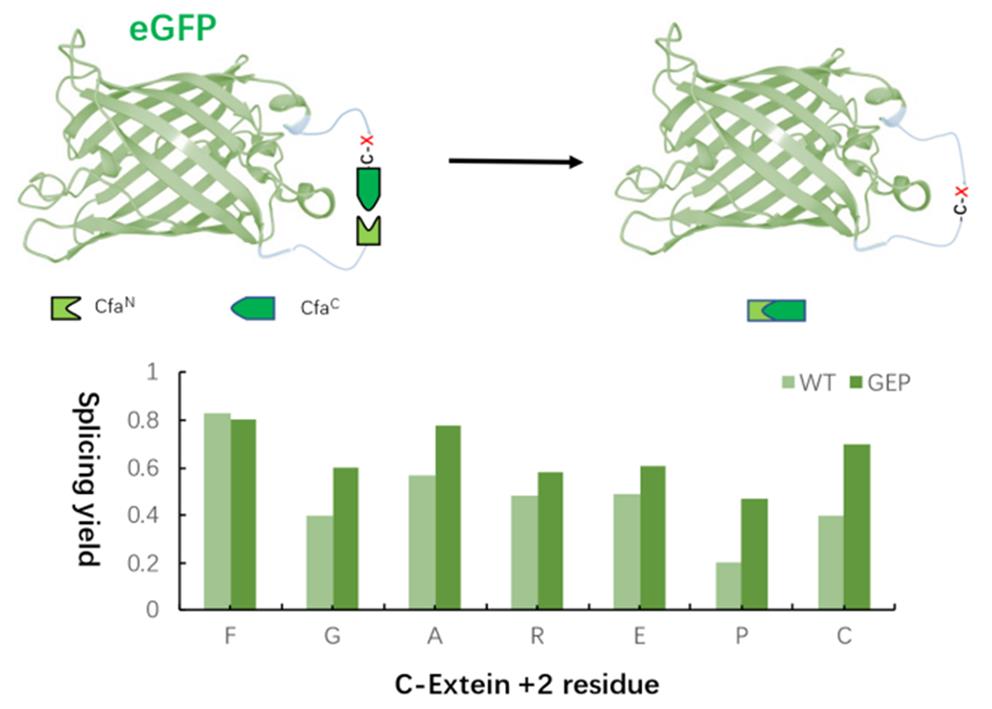
Fig.10 Compatibility of extein+2 positionCompared with WT, the split endopeptides modified by mutation in key regions generally have higher splicing yield for different exopeptides+2 amino acid residues except for F.
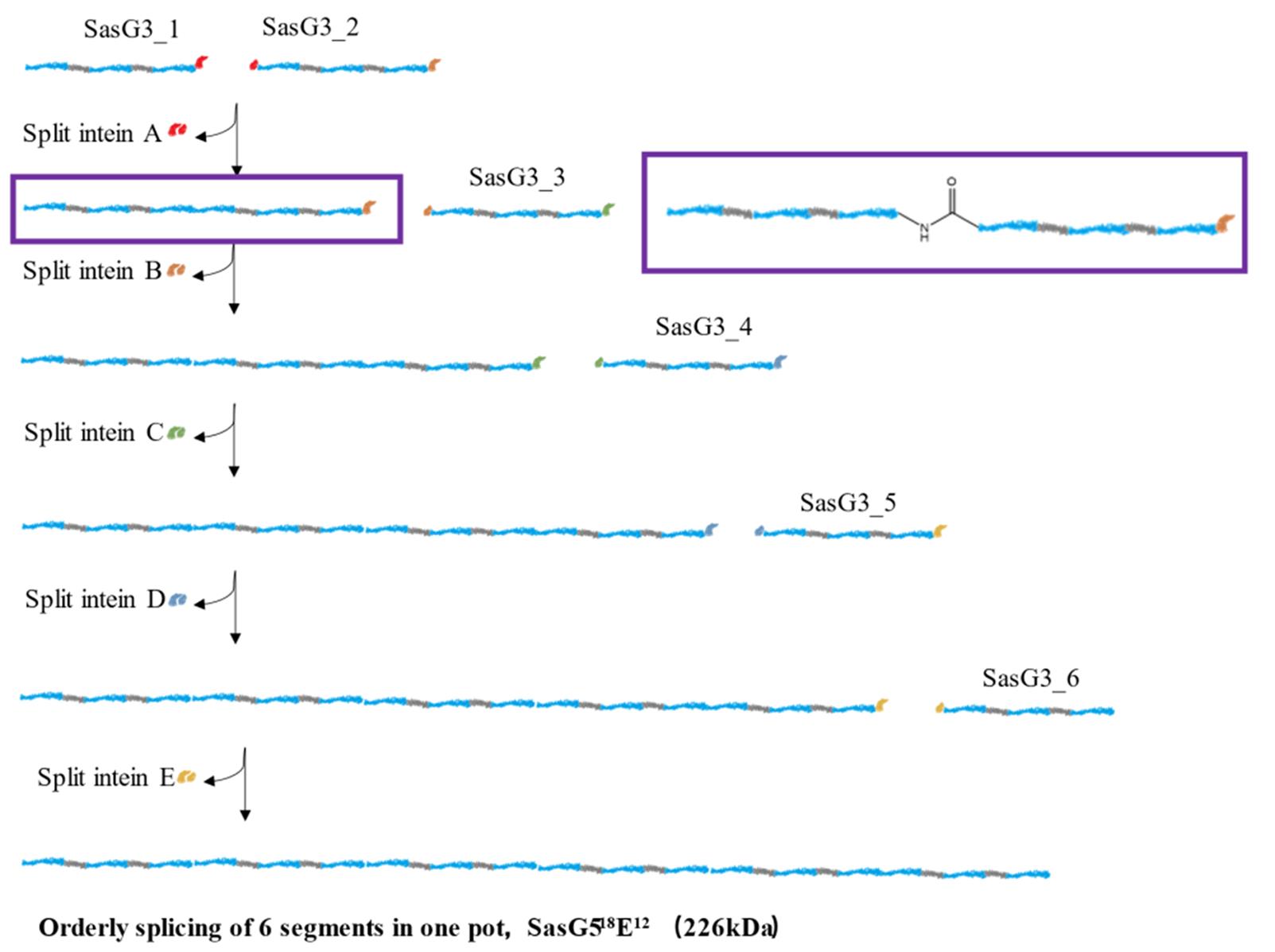
Fig.11 The application of the orthogonal split intein in the multi⁃segment one⁃pot ligation[87]Through five groups of mutually orthogonal split inteins, the sequential ligation of six large proteins was achived in a one-pot manner.
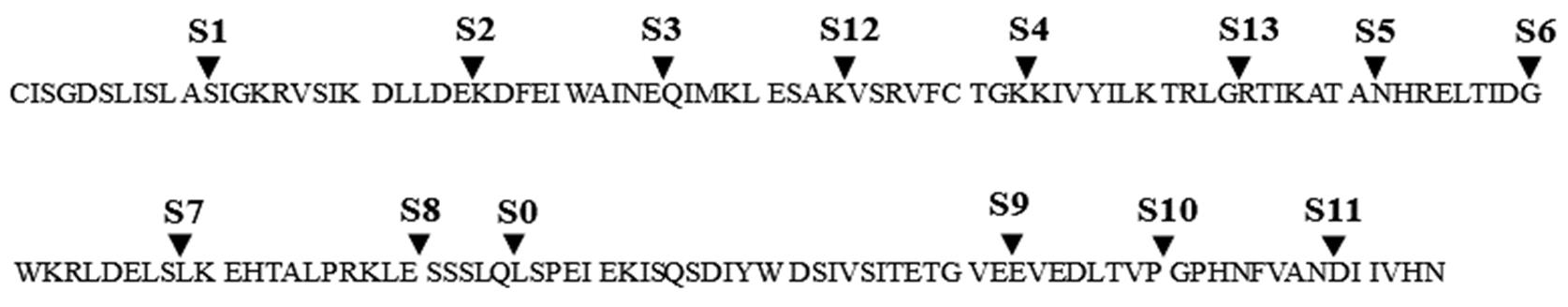
Fig.13 Potential divisible sites in the intein sequenceMost of the natural split inteins split from S0. Researchers have tried to develop a variety of atypical split intein from other potential split sites.
| 78 | Mujika J. I., Lopez X., Mulholland A. J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113(16), 5607—5616 |
| 79 | Shah N. H., Eryilmaz E., Cowburn D., Muir T. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(15), 5839—5847 |
| 80 | Shao Y., Paulus E., J. Pept. Res., 2009, 50(3), 193—198 |
| 81 | Lockless S. W., Muir T. W., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106(27), 10999—11004 |
| 82 | Schwarzer D., Ludwig C., Thiel I. V., Mootz H. D., Biochem., 2012, 51(1), 233—242 |
| 83 | Stevens A. J., Brown Z. Z., Shah N. H., Sekar G., Cowburn D., Muir T. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(7), 2162—2165 |
| 84 | Appleby⁃Tagoe J. H., Thiel I. V., Wang Y., Wang Y., Mootz H. D., Liu X. Q., J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 286(39), 34440—34447 |
| 85 | Stevens A. J., Sekar G., Shah N. H., Mostafavi A. Z., Cowburn D., Muir T. W., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2017, 114(32), 8538—8543 |
| 86 | Beyer H. M., Mikula K. M., Li M., Wlodawer A., Iwaï H., FEBS J., 2020, 287(9), 1886—1898 |
| 87 | Pinto F., Thornton E. L., Wang B., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 1529 |
| 88 | Shi J., Muir T. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(17), 6198—6206 |
| 89 | Dawson P. E., Churchill M. J., Ghadiri M. R., Kent S. B. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119(19), 4325—4329 |
| 1 | Aebersold R., Agar J. N., Amster I. J., Baker M. S., Bertozzi C. R., Boja E. S., Costello C. E., Cravatt B. F., Fenselau C., Garcia B. A., Ge Y., Gunawardena J., Hendrickson R. C., Hergenrother P. J., Huber C. G., Ivanov A. R., Jensen O. N., Jewett M. C., Kelleher N. L., Kiessling L. L., Krogan N. J., Larsen M. R., Loo J. A., Ogorzalek Loo R. R., Lundberg E., MacCoss M. J., Mallick P., Mootha V. K., Mrksich M., Muir T. W., Patrie S. M., Pesavento J. J., Pitteri S. J., Rodriguez H., Saghatelian A., Sandoval W., Schlüter H., Sechi S., Slavoff S. A., Smith L. M., Snyder M. P., Thomas P. M., Uhlén M., Van Eyk J. E., Vidal M., Walt D. R., White F. M., Williams E. R., Wohlschlager T., Wysocki V. H., Yates N. A., Young N. L., Zhang B., Nat. Chem. Biol., 2018, 14(3), 206—214 |
| 2 | Scott C. P., Abel⁃Santos E., Wall M., Wahnon D. C., Benkovic S. J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96(24), 13638—13643 |
| 3 | Kent S. B. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(2), 338—351 |
| 4 | Oza J. P., Aerni H. R., Pirman N. L., Barber K. W., Ter Haar C. M., Rogulina S., Amrofell M. B., Isaacs F. J., Rinehart J., Jewett M. C., Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8168 |
| 5 | Pan M., Zheng Q., Gao S., Qu Q., Yu Y., Wu M., Lan H., Li Y., Liu S., Li J., Sun D., Lu L., Wang T., Zhang W., Wang J., Li Y., Hu H. G., Tian C., Liu L., CCS Chem., 2019, 1(5), 476—489 |
| 6 | Sui X., Wang Y., Du Y. X., Liang L. J., Zheng Q., Li Y. M., Liu L., Chem. Sci., 2020, 11(47), 12633—12646 |
| 7 | Zheng Q., Su Z., Yu Y., Liu L., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2022, 70, 102187 |
| 8 | Zhang B.C., Li Y. L., Shi W. W., Wang T. Y., Zhang F., Liu L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2020, 36(5), 733—747 |
| 9 | Merrifield R. B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1963, 85(14), 2149—2154 |
| 10 | Mijalis A. J., Thomas D. A., Simon M. D., Adamo A., Beaumont R., Jensen K. F., Pentelute B. L., Nat. Chem. Biol., 2017, 13(5), 464—466 |
| 11 | Ludwig C., Pfeiff M., Linne U., Mootz H. D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45(31), 5218—5221 |
| 12 | Busche A. E. L., Aranko A. S., Talebzadeh⁃Farooji M., Bernhard F., Dötsch V., Iwaï H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(33), 6128—6131 |
| 13 | Kurpiers T., Mootz H. D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46(27), 5234—5237 |
| 14 | Schnölzer M., Kent S. B. H., Science, 1992, 256(5054), 221—225 |
| 90 | Li Y. T., Yi C., Chen C. C., Lan H., Pan M., Zhang S. J., Huang Y. C., Guan C. J., Li Y. M., Yu L., Liu L., Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 14846 |
| 91 | Li Y., Heng J., Sun D., Zhang B., Zhang X., Zheng Y., Shi W. W., Wang T. Y., Li J. Y., Sun X., Liu X., Zheng J. S., Kobilka B. K., Liu L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(42), 17566—17576 |
| 92 | Ai H., Chu G. C., Gong Q., Tong Z. B., Deng Z., Liu X., Yang F., Xu Z., Li J. B., Tian C., Liu L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(40), 18329—18337 |
| 93 | Appleby J. H., Zhou K., Volkmann G., Liu X. Q., J. Biol. Chem., 2009, 284(10), 6194—6199 |
| 94 | Aranko A. S., Züger S., Buchinger E., Iwaï H., PloS One, 2009, 4(4), e5185 |
| 95 | Kurpiers T., Mootz H. D., ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(14), 2317—2325 |
| 96 | Khoo K. K., Galleano I., Gasparri F., Wieneke R., Harms H., Poulsen M. H., Chua H. C., Wulf M., Tampé R., Pless S. A., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 2284 |
| 97 | Yagi H., Tsujimoto T., Yamazaki T., Yoshida M., Akutsu H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(50), 16632—16638 |
| 98 | Muona M., Aranko A. S., Iwai H., ChemBioChem., 2008, 9(18), 2958—2961 |
| 99 | Züger S., Iwai' H., Nat. Biotechnol., 2005, 23(6), 736—740 |
| 100 | Naumann T. A., Tavassoli A., Benkovic S. J., ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(2), 194—197 |
| 101 | Young T. S., Young D. D., Ahmad I., Louis J. M., Benkovic S. J., Schultz P. G., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2011, 108(27), 11052—11056 |
| 102 | Kritzer J. A., Hamamichi S., McCaffery J. M., Santagata S., Naumann T. A., Caldwell K. A., Caldwell G. A., Lindquist S., Nat. Chem. Biol., 2009, 5(9), 655—663 |
| 15 | Dawson P. E., Muir T. W., Clark⁃Lewis I., Kent S. B., Science, 1994, 266(5186), 776—779 |
| 16 | Shi W. W., Shi C., Wang T. Y., Li Y. L., Zhou Y. K., Zhang X. H., Bierer D., Zheng J. S., Liu L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(1), 349—357 |
| 17 | Liang L. J., Chu G. C., Qu Q., Zuo C., Mao J., Zheng Q., Chen J., Meng X., Jing Y., Deng H., Li Y. M., Liu L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(31), 17171—17177 |
| 18 | Pan M., Gao S., Zheng Y., Tan X., Lan H., Tan X., Sun D., Lu L., Wang T., Zheng Q., Huang Y., Wang J., Liu L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(23), 7429—7435 |
| 19 | Tang S., Si Y. Y., Wang Z. P., Mei K. R., Chen X., Cheng J. Y., Zheng J. S., Liu L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(19), 5713—5717 |
| 20 | Fang G. M., Li Y. M., Shen F., Huang Y. C., Li J. B., Lin Y., Cui H. K., Liu L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(33), 7645—7649 |
| 21 | Cheng X., Smith J. C., Chem. Rev., 2019, 119(9), 5849—5880 |
| 22 | Zheng J. S., He Y., Zuo C., Cai X. Y., Tang S., Wang Z. A., Zhang L. H., Tian C. L., Liu L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(10), 3553—3561 |
| 23 | Zhang B., Deng Q., Zuo C., Yan B., Zuo C., Cao X. X., Zhu T. F., Zheng J. S., Liu L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(35), 12231—12237 |
| 24 | Ficht S., Mattes A., Seitz O., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(32), 9970—9981 |
| 25 | Chisholm T. S., Kulkarni S. S., Hossain K. R., Cornelius F., Clarke R. J., Payne R. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(2), 1090—1100 |
| 26 | Chu G. C., Pan M., Li J., Liu S., Zuo C., Tong Z. B., Bai J. S., Gong Q., Ai H., Fan J., Meng X., Huang Y. C., Shi J., Deng H., Tian C., Li Y. M., Liu L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(8), 3654—3663 |
| 27 | Zheng Q., Wang T., Chu G. C., Zuo C., Zhao R., Sui X., Ye L., Yu Y., Chen J., Wu X., Zhang W., Deng H., Shi J., Pan M., Li Y. M., Liu L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(32), 13496—13501 |
| 28 | Wang T., Li C., Wang M., Zhang J., Zheng Q., Liang L., Chu G., Tian X., Deng H., He W., Liu L., Li J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(40), e202206205 |
| 29 | Mazmanian S. K., Liu G., Ton⁃That H., Schneewind O., Science, 1999, 285(5428), 760—763 |
| 30 | Wang Z. A., Whedon S. D., Wu M., Wang S., Brown E. A., Anmangandla A., Regan L., Lee K., Du J., Hong J. Y., Fairall L., Kay T., Lin H., Zhao Y., Schwabe J. W. R., Cole P. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(8), 3360—3364 |
| 31 | Podracky C. J., An C., DeSousa A., Dorr B. M., Walsh D. M., Liu D. R., Nat. Chem. Biol., 2021, 17(3), 317—325 |
| 32 | Schmohl L., Bierlmeier J., Gerth F., Freund C., Schwarzer D., J. Pept. Sci. Off. Publ. Eur. Pept. Soc., 2017, 23(7/8), 631—635 |
| 33 | Piper I. M., Struyvenberg S. A., Valgardson J. D., Johnson D. A., Gao M., Johnston K., Svendsen J. E., Kodama H. M., Hvorecny K. L., Antos J. M., Amacher J. F., J. Biol. Chem., 2021, 297(2), 655—660 |
| 34 | Zuo C., Ding R., Wu X., Wang Y., Chu G. C., Liang L. J., Ai H., Tong Z. B., Mao J., Zheng Q., Wang T., Li Z., Liu L., Sun D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(28), e202201887 |
| 35 | Li Y. M., Li Y. T., Pan M., Kong X. Q., Huang Y. C., Hong Z. Y., Liu L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(8), 2198—2202 |
| 36 | Passmore L. A., Barford D., Biochem. J., 2004, 379(3), 513—525 |
| 37 | Hodges R. A., Perler F. B., Noren C. J., Jack W. E., Nucleic Acids Res., 1992, 20(23), 6153—6157 |
| 38 | Davis E. O., Jenner P. J., Brooks P. C., Colston M. J., Sedgwick S. G., Cell, 1992, 71(2), 201—210 |
| 39 | Pietrokovski S., Protein Sci., 1994, 3(12), 2340—2350 |
| 40 | Kato I., Anfinsen C. B., J. Biol. Chem., 1969, 244(3), 1004—1007 |
| 41 | Southworth M. W., Adam E., Panne D., Byer R., Kautz R., Perler F. B., EMBO J., 1998, 17(4), 918—926 |
| 42 | Mills K. V., Lew B. M., Jiang S., Paulus H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95(7), 3543—3548 |
| 43 | Dai X., Xun Q., Liu X. Q., Meng Q., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 99(19), 8151—8161 |
| 44 | Wu H., Xu M. Q., Liu X. Q., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1998, 1387(1—2), 422—432 |
| 45 | Brenzel S., Kurpiers T., Mootz H. D., Biochem., 2006, 45(6), 1571—1578 |
| 46 | Yamazaki T., Otomo T., Oda N., Kyogoku Y., Uegaki K., Ito N., Ishino Y., Nakamura H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120(22), 5591—5592 |
| 47 | Otomo T., Ito N., Kyogoku Y., Yamazaki T., Biochemistry, 1999, 38(49), 16040—16044 |
| 48 | Li X., Zhang X. L., Cai Y. M., Zhang L., Lin Y., Meng Q., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 109, 921—931 |
| 49 | Wu H., Hu Z., Liu X. Q., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95(16), 9226—9231 |
| 50 | Zettler J., Schütz V., Mootz H. D., FEBS Lett., 2009, 583(5), 909—914 |
| 51 | Iwai H., Züger S., Jin J., Tam P. H., FEBS Lett., 2006, 580(7), 1853—1858 |
| 52 | Dassa B., Amitai G., Caspi J., Schueler⁃Furman O., Pietrokovski S., Biochem., 2007, 46(1), 322—330 |
| 53 | Wei X. Y., Sakr S., Li J. H., Wang L., Chen W. L., Zhang C. C., Res. Microbiol., 2006, 157(3), 227—234 |
| 54 | Matsumura H., Takahashi H., Inoue T., Yamamoto T., Hashimoto H., Nishioka M., Fujiwara S., Takagi M., Imanaka T., Kai Y., Proteins, 2006, 63(3), 711—715 |
| 55 | Choi J. J., Nam K. H., Min B., Kim S. J., Söll D., Kwon S. T., J. Mol. Biol., 2006, 356(5), 1093—1106 |
| 56 | Carvajal⁃Vallejos P., Pallissé R., Mootz H. D., Schmidt S. R., J. Biol. Chem., 2012, 287(34), 28686—28696 |
| 57 | Neugebauer M., Böcker J. K., Matern J. C. J., Pietrokovski S., Mootz H. D., Biol. Chem., 2017, 398(1), 57—67 |
| 58 | Hoffmann S., Terhorst T. M. E., Singh R. K., Kümmel D., Pietrokovski S., Mootz H. D., ChemBioChem, 2021, 22(2), 364—373 |
| 59 | Thiel I. V., Volkmann G., Pietrokovski S., Mootz H. D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(5), 1306—1310 |
| 60 | Perler F. B., Nucleic Acids Res., 2000, 28(1), 344—345 |
| 61 | Perler F. B., Olsen G. J., Adam E., Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, 25(6), 1087—1093 |
| 62 | Al⁃Ali H., Ragan T. J., Gao X., Harris T. K., Bioconjug. Chem., 2007, 18(4), 1294—1302 |
| 63 | Sun W., Yang J., Liu X. Q., J. Biol. Chem., 2004, 279(34), 35281—35286 |
| 64 | Gordo V., Aparicio D., Pérez⁃Luque R., Benito A., Vilanova M., Usón I., Fita I., Ribó M., Cell Chem. Biol., 2018, 25(7), 871-879.e2 |
| 65 | Eryilmaz E., Shah N. H., Muir T. W., Cowburn D., J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289(21), 14506—14511 |
| 66 | Shah N. H., Eryilmaz E., Cowburn D., Muir T. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(49), 18673—18681 |
| 67 | Stevens A. J., Sekar G., Gramespacher J. A., Cowburn D., Muir T. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(37), 11791—11799 |
| 68 | Zheng Y., Wu Q., Wang C., Xu M., Liu Y., Biosci. Rep., 2012, 32(5), 433—442 |
| 69 | Shah N. H., Vila⁃Perelló M., Muir T. W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(29), 6511—6515 |
| 70 | van Roey P., Pereira B., Li Z., Hiraga K., Belfort M., Derbyshire V., J. Mol. Biol., 2007, 367(1), 162—173 |
| 71 | Du Z., Zheng Y., Patterson M., Liu Y., Wang C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(26), 10275—10282 |
| 72 | Mujika J. I., Lopez X., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2017, 121(33), 7786—7796 |
| 73 | Friedel K., Popp M. A., Matern J. C. J., Gazdag E. M., Thiel I. V., Volkmann G., Blankenfeldt W., Mootz H. D., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(1), 239—251 |
| 74 | Callahan B. P., Topilina N. I., Stanger M. J., van Roey P., Belfort M., Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2011, 18(5), 630—633 |
| 75 | Dearden A. K., Callahan B., Roey P. V., Li Z., Kumar U., Belfort M., Nayak S. K., Protein Sci., 2013, 22(5), 557—563 |
| 76 | Pereira B., Shemella P. T., Amitai G., Belfort G., Nayak S. K., Belfort M., J. Mol. Biol., 2011, 406(3), 430—442 |
| 77 | Ding Y., Xu M. Q., Ghosh I., Chen X., Ferrandon S., Lesage G., Rao Z., J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278(40), 39133—39142 |
| 103 | Horswill A. R., Savinov S. N., Benkovic S. J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2004, 101(44), 15591—15596 |
| 104 | Palei S., Mootz H. D., Chem. Commun., 2021, 57(34), 4194—4197 |
| 105 | Bionda N., Fasan R., ChemBioChem, 2015, 16(14), 2011—2016 |
| 106 | Kang D., Kim D. W., Kim J. C., Park H. S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023, 62(7), e202214815 |
| 107 | Mootz H. D., Muir T. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(31), 9044—9045 |
| 108 | Brenzel S., Mootz H. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(12), 4176—4177 |
| 109 | Tyszkiewicz A. B., Muir T. W., Nat. Methods, 2008, 5(4), 303—305 |
| 110 | Selgrade D. F., Lohmueller J. J., Lienert F., Silver P. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(20), 7713—7719 |
| 111 | Vila⁃Perelló M., Hori Y., Ribó M., Muir T. W., Angew. Chem., 2008, 120(40), 7878—7881 |
| 112 | Böcker J. K., Dörner W., Mootz H. D., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(9), 1287—1290 |
| [1] | 安群星, 雷迎峰, 杨敬, 黎志东, 穆士杰, 徐志凯. 天花粉蛋白的聚乙二醇定点修饰及其性质的初步研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(8): 1586. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||