

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 1146.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200583
樊文倩1, 钟正祥2, 田宫伟2, 王宇3, 巩桂芬1, 齐殿鹏2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-21
出版日期:2021-04-10
发布日期:2020-12-21
通讯作者:
齐殿鹏
E-mail:dpqi@hit.edu.cn
基金资助:
FAN Wenqian1, ZHONG Zhengxiang2, TIAN Gongwei2, WANG Yu3, GONG Guifen1, QI Dianpeng2( )
)
Received:2020-08-21
Online:2021-04-10
Published:2020-12-21
Contact:
QI Dianpeng
E-mail:dpqi@hit.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
神经界面电极作为人体和外部器件间信息融合的媒介, 为人们进一步探究神经系统高级功能的机制提供了有效工具. 传统的神经电极多以金属和半导体材料为主, 这两类材料因具有惰性材料的特性及优越的 导电性能而成为早期神经电极的主要制备材料, 但由于其刚性过大和光滑表面导致的机械失配及与生物组织间过高的电化学阻抗限制了神经电极的进一步发展. 导电高分子作为一种有机导电材料, 同时具备柔软性 (杨氏模量约在0.01~10 GPa)和导电性(高掺杂度的导电高分子的电导率在金属范围, 100~105 S/cm)的特征, 是制备神经电极的有效材料. 近年来, 人们利用导电高分子材料对传统电极材料进行改性甚至替代, 以提高电极比表面积、 减小界面阻抗, 并提高电极检测的灵敏性; 同时减小电极与组织间的应变失配, 减少炎症反应, 并进一步在导电高分子中引入功能性生物大分子, 减少生物组织对电极的排异反应, 增加电极在体内长期植入的稳定性. 本文讨论和总结了导电高分子材料在神经电极中的应用, 分别对导电高分子作为涂层修饰神经电极、 全导电高分子材料神经电极及导电高分子复合材料神经电极等展开讨论, 分析了导电高分子在神经界面电极中的应用前景及存在的问题, 以期对神经界面电极在脑科学和生物电子医疗等前沿领域的进一步发展提供参考.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
樊文倩, 钟正祥, 田宫伟, 王宇, 巩桂芬, 齐殿鹏. 导电高分子在神经界面电极中的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1146.
FAN Wenqian, ZHONG Zhengxiang, TIAN Gongwei, WANG Yu, GONG Guifen, QI Dianpeng. Application of Conductive Polymer in Nerve Interface Electrode. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1146.
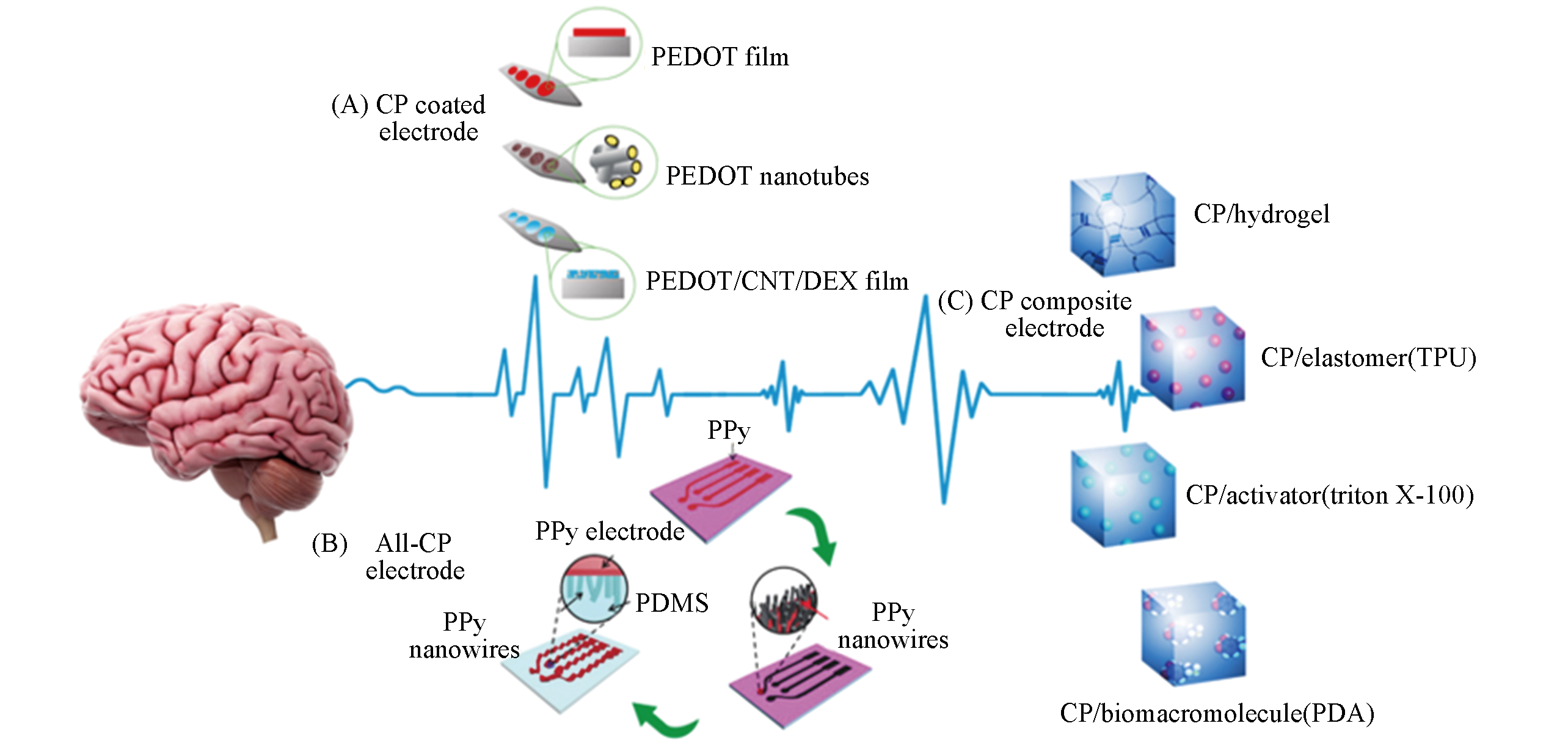
Fig.1 Classification of neural interfacial electrode based on conducting polymer(A) Conductive polymer coated electrode; (B) all conducting polymer electrode; (C) conductive polymer composite electrode.
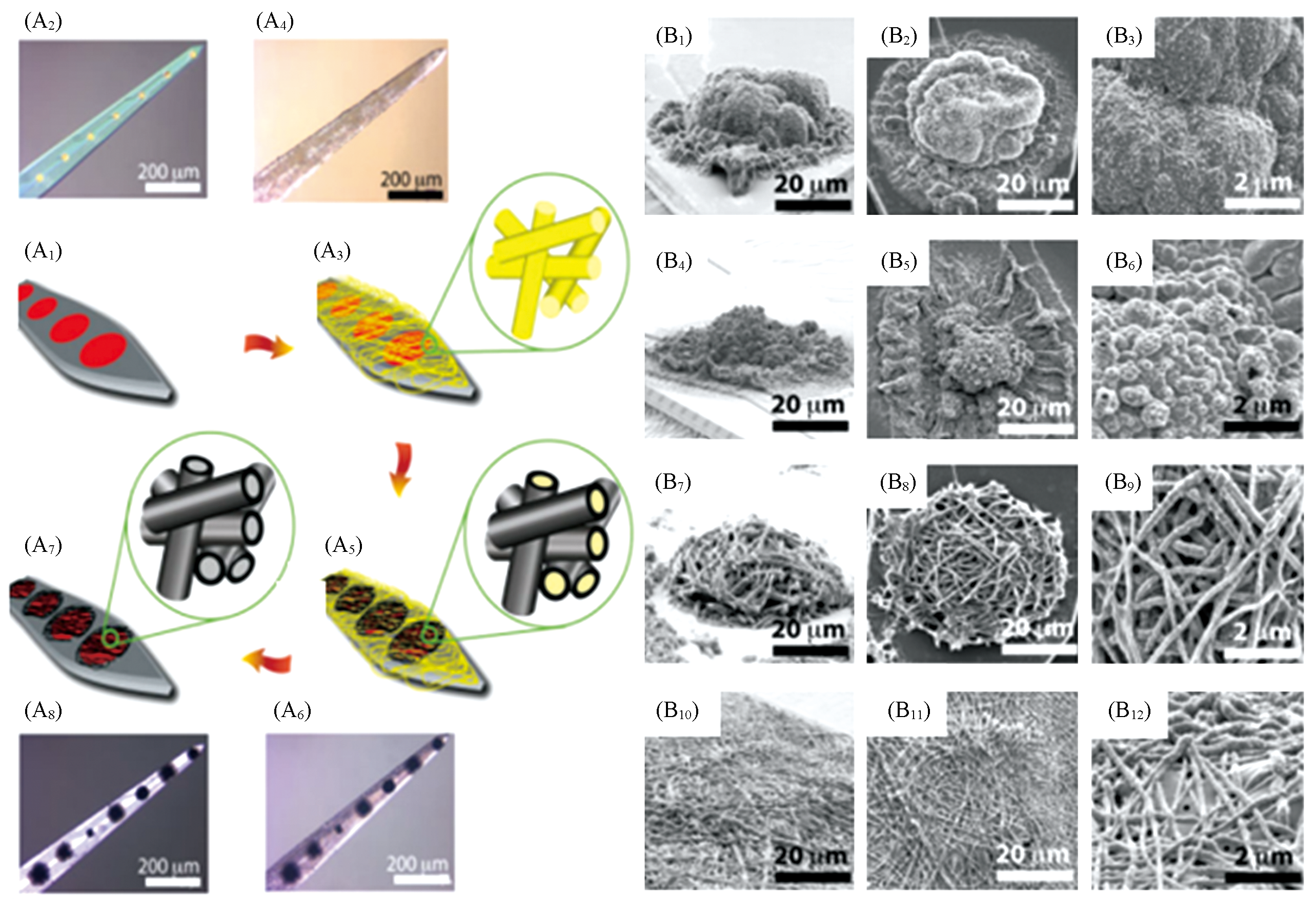
Fig.2 Schematic illustration and optical micrographs of fabrication process of conducting?polymer nanotubes on the surface of neural microelectrodes(A1—A8) and SEM images of electropolymerized nanostructured conducting polymers on the electrode sites(B1—B12)[43](A1) Schematic illustration; (A2) optical micrographs of neural microelectrode before surface modification; (A3) schematic illustration; (A4) optical micrographs of poly(lactic acid)(PLLA) nanofibers; (A5) schematic illustration; (A6) optical micrographs of conductive polymer(PEDOT) deposited on PLLA nanofiber template at electrode sites; (A7) schematic illustration; (A8) optical micrographs of conducting?polymer nanotubes; (B1)―(B3) PPy film; (B4)―(B6) PEDOT film; (B7)―(B9) PPy nanotubes; (B10)―(B12) PEDOT nanotubes. Copyright 2010, Wiley-VCH.
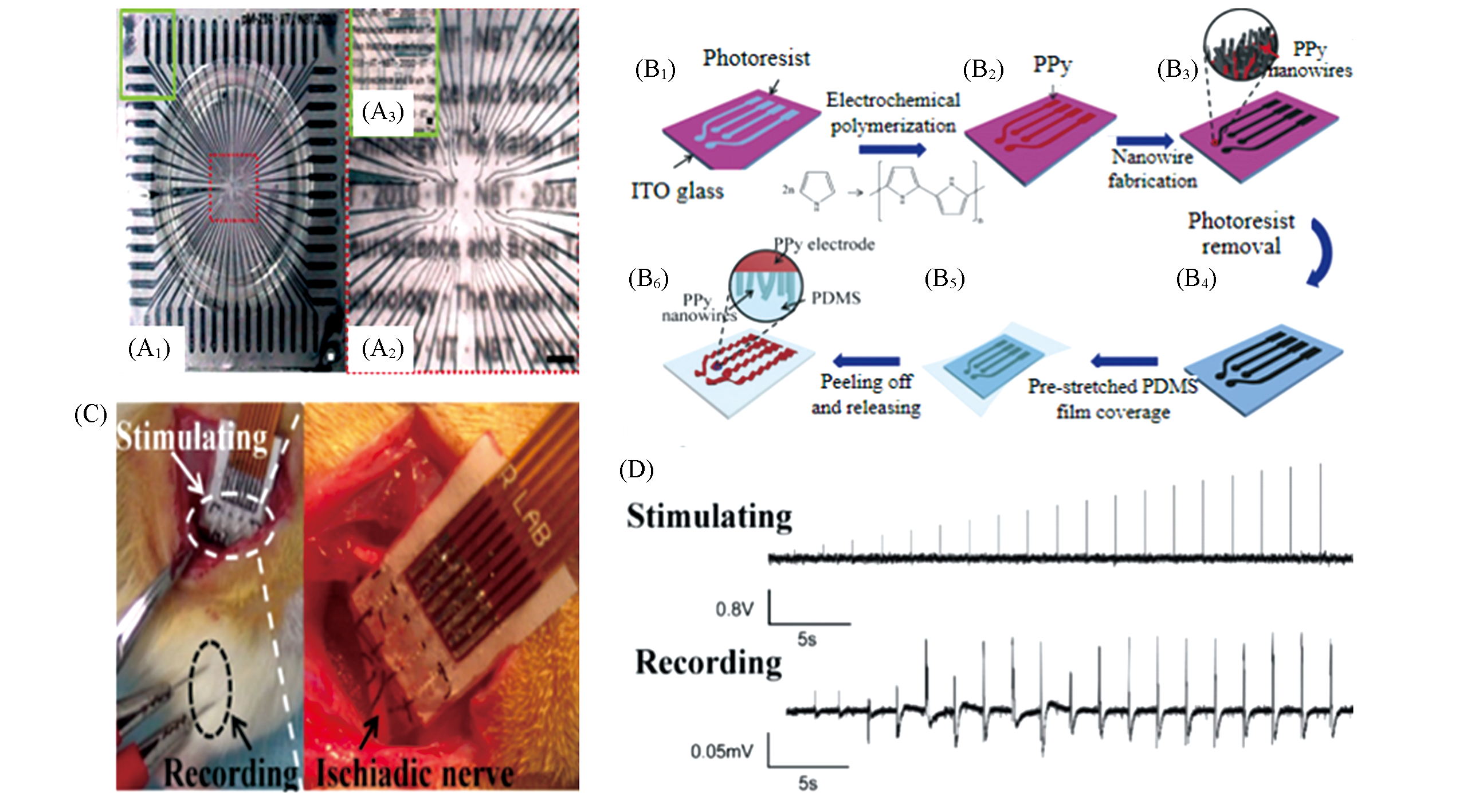
Fig.3 Digital image of polyMEAs(A1―A3)[60] and scheme for the fabrication of fully polymeric microelectrode arrays(B1―B6) and image of a four?channels?MEA(C) and EMG signal(D)[76](A1) PolyMEA; (A2) zoom onto the central matrix; (A3) zoom on to five contact pads. Copyright 2010, Elsevier. (B1) The fabrication of photoresist pattern on ITO glass via a photolithography process; (B2) Deposition of PPy film on the exposed ITO surface by electropolymerization; (B3) synthesis of PPy nanowires on the surface of PPy film; (B4) PPy electrode on ITO surface; (B5) the prestretched PDMS thin film was covered on the PPy electrode surface; (B6) the stretchable all?polymeric electrode arrays (inset is a magnified scheme of the PPy nanowires buried in PDMS substrate). Copyright 2010, Wiley?VCH.
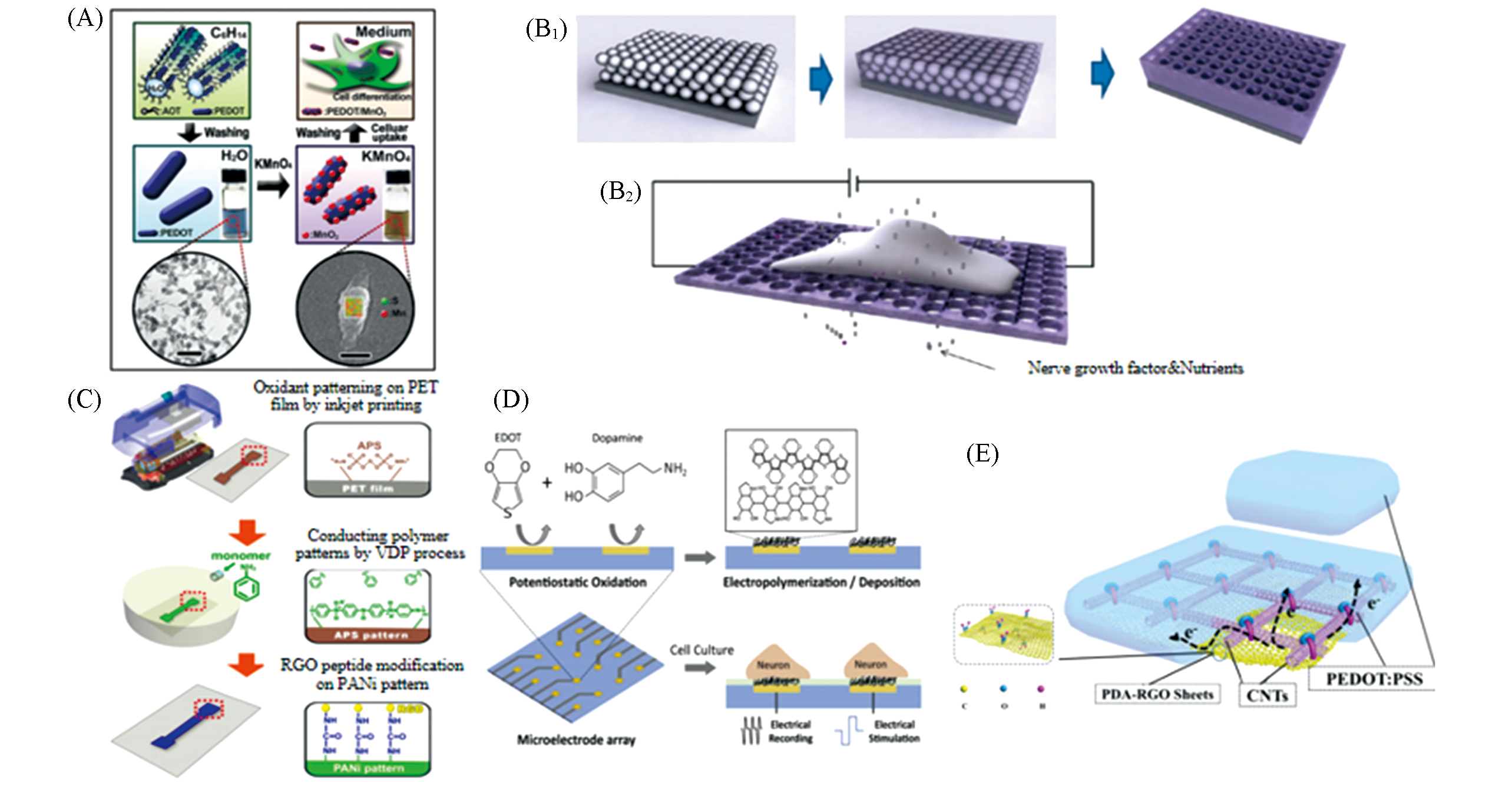
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of fabrication of different conducting polymer composite electrode(A) PEDOT/MnO2 nanoellipsoids[81]. Copyright 2013, Wiley?VCH. (B1, B2) NGF?doped porous polypyrrole surfaces[82]. Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society. (C) Strategy for selective cell patterning. Copyright 2013, Elsevier. (D) PEDOT/PDA deposited microelectrodes[84]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier. (E) Composition and structure of PDA?RGO/CNT/PEDOT:PSS[85]. Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
| 1 | Wu D. D., Synthesis of PANI Composite Material Coatings and Their Effect on Interface Properties of Neural Microelectrode, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 2014(吴栋栋. 聚苯胺复合材料涂层的合成及其对神经电极界面性能的影响, 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014) |
| 2 | Pine J., J. Neurosci., 1980, 2(1), 19—31 |
| 3 | Zhao S. Y., Liu X. J., Xu Z., Ren H., Deng B., Tang M., Lu L. L., Fu X. F., Peng H. L., Liu Z. F., Duan X. J., Nano Lett., 2016, 16(12), 7731—7738 |
| 4 | Lee S., Sheshadri S., Xiang Z. L., Delgado⁃Martinez I., Xue N., Sun T., Thakor N. V., Yen S. C., Lee C. K., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2016, 242, 1165—1170 |
| 5 | Li H., Edin F., Hayashi H., Gudjonsson O., Danckwardt⁃Lillieström N., Engqvist H., Rask⁃Andersen H., Xia W., Biomaterials, 2017,122, 1—9 |
| 6 | Xiang Z. L., Yen S. C., Sheshadri S., Wang J. H., Lee S., Liu Y. H., Liao L. D., Thakor N. V., Lee C. K., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(22), 4472—4479 |
| 7 | Liu Z. Y., Wang X. T., Qi D. P., Xu C., Yu J. C., Liu Y. Q,. Jiang Y., Liedberg B., Chen X. D., Adv. Mater., 2017,29(2), 1603382 |
| 8 | Apollo N. V., Maturana M., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(23), 3551—3559 |
| 9 | Branner A., Stein R. B., Normann R. A., J. Neurophysiology, 2001, 85(4), 1585—1594 |
| 10 | Sui X. H., Zhang R. X., Pei W. H., Lu L., Chen H. D., Journal of Semiconductors, 2006, 27(10), 1703—1706(隋晓红, 张若昕, 裴为华, 鲁琳, 陈弘达. 半导体学报, 2006, 27(10), 1703—1706) |
| 11 | Blanche T. J., Spacek M. A., Hetke J. F., Swindale N. V., J. Neurophysiology, 2005, 93(5), 2987—3000 |
| 12 | Campbell P. K., Jones K. E., Huber R. J., Horch K. W., Normann R. A., IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng., 1991, 38(8), 758—768 |
| 13 | Kim S., Bhandari R., Klein M., Negi S., Rieth L., Tathireddy P., Toepper M., Oppermann H., Solzbacher F., Biomedical Microde⁃ vices, 2009, 11(2), 453—466 |
| 14 | Matthias K., Matthias F., Norbert B., Thomas L., Peter W., Gernot R., Michaela V. P., Ralf H., Gisbert R., Acta Ophthalmol., 2012, 90(1), 1—8 |
| 15 | Logothetis N. K., Augath M., Murayama Y., Rauch A., Sultan F., Goense J., Oeltermann A., Merkle H., Nat Neurosci., 2010, 13(10), 1283—1291 |
| 16 | Zhang H., Zhu Z. H, Wu L., Zhou H. B., Sun X. N., Zhou L., Li G., Jin Q. Y., Zhao J. L., J. Functional Materials and Devices., 2010, 16(5), 457—464(张华, 朱壮晖, 吴蕾, 周洪波, 孙晓娜, 周亮, 李刚, 金庆辉, 赵建龙. 功能材料与器件学报, 2010, 16(5), 457—464) |
| 17 | Green R., Abidian M. R., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(46), 7620—7637 |
| 18 | Scaini D., Ballerini L., Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2018, 50, 50—55 |
| 19 | Cogan., Stuart F., Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 2008, 10(1), 275—309 |
| 20 | Green R. A., Matteucci P. B., Dodds C. W. D., Palmer J., Dueck W. F., Hassarati R. T., Byrnes⁃Preston P. J., Lovell N. H., Suaning G. J., J. Neural Eng., 2014, 11(5), 056017 |
| 21 | Polikov V. S., Tresco P. A., Reichert W. M., J. Neuro Methods., 2005, 148(1), 1—18 |
| 22 | Marin C., Eduardo F., Front.Neuroeng., 2010, 3(8), 8 |
| 23 | Young A. T., Cornwell N., Daniele M. A., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(12), 1700239 |
| 24 | Shirakawa H., Angewandte Chemie., 2001,40(14), 2574—2580 |
| 25 | Roncali J., Garreau R., Lemaire M., J. Electroanal Chem., 1990, 278(1), 373—378 |
| 26 | Bin H. J., Zhang Z. G., Gao L., Chen S. S., Zhong L., Xue L. W., Yang C., Li Y. F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(13), 4657—4664 |
| 27 | Fratini S., Nikolka M., Salleo A., Schweicher G., Sirringhaus H., Nat. Mater., 2020, 19(5), 1—12 |
| 28 | Deslouis C., Moustafid T. E., Musiani M. M., Tribollet B., Electrochim. Acta, 1996, 41(7/8), 1343—1349 |
| 29 | Heeger A. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40(14), 2591—2611 |
| 30 | Macdiarmid A. G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40(14), 2581 |
| 31 | Hu H. L., Electrochemical Measurement Methods, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2019(胡会利. 电化学测量方法, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2019) |
| 32 | Paulsen B. D., Tybrandt K., Stavrinidou E., Rivnay J., Nat. Mater., 2019, 19(1), 1—14 |
| 33 | Giglio E. D., Sabbatini L., Colucci S., Zambonin G., J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed., 2000, 11(10), 1073—1083 |
| 34 | George P. M., LaVan D. A., Burdick J. A., Chen C. Y., Liang E., Langer R., Adv. Mater., 2006, 18(5), 577—581 |
| 35 | Keene S. T., Lubrano C., Kazemzadeh S., Melianas A., Santoro F., Nat. Mater., 2020,19, 969—973 |
| 36 | Wang L. P., Wang J. Y., Polymer Bulletin, 2019, (1), 102—109(王莉萍, 王瑾晔. 高分子通报, 2019, (1), 102—109) |
| 37 | Ludwig K. A., Langhals N. B., Joseph M. D., Richardson⁃Burns S. M., Hendricks J. L., Kipke D. R., J. Neural Eng., 2011, 8(1), 014001 |
| 38 | Harris A. R., Morgan S. J., Chen J., Kapsa R. M., Wallace G. G., Paolini A. G., J. Neural Eng., 2013, 10(1), 1741—2560 |
| 39 | Green R. A., Lovell N. H., Poole⁃Warren L. A., Biomaterials, 2009, 30(22), 3637—3644 |
| 40 | Cui X. Y., Martin D. C., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2003, 89(1/2), 92—102 |
| 41 | Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G., Q. Rev. Biol., 1976, 94(1), 303—322 |
| 42 | Abidian M. R., Martin D. C., Biomaterials, 2008, 29(9), 1273—1283 |
| 43 | Abidian M. R., Corey J. M., Kipke D. R., Martin D. C., Small, 2010, 6(3), 421—429 |
| 44 | Thomas C. A., Zong K., Schottland P., Reynolds J. R., Adv. Mater., 2000, 12(3), 222—225 |
| 45 | Jian Z., Mutsumi K., J. Fiber Sci. Technol., 2011, 67(6), 125—131 |
| 46 | Baek S., Green R. A., Poole⁃Warren L. A., J. Biomed. Mater Res. A, 2014, 102(8), 2743—2754 |
| 47 | Tamburri E., Orlanducci S., Toschi F., Terranova M. L., Passeri D., Synth. Met., 2009,159(56), 406—414 |
| 48 | Green R. A., Hassarati R. T., Bouchinet L., Lee C. S., Cheong G. L. M., Yu J. F., Dodds C. W., Suaning G. J., Poole⁃Warren L. A., Lovell N. H., Biomaterials, 2010, 33(25), 5875—5886 |
| 49 | Yang J., Martin D. C., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2004, 101(1/2), 133—142 |
| 50 | Zhou H. H., Cheng X., Rao L., Li T., Acta Biomater., 2013,9(5), 6439—6449 |
| 51 | Charkhkar H., McHail D. G., Kasteea J. S., Dumas T. C., Peixoto N., Rubinson J. F., Pancrazio J. J., Acta Biomater., 2014, 10(6), 2446—2454 |
| 52 | Green R. A., Lovell N. H., Wallace G. G., Poole⁃Warren L. A., Biomaterials, 2008, 29(24/25), 3393—3399 |
| 53 | Ludwig K. A., Uram J. D., Yang J., Martin D. C., Kipke D. R., Neural Eng., 2006, 3(1), 59—70 |
| 54 | Cui X. Y., Hetke J. F., Wiler J. A., Anderson D. J., Martin D. C., Sensor Actuat A: Phys., 2001, 93(1), 8—18 |
| 55 | Kim D. H., Richardson⁃Burns S. M., Hendricks J. L., Sequera C., Adv. Funct. Mater.,2007, 17(1), 79—86 |
| 56 | Owen A. M., Neuroscientist, 2004, 10(6), 525—537 |
| 57 | Michele S., Dion K., Jonathan R., Adv. Maters., 2013, 25(15), 2135—2139 |
| 58 | Wilks S. J., Richardson⁃Burns S. M., Hendricks J. L., Martin D. C., Otto K. J., Front. Neuroeng., 2009,2, 7 |
| 59 | Venkatraman S., Hendricks J., King Z. A., Sereno A. J., Sarah R. B., David M., Jose M. C., IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., 2011, 19(3), 307—316 |
| 60 | Blau A., Murr A., Wolff S., Sernagor E., Medini P., Iurilli G., Ziegler C., Benfenati F., Biomaterials, 2010,32(7), 1778—1786 |
| 61 | Cui X. Y., Martin D. C., Sensor Actuat A: Phys., 2003, 103(3), 384—394 |
| 62 | Michalska A., Galuszkiewicz A., Ogonowska M., Ocypa M., Maksymiuk K., J. Solid State Electr., 2004, 8(6), 381—389 |
| 63 | Mercedes V., Johan B., Ari I., Andrzej L., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2002, 82(1), 7—13 |
| 64 | Yamato H., Ohwa M., Wernet W., J. Electroanal Chem., 1995, 397(1/2), 163—170 |
| 65 | Pfluger P., Street G. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1984, 80(1), 544—553 |
| 66 | Green R., Abidian M. R., Adv. Mater., 2016, 27(46), 7620—7637 |
| 67 | Charkhkar H., Knaack G. L., McHail D. G., Mandal H. S., Peixoto N., Rubinson J. F., Dumas T. C., Pancrazio J. J., Acta Biomater., 2016, 32, 57—67 |
| 68 | Abidian M. R., Ludwig K. A., Marzullo T. C, Martin D. C, Kipke D. R., Adv.Mater., 2009, 21(37), 3764—3770 |
| 69 | Wang L. P., Wang W., Di L., Lu Y. N., Wang J. Y., Colloids Surf. B, 2010, 80(1), 72—78 |
| 70 | Di L., Wang L. P., Lu Y. N., He L., Lin Z. X., Wu K. J., Ren Q. S., Wang J. Y., Acta Biomater., 2011, 7, 3738—3745 |
| 71 | Zhu B., Luo S. C., Zhao H. C., Lin H. A., Sekine J., Nakao A., Chen C., Yamashita Y., Yu H. H., Nat.Commun., 2014, 5(1), 1065—1073 |
| 72 | Asplund M., Thaning E., Lundberg J., Sandberg⁃Nordqvist A. C., Kostyszyn B., Inganäs O., Holst H., Biomed. Mater., 2009, 4(4), 045009 |
| 73 | Kolarcik C. L., Catt K., Rost E., Albrecht I. N., Bourbeau D., Du Z. H., Kozai T. D. Y., Luo X. L., Weber D. J., Cui X. T., Neural. Eng., 2015, 12(1), 016008 |
| 74 | Lee C. D., Hara S. A., Yu L., J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2016,104(2), 357—368 |
| 75 | Khodagholy D., Doublet T., Gurfinkel M., Quilichini P., Ismailova E., Leleux P., Herve T., Sanaur S., Bernard C., Malliaras G. G., Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(36), 268—272 |
| 76 | Qi D. P., Liu Z. Y., Liu Y., Jiang Y., Leow W. R., Pal M., Pan S., Yang H., Wang Y., Zhang X. Q., Yu J. C., Li B., Yu Z., Wang W., Chen X. D., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(40), 1702800 |
| 77 | Sasaki M., Karikkineth B. C., Nagamine K., Kaji H., Torimitsu K., Nishizawa M., Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2014, 3(11), 1919—1927 |
| 78 | Green R. A., Hassarati R. T., Goding J. A., Baek S., Lovell N. H., Martens P. J., Poole⁃Warren L. A., Macromol. Biosci., 2012, 12(4), 494—501 |
| 79 | Shenoy S. L., Kaya I., Erkey C., Weiss R. A., Synth. Met., 2001, 123(3), 509—514 |
| 80 | Wang Y., Sotzing G. A., Weiss R. A., Chem. Mater., 2003, 15(2), 375—377 |
| 81 | Luo R. B., Li H. B., Du B., Zhou S. S., Zhu Y. X., Org. Electron., 2019, 76, 105451 |
| 82 | Kim S., Oh W. K., Jeong Y. S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(15), 1947—1956 |
| 83 | Kang G., Borgens R. B., Cho Y., Langmuir the ACS J. Surfaces & Colloids, 2011, 27(10), 6179—6184 |
| 84 | Oh W. K., Kim S., Shin K. H., Jang Y. J., Choi M., Jang J., Talanta, 2013, 105, 333—339 |
| 85 | Kim R., Nam Y., J. Neurosci., 2019, 326, 108369 |
| 86 | Wang T., Jing L. C., Zhu Q. X., Ethiraj A. S., Tian Y., Zhao H., Yuan X. T., Wen J. G., Li L. K., Geng H. Z., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 500, 143997 |
| [1] | 周明娟, 闫莹, 晁单明. 电致变色/电控荧光双功能聚合物的合成及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 147. |
| [2] | 郑博元, 纪锋颖, 侯智善, 孙思明, 孙允陆, 杨蕊竹. 生物兼容蛋白水凝胶微图案的光刻平版印刷[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(4): 715. |
| [3] | 毛健新, 乜广弟, 卢晓峰, 高木, 王威, 王策. 导电高分子及其纳米复合材料的热电性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2): 213. |
| [4] | 邬海涛, 于婷, 朱庆三, 焦自学, 危岩, 章培标, 陈学思. 电活性可生物降解纳米复合材料PAP/op-HA/PLGA的制备及成骨活性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(5): 1181. |
| [5] | 黄春玉,卜凤泉, 马任平, 齐殿鹏, 吕男. 在导电高分子薄膜表面沉积密度可控的银纳米粒子[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(7): 1288. |
| [6] | 朱召进, 卢宝阳, 刘聪聪, 王庐岩, 徐景坤, 裴梅山. 烷基步长对聚丙烯酸修饰咔唑电聚合的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(10): 2102. |
| [7] | 闫建红 , 黄俐研, 刘正平 , 张军刚 , 侯文博. 单分散P(St-BA-AN)/PANI核壳结构复合微球的制备与电性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(10): 2090. |
| [8] | 张庆武, 周啸. 聚3-(4-氟苯基)噻吩/碳化聚丙烯腈泡沫复合电极的电化学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(4): 781. |
| [9] | 杨正龙, 侯文博, 刘正平, 黄俐研, 彭笑刚. 单分散核/壳结构导电高分子复合材料的研究(Ⅰ)——单分散核/壳结构聚苯乙烯/聚吡咯的结构表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 23(10): 2014. |
| [10] | 封伟, 韦玮, 吴洪才. 乳液法制备掺杂聚苯胺的微观结构研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1999, 20(2): 318. |
| [11] | 刘承美, 廖春花, 过俊石, 谢洪泉. 相转移催化法合成聚(2,5-二丁氧基对苯乙炔)[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1995, 16(7): 1124. |
| [12] | 朴建辉, 汤浩, 杨华礼, 陈欣方, 罗云霞, 李淑华. 乙烯类聚合物-炭黑复合物的PTC效应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1992, 13(9): 1278. |
| [13] | 王荣顺, 谢德民, 张喜艳, 王玉松, 傅玉杰, 赵成大. 酚醛树脂热裂解产物的结构研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1990, 11(10): 1161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||